Nerve Chart Spine
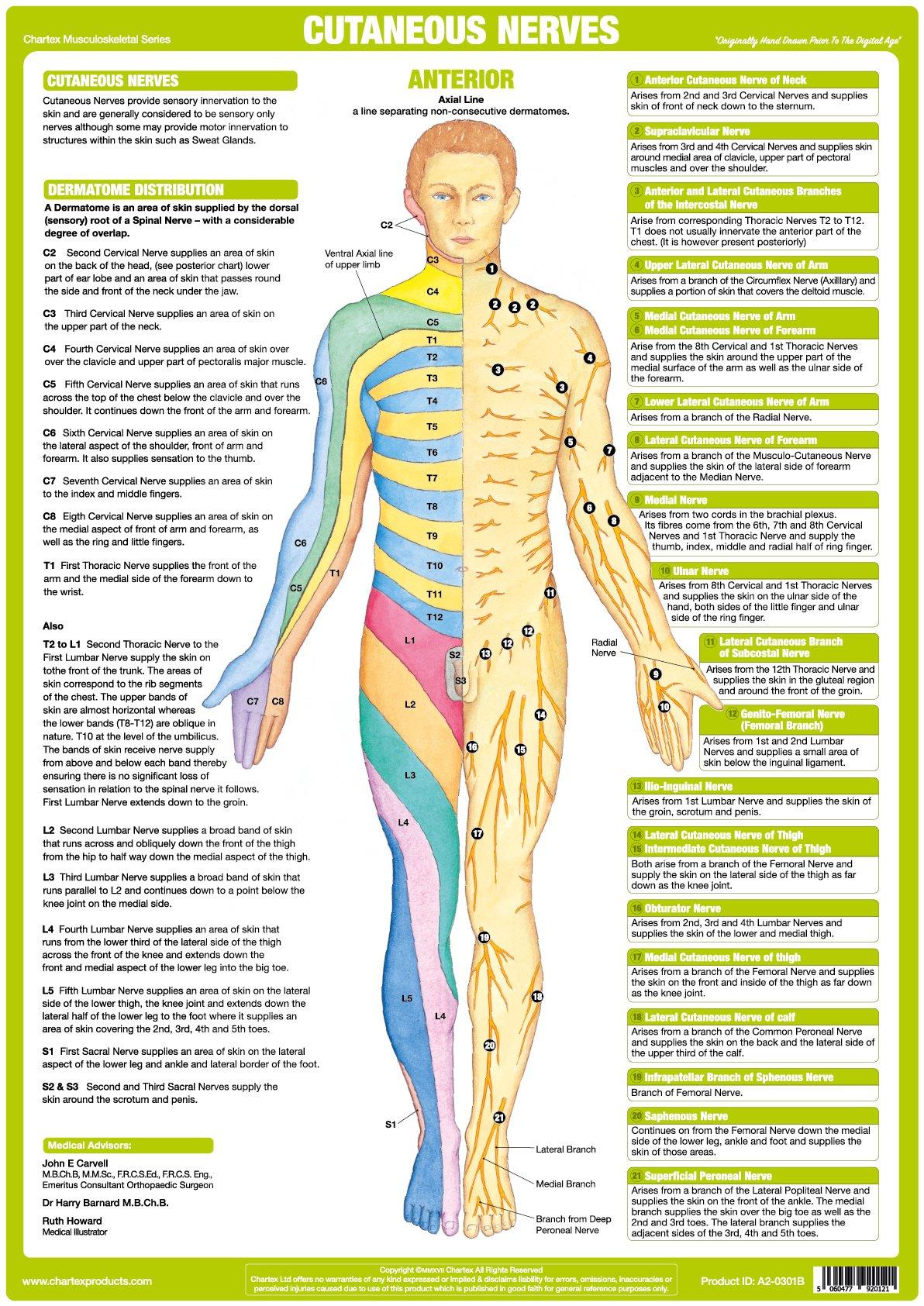
Nerve Chart Spine - This article will explore the key factors that impact visualizing spinal nerves and the importance of considering these factors when making decisions about creating a chart for anatomy and physiology enthusiasts. Web spinal nerves are mixed nerves that interact directly with the spinal cord to modulate motor and sensory information from the body’s periphery. The spinal cord starts at the base of the brain, runs throughout the cervical and thoracic spine, and typically ends at the lower part of the thoracic spine. Web these relay motor (movement), sensory (sensation), and autonomic (involuntary functions) signals between the spinal cord and other parts of the body. Web to understand this intricate region, we will consider the bony structures first, and then discuss the ligaments, nerves, and musculature that are associated with this region of the spinal column, concluding with some clinical implications of damage to some of these structures. You have 31 spinal nerves and 30 dermatomes. Web l1 spinal nerve provides sensation to your groin and genital area and helps move your hip muscles. Ralph rashbaum, md, orthopedic surgeon. Spinal cord and spinal nerve roots. Your spinal cord is a column of nerves that travels through your spinal canal. Numbers indicate the types of nerve fibers: Throughout the spine, intervertebral discs made of. Web the spine’s four sections, from top to bottom, are the cervical (neck), thoracic (abdomen,) lumbar (lower back), and sacral (toward tailbone). It comprises the vertebral column (spine) and two compartments of back muscles; Web l1 spinal nerve provides sensation to the groin and genital regions. Spinal nerves emerge from the spinal cord and reorganize through plexuses, which then give rise to systemic nerves. The spinal cord starts at the base of the brain, runs throughout the cervical and thoracic spine, and typically ends at the lower part of the thoracic spine. Web to understand this intricate region, we will consider the bony structures first, and. Web to understand this intricate region, we will consider the bony structures first, and then discuss the ligaments, nerves, and musculature that are associated with this region of the spinal column, concluding with some clinical implications of damage to some of these structures. Most cases of cervical radiculopathy go away with nonsurgical treatment. Spinal cord and spinal nerve roots. Your. The cord extends from your skull to your lower back. Web spinal cord and nerves: Each nerve forms from nerve fibers, known as fila radicularia, extending from the posterior (dorsal) and anterior (ventral) roots of the spinal cord. The back is the body region between the neck and the gluteal regions. It comprises the vertebral column (spine) and two compartments. Web spinal cord and nerves: The back functions are many, such as to house and protect the spinal cord, hold the body and head upright, and adjust the movements of the upper. L2, l3, and l4 spinal nerves provide sensation to the front part of the thigh and inner side of the lower leg. Web l1 spinal nerve provides sensation. Web dermatomes are areas of skin that are connected to a single spinal nerve. The cord extends from your skull to your lower back. These nerves also control movements of the hip and knee muscles. The vertebral column’s most important physiologic function is protecting the spinal cord,. This article will explore the key factors that impact visualizing spinal nerves and. Thoracic spinal nerves are not part of any plexus, but give rise to the intercostal nerves directly. Web spinal nerves are mixed nerves that interact directly with the spinal cord to modulate motor and sensory information from the body’s periphery. Web to understand this intricate region, we will consider the bony structures first, and then discuss the ligaments, nerves, and. Web spinal cord and nerves: Web these relay motor (movement), sensory (sensation), and autonomic (involuntary functions) signals between the spinal cord and other parts of the body. These nerves carry messages between your brain and muscles. The cord extends from your skull to your lower back. Web spinal nerves are mixed nerves that interact directly with the spinal cord to. 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal, named according to their corresponding vertebral levels. Spinal nerves emerge from the spinal cord and reorganize through plexuses, which then give rise to systemic nerves. Web to understand this intricate region, we will consider the bony structures first, and then discuss the ligaments, nerves, and musculature that are associated. These nerves also control movements of the hip and knee muscles. Most cases of cervical radiculopathy go away with nonsurgical treatment. L2, l3 and l4 spinal nerves provide sensation to the front part of your thigh and inner side of your lower leg. You have 31 spinal nerves and 30 dermatomes. It comprises the vertebral column (spine) and two compartments. It is important to mention that after the spinal nerves exit from the spine, they join together to form four paired clusters of. The human nervous system has a tremendous capacity to constantly relay vital messages throughout the body. The exact area that each dermatome covers can be different from person to. Web l1 spinal nerve provides sensation to your groin and genital area and helps move your hip muscles. Each nerve forms from nerve fibers, known as fila radicularia, extending from the posterior (dorsal) and anterior (ventral) roots of the spinal cord. Your spinal cord is a column of nerves that travels through your spinal canal. Web dermatomes are areas of skin that are connected to a single spinal nerve. You have 31 spinal nerves and 30 dermatomes. Numbers indicate the types of nerve fibers: This article will explore the key factors that impact visualizing spinal nerves and the importance of considering these factors when making decisions about creating a chart for anatomy and physiology enthusiasts. These nerves carry messages between your brain and muscles. Web the spine’s four sections, from top to bottom, are the cervical (neck), thoracic (abdomen,) lumbar (lower back), and sacral (toward tailbone). The roots connect via interneurons. On the chart below you will see 4 columns (vertebral level, nerve root, innervation, and possible symptoms). Ralph rashbaum, md, orthopedic surgeon. L2, l3, and l4 spinal nerves provide sensation to the front part of the thigh and inner side of the lower leg.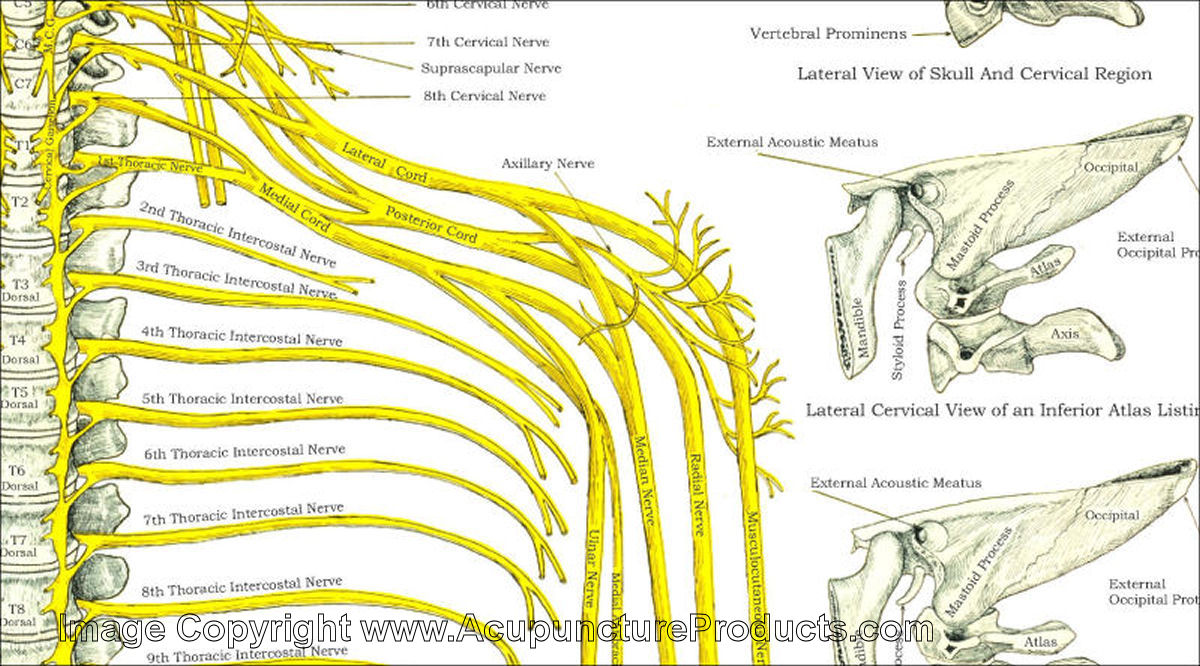
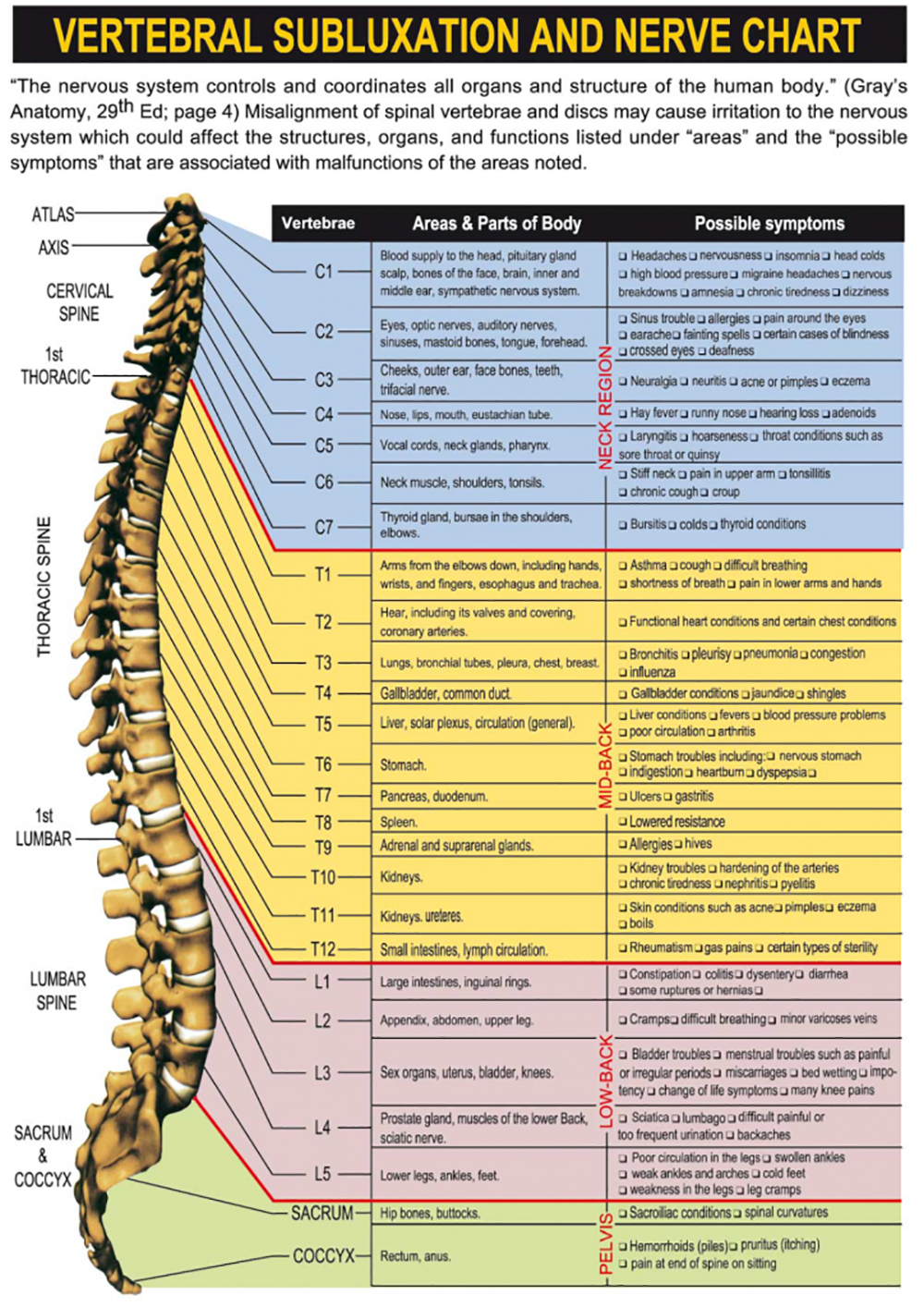
Vertebral Subluxation Spinal Nerves Chart
Nervous System Anatomy Posters Set of 6

Spinal nerve function Medicina Pinterest Anatomía, Salud y Acupuntura

Spinal Nerve Function , Vintage , Spinal Nerve Function Chart, Root

Chiropractic Spinal Nerve Chart Nerve Function Chart

Spinal Nerve Function Anatomical Chart Anatomy Models and Anatomical
Anatomical Pain Chart
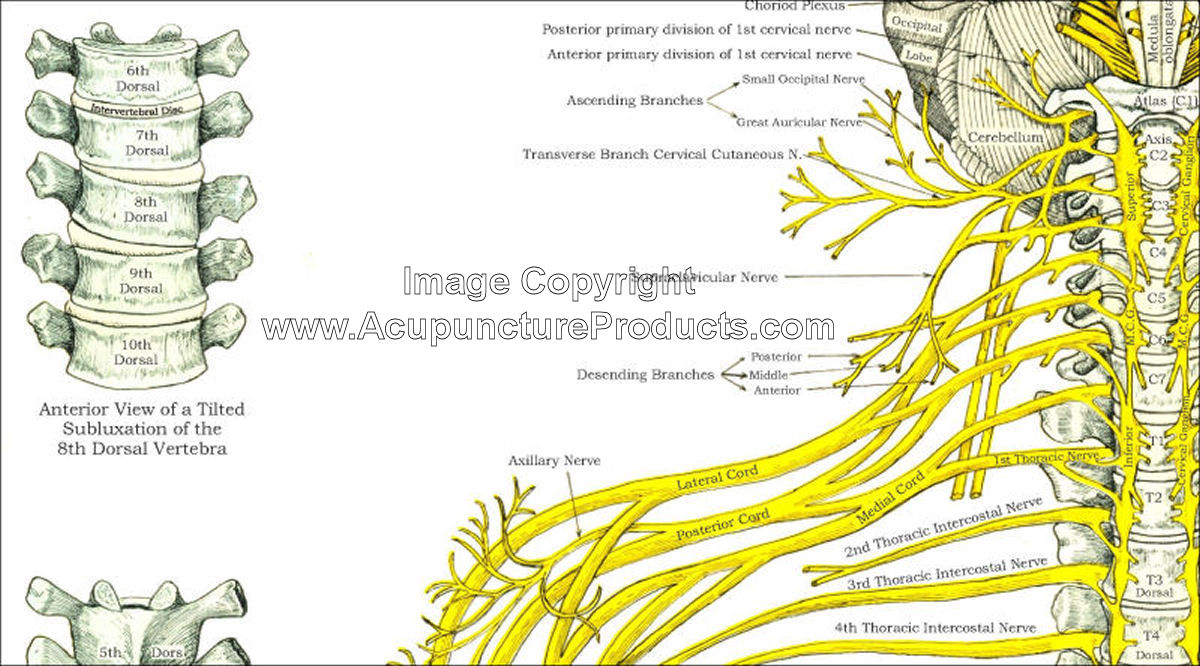
Chart Of Spine And Nerves
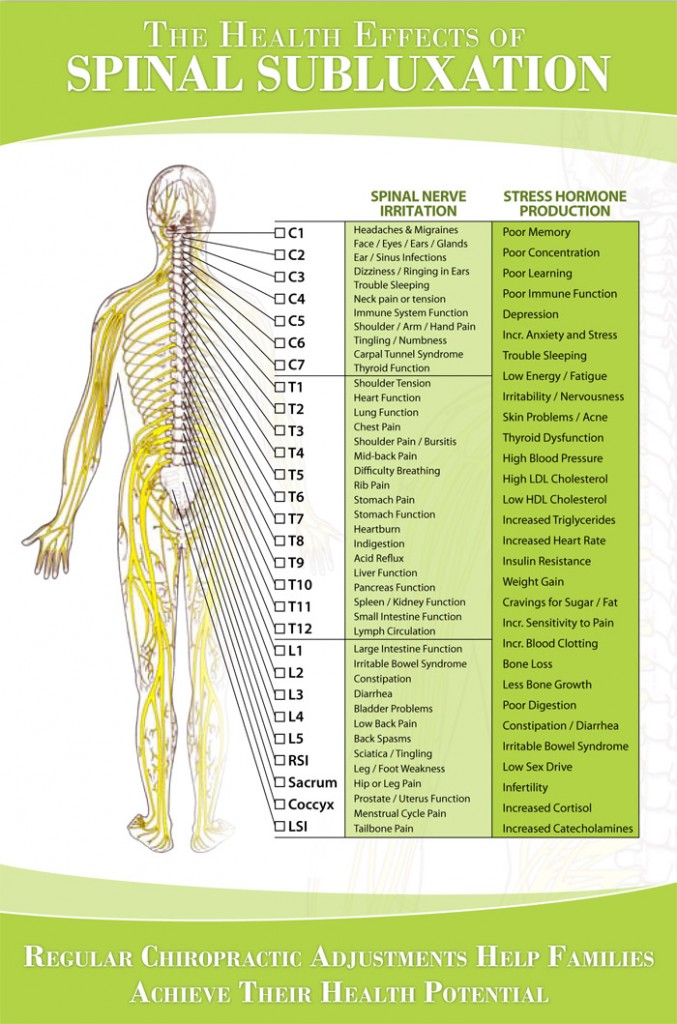
Printable Spinal Nerve Chart Free Printable Calendar

Printable Spinal Nerve Chart
These Nerves Also Control Movements Of The Hip And Knee Muscles.
If This Complex System Is Damaged, Nerve Signals Can Go Awry, Causing Intense Pain.
Web Below Is A Chart That Outlines The Main Functions Of Each Of The Spine Nerve Roots:
Thoracic Spinal Nerves Are Not Part Of Any Plexus, But Give Rise To The Intercostal Nerves Directly.
Related Post: