Pressure Temperature Chart Nitrogen
Pressure Temperature Chart Nitrogen - N is the amount of gas, and r is the ideal gas constant. Please choose the units you wish to use: Figures 3.2.1 and 3.2.2 illustrate the compressibility factors of hydrogen and nitrogen, respectively,. Liquid nitrogen has many uses, but poses risks of frostbite, explosion, and suffocation if handled incorrectly. What is an ideal gas? Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, equal volumes of all gases contain the same number of. Web the thermometer and pressure gauge indicate the temperature and the pressure qualitatively, the level in the flask indicates the volume, and the number of particles in each flask indicates relative amounts. You can make ads in the engineering toolbox more useful to you! Accurate thermophysical properties are available for several fluids. For real gases, the compressibility factor may be very different from one. U = specific internal energy. His nitrogen pressure calculator used the ideal gas law to solve for final pressure. Web the volume of a given amount of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure when temperature is held constant (boyle’s law). Jahangiri, m., termodynamic properties of nitrogen from the freezing line to 2000 k at pressures to 1000 mpa, j.. Web thermophysical properties of fluid systems. Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, equal volumes of all gases contain the same number of. Web the temperature of liquid nitrogen is −195.79 °c (77 k; The values above apply to undissociated states. At high temperatures above 1500 k dissociation becomes appreciable and pressure is a significant variable. The calculator below can be used to estimate the thermal conductivity of nitrogen at given temperature and atmospheric pressure. Web calculation of thermodynamic state variables of nitrogen in saturation state, boiling curve. Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, equal volumes of all gases contain the same number of. U = specific internal energy. You can make ads in. Web the vapor pressure of liquid nitrogen. For real gases, the compressibility factor may be very different from one. By abraham solomon friedman nd davidwhite. What is an ideal gas? N is the amount of gas, and r is the ideal gas constant. Liquid nitrogen is very cold! The values above apply to undissociated states. Absolute entropy at standard reference pressure. The calculator below can be used to estimate the thermal conductivity of nitrogen at given temperature and atmospheric pressure. For real gases, the compressibility factor may be very different from one. Web the temperature of liquid nitrogen is −195.79 °c (77 k; Web thermophysical properties of fluid systems. Web hvacr training equipment component sizing psychrometric resource. Please select the species of interest : The molecular weight is m = 28.016 kg/kmol. Web calculate a boiling point or pressure using the antoine equation: Please be patient while the web interface loads. The values above apply to undissociated states. [ all data ] streng, 1971 Ideal gas law equation ideal gas constant faqs. Online nitrogen thermal conductivity calculator. Download and print nitrogen gas enthalpy, internal energy and entropy chart. Consider a closed system, a tire for instance. Absolute entropy at standard reference pressure. At high temperatures above 1500 k dissociation becomes appreciable and pressure is a significant variable. Web the thermal conductivity of nitrogen depends on temperature and pressure as shown in the figures and tables below. Accurate thermophysical properties are available for several fluids. Icemeister was curious as to how high pressures would be in his nitrogen cylinder when it was stored in a hot ares. Consider a closed system, a tire for instance. This ideal gas. Web the thermal conductivity of nitrogen depends on temperature and pressure as shown in the figures and tables below. Consider a closed system, a tire for instance. This ideal gas law calculator will help you establish the properties of an ideal gas subject to pressure, temperature, or volume changes. Web nitrogen is an inert, neutral and colorless gas. Web hvacr. Icemeister was curious as to how high pressures would be in his nitrogen cylinder when it was stored in a hot ares. Web the vapor pressure of liquid nitrogen. At room temperature and pressure, liquid nitrogen boils into nitrogen gas. Web the thermal conductivity of nitrogen depends on temperature and pressure as shown in the figures and tables below. In this way table 5, rg versus p and t, can be extended beyond t = 350k. His nitrogen pressure calculator used the ideal gas law to solve for final pressure. Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, equal volumes of all gases contain the same number of. For real gases, the compressibility factor may be very different from one. Please choose the units you wish to use: Online nitrogen thermal conductivity calculator. Figures 3.2.1 and 3.2.2 illustrate the compressibility factors of hydrogen and nitrogen, respectively,. Ideal gas law equation ideal gas constant faqs. Accurate thermophysical properties are available for several fluids. Web gas for temperatures t > 350k and pressures p <, 10 bar. Web thermophysical properties of fluid systems. U = specific internal energy.
Nitrogen Density and Specific Weight vs. Temperature and Pressure

Nitrogen Thermal Conductivity vs. Temperature and Pressure
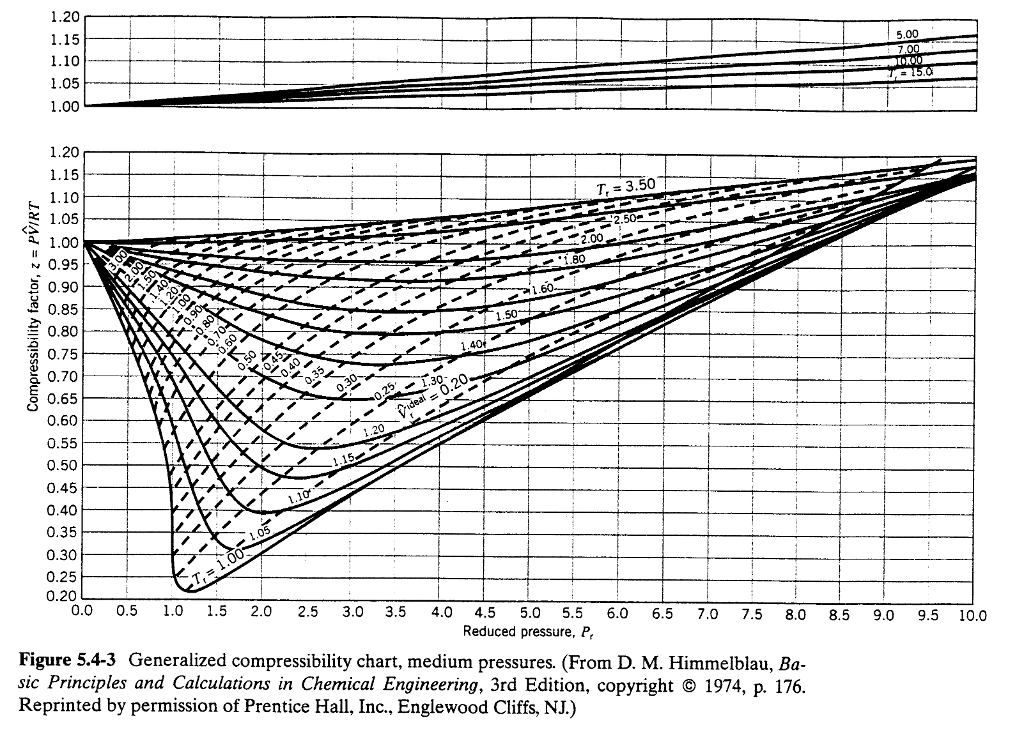
Nitrogen Pressure Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
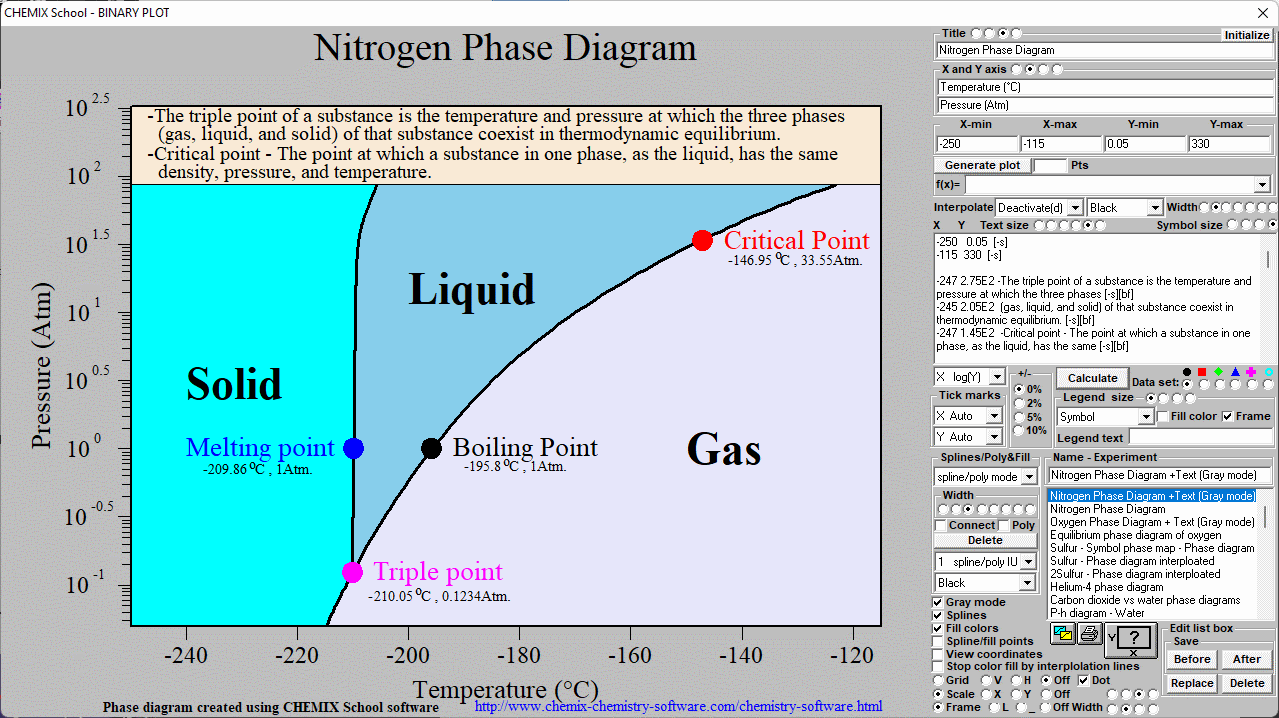
Nitrogen phase diagram

Nitrogen Thermal Conductivity vs. Temperature and Pressure

Nitrogen Pressure Temperature Chart A Visual Reference of Charts

Nitrogen Thermal Diffusivity vs. Temperature and Pressure
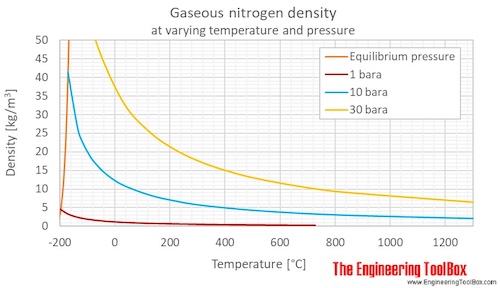
Nitrogen Density and Specific Weight vs. Temperature and Pressure

Nitrogen Thermal Diffusivity vs. Temperature and Pressure

Nitrogen Phase Diagram Pressure Temperature General Wiring Diagram
Web Calculation Of Thermodynamic State Variables Of Nitrogen In Saturation State, Boiling Curve.
Web This Page Relies On The Ideal Gas Law To Calculate Values Of Pressure At Different Temperatures:
We Then Have The Law For An Ideal Gas:
Pv = Nrt, Where P, V And T Is The Pressure, Volume And Temperature Of Gas Respectively;
Related Post: