Reflex Arc Flow Chart
Reflex Arc Flow Chart - When a reflex arc in an animal consists of only one sensory neuron and one motor neuron, it is defined as monosynaptic, referring to the presence of a single chemical synapse. Did this video help you? The neurones of the reflex arc. Web revision notes on 6.1.5 reflex arcs for the aqa a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at save my exams. This is like an electrochemical circuit which generate electrical signals in the motor neur. Web this labelled diagram of a reflex arc indicates the neural pathway controlling a reflex. Reflex or reflex action refers to the instantaneous response to the stimuli without thinking. Web the primary components of the reflex arc are the sensory neurons (or receptors) that receive stimulation and in turn connect to other nerve cells that activate muscle cells (or effectors), which perform the reflex action. The last neuron generally innervates the effector tissue, which is usually a muscle. Sensory or nerve fibres which transmit sensory impulses generated by the receptor, to the central nervous system. Reflex arcs are highly beneficial in situations that require a quick response and do not involve conscious thought. When a reflex arc in an animal consists of only one sensory neuron and one motor neuron, it is defined as monosynaptic, referring to the presence of a single chemical synapse. Web describe the following reflexes and name all components of each. We have mentioned earlier that a stimulus is any change in the environment that causes a response in the body. Awareness of a response having happened occurs after the response has been carried out. Web this labelled diagram of a reflex arc indicates the neural pathway controlling a reflex. Reflex arcs are highly beneficial in situations that require a quick. This characteristic allows reflex actions to occur relatively quickly by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of routing signals through the brain, although the. In reflex arc as soon as the spinal cord receives a signal the response will be seen even before the brain gets the single. Web the reflex arc is an involuntary response so it does. Reflexes can be spinal or cranial, depending on the nerves and central components that are involved. These reflexes are executed by the successive activation of a certain number of neurons that are mutually connected. Web in a reflex arc, there are synapses between the sensory and relay neurones, and the relay and motor neurones; First, there is the stimulus. Web. Web a reflex action is an automatic (involuntary) and rapid response to a stimulus, which minimises any damage to the body from potentially harmful conditions, such as touching something hot. The reflex arc typically consists of five components: Chemicals called neurotransmitters (such as dopamine and serotonin) are released into the synaptic cleft and diffuse across it (down a concentration gradient). The last neuron generally innervates the effector tissue, which is usually a muscle. A neural pathway that controls an action reflex. Web the junctions between neurons through which the signals can be sent are called the chemical synapses. Web a reflex action is an automatic (involuntary) and rapid response to a stimulus, which minimises any damage to the body from. Reflex arcs are highly beneficial in situations that require a quick response and do not involve conscious thought. The muscle stretch reflex is the most basic reflex pathway in the body and as such, understanding this allows understanding of more complex reflexes. Web reflex arc is the pathway of nerve impulses that are generated at the receptor due to stimulus. When a reflex arc in an animal consists of only one sensory neuron and one motor neuron, it is defined as monosynaptic, referring to the presence of a single chemical synapse. Web this labelled diagram of a reflex arc indicates the neural pathway controlling a reflex. Reflexes can be spinal or cranial, depending on the nerves and central components that. Reflexes can be spinal or cranial, depending on the nerves and central components that are involved. A typical example of a reflex action is the patellar reflex (‘knee jerk’ response), which occurs when the patellar tendon is tapped. The muscle stretch reflex is the most basic reflex pathway in the body and as such, understanding this allows understanding of more. They produce some chemicals when electrical signals reach them. Reflexes can be spinal or cranial, depending on the nerves and central components that are involved. Web a reflex arc is a pathway that a nerve impulse follows during a reflex action. Web reflex arc is the pathway of nerve impulses that are generated at the receptor due to stimulus to. Web a reflex arc can be defined as the complete pathway taken by the nerve impulses in order to facilitate a response during a reflex action. Web reflex arc is the pathway of nerve impulses that are generated at the receptor due to stimulus to reach the effector organ when a reflex action is performed. This is like an electrochemical circuit which generate electrical signals in the motor neur. These reflexes are executed by the successive activation of a certain number of neurons that are mutually connected. Web the reflex arc is an involuntary response so it does not involve the conscious part of the brain as the coordinator of the reaction. The reflex arc describes the pathway in which the nerve impulse is carried and the response is generated and shown by the effector organ. An example is reaching out to pick up a cup of coffee. Reflex is a neurological mechanism or pathway that controls reflex. Web the primary components of the reflex arc are the sensory neurons (or receptors) that receive stimulation and in turn connect to other nerve cells that activate muscle cells (or effectors), which perform the reflex action. Web in a reflex arc, there are synapses between the sensory and relay neurones, and the relay and motor neurones; Web this labelled diagram of a reflex arc indicates the neural pathway controlling a reflex. 470 views 10 months ago nervous system. They produce some chemicals when electrical signals reach them. Web the junctions between neurons through which the signals can be sent are called the chemical synapses. Web by definition, a reflex is an involuntary, stereotypical response of the effector tissue from the stimulation of receptors. Web revision notes on 6.1.5 reflex arcs for the aqa a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at save my exams.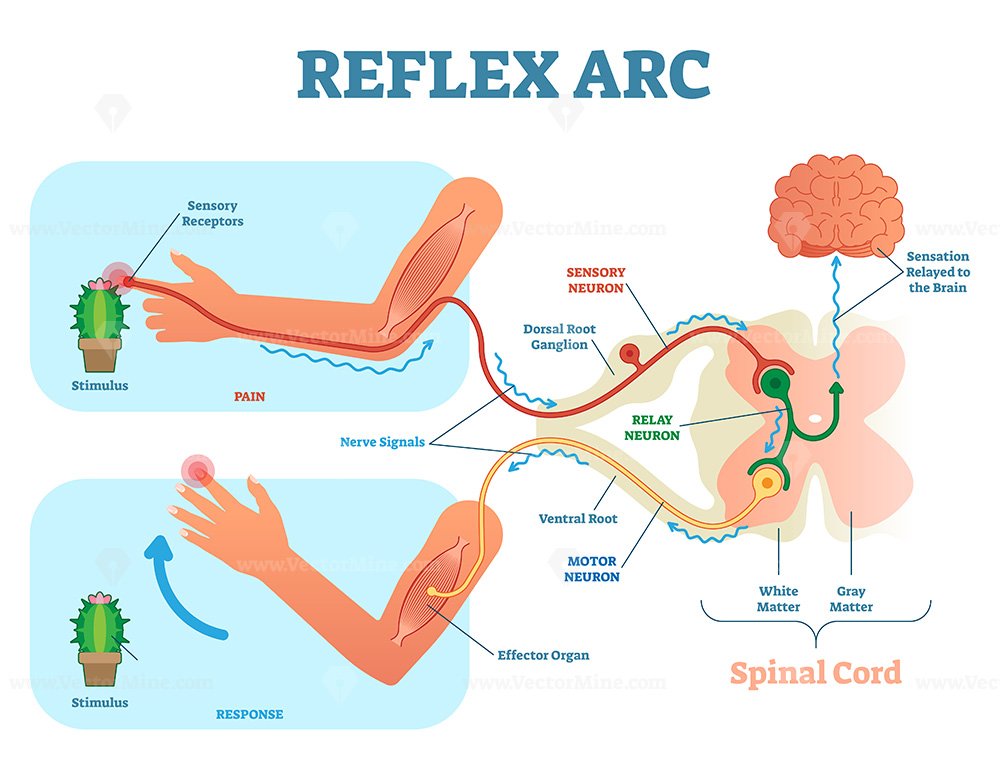
Spinal Reflex Arc anatomical scheme, vector illustration VectorMine

118 Control and coordination in mammals, the nervous system Biology
Reflex Arc Flow Chart

The Reflex Arc (14.1.3) CIE IGCSE Biology Revision Notes 2023 Save

Define reflex arc Give the flow chart of a spinal reflex arc
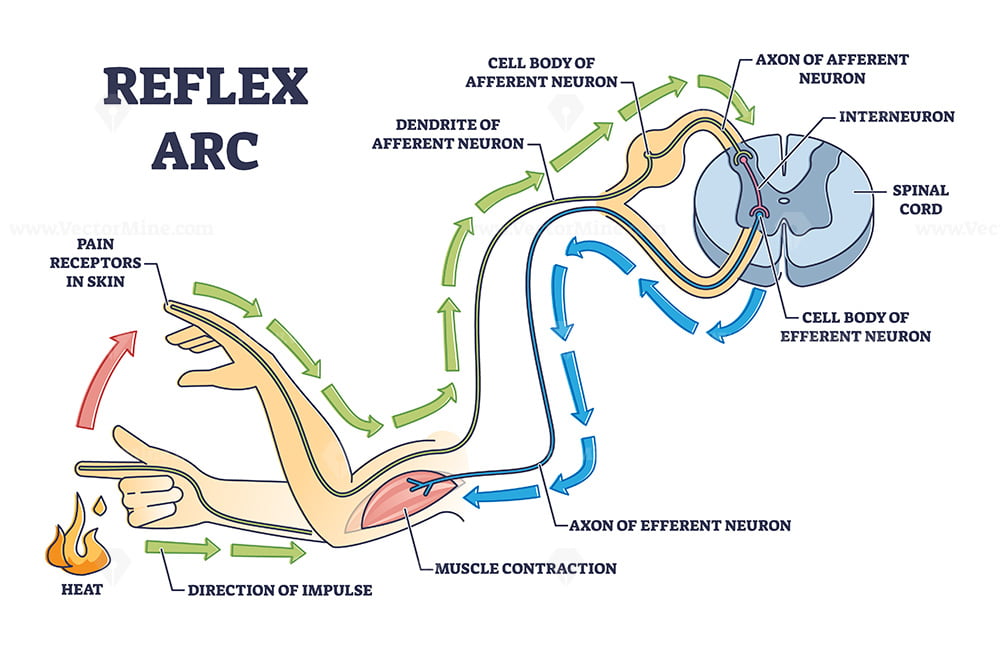
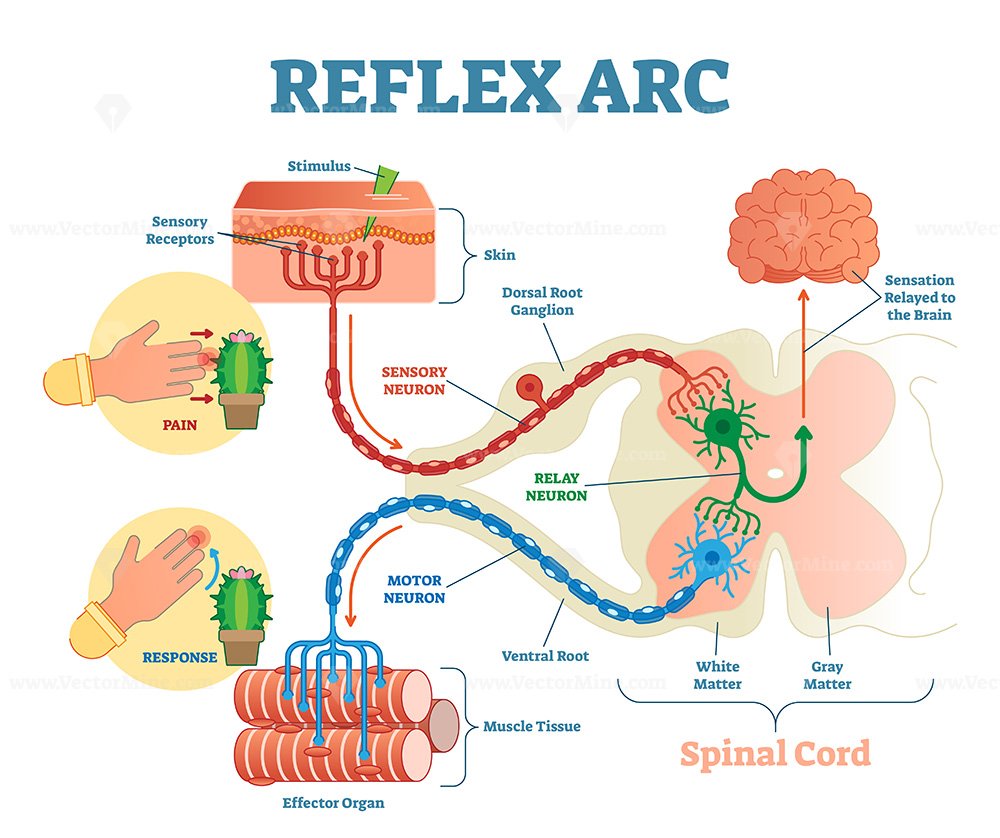
Reflex arc explanation with pain signals and receptor impulse outline
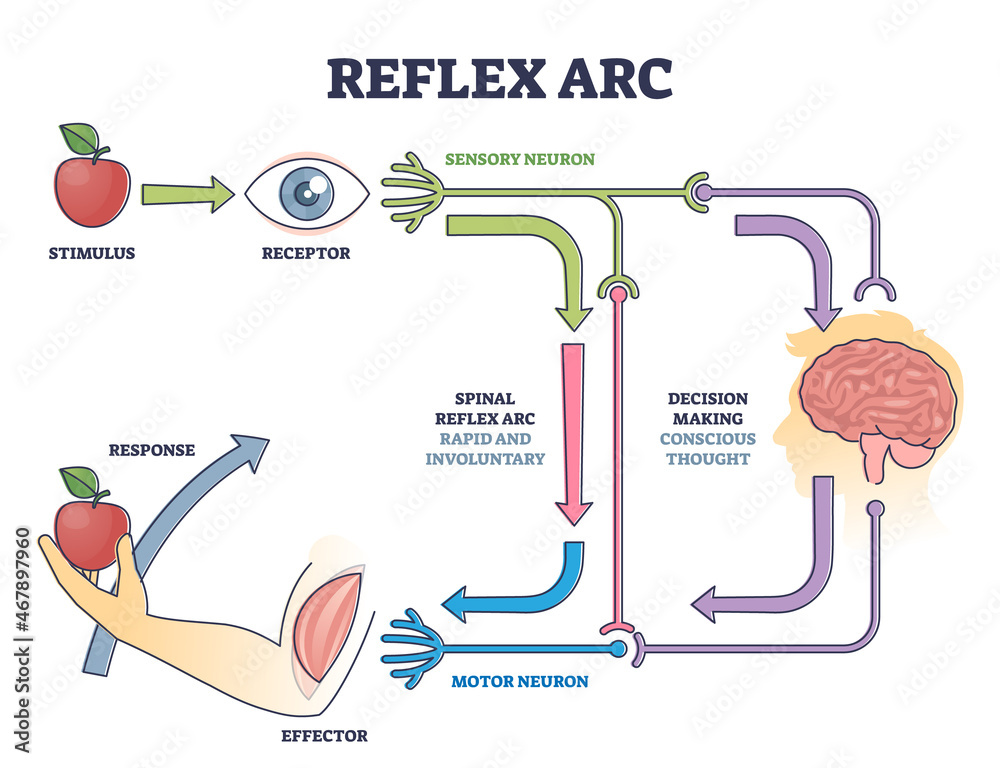
Reflex ARC sensory neuron pathway from stimulus to response outline
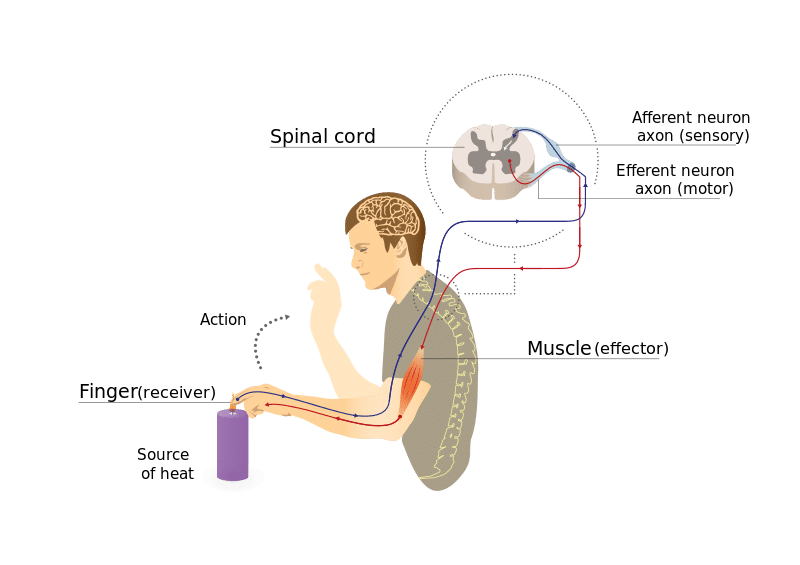
5 Elements of a Reflex Arc
Testing Reflexes Redefining Spinal Shock Wheelchair Lifestyles
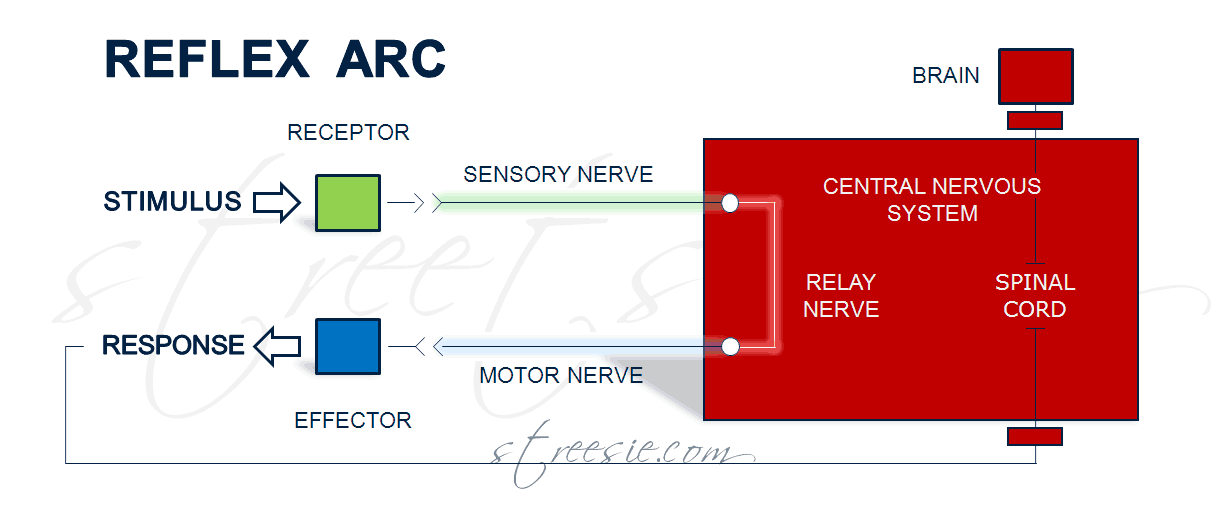
Reflex Arc Diagram Labelled
It Clearly Indicates The Route Adapted When A Stimulus Occurs And How The Reaction Takes Place.
Reflex Arcs Are Highly Beneficial In Situations That Require A Quick Response And Do Not Involve Conscious Thought.
When A Reflex Arc In An Animal Consists Of Only One Sensory Neuron And One Motor Neuron, It Is Defined As Monosynaptic, Referring To The Presence Of A Single Chemical Synapse.
In Higher Animals, Most Sensory Neurons Do Not Pass Directly Into The Brain, But Synapse In The Spinal Cord.
Related Post:
