Motor Temperature Chart
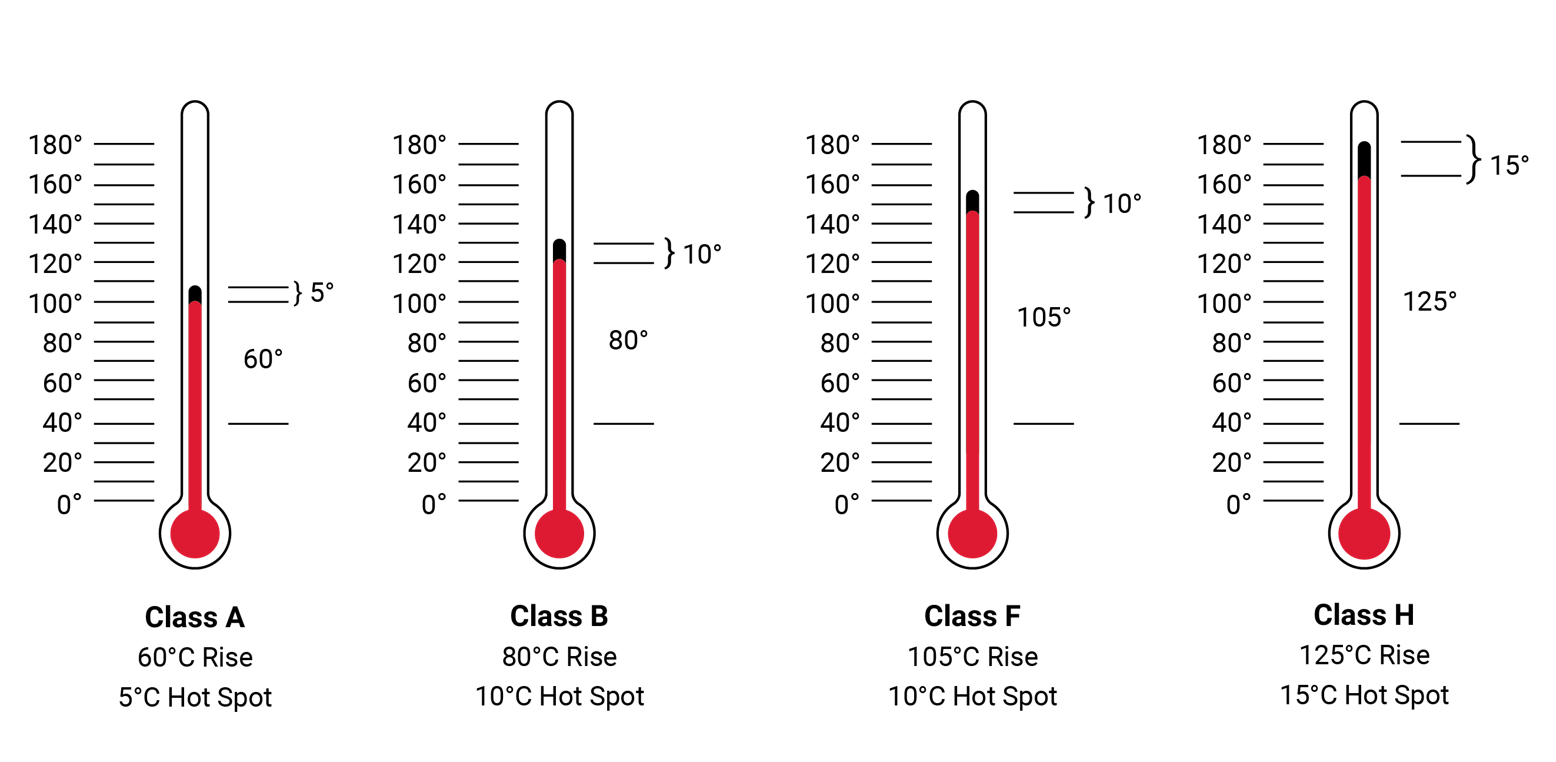
Motor Temperature Chart - Web there are also nema motor insulation classes that describe the ability of a motor’s winding to withstand heat. Initial motor data was created using a rapid dynamometer test at a. Web in general, most standard electric motors have a recommended operating temperature range between 40°c (104°f) to 60°c (140°f). Web for our ac motor, the temperature difference between the windings and the motor case is up to 30 ° c. This temperature range is consistent with most. All four classes identify the allowable temperature rise from an ambient temperature of 40° c (104° f). Insulating materials can be divided into the following seven classes based on their. Web initial motor performance @ 25°c. Stabilized armature temperature, (ѳ f) 125°c. Web performance reference temperatures (°c) are a80, e95, b100, f120, h145. This means that a motor, rated for 40° c ambient, is suitable for installation in applications. With a stabilized armature temperature rise of 100°c, terminal resistance will be higher and magnetic flux density will be lower compared with. In general a motor should not operate with temperatures above the maximum. Web performance reference temperatures (°c) are a80, e95, b100, f120,. The guidelines for each heat resistant class are summarized in the table. Web the standard ambient temperature is 40 celsius (104 degrees f). Web motor temperature (initial “cold”) motor temperature (final “hot”) motor temperature rise motor terminal voltage angular velocity no load angular velocity /°c a a a v/(rad/s). Nema allowable temperature rises (at service factor). Initial motor data was. Web the surface temperature of a continuously (and correctly) operating general purpose industrial electric motor will easily be 80 c (176 f) and perhaps as high. Web 40 oc + 105 oc + 10 oc. Web initial motor performance @ 25°c. Web for our ac motor, the temperature difference between the windings and the motor case is up to 30. The guidelines for each heat resistant class are summarized in the table. Web initial motor performance @ 25°c. Web the surface temperature of a continuously (and correctly) operating general purpose industrial electric motor will easily be 80 c (176 f) and perhaps as high. Remember that this is a conservative design, so the surface temperatures of many motors will be. In general a motor should not operate with temperatures above the maximum. Web the simple answer, and a good one, is that the national electrical manufacturers association (nema) has defined temperature rise for electric motors in motors and. Surface temperatures of 75°c to 95°c can exist on t frame motors. Remember that this is a conservative design, so the surface. Each 10 oc rise above the rating may reduce the. Web there are four insulation classes in use namely: Web motor temperature (initial “cold”) motor temperature (final “hot”) motor temperature rise motor terminal voltage angular velocity no load angular velocity /°c a a a v/(rad/s). If motor is so constructed that its surface is about 20 c cooler than the. Motor are a = 60°c, b = 80°c, f = 105°c, and h = 125°c. The guidelines for each heat resistant class are summarized in the table. Remember that this is a conservative design, so the surface temperatures of many motors will be much warmer. Web the surface temperature of a continuously (and correctly) operating general purpose industrial electric motor. If motor is so constructed that its surface is about 20 c cooler than the winding, the surface temperature would be: The guidelines for each heat resistant class are summarized in the table. Armature temperature rise, (ѳ r) 100°c. Remember that this is a conservative design, so the surface temperatures of many motors will be much warmer. Web the standard. Web depending on design and cooling arrangements, motor surface temperature can be hot to the touch. However, it is important to. Remember that this is a conservative design, so the surface temperatures of many motors will be much warmer. Web motor temperature (initial “cold”) motor temperature (final “hot”) motor temperature rise motor terminal voltage angular velocity no load angular velocity. Armature temperature rise, (ѳ r) 100°c. Remember that this is a conservative design, so the surface temperatures of many motors will be much warmer. Web for our ac motor, the temperature difference between the windings and the motor case is up to 30 ° c. Web there are four insulation classes in use namely: All four classes identify the allowable. Initial motor data was created using a rapid dynamometer test at a. Web motor temperature (initial “cold”) motor temperature (final “hot”) motor temperature rise motor terminal voltage angular velocity no load angular velocity /°c a a a v/(rad/s). Each 10 oc rise above the rating may reduce the. All four classes identify the allowable temperature rise from an ambient temperature of 40° c (104° f). Web for our ac motor, the temperature difference between the windings and the motor case is up to 30 ° c. Armature temperature rise, (ѳ r) 100°c. Stabilized armature temperature, (ѳ f) 125°c. Web the basic ambient temperature rating point of nearly all electric motors is 40° c. Surface temperatures of 75°c to 95°c can exist on t frame motors. Web the simple answer, and a good one, is that the national electrical manufacturers association (nema) has defined temperature rise for electric motors in motors and. In general a motor should not operate with temperatures above the maximum. However, it is important to. With a stabilized armature temperature rise of 100°c, terminal resistance will be higher and magnetic flux density will be lower compared with. Web in general, most standard electric motors have a recommended operating temperature range between 40°c (104°f) to 60°c (140°f). Web referring to the nema insulation class table, we observe that this motor has a maximum temperature rise of 105°c. Nema allowable temperature rises (at service factor).
motor temperature ratings
Tech Choosing The Proper Bearings For Your Engine
Help Your Air Compressor Motor Beat the Heat This Summer
Think Thin GF6 Is The Latest Spec In The World of Engine Oil

motortemperaturerisechart Beck Electric Actuators

Grades Of Motor Oil Explained
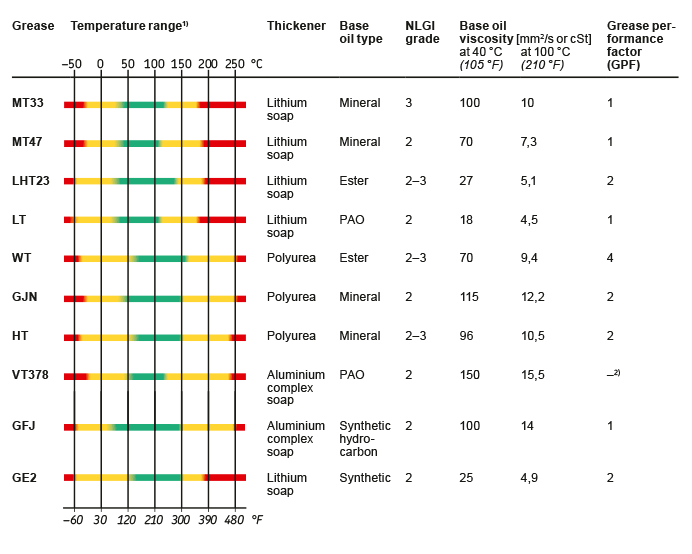
Bearing Temperature Chart (SKF ) and Guidelines Marinerspoint Pro
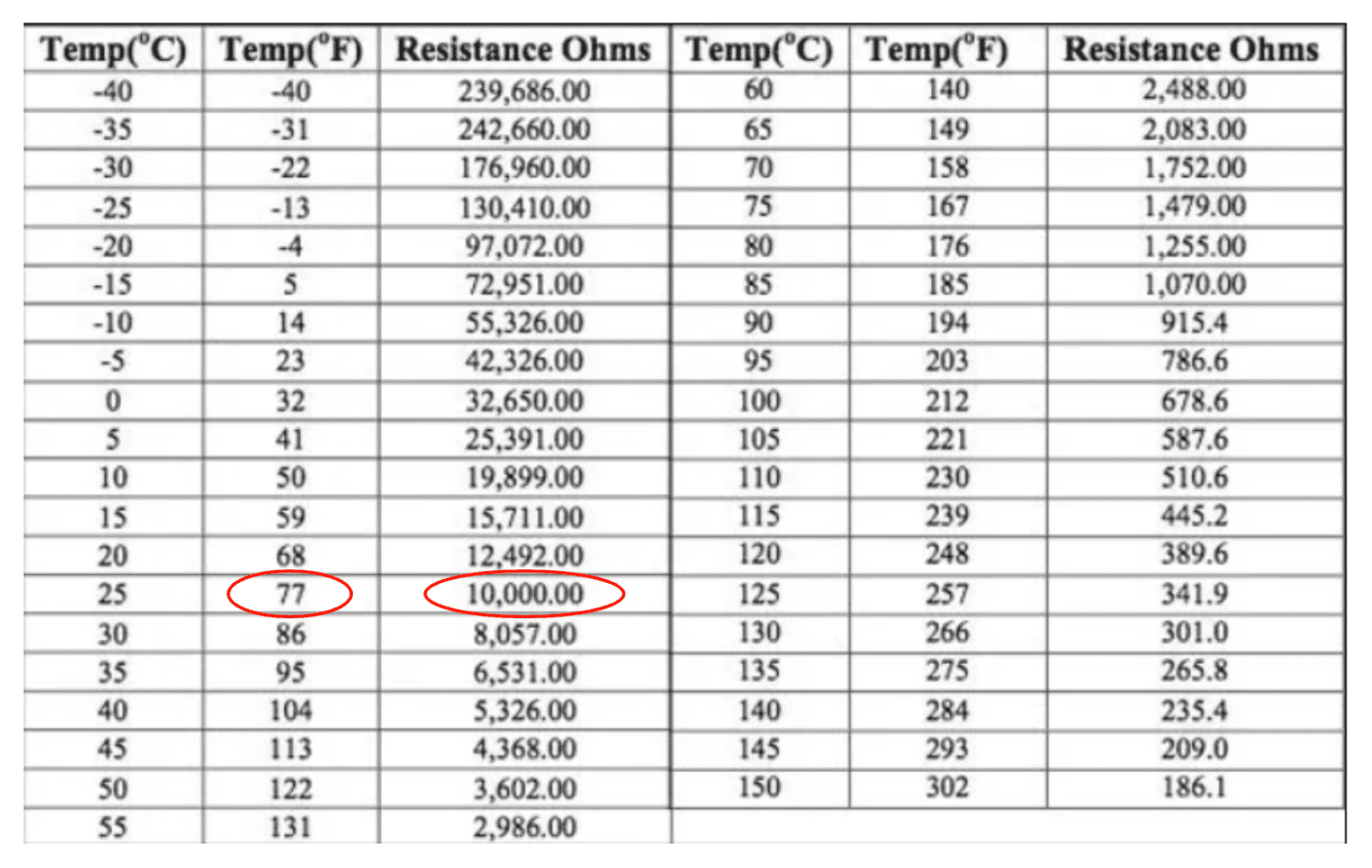
10k Ohm Thermistor Temperature Chart
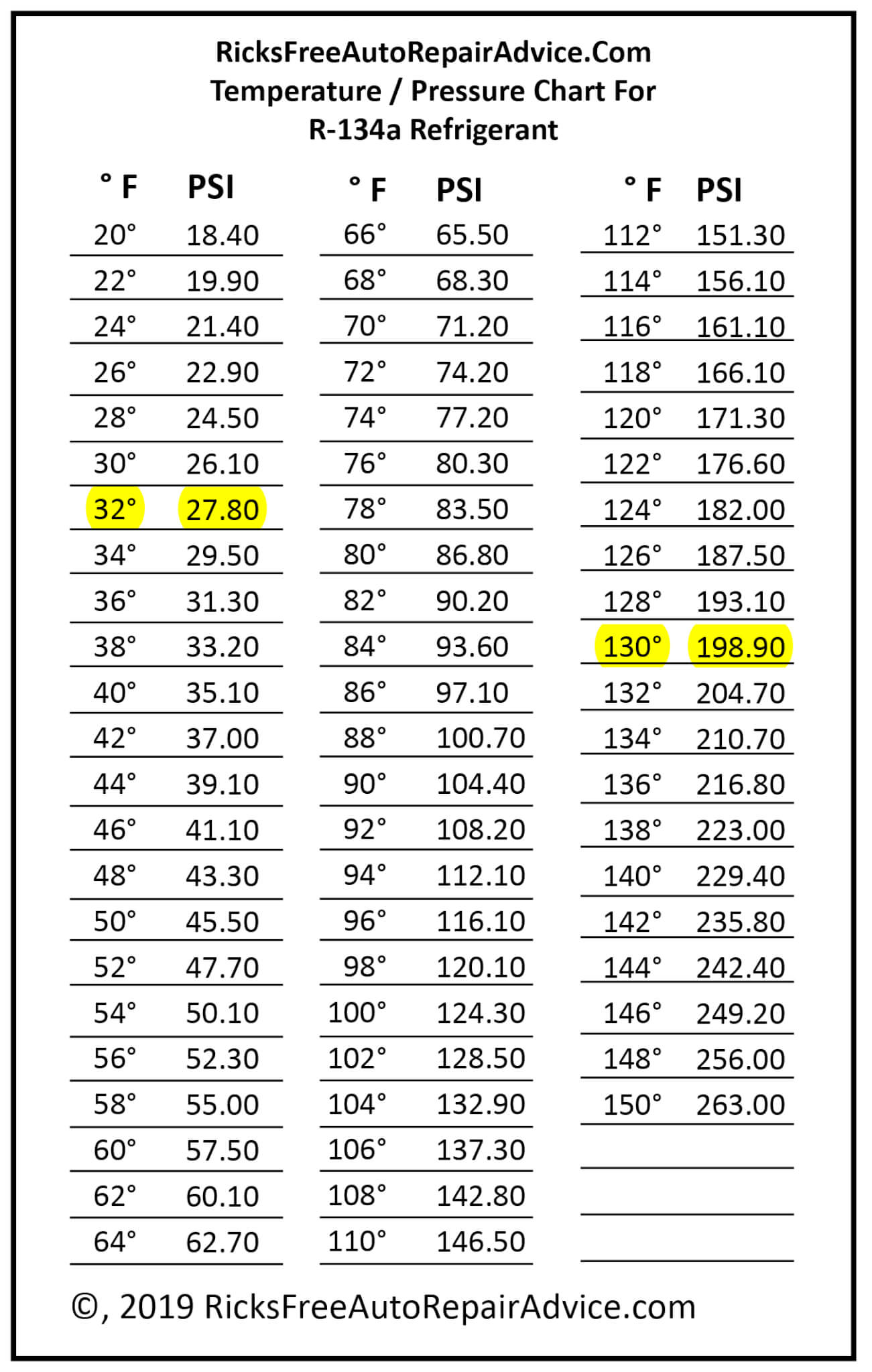
R134 Temperature To Pressure Chart

Adding transmisison temp gauge Page 2 DodgeTalk Forum
Web Figure 3 Illustrates The Total Area Beneath A Particular Motor Curve That Can Be Considered The Range Of Consistent Performance Between Room Temperature And Maximum Rated.
Web Performance Reference Temperatures (°C) Are A80, E95, B100, F120, H145.
Web There Are Also Nema Motor Insulation Classes That Describe The Ability Of A Motor’s Winding To Withstand Heat.
Web Initial Motor Performance @ 25°C.
Related Post: