Stoichiometry Conversion Chart
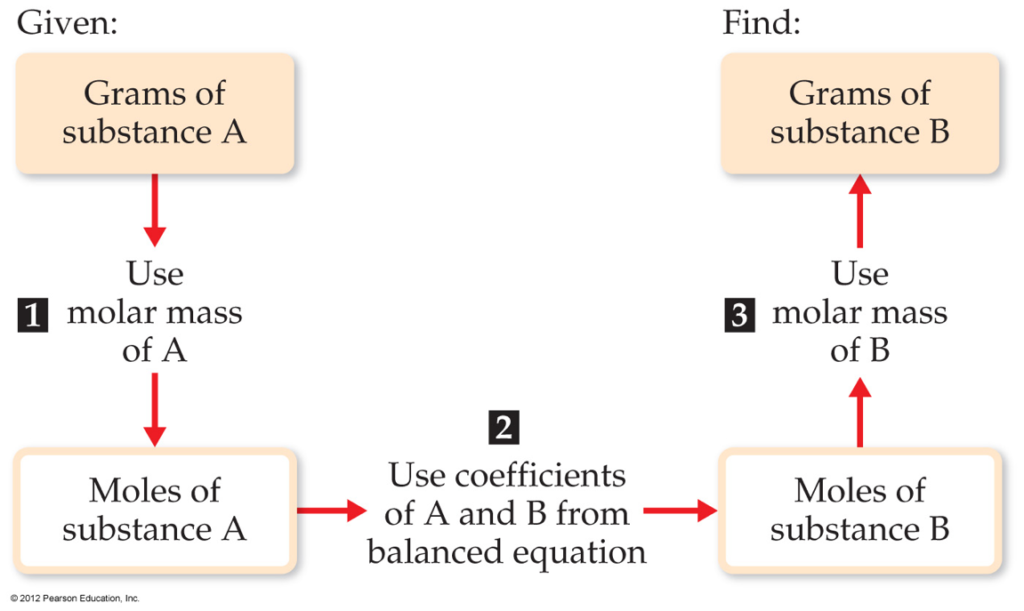
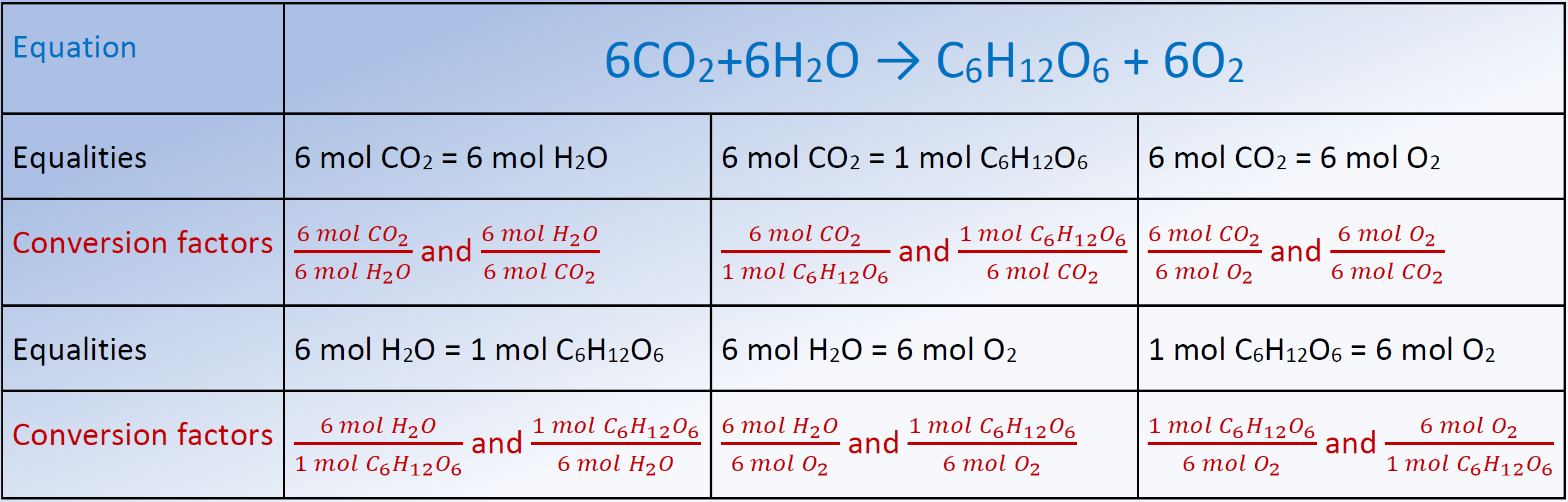
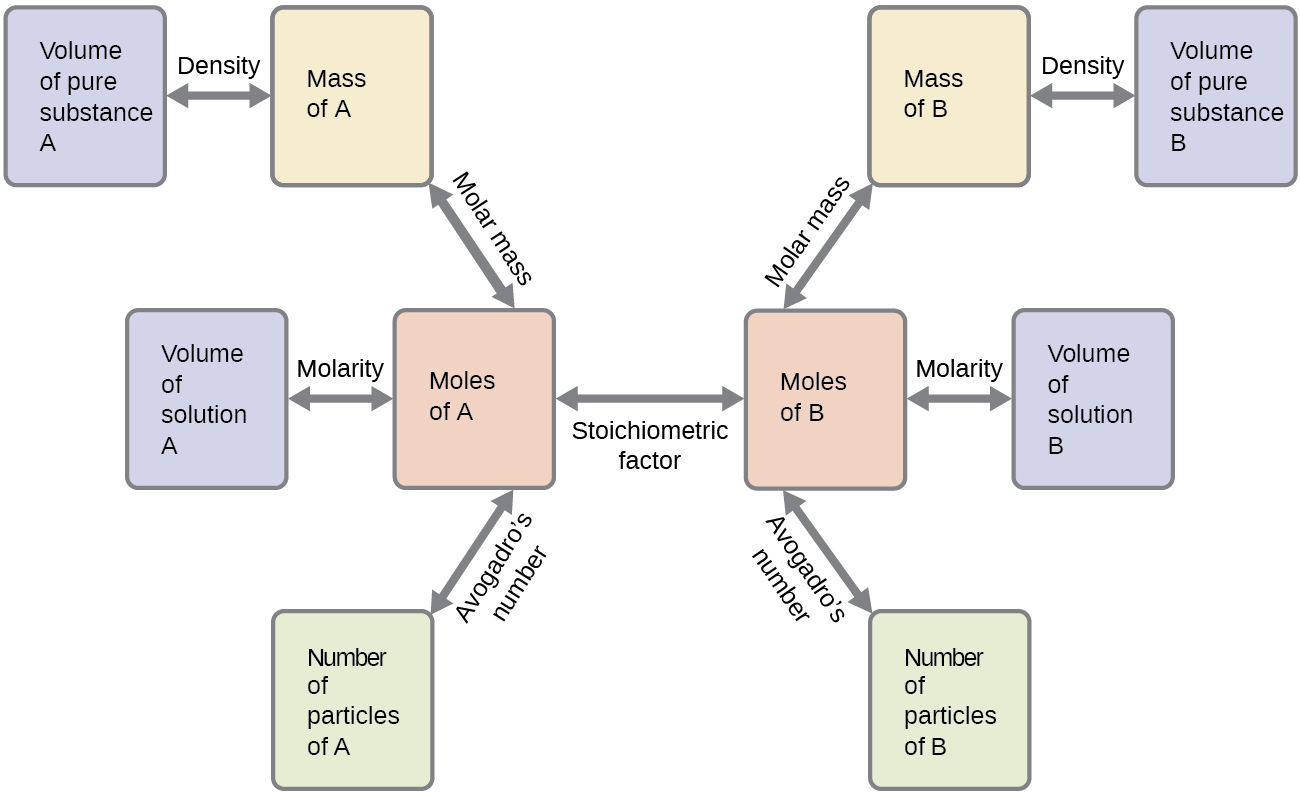
Stoichiometry Conversion Chart - Start calculation by writing down what you know step 3: September 13th, 2011 | author: 3.10 g h 2 so 4 × 1 mol h 2 so 4 98.08 g h 2 so 4 = 3.16 × 10 − 2 mol h 2 so 4. 1 cm 3 = 1ml. Web n 2 ( g) + 3 h 2 ( g) 2 nh 3 ( g) this equation shows ammonia molecules are produced from hydrogen molecules in a 2:3 ratio, and stoichiometric factors may be derived using any amount (number) unit: 1 lb = 16 oz = 453.6 g. Moles of a is converted to moles of b by multiplying by the molar ratio. Fe2 (so4)3 + agno3 = fe (no3)3 + ag2so4. Web apply a stoichiometric conversion factor to convert between the molar quantities of two substances that participate in a chemical reaction. Web flowchart of steps in stoichiometric calculations. Moles of a is converted to moles of b by multiplying by the molar ratio. Stoichiometry conversions conversions procedure step 1: 1 gal = 3.7854 l. Use the mole ratio to find moles of other reactant. Our tools helps you to know the exact number of moles or grams of the entities involved in a chemical equation. Web this stoichiometry calculator lets you calculate the relative amounts of reactants and products involved in a chemical reaction. Stoichiometry conversions conversions procedure step 1: 1 kg = 1000 g = 2.20462 lb. Determine where you are starting and finishing step 2: Web conversion table for problems below. This tutorial provides a brief overview of dimensional analysis, including conversion. Our tools helps you to know the exact number of moles or grams of the entities involved in a chemical equation. 1 cm 3 = 1ml. Determine where you are starting and finishing step 2: Web this stoichiometry calculator lets you calculate the relative amounts of reactants and products. Fe2 (so4)3 + agno3 = fe (no3)3 + ag2so4. Web conversion table for problems below. Web the conversion factors are used to calculate the unknown quantity in the mole from the known quantity in the mole of any other reactant or product in the same chemical equation, as explained in the following examples. 1 lb = 16 oz = 453.6. 2 nh 3 molecules 3 h 2 molecules or 2 doz nh 3 molecules 3 doz h 2 molecules or 2 mol nh 3 molecules 3 mol h 2 molecules. I2o5 + brf3 = if5 + o2 + br2. Our tools helps you to know the exact number of moles or grams of the entities involved in a chemical equation.. 2 nh 3 molecules 3 h 2 molecules or 2 doz nh 3 molecules 3 doz h 2 molecules or 2 mol nh 3 molecules 3 mol h 2 molecules. Web we can convert the 3.10 grams of h a 2 so a 4 to moles using the molar mass of h a 2 so a 4 ( 98.08 g. Fe2 (so4)3 + agno3 = fe (no3)3 + ag2so4. C2h6 + ch3cooh = c4h8o2 + h2o. Web flowchart of steps in stoichiometric calculations. Web n 2 ( g) + 3 h 2 ( g) 2 nh 3 ( g) this equation shows ammonia molecules are produced from hydrogen molecules in a 2:3 ratio, and stoichiometric factors may be derived using. 1 gal = 3.7854 l. Web conversion table for problems below. Web using stoichiometry in conversions. Moles of a is converted to moles of b by multiplying by the molar ratio. Koh + hcooh = hcook + h2o. Web using stoichiometry in conversions. Start calculation by writing down what you know step 3: Grams of a is converted to moles by multiplying by the inverse of the molar mass. 1 gal = 3.7854 l. I2o5 + brf3 = if5 + o2 + br2. Fe2 (so4)3 + agno3 = fe (no3)3 + ag2so4. Grams of a is converted to moles by multiplying by the inverse of the molar mass. Web using stoichiometry in conversions. 2 nh 3 molecules 3 h 2 molecules or 2 doz nh 3 molecules 3 doz h 2 molecules or 2 mol nh 3 molecules 3 mol h 2 molecules.. Web n 2 ( g) + 3 h 2 ( g) 2 nh 3 ( g) this equation shows ammonia molecules are produced from hydrogen molecules in a 2:3 ratio, and stoichiometric factors may be derived using any amount (number) unit: C5h12 + h2so4 = c5h11hso3 + h2o. N2h4 + h2so4 + feso4 = (nh4)2so4 + fe2 (so4)3. Stoichiometry conversions conversions procedure step 1: Grams of a is converted to moles by multiplying by the inverse of the molar mass. Ch3ch2br + ch3oh = ch3ch2och3 + hbr. Web this stoichiometry calculator lets you calculate the relative amounts of reactants and products involved in a chemical reaction. Web we can convert the 3.10 grams of h a 2 so a 4 to moles using the molar mass of h a 2 so a 4 ( 98.08 g / mol ): Fe2 (so4)3 + agno3 = fe (no3)3 + ag2so4. C2h6 + ch3cooh = c4h8o2 + h2o. 1 kg = 1000 g = 2.20462 lb. Mgsio3 + h2co3 = mgco3 + h2sio3. I2o5 + brf3 = if5 + o2 + br2. Web conversion table for problems below. Our tools helps you to know the exact number of moles or grams of the entities involved in a chemical equation. September 13th, 2011 | author: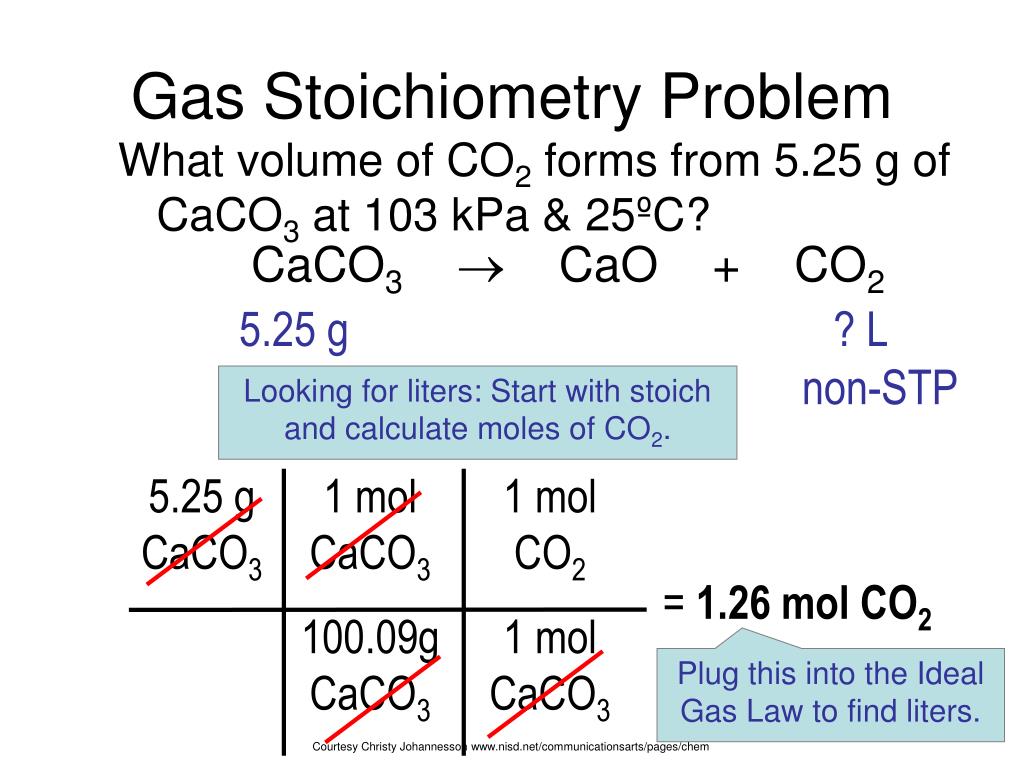
PPT Gas Stoichiometry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2956253
Stoichiometry Chemistry Activities
Chemistry Conversion Chart Moles

Ch. 5 Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry Chemistry Activities
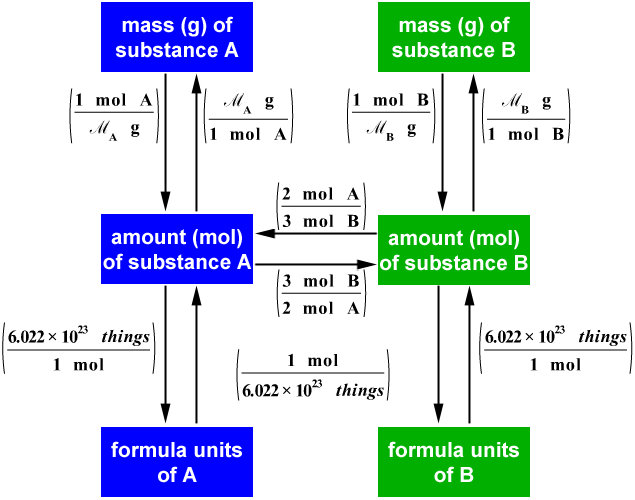
C&J&S&B's Class Chemisty ) What is Stoichiometry?
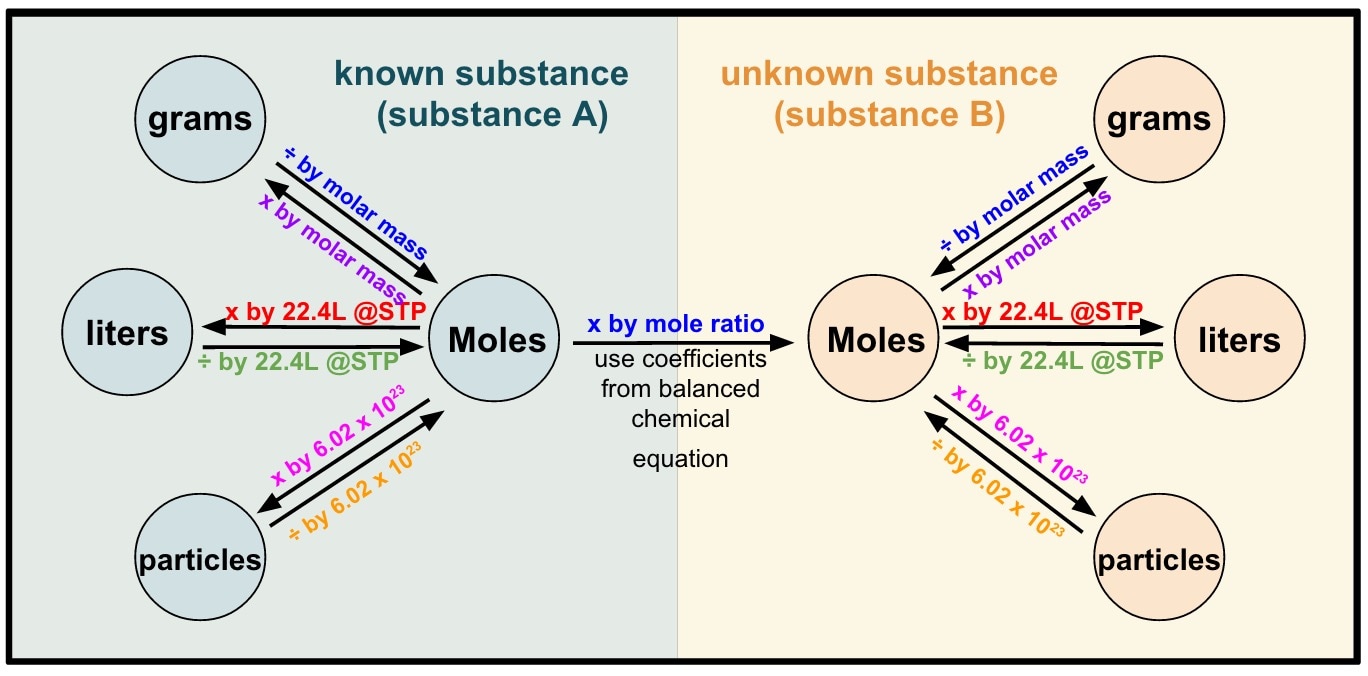
Stoichiometry Review Mr. Siemianowski Eisenhower High School
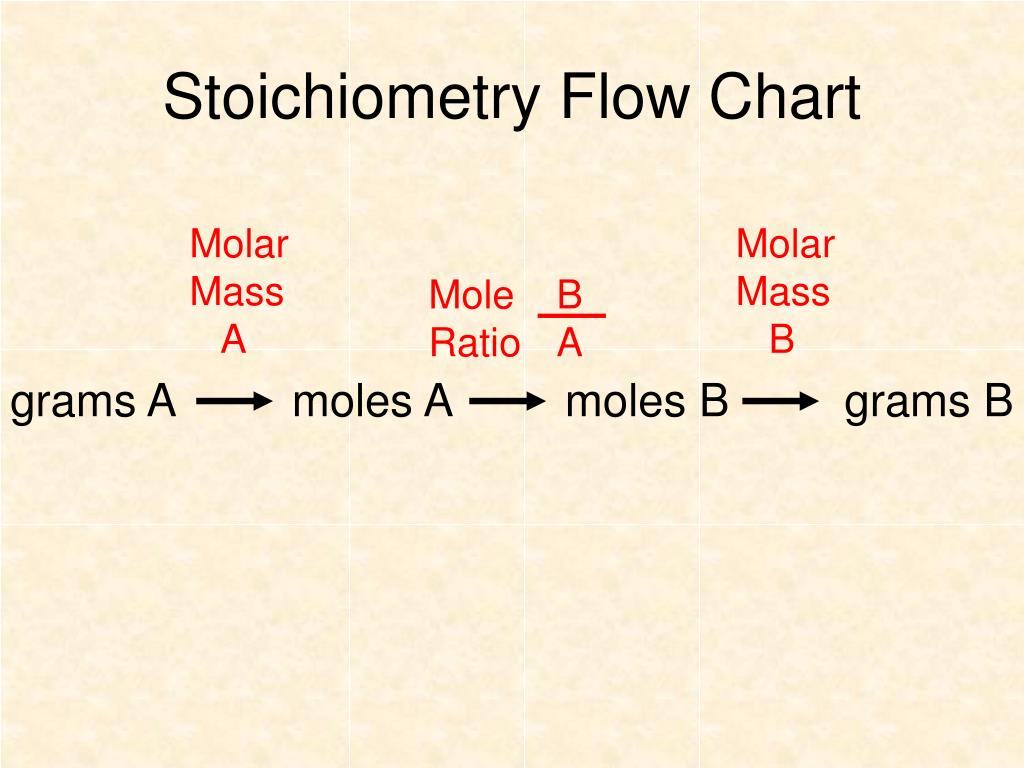
PPT Chapter 12 Stoichiometry PowerPoint Presentation, free download

Stoichiometry Lessons TES chemistry & physics Pinterest
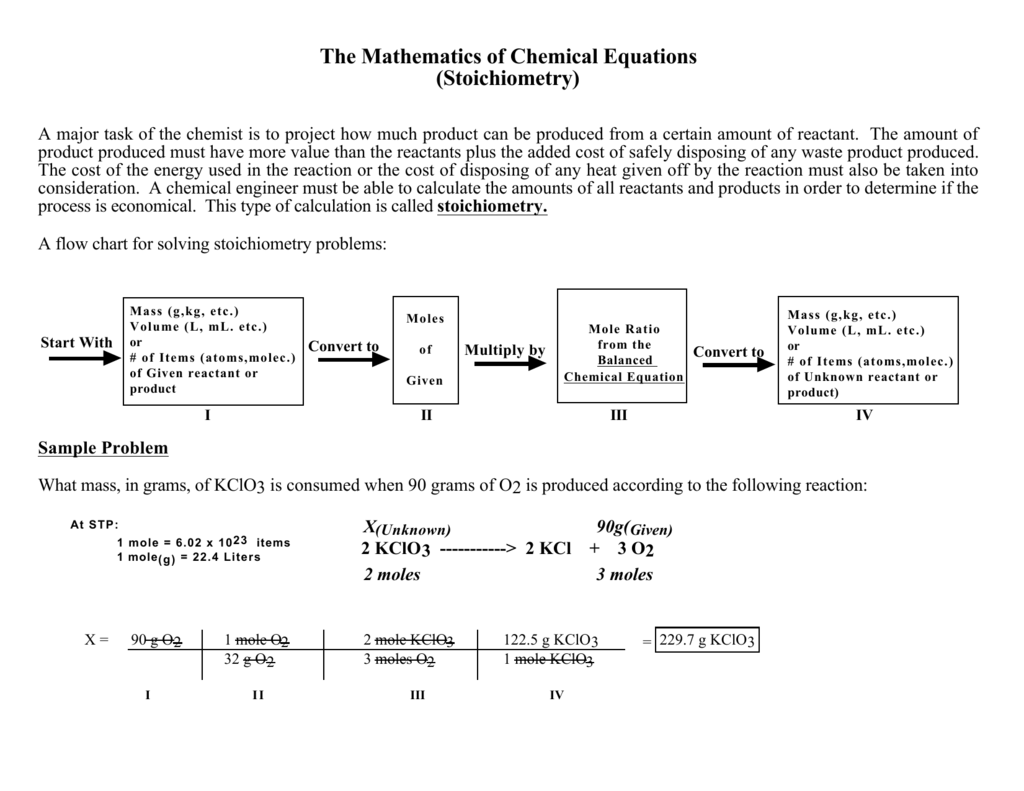
Stoichiometry Chart
Start Calculation By Writing Down What You Know Step 3:
1 Cm 3 = 1Ml.
This Tutorial Provides A Brief Overview Of Dimensional Analysis, Including Conversion.
Koh + Hcooh = Hcook + H2O.
Related Post: