Endometrial Polyp Size Chart In Mm
Endometrial Polyp Size Chart In Mm - Endometrial polyps vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. Web endometrial polyps vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. Web hysteroscopy with guided biopsy remains the gold standard for diagnosis of endometrial polyps (high). Polyps may be round or oval and range in size from a few millimeters (the size of a sesame seed) to a few centimeters (the size of a golf ball) or larger. They also range in number women can have one or many endometrial polyps. Web an endometrial polyp represents the extreme end of macroscopic hyperplasia of the endometrium when tissue grows so fast that parts of the endometrium are pushed into the cavity of the uterus. Web the prevalence of endometrial polyps was 7.8% (48/619; A fine telescope called a hysterocope is introduced into the uterus (womb) through the. On average, these polyps are typically less than 1 cm. Endometrial polyps form from an overgrowth of cells within the uterine lining. Endometrial polyps may be diagnosed at all ages; Endometrial polyps form from an overgrowth of cells within the uterine lining. Web endometrial polyps greater than 15mm showed a hyperplasia rate of 14.8%, compared with 7.7% in the group with smaller polyps (p<0.05). A mostly benign pathology finding. Web endometrial polyps are localized hyperplastic overgrowths of endometrial glands and stroma around. Can affect up to 25% of females presenting with abnormal uterine bleeding ( case rep obstet gynecol 2014;2014:518398 ) prevalence in asymptomatic females: Web an endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is an abnormal growth containing glands, stroma and blood vessels projecting from the lining of the uterus (endometrium) that occupies spaces small or large enough to fill the uterine cavity.. On average, these polyps are typically less than 1 cm. On hysteroscopy, there was hyperplastic endometrium with large endometrial polyp of size 8.5 cm. Incidence in asymptomatic females with infertility: Can range in size from millimeters (about the size of a sesame seed) to centimeters (about the size of a golf ball and even larger). Can affect up to 25%. Web hysteroscopy with guided biopsy remains the gold standard for diagnosis of endometrial polyps (high). Polypectomy was done and the same was sent for histopathological evaluation. Polyps may be found as a single lesion or multiple lesions filling the entire endometrial cavity. Can range in size from millimeters (about the size of a sesame seed) to centimeters (about the size. Web endometrial polyps vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. In women below the age of 30 years, the prevalence was 0.9%. Web asymptomatic endometrial polyps in postmenopausal women should be removed in case of large diameter (> 2 cm) or in patients with risk factors for endometrial carcinoma (level b). These polyps usually stay. Removal of asymptomatic polyps in premenopausal women should be considered in patients with risk factors for endometrial cancer (level b). Web the polyp attaches to the endometrium by a thin stalk or a broad base and extends into your uterus. Abnormal cell changes are often associated with malignancy, but the vast majority of endometrial polyps do not cause cancer. Web. Web endometrial polyps vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. Web the polyp attaches to the endometrium by a thin stalk or a broad base and extends into your uterus. Web the mean polyp size was 17.7 ± 0.5 mm in benign patients and 23.7 ± 1.8 mm in premalignant/malignant individuals ( p < 0.001).. Can range in size from millimeters (about the size of a sesame seed) to centimeters (about the size of a golf ball and even larger). Endometrial polyps are localized tumors within the mucosa of the uterine cavity. The prevalence was influenced significantly by age ( p < 0.005); However, peak incidence occurs between the age of 40 to 49 years. Polypectomy was done and the same was sent for histopathological evaluation. Web the sonographic finding suggestive of an endometrial polyp is a bright, hyperechoic area visualized within the endometrium (table 1). In women below the age of 30 years, the prevalence was 0.9%. Polyps may be found as a single lesion or multiple lesions filling the entire endometrial cavity. Web. Polyps may be found as a single lesion or multiple lesions filling the entire endometrial cavity. Web hysteroscopy with guided biopsy remains the gold standard for diagnosis of endometrial polyps (high). On hysteroscopy, there was hyperplastic endometrium with large endometrial polyp of size 8.5 cm. Endometrial polyps vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. Web. Web an endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is a mass in the inner lining of the uterus. They contain glands, connective tissues, and blood vessels. Web an endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is an abnormal growth containing glands, stroma and blood vessels projecting from the lining of the uterus (endometrium) that occupies spaces small or large enough to fill the uterine cavity. Polyps may be found as a single lesion or multiple lesions filling the entire endometrial cavity. You may have one or several polyps present. On average, these polyps are typically less than 1 cm. Can range in size from millimeters (about the size of a sesame seed) to centimeters (about the size of a golf ball and even larger). Polyps may be round or oval and range in size from a few millimeters (the size of a sesame seed) to a few centimeters (the size of a golf ball) or larger. They may have a large flat base ( sessile) or be attached to the uterus by an elongated pedicle ( pedunculated ). Polyps may be found as a single lesion or multiple lesions filling the entire endometrial cavity. Polypectomy was done and the same was sent for histopathological evaluation. Incidence in asymptomatic females with infertility: Web patient was planned for hysteroscopic guided biopsy as her ultrasonography (usg) showed endometrial thickness to be 12.3 mm. [2] [3] pedunculated polyps are more common than sessile ones. The lesions may contain blood vessels and cause irregular menstrual bleeding, spotting, menorrhagia, and postmenopausal bleeding. They also range in number women can have one or many endometrial polyps.
Clinical by individual endometrial thickness Download Table
![[PDF] Giant endometrial polyp protruding from the external cervical os](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/8ee776e2c239fe8f6fe5bef07581c99c4de87bae/5-Figure4-1.png)
[PDF] Giant endometrial polyp protruding from the external cervical os
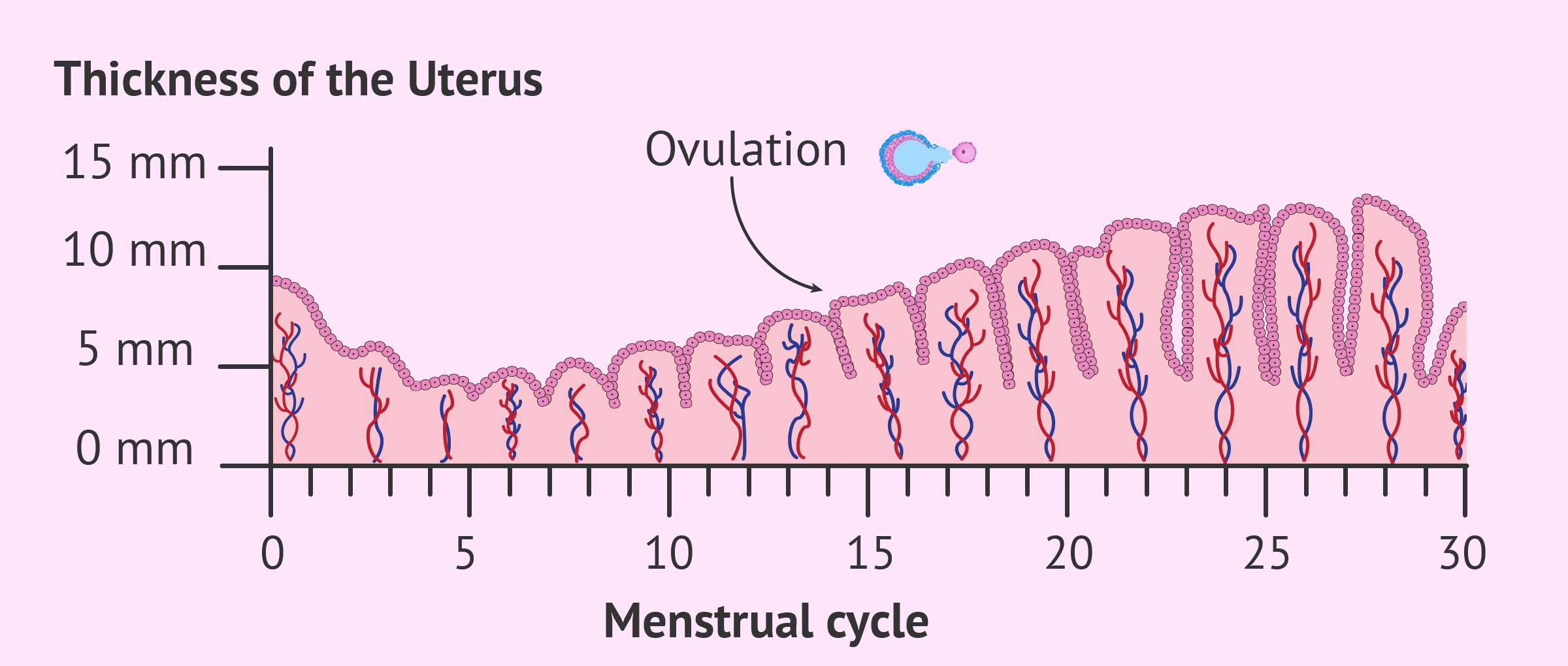
Endometrial Lining Thickness Chart Labb by AG

Narrowband imaging without high magnification to differentiate polyps
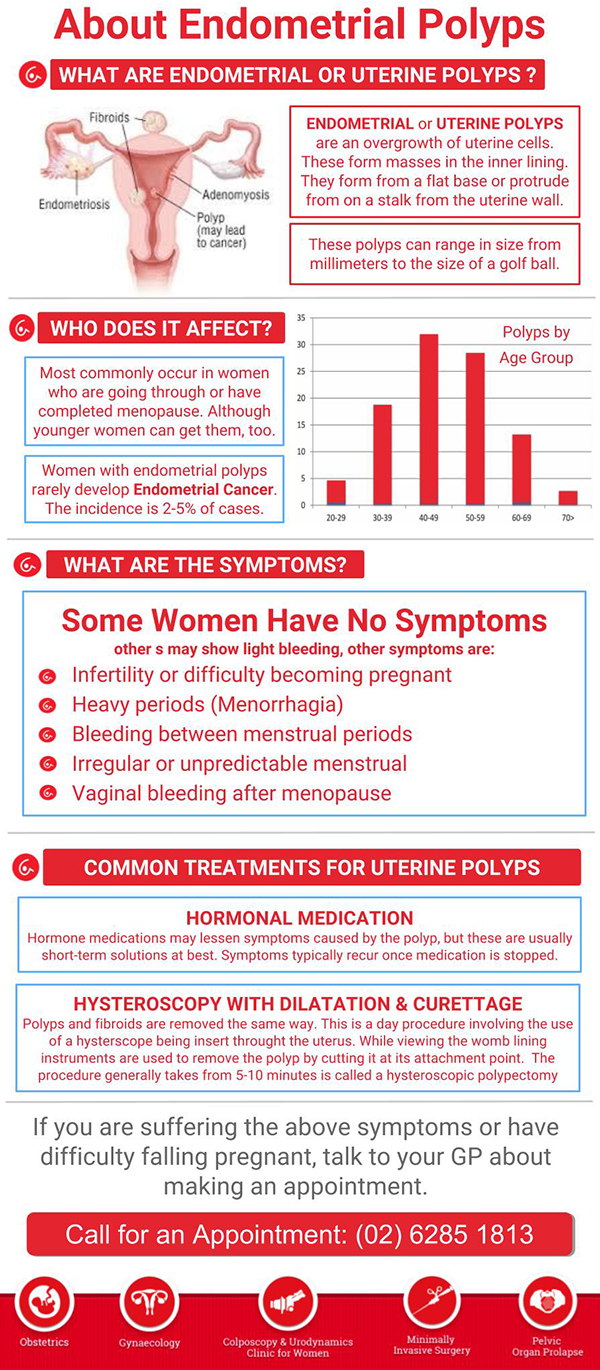
Endometrial & Uterine Polyps Canberra Deakin, ACT
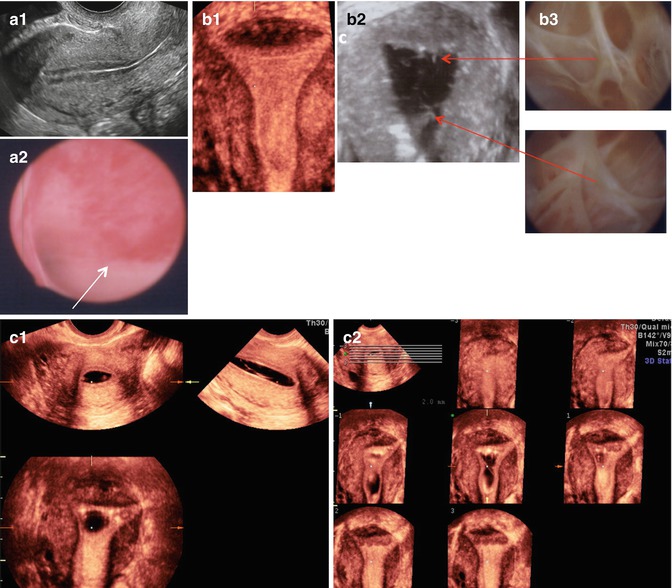
Representative size measurement and appearance of endometrial polyps

Endometrial Polyp Size Chart In Mm
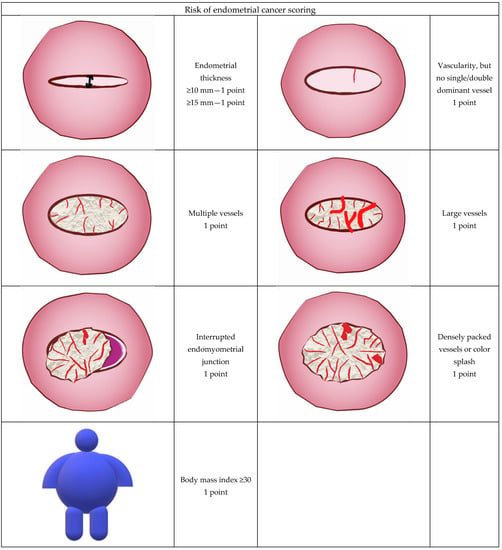
Diagnostics Free FullText Risk Assessment of Endometrial

Uterine Polyp Size Chart
Endometrial Polyp Size Chart
Endometrial Polyps Vary In Size From A Few Millimeters To Several Centimeters In Diameter.
Web The Sonographic Finding Suggestive Of An Endometrial Polyp Is A Bright, Hyperechoic Area Visualized Within The Endometrium (Table 1).
Abnormal Cell Changes Are Often Associated With Malignancy, But The Vast Majority Of Endometrial Polyps Do Not Cause Cancer.
A Fine Telescope Called A Hysterocope Is Introduced Into The Uterus (Womb) Through The.
Related Post: