Burn Pediatric Chart
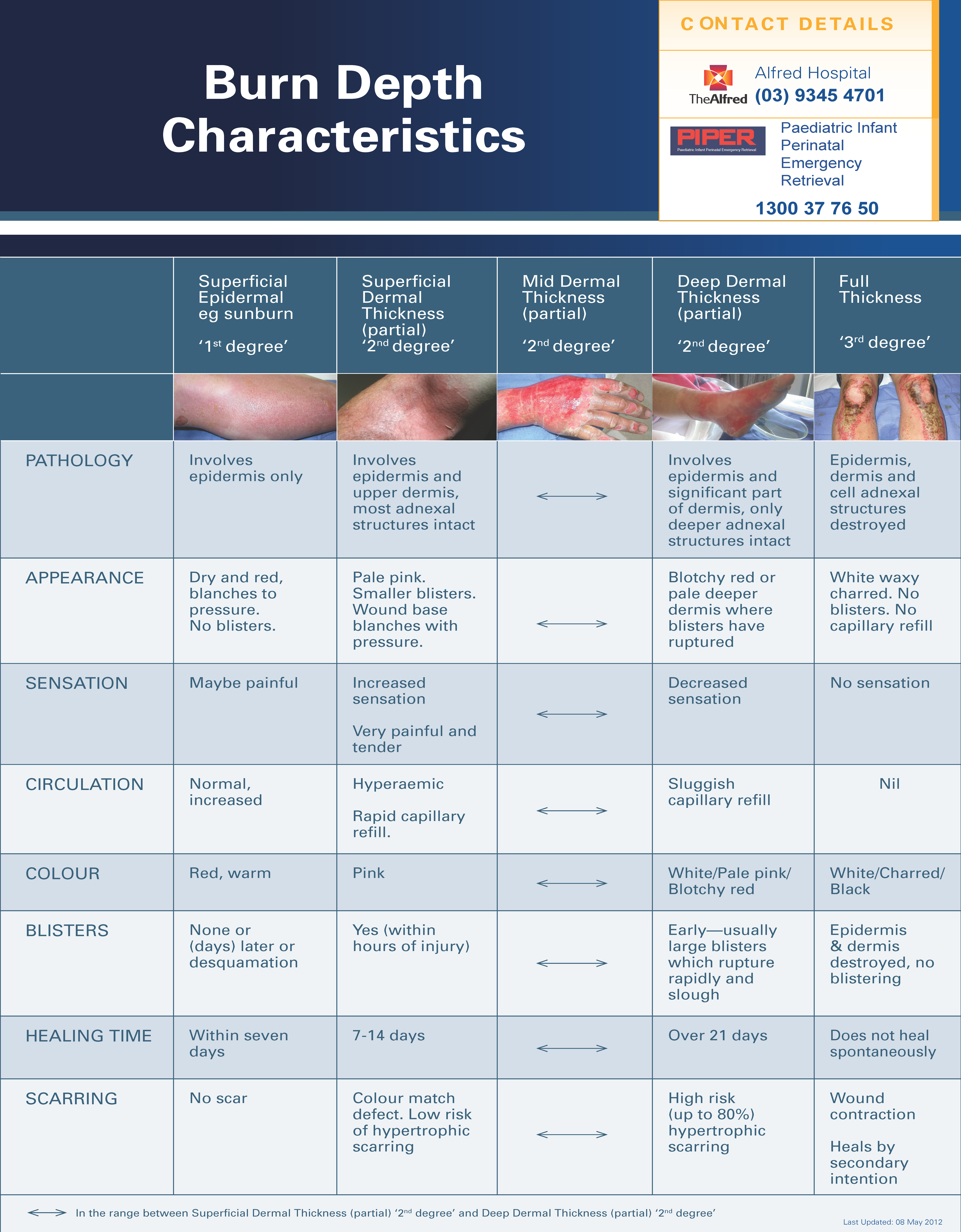
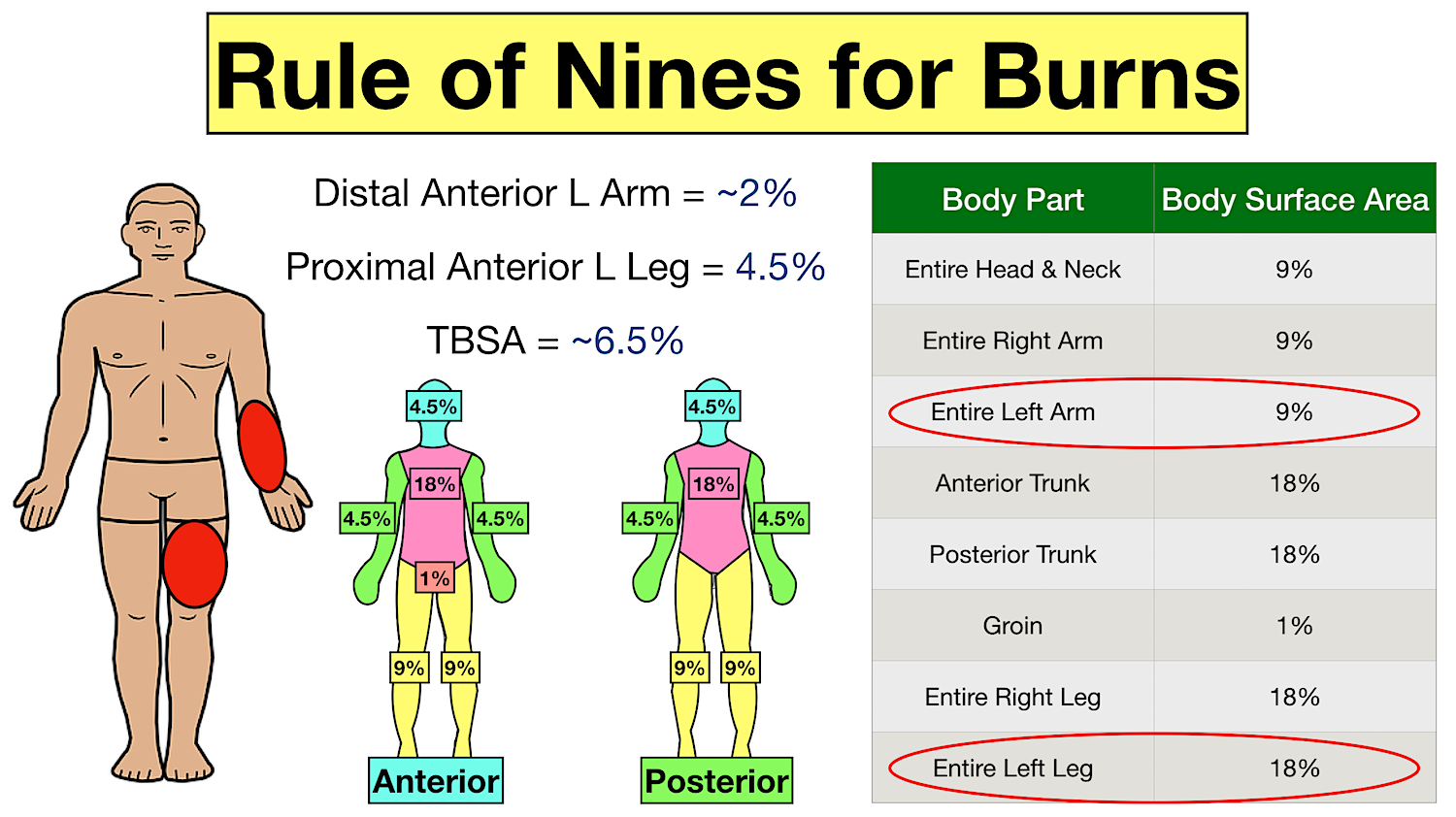
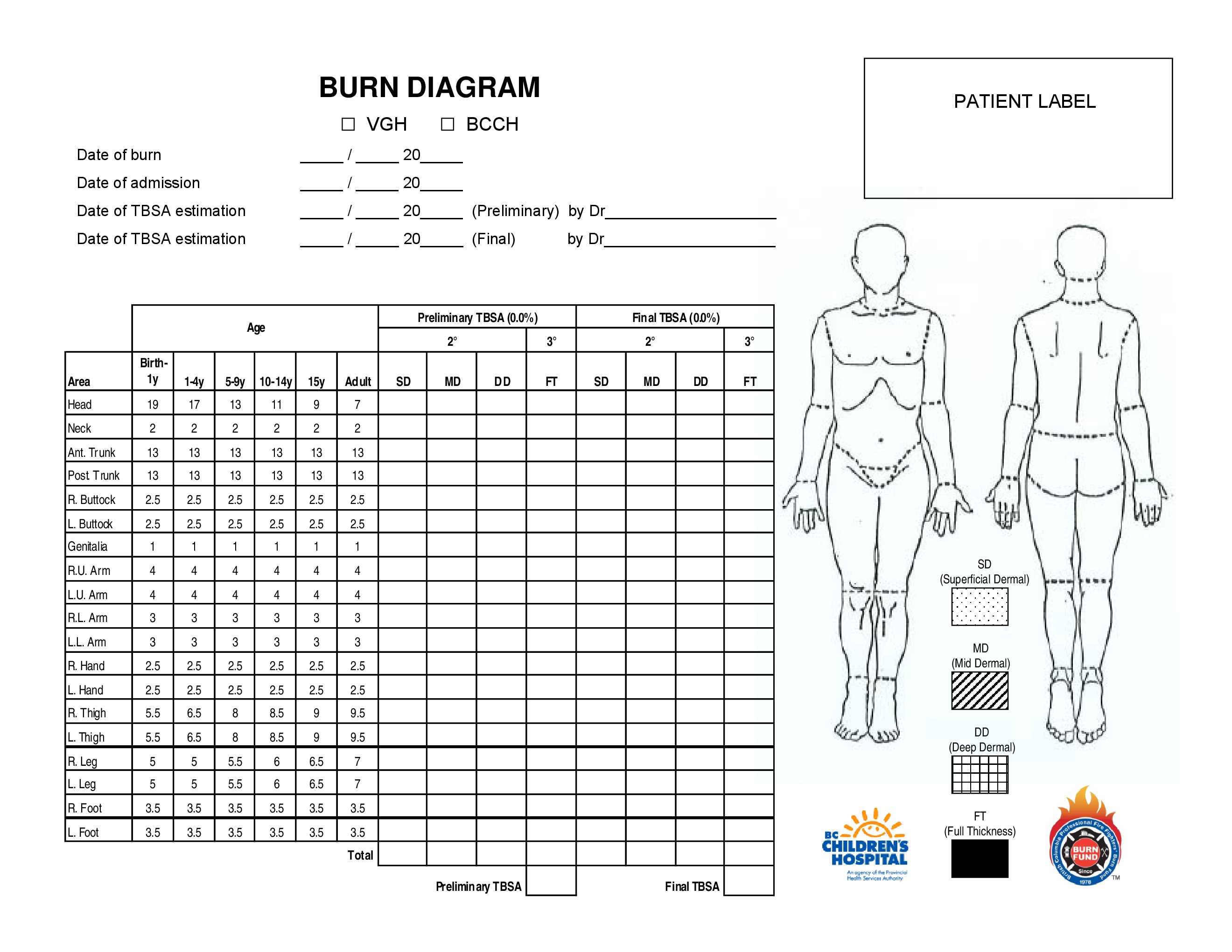
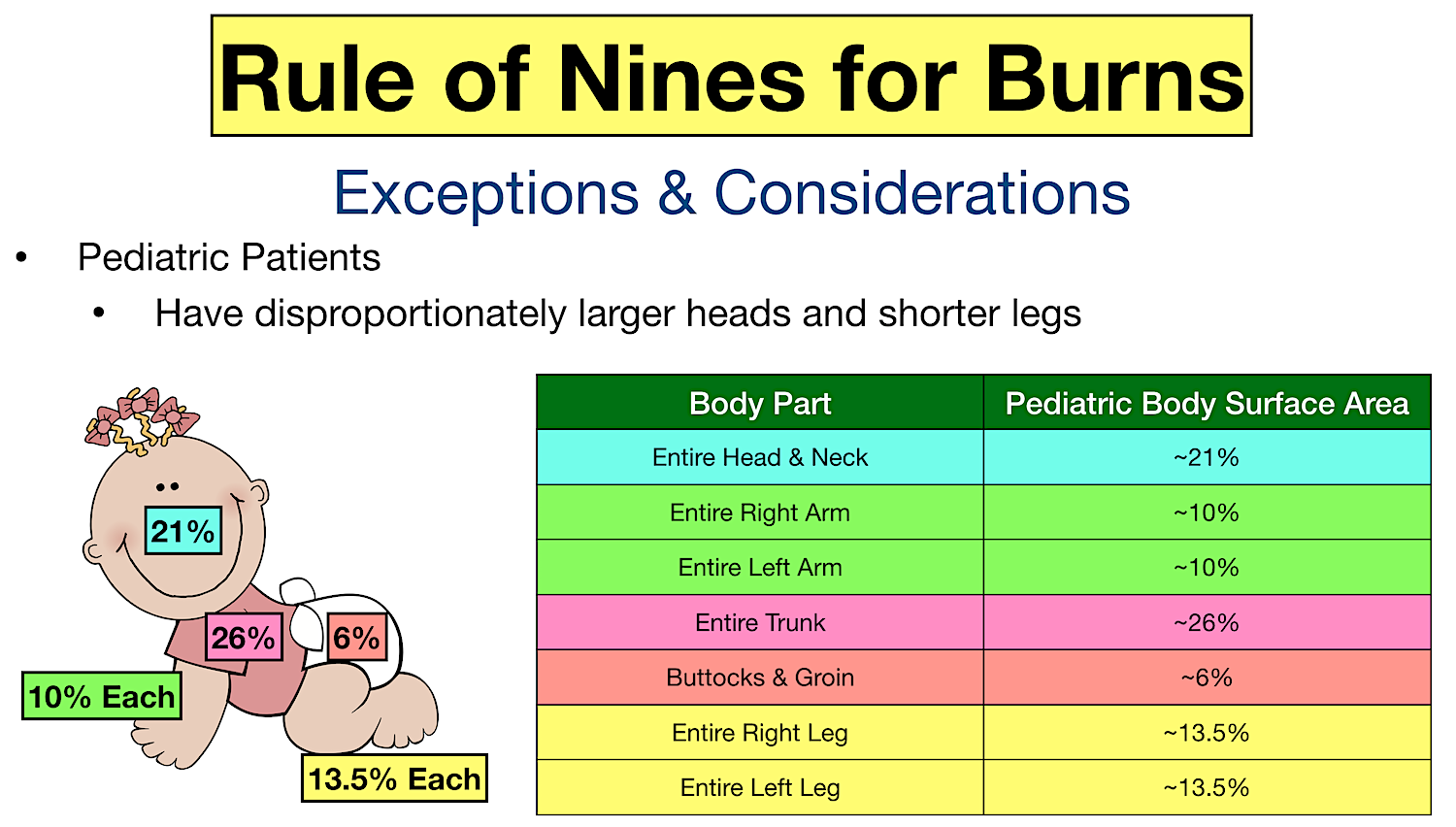
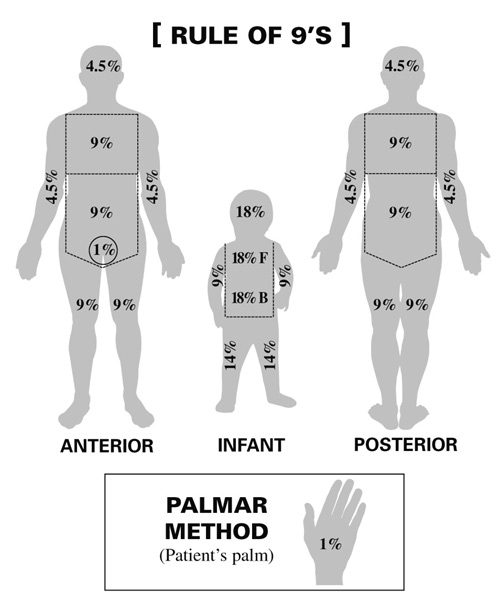
Burn Pediatric Chart - To appropriately triage, diagnose and classify burns in the pediatric patient. Burns in children < 6 months of age. Web the initial approach to the child should follow advanced paediatric life support principles, with an ‘airway, breathing, circulation, disability and exposure’ (abcde) approach, and vigilance for other injuries in addition to the burn. It was created by dr. When a child has a burn injury, immediate care is essential. The front and back of each arm and hand are 10% of the body's surface area. Newton browder, based on their experiences in treating over 300 burn victims injured at the cocoanut grove fire in boston in 1942. Web to estimate the total body surface area (tbsa) burns in children, lund and browder charts may be used, which takes into account changes in the body proportions of growing children. An alternative rule is that the patient's palm and fingers represent 1% of the body surface. Toddlers and children are more often burned by a scalding or flames. Date/time ______________ *areas of difference between the pediatric and adult population are represented by bold italics. Local injury, systemic response, and metabolic changes combine to determine the severity of a burn injury as follows: The front and back of each arm and hand are 10% of the body's surface area. Roughly 25% of all burn injuries occur in children under. Great for emts, pediatrics, nursing, and more! Resuscitation and wound care are essential in the initial management. Newton browder, based on their experiences in treating over 300 burn victims injured at the cocoanut grove fire in boston in 1942. The front and back of the head and neck are 21% of the body's surface area. Web the initial approach to. To decrease variability in the management of patients with burns. However, there is tremendous variability in practice among burn centers. Fluid administration and treatment resources needed are decisions made in the field by emergency medical technicians (emts) and paramedics. Nearly 75% of all scalding burns in children are preventable. Date/time ______________ *areas of difference between the pediatric and adult population. Burn + requirement for inotropic support. Burns + inhalation injury or need to ventilate. To decrease variability in the management of patients with burns. Web the goal is management of burns shock, through optimal replacement of fluid losses to maximise wound and body perfusion, and minimise wound and body oedema and associated adverse effects. Different percentages are used in paediatrics. Web this guideline applies to all medical and nursing staff within qh who are treating a paediatric burns patient. This practice guideline will outline the essential elements of. Different percentages are used in paediatrics because the surface area of the head and neck relative to the surface area of the limbs is typically larger in children than adults. Nearly 75%. In children, the head and neck occupy a larger, and the lower extremities occupy a smaller, proportion of the total body area. Date/time ______________ *areas of difference between the pediatric and adult population are represented by bold italics. Toddlers and children are more often burned by a scalding or flames. The new chart reduces math errors, improving accuracy for better. Local injury, systemic response, and metabolic changes combine to determine the severity of a burn injury as follows: Most patients treated in the burn program are managed as outpatients with closed dressings,. For pediatric burn patients requiring resuscitation, the lund and browder chart is the preferred method toestimate tbsa. Web what is a clinical pathway? Resuscitation and wound care are. Web burns and fires are the fifth most common cause of accidental death in children and adults, and account for an estimated 3,500 adult and child deaths per year. Child & adult chart calculations. Fluid administration and treatment resources needed are decisions made in the field by emergency medical technicians (emts) and paramedics. An alternative rule is that the patient's. Roughly 25% of all burn injuries occur in children under the age of 15 years. Web the size of a burn for a baby or young child can be quickly estimated by using the rule of nines. this method divides a baby's body surface area into percentages. Web overall severity of burn injury — a combination of the burn mechanism,. Includes charts, calculations, definitions, formulas, and example practice questions! Great for emts, pediatrics, nursing, and more! Resuscitation and wound care are essential in the initial management. The new chart reduces math errors, improving accuracy for better outcomes. To decrease variability in the management of patients with burns. Web the lund and browder chart is a tool useful in the management of burns for estimating the total body surface area affected. Web the goal is management of burns shock, through optimal replacement of fluid losses to maximise wound and body perfusion, and minimise wound and body oedema and associated adverse effects. This practice guideline will outline the essential elements of. Toddlers and children are more often burned by a scalding or flames. To appropriately triage, diagnose and classify burns in the pediatric patient. Web the total body surface area (tbsa) of a burn was traditionally assessed using lund and browder burns chart that denotes the percentage of body surface and changes with age of the child (fig 2). Web scald burns are the most common cause of thermal injury in pediatric patients. Calculate requirements from time of. When a child has a burn injury, immediate care is essential. The front and back of each arm and hand are 10% of the body's surface area. Local injury, systemic response, and metabolic changes combine to determine the severity of a burn injury as follows: An alternative rule is that the patient's palm and fingers represent 1% of the body surface. Web there are various methods used to estimate tbsa. Web this guideline applies to all medical and nursing staff within qh who are treating a paediatric burns patient. Web the initial approach to the child should follow advanced paediatric life support principles, with an ‘airway, breathing, circulation, disability and exposure’ (abcde) approach, and vigilance for other injuries in addition to the burn. Resuscitation and wound care are essential in the initial management.
Major Burns in Children Pediatric Emergency Playbook

Paediatric TraumaPaediatric Burns Sub Guideline Trauma Victoria
Paediatric TraumaPaediatric Burns Sub Guideline Trauma Victoria
Rule Of Nines Burn Chart Printable

Rule Of Nines Pediatric Burn Chart
Pediatric Burn Diagram
Rule of Nines for Burns Child and Adult Chart, Calculator, Definition
Paediatric Emergency Medicine Minor Burns in Children

Burn Rule Of Nines Chart
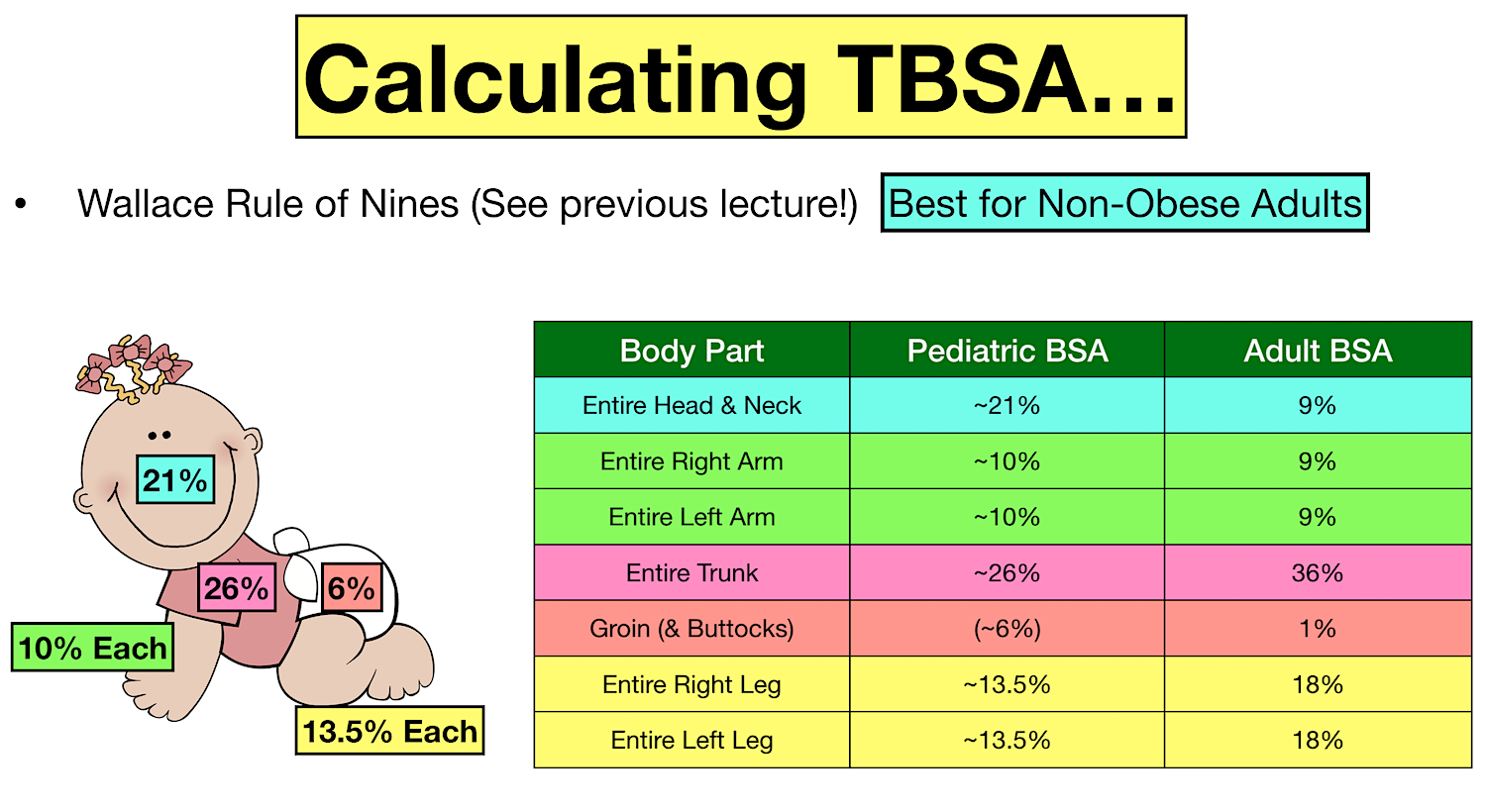
Parkland Formula for Burns Pediatric and Adult Examples, Calculator
Web What Is A Clinical Pathway?
Web Infant/Pediatric Lund And Browder Burn Chart.
Charles Lund, Senior Surgeon At Boston City Hospital, And Dr.
Date/Time ______________ *Areas Of Difference Between The Pediatric And Adult Population Are Represented By Bold Italics.
Related Post: