Clast Size Chart
Clast Size Chart - Granular material can range from very small colloidal particles, through clay, silt, sand, gravel, and cobbles, to boulders. Lithogenous sediments (described above) are mostly clastic sediments. This is different from the crystallite size, which refers to the size of a single crystal inside a particle or grain. Web although roundness can be numerically quantified, for practical reasons geologists typically use a simple visual chart with up to six categories of roundness: Web grain size varies from clay in shales and claystones; When studying sedimentary rocks, the one of the most obvious aspects will be the particle or clast size. Web gravel, sand, and silt are examples of clastic sediments. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. Grain size (or particle size) is the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic rocks. Type description size range (millimeters) size range. This is different from the crystallite size, which refers to the size of a single crystal inside a particle or grain. And gravel, cobble, to boulder sized fragments in conglomerates and. Web grain size varies from clay in shales and claystones; Clastic sediments form a wide range of rocks, from mudstone to. The term may also be applied to other. Web grain size varies from clay in shales and claystones; The term may also be applied to other granular materials. The average grain size of a clastic rock is measured in mm and is used to assign a description of the grain size by a set of size. When studying sedimentary rocks, the one of the most obvious aspects will. When studying sedimentary rocks, the one of the most obvious aspects will be the particle or clast size. Clastic sediments form a wide range of rocks, from mudstone to. This is different from the crystallite size, which refers to the size of a single crystal inside a particle or grain. Type description size range (millimeters) size range. Determining whether a. Web although roundness can be numerically quantified, for practical reasons geologists typically use a simple visual chart with up to six categories of roundness: Determining whether a sedimentary rock is. Web gravel, sand, and silt are examples of clastic sediments. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. And gravel, cobble, to boulder sized fragments in conglomerates and. Web learn about clasts, the fragments of rock or mineral that make up sedimentary rocks. Web although roundness can be numerically quantified, for practical reasons geologists typically use a simple visual chart with up to six categories of roundness: A single grain can be composed of several crystals. Web gravel, sand, and silt are examples of clastic sediments. When studying. Type description size range (millimeters) size range. And gravel, cobble, to boulder sized fragments in conglomerates and. Clastic sediments form a wide range of rocks, from mudstone to. Lithogenous sediments (described above) are mostly clastic sediments. The average grain size of a clastic rock is measured in mm and is used to assign a description of the grain size by. Web grain size determines just how far a piece of sediment can travel before coming to a halt. Web gravel, sand, and silt are examples of clastic sediments. Determining whether a sedimentary rock is. Determining whether a sedimentary rock is. Web the size grade for conglomerates should immediately precede conglomerate. some common nonmineral constituent terms are: And gravel, cobble, to boulder sized fragments in conglomerates and. Web clast size & sorting. When studying sedimentary rocks, the one of the most obvious aspects will be the particle or clast size. Type description size range (millimeters) size range. Clastic sediments form a wide range of rocks, from mudstone to. Web average grain size and grain size categories. Clastic sediments form a wide range of rocks, from mudstone to. Determining whether a sedimentary rock is. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. This is different from the crystallite size, which refers to the size of a single crystal inside a particle or grain. Determining whether a sedimentary rock is. Web grain size determines just how far a piece of sediment can travel before coming to a halt. And gravel, cobble, to boulder sized fragments in conglomerates and. When studying sedimentary rocks, the one of the most obvious aspects will be the particle or clast size. This is different from the crystallite size, which. Web learn about clasts, the fragments of rock or mineral that make up sedimentary rocks. When studying sedimentary rocks, the one of the most obvious aspects will be the particle or clast size. Web grain size determines just how far a piece of sediment can travel before coming to a halt. Clastic sediments form a wide range of rocks, from mudstone to. Web gravel, sand, and silt are examples of clastic sediments. Web grain size varies from clay in shales and claystones; When studying sedimentary rocks, the one of the most obvious aspects will be the particle or clast size. Determining whether a sedimentary rock is. A single grain can be composed of several crystals. Granular material can range from very small colloidal particles, through clay, silt, sand, gravel, and cobbles, to boulders. Web the size grade for conglomerates should immediately precede conglomerate. some common nonmineral constituent terms are: The average grain size of a clastic rock is measured in mm and is used to assign a description of the grain size by a set of size. Web most clasts that are smaller than sand size (clasts</strong> larger than sand size (>2 mm) are actual fragments of rock, and commonly these. This is different from the crystallite size, which refers to the size of a single crystal inside a particle or grain. A classification of clastic sediments and. Web clast size & sorting.
Describing and Naming Clastic Sedimentary Rocks Laboratory Manual for
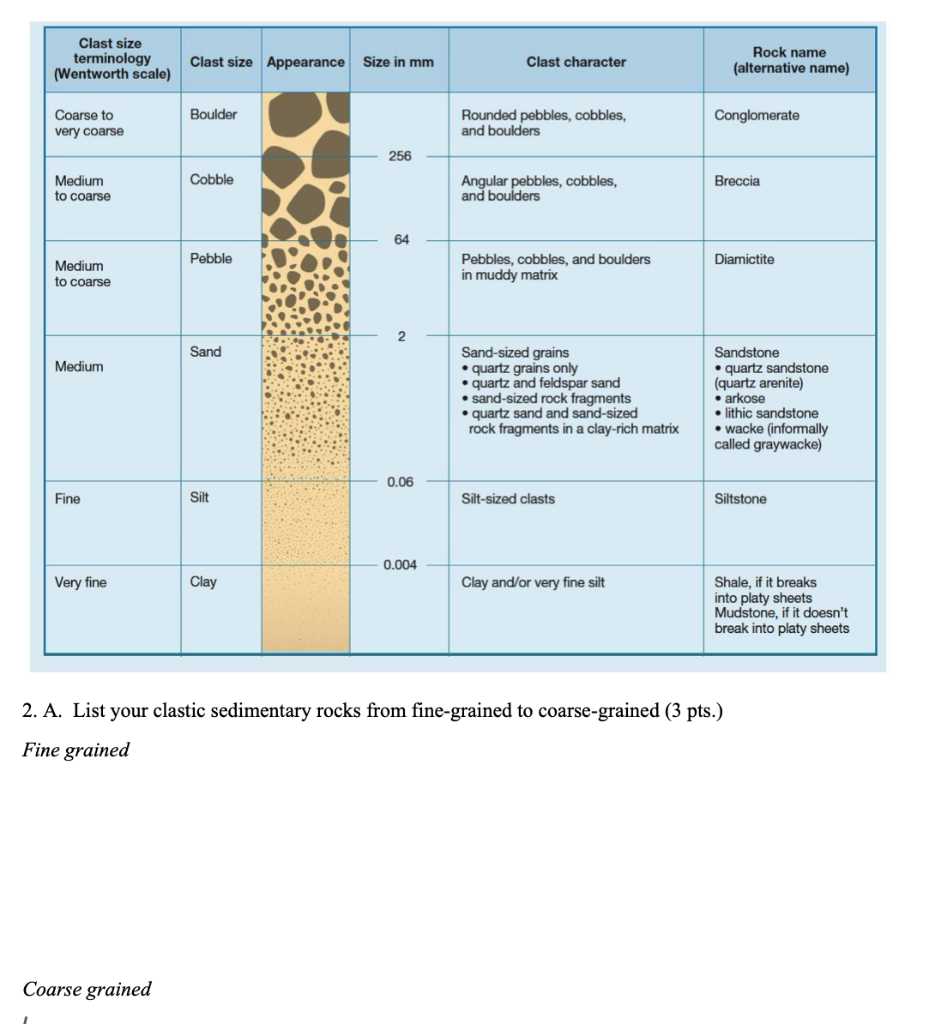
Solved Clast size terminology ( Wentworth scale) Clast size

PPT Sedimentary Rocks and Sedimentary Environments PowerPoint
5.3 Clastic Sedimentary Rocks A Practical Guide to Introductory Geology

Lithostratigraphic log, gravel clast sizes, paleocurrent directions

Solved Drag the names of clast sizes into the correct order,

Histograms showing A, clast lithology, and B, average clast size, for

Example of a clast size distribution histogram for a conglomeratic ore

Chapter 9 Sedimentary Rocks Physical Geology

Clast type, roundness and size data. a Clast type versus distance. b
And Gravel, Cobble, To Boulder Sized Fragments In Conglomerates And.
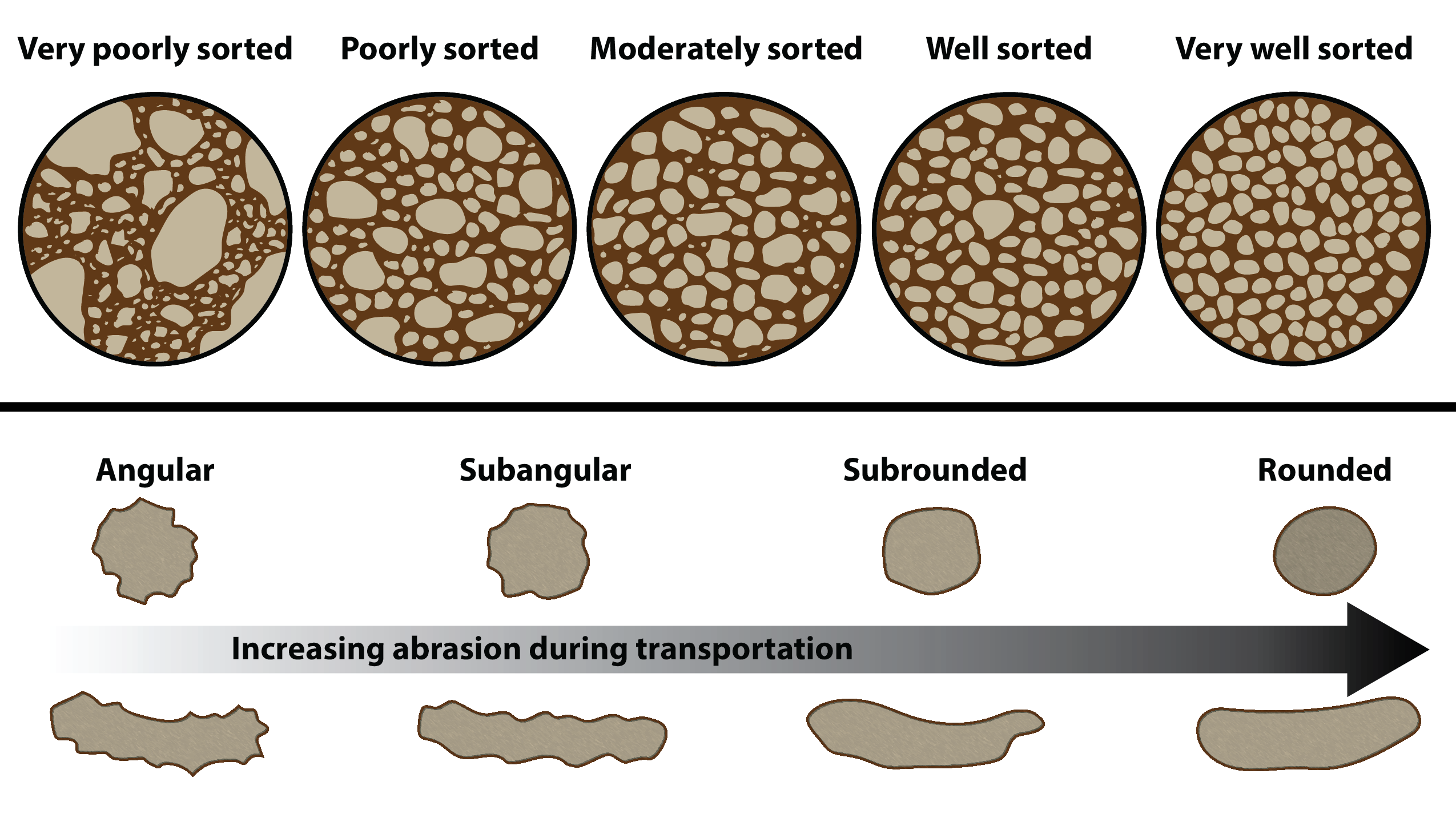
Web Although Roundness Can Be Numerically Quantified, For Practical Reasons Geologists Typically Use A Simple Visual Chart With Up To Six Categories Of Roundness:
Type Description Size Range (Millimeters) Size Range.
The Term May Also Be Applied To Other Granular Materials.
Related Post: