Violin Harmonics Chart
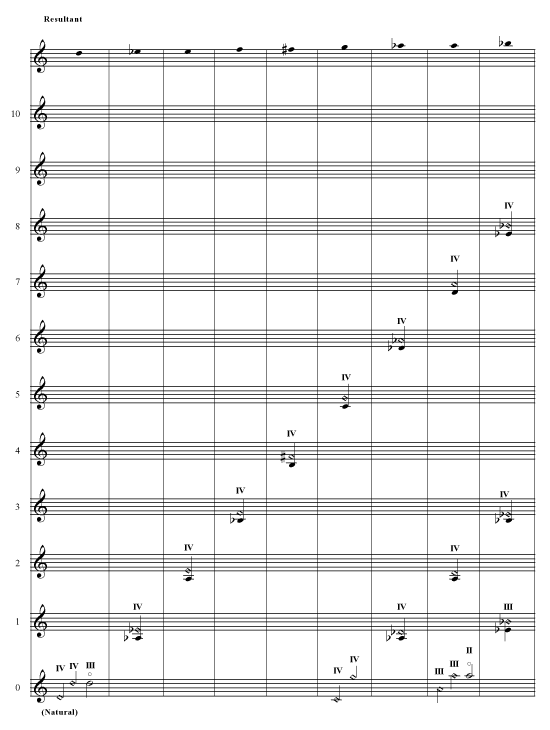
Violin Harmonics Chart - By touching the string a quarter of the way down he gets the next harmonic. Web the chart of the various harmonics is read as follows: Web the natural harmonics that can be produced on the violin are shown in the diagram below. Web get a free violin harmonics chart, exercises, and learn how to play harmonics on your violin. Web a violinist will hear a harmonic (the note an octave higher than the open string). Natural and artificial harmonics are listed, as well as explanatory text. Web to be completely accurate, a harmonic would be notated thus: The 0 staff gives the natural harmonics, which are. They are great for varying effects on this versatile instrument. The chart follows the standard notation of iv, iii, ii, and i being the g, d, a, and e strings, respectively. Learn to play your violin like a flute. Web to be completely accurate, a harmonic would be notated thus: Web when a composer wants the violin or viola to play an artificial harmonic, a base note will be placed on the staff and another note will be added that is a perfect fourth above the base. Web explanations of the. Web the natural harmonics that can be produced on the violin are shown in the diagram below. Natural and artificial harmonics are listed, as well as explanatory text. The roman numeral denotes the string (iv = g, iii = d, ii = a, i = e) the small circle shows that it is a harmonic. The performer must do a. Web violin harmonics (click note to hear harmonic) natural harmonics. Web the chart of the various harmonics is read as follows: Web the chart of the various harmonics is read as follows: Web finally understand and learn how to play all possible harmonics on the violin and how they look in sheet music without confusing tables and theories. The note. Reading vertically will give you all the possible ways to produce a given resultant; The 0 staff gives the natural harmonics, which are. 10k views 2 years ago. The roman numeral denotes the string (iv = g, iii = d, ii = a, i = e) the small circle shows that it is a harmonic. The performer must do a. Understand basic violin construction and physics of sound. They are great for varying effects on this versatile instrument. What’s the difference between natural and artificial harmonics on the violin? Students will naturally discover these principles if they are focused on the tone they produce. Web here’s some common questions about violin harmonics that we’ll cover in this easy guide to. Reading vertically will give you all the possible ways to produce a given resultant; The chart follows the standard notation of iv, iii, ii, and i being the g, d, a, and e strings, respectively. The artificial harmonics are grouped on the bottom five staves by What’s the difference between natural and artificial harmonics on the violin? Natural and artificial. What’s the difference between natural and artificial harmonics on the violin? Sometimes composers of string music like to give the performer a chance to showoff by specifying harmonics. These points are called “nodes”. How to play violin harmonics? Web they should listen for a clear, flutelike, pure tone that will be achieved best when the bow hair is flat on. Reading vertically will give you all the possible ways to produce a given resultant; Understand basic violin construction and physics of sound. 10k views 2 years ago. The note head of the base looks like any other note, but the harmonic note head is always a hollow diamond laying on its side. Web violin harmonics (click note to hear harmonic). These points are called “nodes”. What are the different types of harmonics? Web they should listen for a clear, flutelike, pure tone that will be achieved best when the bow hair is flat on the string and the contact point is closer to the bridge. Learn to play your violin like a flute. Reading vertically will give you all the. Sometimes composers of string music like to give the performer a chance to showoff by specifying harmonics. How to play violin harmonics? Web the most comprehensive guide to violin harmonics! Web they should listen for a clear, flutelike, pure tone that will be achieved best when the bow hair is flat on the string and the contact point is closer. Web a violinist will hear a harmonic (the note an octave higher than the open string). Web get a free violin harmonics chart, exercises, and learn how to play harmonics on your violin. Web the most comprehensive guide to violin harmonics! These points are called “nodes”. The chart follows the standard notation of iv, iii, ii, and i being the g, d, a, and e strings, respectively. Web in this video, i show you how to play natural, artificial and double harmonics on the violin. The performer must do a lot of shifting, but the result is a chime like, or soft flute sound that is unlike the normal sound associated with a violin, viola, cello, or bass. What’s the difference between natural and artificial harmonics on the violin? By placing his fingers in other places he can get more harmonics, e.g. The strings are tuned a fifth apart at g3 (196 hz), d 4 (293.7 hz), a4, e5 (659.3 hz) if tuned in equal temperament with the a 4 = 440hz standard. Natural and artificial harmonics are listed, as well as explanatory text. Web they should listen for a clear, flutelike, pure tone that will be achieved best when the bow hair is flat on the string and the contact point is closer to the bridge. Harmonics are easy and convenient to do on all the open strings when improvising. The note head of the base looks like any other note, but the harmonic note head is always a hollow diamond laying on its side. What are the different types of harmonics? The artificial harmonics are grouped on the bottom five staves by
Violin Harmonics Chart
Violin Harmonics Chart

Violin Harmonics Chart Violin, Free violin sheet music, Violin sheet

Violin Harmonics Montgomery Philharmonic

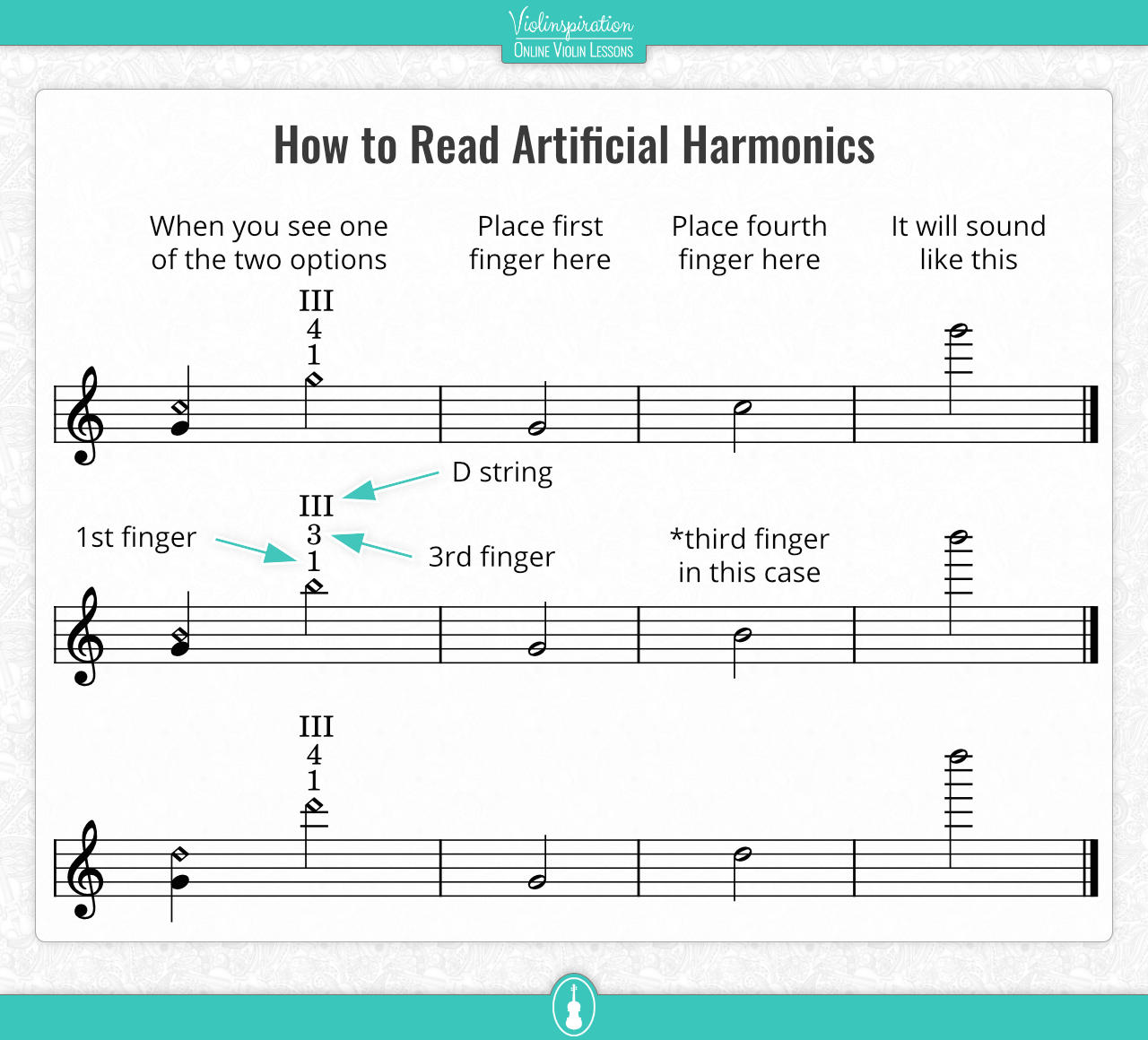
Violin Harmonics Chart and Exercises Violinspiration

Violin Harmonics Montgomery Philharmonic
Violin Harmonics Chart and Exercises Violinspiration

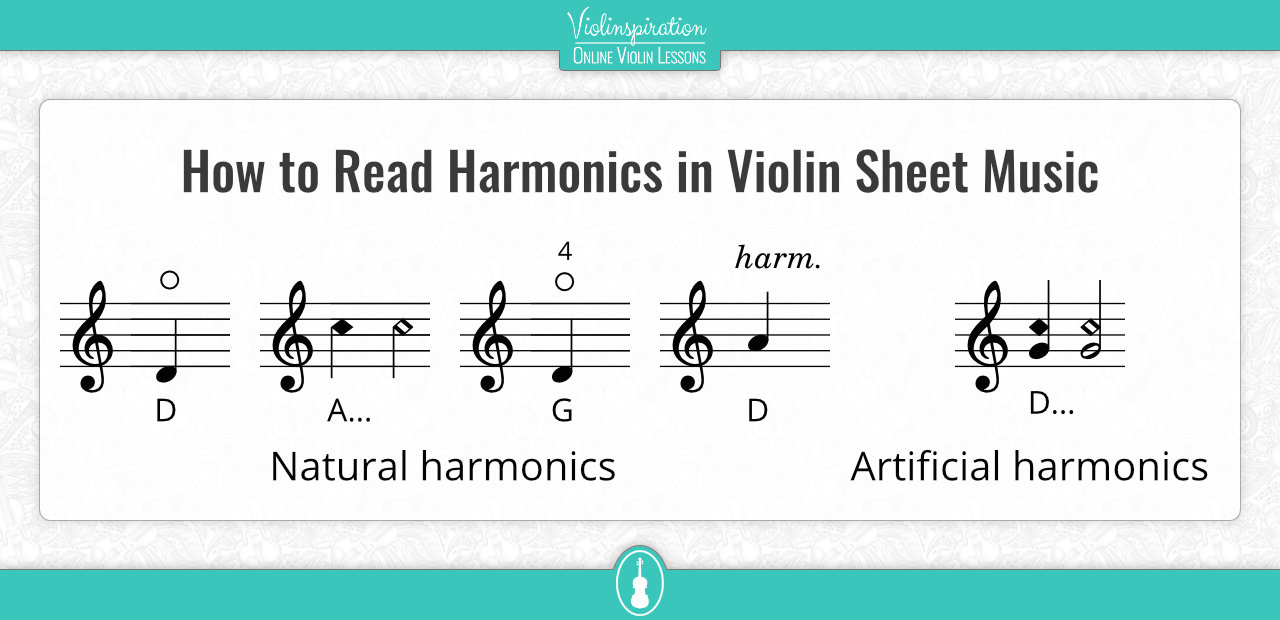
Violin Harmonics Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Violin Harmonics Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master

GitHub geometrian/violinharmonicschart A Modernized Chart for
Web Here’s Some Common Questions About Violin Harmonics That We’ll Cover In This Easy Guide To Harmonics.
Learn To Play Your Violin Like A Flute.
The Note Itself Is The Sounding Pitch (Not Where You Touch The String)
How To Read Natural And Artificial Harmonics In Violin Sheet Music.
Related Post: