Subcool And Superheat Chart
Subcool And Superheat Chart - If you read my previous post about sealed system basics, you know that understanding the thermodynamic states of refrigerants (saturated, subcooled, and superheated) is essential to sealed system troubleshooting. Web superheat measures the freon boiling point in gas form while subcooling measures the freon in liquid form below the evaporation level. Web you get superheat when you have 100% vapor, and you have subcooling when you have 100% liquid; Then take the temperature of the liquid line as close to evaporator as possible before the metering device. Take the difference between the above readings. You will find the chart that summarizes all total superheats further on. Evaporative superheat and target superheat. Web since now we know what latent heat is as well as saturation temperature, we can now understand what exactly is superheat & subcooling. Learn about the implications of normal subcooling with low superheat and discover the potential causes and solutions for this unique situation. Troubleshooting often requires simultaneous knowledge of temperature, pressure, voltage, and current values in a system. Charge your refrigeration system accurately with the help of our subcooling charging chart, tailored for different refrigerants and conditions… Web superheat measures the freon boiling point in gas form while subcooling measures the freon in liquid form below the evaporation level. In this article, we will define subcooling, calculate subcooling, explain how to use subcooling to check the refrigerant charge,. Web in determining a target superheat cross referencing the indoor wet bulb and outdoor dry bulb temperatures, the charging chart will recommend the proper target superheat for that system. Web a solid understanding of superheat and subcooling is essential. You will find the chart that summarizes all total superheats further on. Web since now we know what latent heat is. If you read my previous post about sealed system basics, you know that understanding the thermodynamic states of refrigerants (saturated, subcooled, and superheated) is essential to sealed system troubleshooting. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications for accurate measurements. Let’s quickly go over them and list if we need to add or remove refrigerant for each of them: We usually measure. Learn about the implications of normal subcooling with low superheat and discover the potential causes and solutions for this unique situation. Web most txvs maintain a required superheat of 8° to 12°f. Web once you determine the indoor wet bulb and outdoor dry bulb temperatures, check the manufacturer’s charging chart to determine the proper suction superheat. You will find the. Web since now we know what latent heat is as well as saturation temperature, we can now understand what exactly is superheat & subcooling. © 2019 ac service tech llc. Web you get superheat when you have 100% vapor, and you have subcooling when you have 100% liquid; Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications for accurate measurements. We usually measure. Web the superheat chart includes target ac superheat for 55°f to 128°f outdoor temperature (db temperature) and for 50°f to 76°f indoor evaporator temperature (wb temperature). In this article, we will define subcooling, calculate subcooling, explain how to use subcooling to check the refrigerant charge, and show where the measurement points are taken on an air conditioning system. Web in. Web the superheat chart includes target ac superheat for 55°f to 128°f outdoor temperature (db temperature) and for 50°f to 76°f indoor evaporator temperature (wb temperature). Superheat is the temperature above its saturation temperature. Learn about the implications of normal subcooling with low superheat and discover the potential causes and solutions for this unique situation. Web most txvs maintain a. Then take the temperature of the liquid line as close to evaporator as possible before the metering device. So, if the condenser brings the refrigerant temperature down to 105 degrees, it has been subcooled by 15 degrees. There are two effect methods of determining a proper superheat refrigerant charge for an hvacr system: Indoor wb 66° f, outdoor db 90°. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications for accurate measurements. Web once you determine the indoor wet bulb and outdoor dry bulb temperatures, check the manufacturer’s charging chart to determine the proper suction superheat. Take the high side pressure and convert it to temperature using chart or gauge. Web normal subcooling low superheat. If you read my previous post about sealed. Web normal subcooling low superheat. In the refrigeration cycle, subcooling is an important process that ensures liquid refrigerant enters the expansion device. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications for accurate measurements. Take the difference between the above readings. What is acceptable superheat and subcooling? What is acceptable superheat and subcooling? To calculate superheat and subcooling measurements, a specific mathematical chart is used, and the process is mostly done by an hvac technician. Web there are a couple of these superheat subcooling scenarios (based on the target superheat and the target subcooling chart for specific refrigerant). Web you get superheat when you have 100% vapor, and you have subcooling when you have 100% liquid; Web superheat measures the freon boiling point in gas form while subcooling measures the freon in liquid form below the evaporation level. Web this free online tool allows hvac professionals to quickly calculate superheat and subcooling measurements for both r22 & r410a refrigerants. Let’s quickly go over them and list if we need to add or remove refrigerant for each of them: There are two effect methods of determining a proper superheat refrigerant charge for an hvacr system: Web measure the outdoor db roughly one foot away from the inlet of the outdoor coil in the shade. Web in this hvac video, i explain superheat and subcooling in the refrigeration cycle to understand the operation easier! We usually measure superheat outside at the suction or vapor line. Indoor wb 66° f, outdoor db 90° f= target superheat of 13 ° f. Web the superheat chart includes target ac superheat for 55°f to 128°f outdoor temperature (db temperature) and for 50°f to 76°f indoor evaporator temperature (wb temperature). Web while superheat indicates how much refrigerant is in the evaporator (high superheat indicates not enough, low superheat indicates too much), subcooling gives an indication of how much refrigerant is in the condenser. Take the difference between the above readings. Web most txvs maintain a required superheat of 8° to 12°f.
Buy Useful HVAC Ultimate Superheat Temperature Chart Paper

Superheat And Subcool Chart
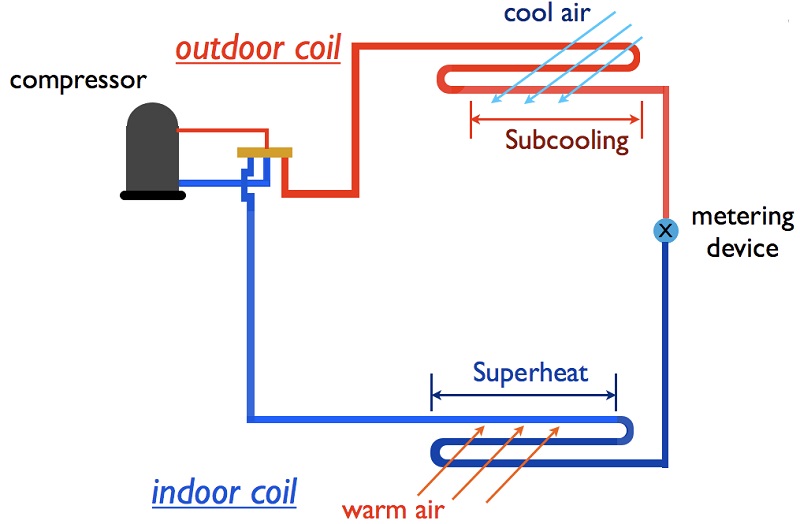
Superheat and Subcooling Defined
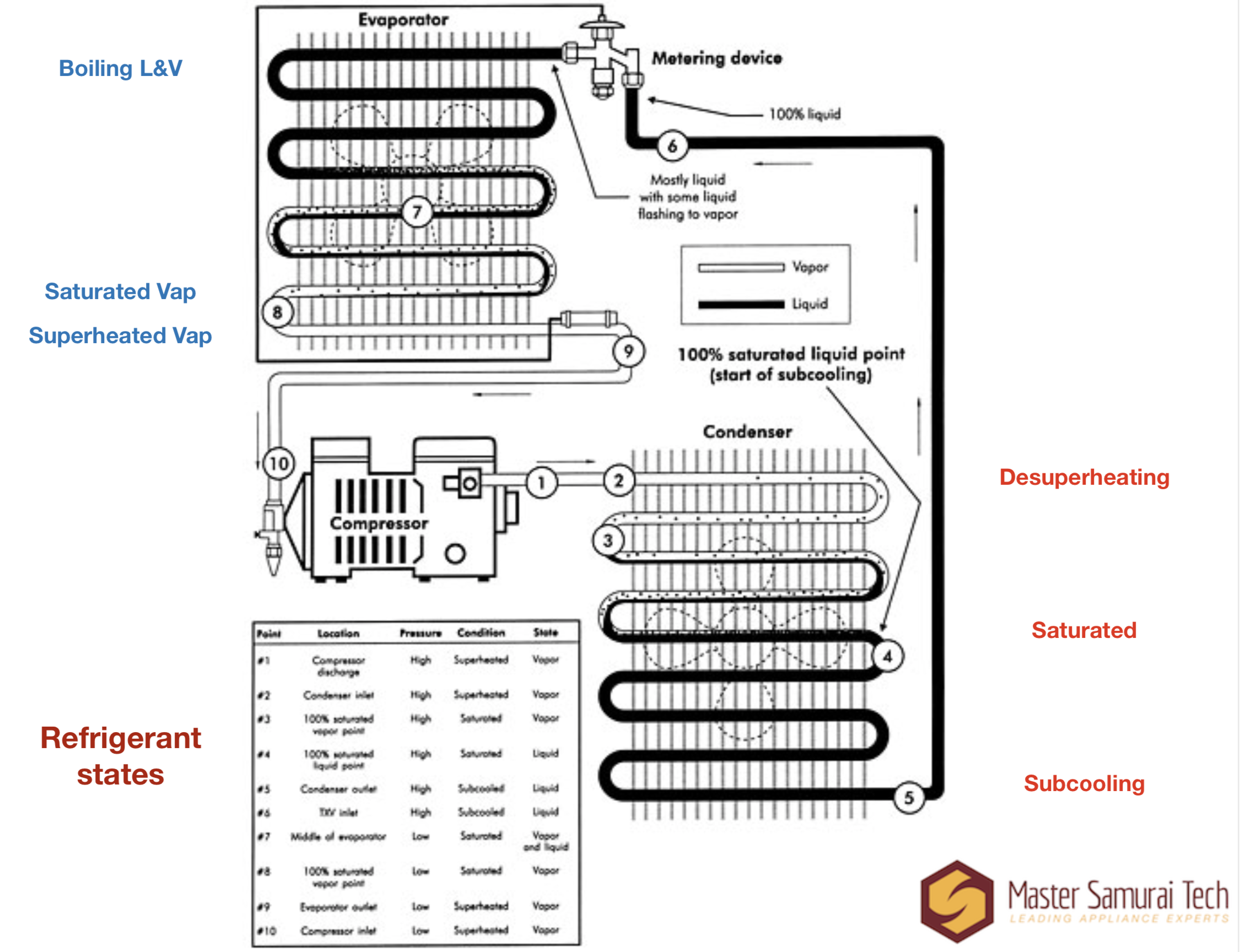
Sealed System Basics Saturation, Subcooling, and Superheat Appliance

Superheat And Subcooling Troubleshooting Chart

Superheat Archives HVAC School
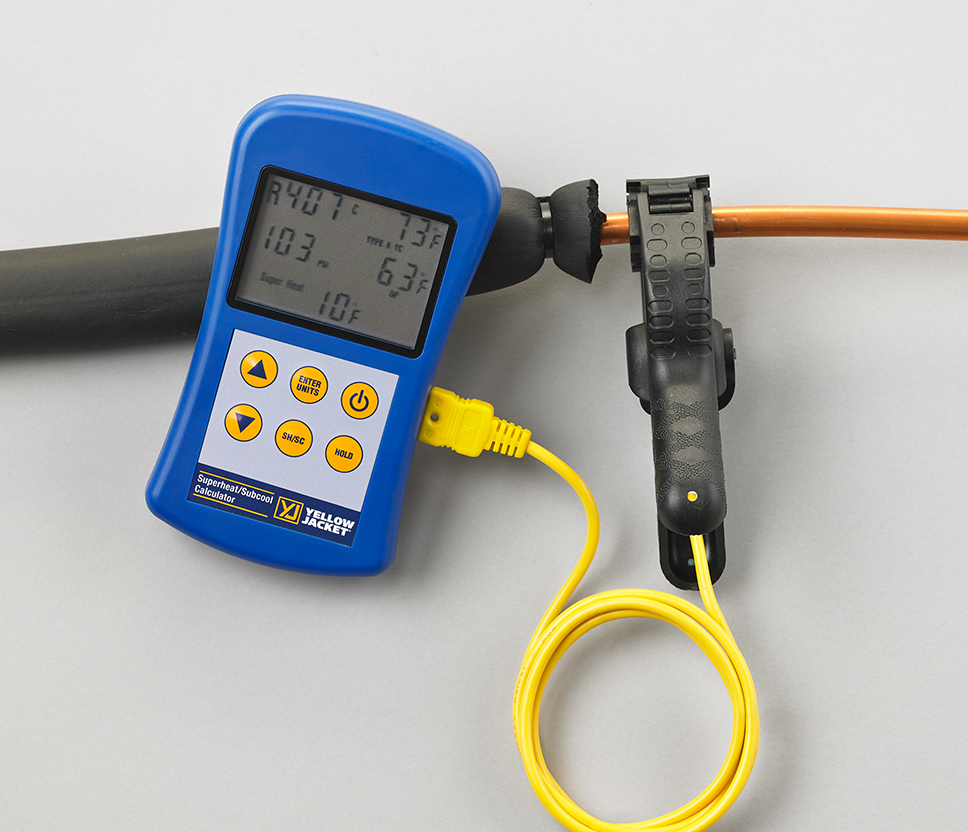

Subcool And Superheat Chart

PH Diagram for Refrigeration Cycle InDepth Explanation aircondlounge
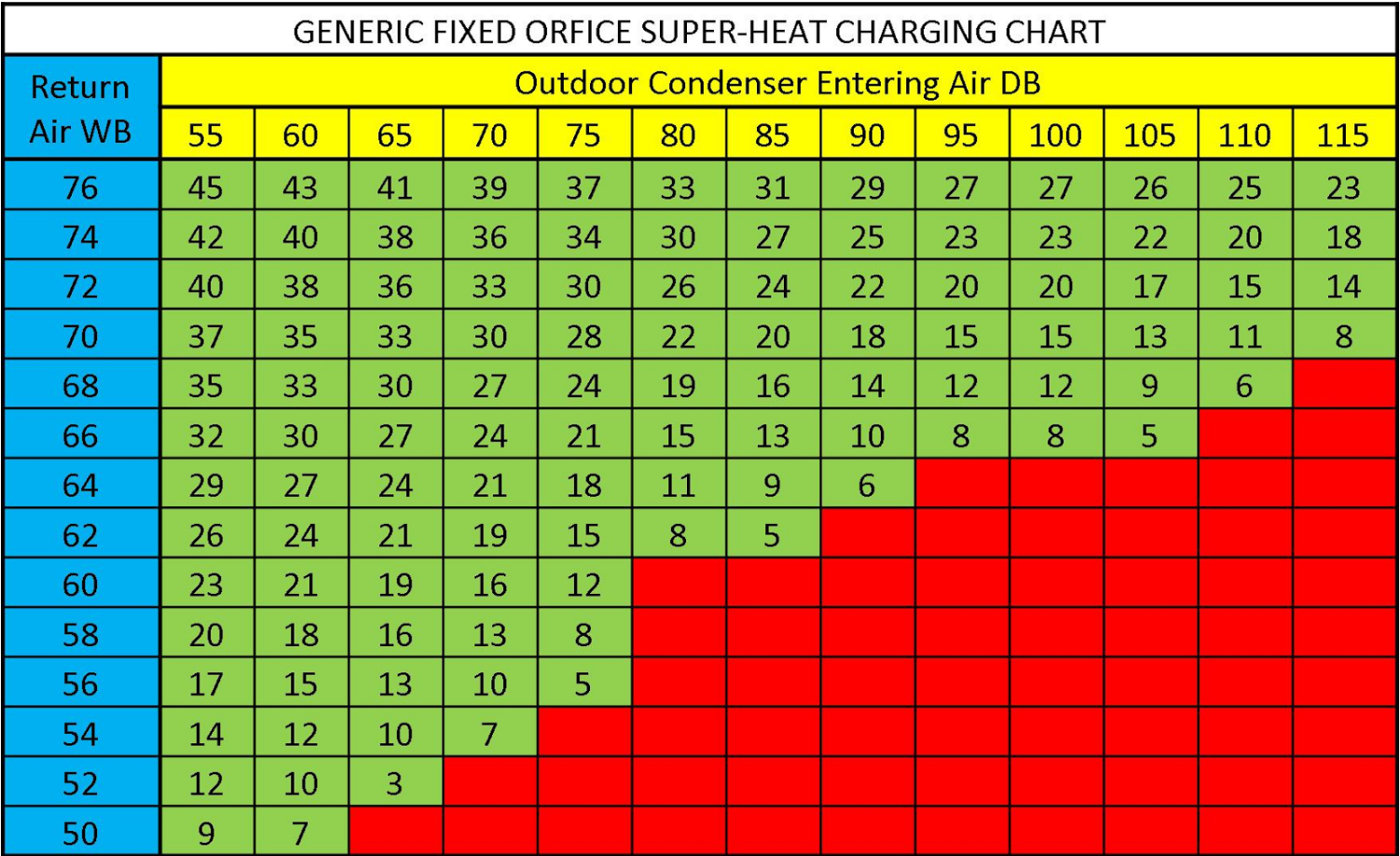
Subcool And Superheat Chart

Superheat and subcool measurements on the air conditioner YouTube
Web Once You Determine The Indoor Wet Bulb And Outdoor Dry Bulb Temperatures, Check The Manufacturer’s Charging Chart To Determine The Proper Suction Superheat.
Always Refer To The Manufacturer's Specifications For Accurate Measurements.
So, If The Condenser Brings The Refrigerant Temperature Down To 105 Degrees, It Has Been Subcooled By 15 Degrees.
In This Article, We Will Define Subcooling, Calculate Subcooling, Explain How To Use Subcooling To Check The Refrigerant Charge, And Show Where The Measurement Points Are Taken On An Air Conditioning System.
Related Post: