Stress Concentration Chart
Stress Concentration Chart - When stress concentration factors that specifically match all of the foregoing conditions are not available, the following equation may be used: Web • a “stress concentration” refers to an area in a object where stress increases over a very short distance (i.e., where a high stress gradient exists) • stress concentrations typically occur due to some localized change in geometry (near holes, filets, corners, grooves, cracks, etc) • these changes in geometry are often called “stress Web this chapter provides a comprehensive guide for stress analysis of any engineering designs, from a part with a single feature and uniaxial load to any level of complexity of a structure with numerous geometric. Only after preparing this edition of this book has it become evident how much effort he put into his two previous books: Web stress concentration factors; Web generalize the concept of stress concentration factor to finite bodies, and explore the consequences of st. For a part subjected to a normal stress, the true stress in the immediate neighborhood of the geometric discontinuity is calculated as: 2.2 stress concentration factors / 90. Web the stress concentration calculator provides a set of interactive plots for common stress concentration factors. 2.3 notches in tension / 92. Each chart is for a specific combination of (i) type of section, (ii) type of geometric feature and (iii) type of loading. Web the stress concentration calculator provides a set of interactive plots for common stress concentration factors. Σ0 = f/a, where a = πd2/4. This localized stress can often surpass the average stress within the member. Web this chapter. We offer a free version of this software. Web 2.1 notation / 89. Once the theoretical stress concentration has been determined, we can account for a reduction in fatigue life due to a notch by introducing a marin factor for notches. Venant’s principle for using analytical “infinite body” stress concentration results to estimate stress concentration associated with. The stress concentration. Web in this tutorial, we will examine the standard method of accounting for stress concentrations caused by geometric features. The body tends to fail at the location of a. The stress concentration factor charts given in this appendix are approximate. Web the stress concentration calculator provides a set of interactive plots for common stress concentration factors. This chapter contains sections. Free download, borrow, and streaming : Venant’s principle for using analytical “infinite body” stress concentration results to estimate stress concentration associated with. Σ0 = f/a, where a = πd2/4. Web generalize the concept of stress concentration factor to finite bodies, and explore the consequences of st. Equivalent elliptical notch / 92. Web generalize the concept of stress concentration factor to finite bodies, and explore the consequences of st. Stress concentration design factors (1953) and stress concentration factors (1974). The body tends to fail at the location of a. Web stress concentration factors; This localized stress can often surpass the average stress within the member. Web a stress concentration is defined as high localized stress, compared to the average stress of the body, and is typically found in a region that has an abrupt geometric change or discontinuity. 2.3.2 opposite single semicircular notches in a finite. Designing to minimize stress concentration. Equivalent elliptical notch / 92. Web t and k ts. The body tends to fail at the location of a. For more accurate values the reader should consult a handbook. Designing to minimize stress concentration. Web stress concentration factors; 2.3 notches in tension / 92. Charts and relations useful in making strength calculations for machine parts and structural elements : Equivalent elliptical notch / 92. Stress concentration is related to type of material, the nature of the stress, environmental conditions, and the geometry of parts. Stress concentration design factors (1953) and stress concentration factors (1974). Index to the stress concentration factors xvii preface for the. The body tends to fail at the location of a. Charts and relations useful in making strength calculations for machine parts and structural elements : 2.3.2 opposite single semicircular notches in a finite. 2.3 notches in tension / 92. Web a stress concentration is defined as high localized stress, compared to the average stress of the body, and is typically. Charts and relations useful in making strength calculations for machine parts and structural elements : Each chart is for a specific combination of (i) type of section, (ii) type of geometric feature and (iii) type of loading. Web in this tutorial, we will examine the standard method of accounting for stress concentrations caused by geometric features. Web 2.1 notation /. This localized stress can often surpass the average stress within the member. 2.3.1 opposite deep hyperbolic notches in an infinite thin element; 2.3.2 opposite single semicircular notches in a finite. Web stress concentration factors for shafts and cylinders: Only after preparing this edition of this book has it become evident how much effort he put into his two previous books: Web • a “stress concentration” refers to an area in a object where stress increases over a very short distance (i.e., where a high stress gradient exists) • stress concentrations typically occur due to some localized change in geometry (near holes, filets, corners, grooves, cracks, etc) • these changes in geometry are often called “stress Web in this tutorial, we will examine the standard method of accounting for stress concentrations caused by geometric features. For more accurate values the reader should consult a handbook. Stress concentration design factors (1953) and stress concentration factors (1974). We offer a free version of this software. Σ0 = f/a, where a = πd2/4. There are 14 different charts; Stress concentration for the past half century. The body tends to fail at the location of a. Τ0 = tc/j, where c = d/2 and j = πd4/32. Web this chapter provides a comprehensive guide for stress analysis of any engineering designs, from a part with a single feature and uniaxial load to any level of complexity of a structure with numerous geometric.
Stress concentration factor for a shaft with a shoulder fillet in axial
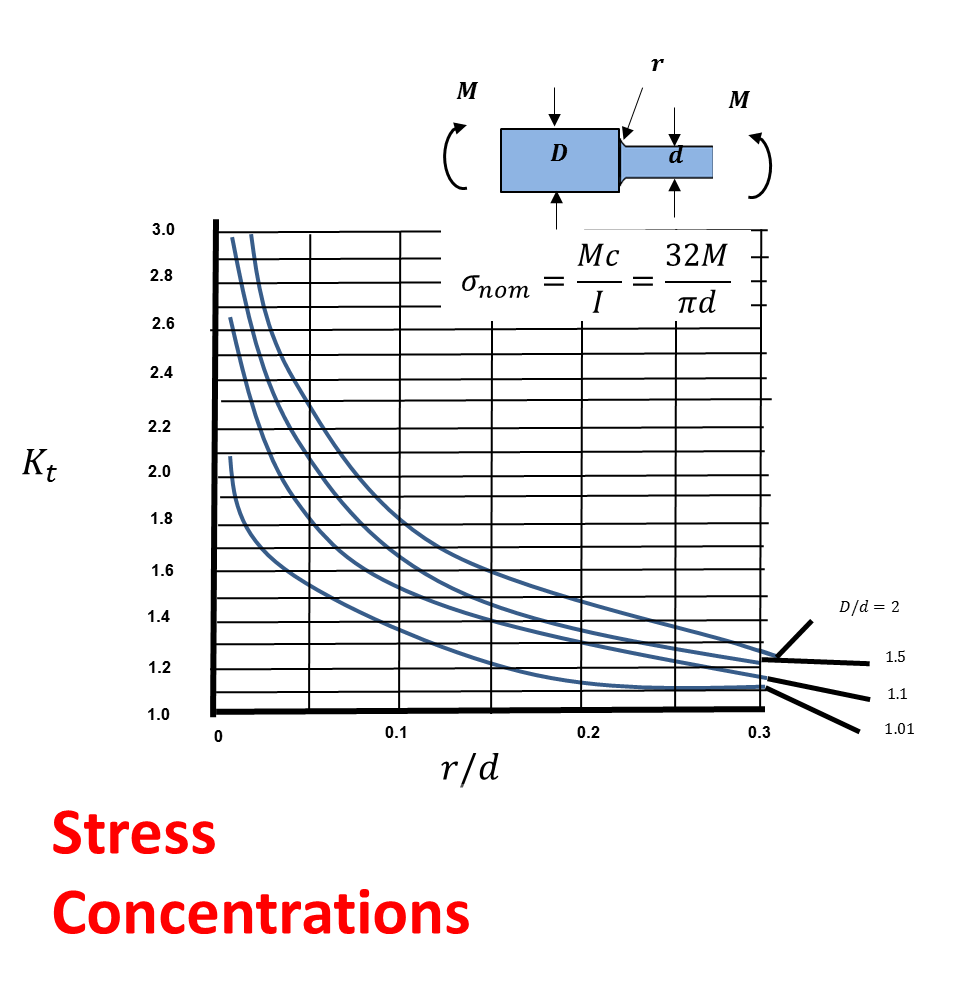
Stress Concentration Factor Chart
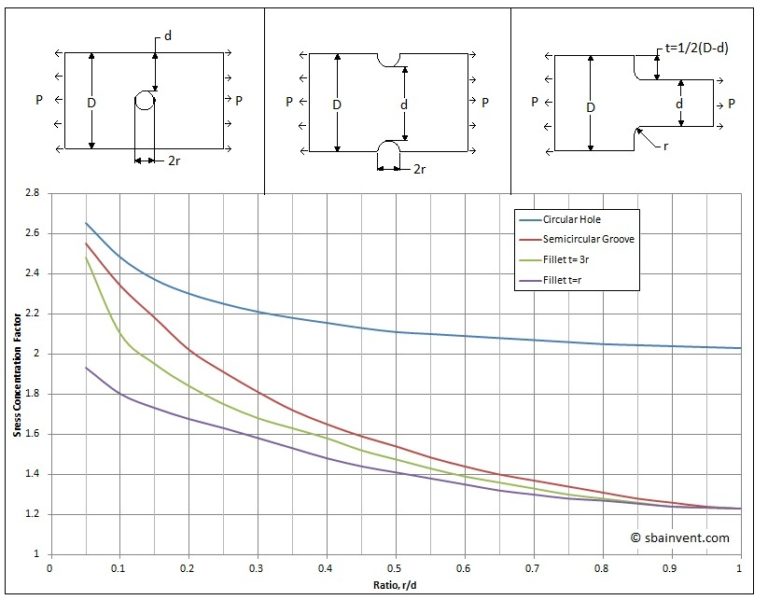
Stress Concentrations S.B.A. Invent
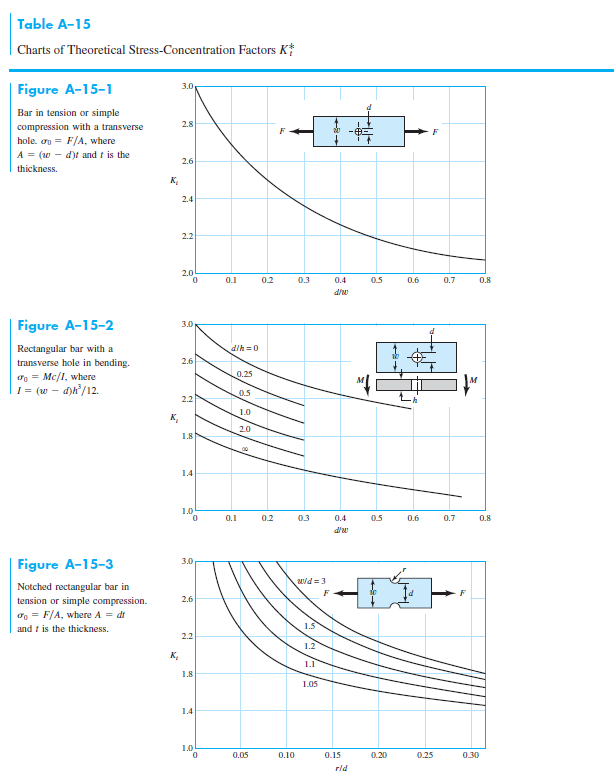
Solved Charts Of Theoretical StressConcentration Factors...

Stress CONCENTRATION Factors and Factor of Safety in 11 Minutes! YouTube
Stress concentration charts3.pdf Stress (Mechanics) Bending

Stress Concentration Factor Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart

Existing stress concentration chart for a notched beam experiencing

Stress concentration factor in a flat plate with central hole Groove
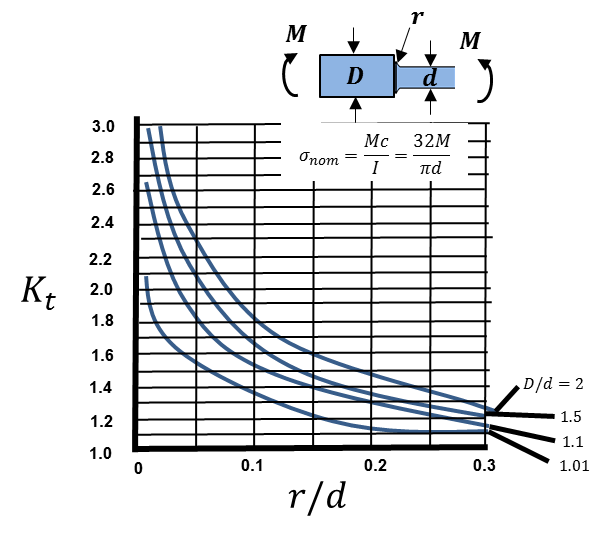
Stress Concentration Factor Chart
Index To The Stress Concentration Factors Xvii Preface For The Third Edition Xxxiii Preface For The Second Edition Xxxv 1 Definitions And Design Relations 1 1.1 Notation / 1 1.2 Stress Concentration / 3 1.2.1 Selection Of Nominal Stresses / 6 1.2.2 Accuracy Of Stress Concentration Factors / 9 1.2.3 Decay.
A “Stress Concentration” Refers To An Area In A Object Where Stress Increases Over A Very Short Distance (I.e., Where A High Stress Gradient Exists) Stress Concentrations Typically Occur Due To Some Localized Change In Geometry (Near Holes, Filets, Corners, Grooves, Cracks, Etc)
Web In Solid Mechanics, A Stress Concentration (Also Called A Stress Raiser Or A Stress Riser Or Notch Sensitivity) Is A Location In An Object Where The Stress Is Significantly Greater Than The Surrounding Region.
Each Chart Is For A Specific Combination Of (I) Type Of Section, (Ii) Type Of Geometric Feature And (Iii) Type Of Loading.
Related Post:
