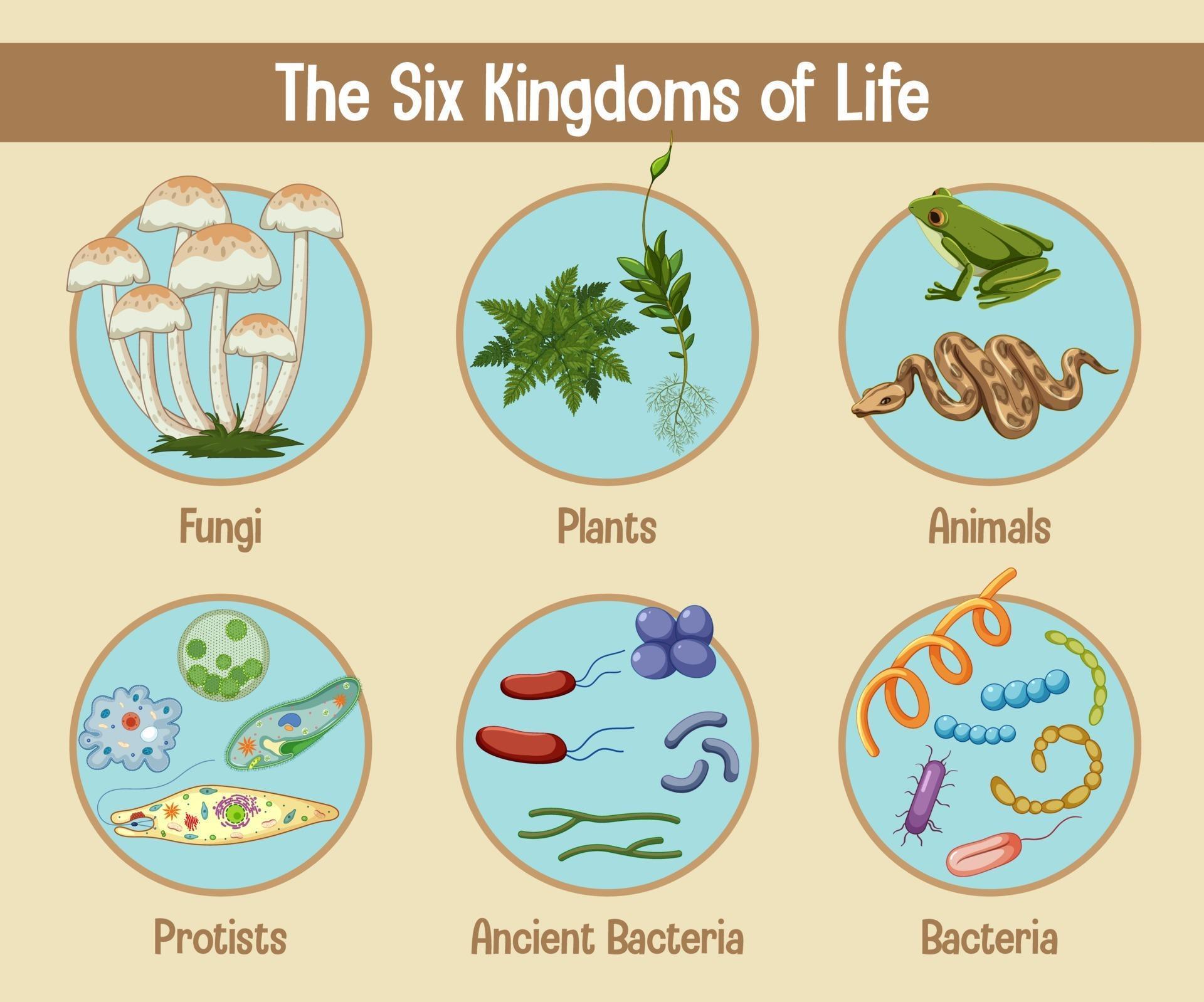
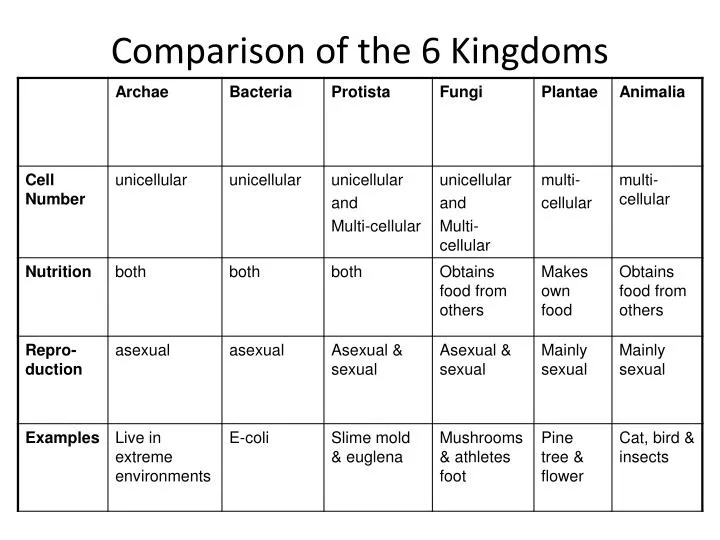
Six Kingdoms Chart
Six Kingdoms Chart - These cards coordinate perfectly with our six kingdom chart & masters. Classification is important for understanding the diversity of life on earth. Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. Web discover which kingdom you belong to and what characteristics you’d have if you fell into one of the other five kingdoms. Which kingdom has the greatest number of species? 6 kingdoms of life, from simplest to most complex, are as follows: Web organisms are traditionally classified into six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia) based on characteristics like cell type, nutrient acquisition, and reproduction. When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. Animal kingdom (animalia) there are lots of different kinds of animals, such as mammals, birds, insects, reptiles and amphibians. Web under the three domains are six kingdoms in taxonomy: These cards coordinate perfectly with our six kingdom chart & masters. This means that their cells have a complex composition, including a nucleus and organelles. The organisms in each kingdom are considered biologically distinct from the others. Organisms in the same kingdom share certain fundamental similarities. The organisms are classified into their kingdoms by cell type (complex/simple), their ability to. Web 6 kingdoms of life, complete your thinking map by putting the title of the kingdom and some illustrated examples of organisms that belong to that kingdom in each box. Animal kingdom (animalia) there are lots of different kinds of animals, such as mammals, birds, insects, reptiles and amphibians. 6 kingdoms of life, from simplest to most complex, are as. Scientist group organisms into kingdoms based on these three factors: Classification is important for understanding the diversity of life on earth. Web there are now six commonly accepted kingdoms. Web this diagram shows multiple branches or divisions of the 6 kingdoms. Well, they have some things in common. These cards coordinate perfectly with our six kingdom chart & masters. Animal kingdom (animalia) there are lots of different kinds of animals, such as mammals, birds, insects, reptiles and amphibians. Web under the three domains are six kingdoms in taxonomy: Archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi, protista, plants and animals. Web 6 kingdoms of life, complete your thinking map by putting the title. Each kingdom includes a set of organisms that share similar characteristics. Before you get started, don’t forget to print out your ontrack biology journal. Classification is important for understanding the diversity of life on earth. Animal kingdom (animalia) there are lots of different kinds of animals, such as mammals, birds, insects, reptiles and amphibians. Web 6 kingdoms of life, complete. Web the six kingdoms are eubacteria, archae, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia. All animals can move on their own. It is ruled by the elected king of the andals and the first men from the red keep in. Examples of protists include algae and amoebas. Web discover which kingdom you belong to and what characteristics you’d have if you fell. Web there are now six commonly accepted kingdoms. Each kingdom has its own unique characteristics and types of organisms. Web organisms are traditionally classified into six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia) based on characteristics like cell type, nutrient acquisition, and reproduction. Web all organisms are classified into six different kingdoms—archaebacteria, eubacteria, protists, fungi, plants and animals. Web. The organisms are classified into their kingdoms by cell type (complex/simple), their ability to. Students should include the major properties of that kingdom and a short description of the organism they selected. Web under the three domains are six kingdoms in taxonomy: Organisms in the same kingdom share certain fundamental similarities. Web 6 kingdoms of life, complete your thinking map. Most consist of a single cell (unicellular), but all protists are eukaryotes, just like fungi, animals, and plants. Previously, eubacteria and archaebacteria were lumped together in the kingdom of monera. Here are some key points to remember about the six kingdoms of life: Animal kingdom (animalia) there are lots of different kinds of animals, such as mammals, birds, insects, reptiles. Not making their own food as plants do. Here are some key points to remember about the six kingdoms of life: This means that their cells have a complex composition, including a nucleus and organelles. Animal kingdom (animalia) there are lots of different kinds of animals, such as mammals, birds, insects, reptiles and amphibians. Most consist of a single cell. Previously, eubacteria and archaebacteria were lumped together in the kingdom of monera. Web the six kingdoms are eubacteria, archae, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia. Web typically however, life is separated into six kingdoms: In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. Through illustrations and interactives you will explore the major divisions (domains, kingdoms) of life. Most consist of a single cell (unicellular), but all protists are eukaryotes, just like fungi, animals, and plants. Well, they have some things in common. Web organisms are traditionally classified into six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia) based on characteristics like cell type, nutrient acquisition, and reproduction. Organisms in the same kingdom share certain fundamental similarities. Each kingdom has its own unique characteristics and types of organisms. Control cards for each card. Once you know about the six kingdoms of life, you’ll be a classification king… or queen! This would later lead to the proposal of three domains of life, of bacteria, archaea, and eukaryota. Students should include the major properties of that kingdom and a short description of the organism they selected. Plantae, contains all plants on earth. The organisms are classified into their kingdoms by cell type (complex/simple), their ability to.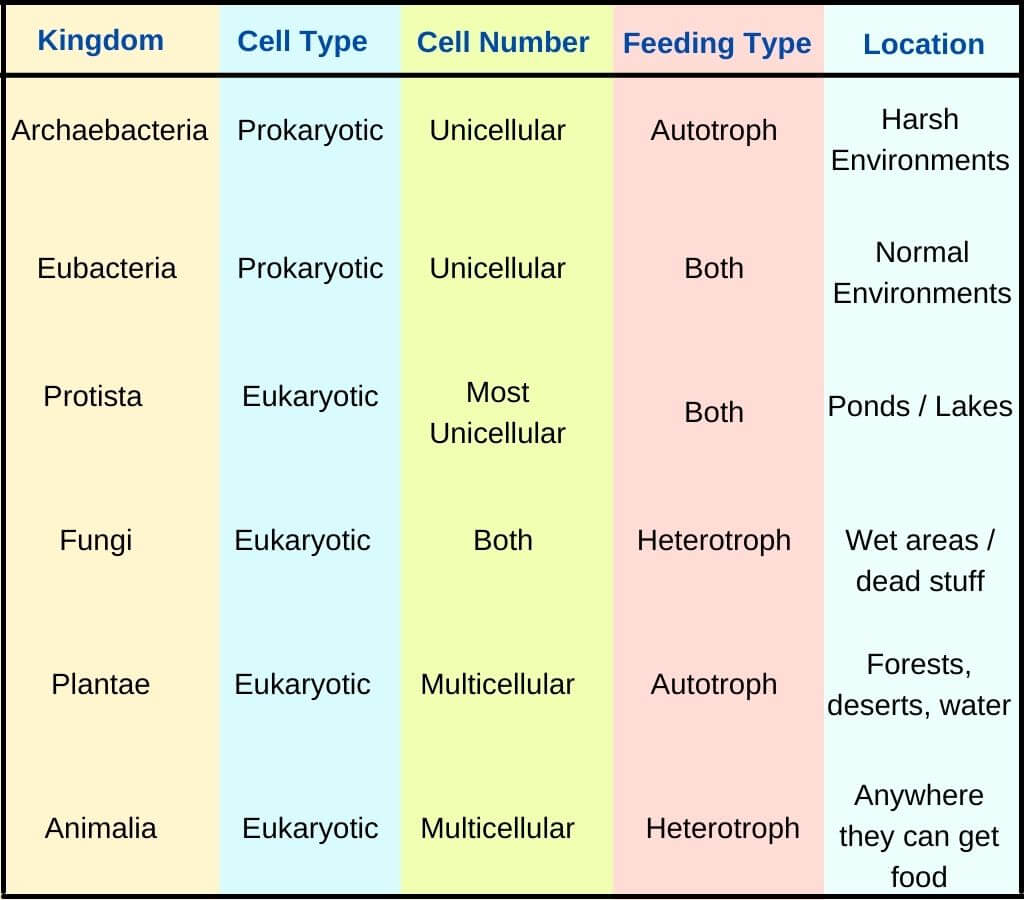
A Simple Explanation of the 6 Kingdoms of Life

Biology Kingdoms Comprehensive Chart Activity
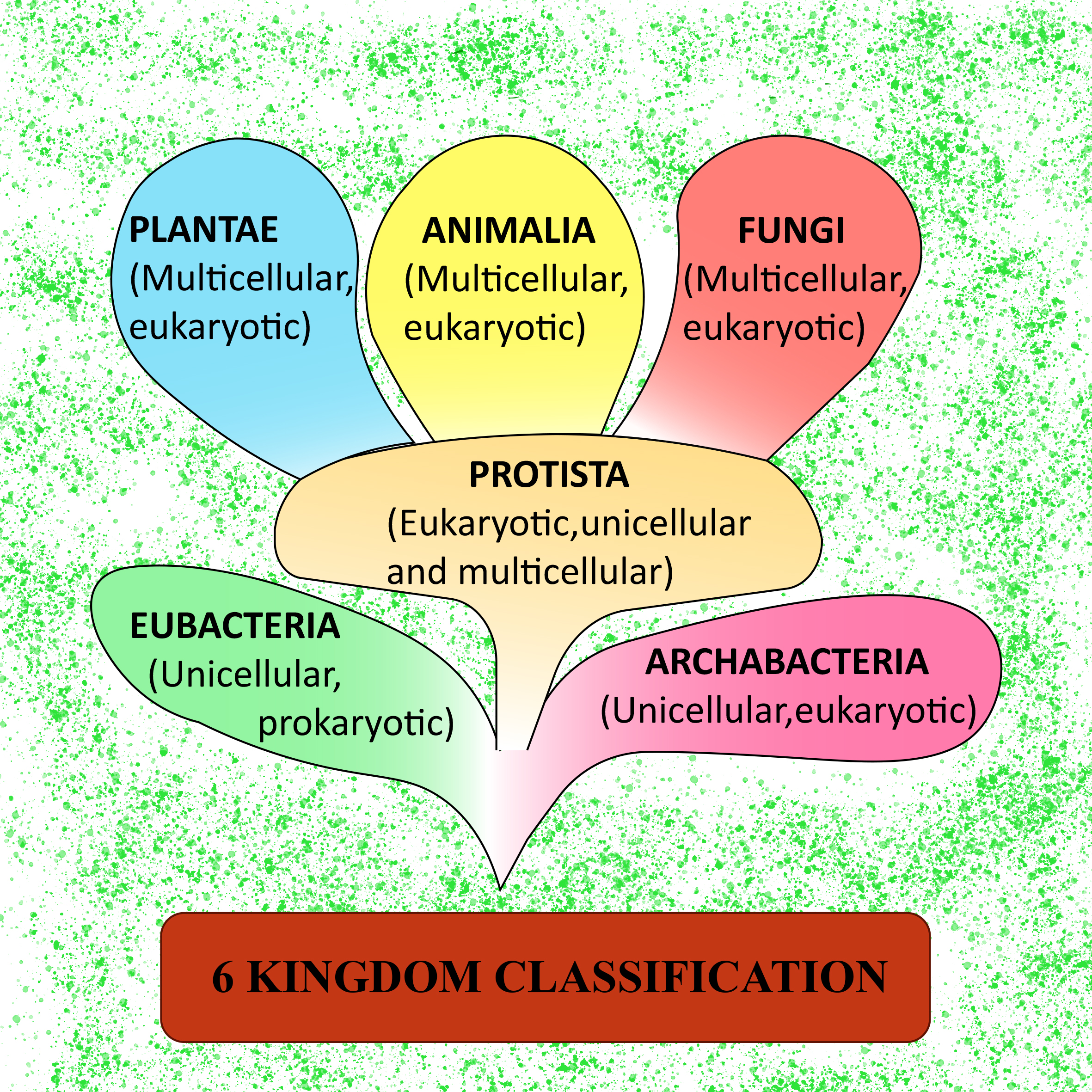
Bacteria Kingdom Classification

biological classification Students Britannica Kids Homework Help
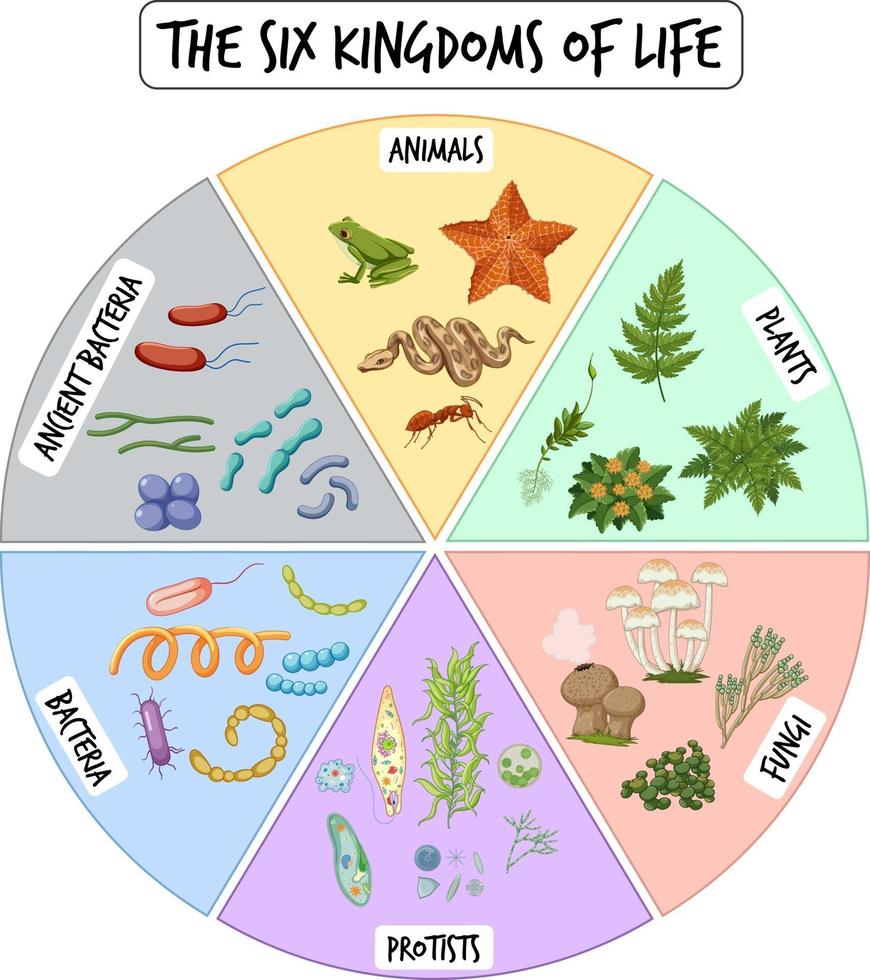
Information poster of six kingdoms of life 2906704 Vector Art at Vecteezy

Diagram showing six kingdoms of life Royalty Free Vector

The 6 Kingdoms of Life Simple Explanation for Kids WeHaveKids
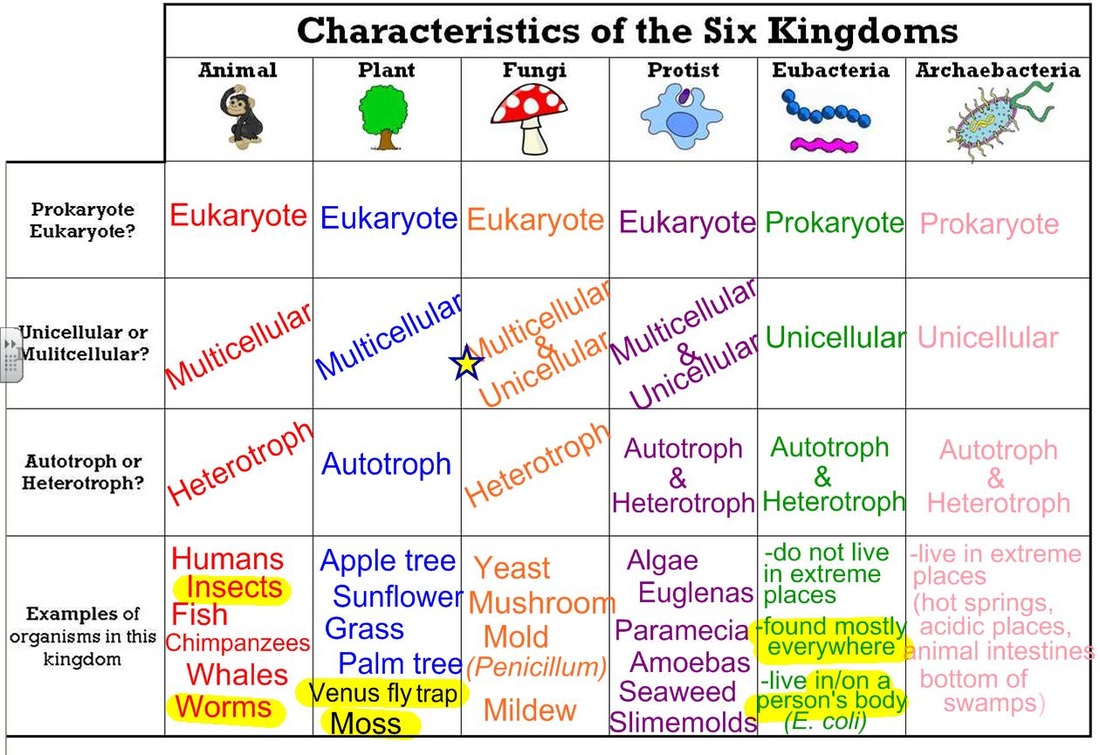
Classification of Organisms Rumney Marsh Academy Science Revere
Science poster of six kingdoms of life 2906732 Vector Art at Vecteezy
6 Kingdoms Of Living Things
Born In 1707, Carl Linnaeus Will Long Be Remembered For His Work In Classifying Plants And Animals.
Which Kingdom Has The Greatest Number Of Species?
Animal Kingdom (Animalia) There Are Lots Of Different Kinds Of Animals, Such As Mammals, Birds, Insects, Reptiles And Amphibians.
What Type Of Animal Is A Dolphin?
Related Post: