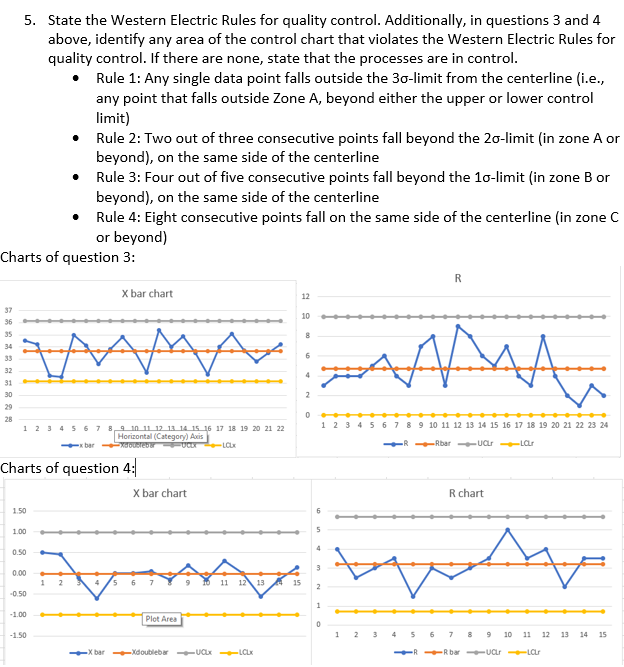
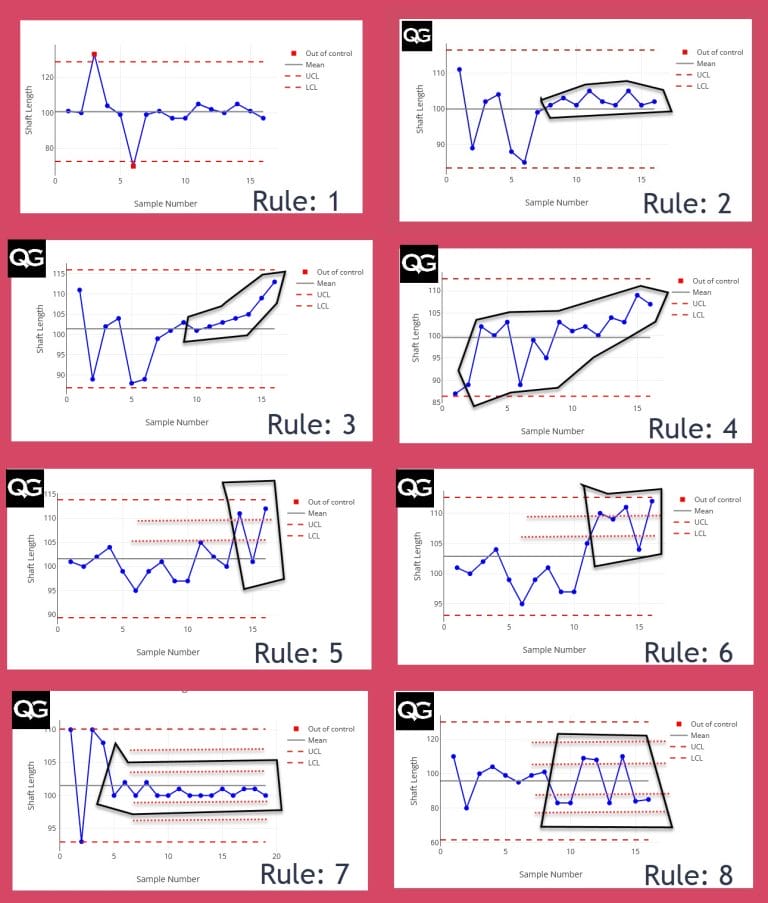
Rules Of Control Chart
Rules Of Control Chart - Web a control chart, also known as a shewhart or process behavior chart, is a time series graph of data collected over time. The charts help us track process statistics over time and help us understand the causes of the variation. Selecting an appropriate control chart is very important in control chart mapping. Web the following rules can be used to properly interpret control charts: Web a control chart (also known as a shewhart chart) is a graph used to study how a system or process changes over time. The eight different rules are mentioned below (source: Processes, whether manufacturing or service in nature, are variable. These patterns give you insights into what may. Web some people with type 2 diabetes can control their blood glucose level by making lifestyle changes. These limits let you know when unusual variability occurs. Web control charts are a simple yet powerful tool that helps us understand if a process is “stable or in control.” control charts are used in the control phase of the dmaic (define, measure, analyze, improve, and control) process. The charts help us track process statistics over time and help us understand the causes of the variation. The center line. Nine or more consecutive points fall on the same side of the centerline. It is composed of a center line representing the average of the data being plotted and upper. Web the three most commonly used control charts are: Web control charts have two general uses in an improvement project. Web choose the appropriate control chart for your data. A process must be stable before you can analyze process capability to determine if it meets customer specifications. Web eight control chart rules. A control chart always has a mean as the centre line, an upper control limit and a lower control limit which show where we would expect future data to lie within. 7_points in a row on the. It plots the number of defects (i, for a number of nonconformities) against the moving range (mr, to monitor variability). A special cause is simply anything which leads to an observation beyond a control limit. Collect data, construct your chart and analyze the data. “thank you very much to the people of wayanad and raebareli for giving me immense love.. Web produced by nina feldman , clare toeniskoetter , rob szypko and diana nguyen. Web a control chart is a statistical tool used to distinguish between variation in a process resulting from common causes and variation resulting from special causes. The following is an excerpt from the quality engineering handbook by thomas pyzdek, © qa publishing, llc. Every production, service,. Data is plotted in time order. Web this month’s publication examines 8 rules that you can use to help you interpret what your control chart is communicating to you. Most control charts include a center line, an upper control limit, and a lower control limit. Original music by marion lozano , elisheba ittoop and sophia lanman. Suitable for small sample. A control chart always has a mean as the centre line, an upper control limit and a lower control limit which show where we would expect future data to lie within. Web nelson rules are a method in process control of determining whether some measured variable is out of control (unpredictable versus consistent). Nine or more consecutive points fall on. It visually displays process data over time and allows you to detect whether a. Control limits (±1, 2, 3 sigma) are calculated from the data. You will not always get the same result each time. A process must be stable before beginning an improvement project. One point is more than 3 standard deviations from the centerline. The control limits are ±3σ from the centerline. These rules help you identify when the variation on your control chart is no longer random, but forms a pattern that is described by one or more of these eight rules. It visually displays process data over time and allows you to detect whether a. Web the most common types are: Web. Used to monitor the mean (average) and range (variability) of a process. Web this month’s publication examines 8 rules that you can use to help you interpret what your control chart is communicating to you. The focus for this month is on interpreting control charts. The eight different rules are mentioned below (source: Web choose the appropriate control chart for. Web a control chart, also known as a shewhart or process behavior chart, is a time series graph of data collected over time. This article provides an overview of the different types of control charts to help practitioners identify the best chart for any monitoring situation. 7_points in a row on the same side of the center. The control limits are ±3σ from the centerline. It visually displays process data over time and allows you to detect whether a. A control chart, also known as a statistical process control chart, is a statistical tool used to monitor, control, and improve the quality of processes. It presents a graphic display of process stability or instability over. Control charts provide the operational definition of the term special cause. The reason for this is that there are sources of variation in all processes. These rules help you identify when the variation on your control chart is no longer random, but forms a pattern that is described by one or more of these eight rules. The national assembly will choose the president for the next five. The control limits represent the process variation. A control chart always has a mean as the centre line, an upper control limit and a lower control limit which show where we would expect future data to lie within. Processes, whether manufacturing or service in nature, are variable. You will not always get the same result each time. Selecting an appropriate control chart is very important in control chart mapping.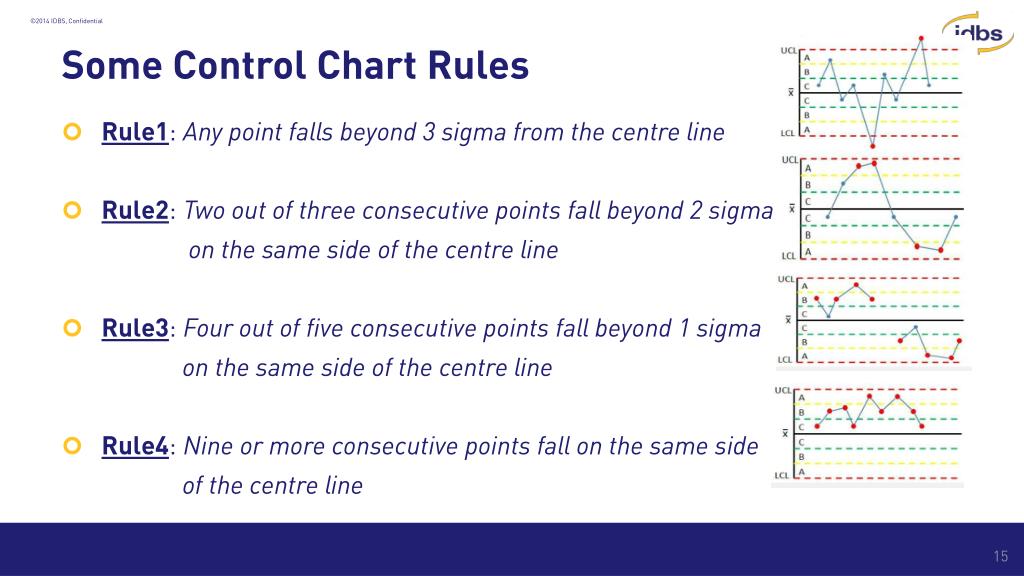
PPT Statistical Process Control PowerPoint Presentation

Control Chart Detailed History, All Concepts & Nelson Rules YouTube
Control Chart Rules A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master

Control Chart The Eight Rules YouTube

Control Chart Rules A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master

The 7 QC Tools Control Charts Enhancing Your Business Performance
Nelson Rules (and Western Electric Rules) for Control Charts Quality

Rule of Seven Control Charts

SPC Control Charting Rules YouTube

8 rules of spc, 8 rules of control chart, SPC, 8 rules of statistical
Data Is Plotted In Time Order.
When One Is Identified, Mark It On The Chart And Investigate The Cause.
It Is Composed Of A Center Line Representing The Average Of The Data Being Plotted And Upper.
A Special Cause Is Simply Anything Which Leads To An Observation Beyond A Control Limit.
Related Post: