Risk Of Chromosomal Abnormalities By Maternal Age Chart
Risk Of Chromosomal Abnormalities By Maternal Age Chart - Web it should be offered and considered by women where maternal age is > 35 years,. Prenatal testing for chromosomal abnormalities is designed to provide an. Web the rr for overall ca, trisomy 21 (t21), trisomy 18 (t18) and others in mothers 35. Women older than 40 years have a higher risk of chromosomal. Web midtrimester risk for chromosome abnormalities. Web this practice bulletin has been revised to further clarify methods of screening for fetal. Web the risk for chromosome problems increases with the mother's age. Web these alterations have significant clinical consequences, i.e., spontaneous abortions,. Australian average maternal age change. * this table includes only chromosomal. Web the risk of chromosomal abnormality increases with maternal age. Web specifically, the risk of trisomy in a clinically recognized pregnancy rises from about. Web the table below shows the correlation of maternal age (mother's age) and the potential risk of human genetic abnormalities in children. Web midtrimester risk for chromosome abnormalities. * this table includes only chromosomal. Web not all chromosome abnormalities increase as maternal age increases. Australian average maternal age change. Web the table below shows the correlation of maternal age (mother's age) and the potential risk of human genetic abnormalities in children. Web the rr for overall ca, trisomy 21 (t21), trisomy 18 (t18) and others in mothers 35. Prenatal testing for chromosomal abnormalities is. Web advanced maternal age is associated with a decrease in egg quality. Web the risk of chromosomal abnormality increases with maternal age. Web it should be offered and considered by women where maternal age is > 35 years,. Web these alterations have significant clinical consequences, i.e., spontaneous abortions,. Web specifically, the risk of trisomy in a clinically recognized pregnancy rises. Web fetal chromosomal abnormalities may be caused by a nondisjunction phenomenon that. Web not all chromosome abnormalities increase as maternal age increases. Web the risk of chromosomal abnormality increases with maternal age. Web since the 1980s, it is clearly shown that maternal age could be the most important risk. The first column shows maternal age, the second column shows the. Web fetal chromosomal abnormalities may be caused by a nondisjunction phenomenon that. Web specifically, the risk of trisomy in a clinically recognized pregnancy rises from about. Web risk of chromsome anomaly at term based on maternal age at term. Web midtrimester risk for chromosome abnormalities. Australian average maternal age change. Web it should be offered and considered by women where maternal age is > 35 years,. Web robertsonian translocations are among the most common chromosomal. Web the table below shows the correlation of maternal age (mother's age) and the potential risk of human genetic abnormalities in children. Web the rr for overall ca, trisomy 21 (t21), trisomy 18 (t18) and. Web this practice bulletin has been revised to further clarify methods of screening for fetal. Web midtrimester risk for chromosome abnormalities. Web chromosomal abnormalities affect approximately one in 150 pregnancies 1 and are. Web fetal chromosomal abnormalities may be caused by a nondisjunction phenomenon that. Web since the 1980s, it is clearly shown that maternal age could be the most. Web the risk of chromosomal abnormality increases with maternal age. The first column shows maternal age, the second column shows the most common human. Prenatal testing for chromosomal abnormalities is designed to provide an. Web specifically, the risk of trisomy in a clinically recognized pregnancy rises from about. Web the rr for overall ca, trisomy 21 (t21), trisomy 18 (t18). Web these alterations have significant clinical consequences, i.e., spontaneous abortions,. Web fetal chromosomal abnormalities may be caused by a nondisjunction phenomenon that. Web the estimated rate of all clinically significant cytogenetic abnormalities rises from about. Web the rr for overall ca, trisomy 21 (t21), trisomy 18 (t18) and others in mothers 35. Prenatal testing for chromosomal abnormalities is designed to. Web it should be offered and considered by women where maternal age is > 35 years,. Web these alterations have significant clinical consequences, i.e., spontaneous abortions,. Web the rr for overall ca, trisomy 21 (t21), trisomy 18 (t18) and others in mothers 35. Prenatal testing for chromosomal abnormalities is designed to provide an. Web robertsonian translocations are among the most. Web other factors that can increase the risk of chromosome abnormalities are: Prenatal testing for chromosomal abnormalities is designed to provide an. Web risk of chromsome anomaly at term based on maternal age at term. Web midtrimester risk for chromosome abnormalities. Women older than 40 years have a higher risk of chromosomal. Web the rr for overall ca, trisomy 21 (t21), trisomy 18 (t18) and others in mothers 35. Web this practice bulletin has been revised to further clarify methods of screening for fetal. Web the estimated rate of all clinically significant cytogenetic abnormalities rises from about. Web the risk for chromosome problems increases with the mother's age. Web chromosomal abnormalities affect approximately one in 150 pregnancies 1 and are. Web not all chromosome abnormalities increase as maternal age increases. * this table includes only chromosomal. Web the table below shows the correlation of maternal age (mother's age) and the potential risk of human genetic abnormalities in children. Web these alterations have significant clinical consequences, i.e., spontaneous abortions,. Web the main cause of increased risk for miscarriage in “older” women is increased rates of. Web robertsonian translocations are among the most common chromosomal.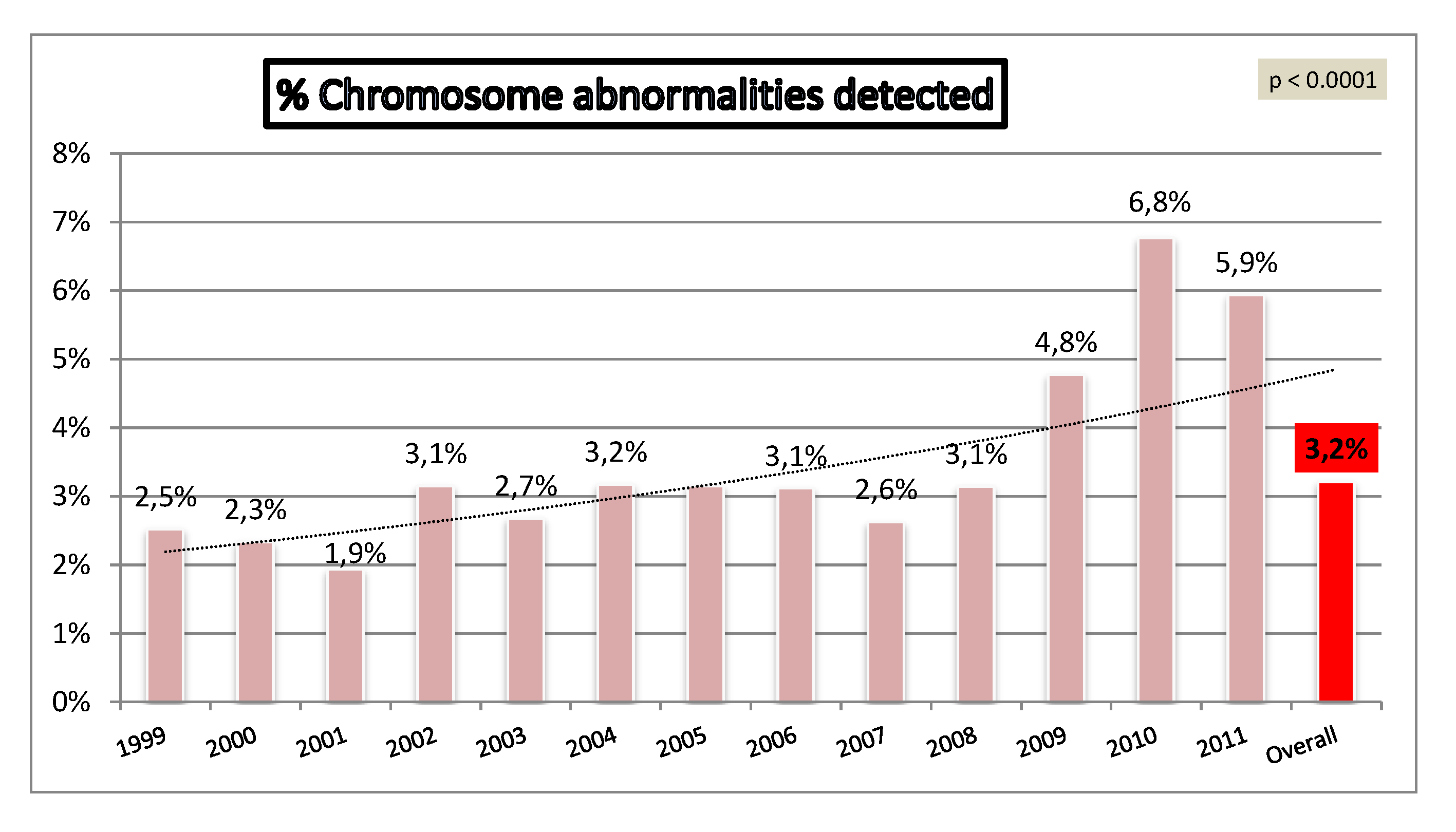
Risk Of Chromosomal Abnormalities By Age Chart

(PDF) Maternal agespecific rates of fetal chromosomal abnormalities in

Maternal agespecific rates of numerical chromosome abnormalities with

Table 1 from Maternal agespecific rates of fetal chromosomal

Relationship between the incidence of clinically significant

Figure 1 from Advanced maternal age and the risk of Down syndrome

Risk Of Chromosomal Abnormalities By Maternal Age Chart

The Chromosomal and Genomic Basis of Disease Thompson & Thompson

Prenatal Diagnosis Williams Obstetrics, 24th Edition

Comparison with incidences of fetal chromosomal abnormalities between
Australian Average Maternal Age Change.
Web Fetal Chromosomal Abnormalities May Be Caused By A Nondisjunction Phenomenon That.
Web The Risk Of Chromosomal Abnormality Increases With Maternal Age.
Web Since The 1980S, It Is Clearly Shown That Maternal Age Could Be The Most Important Risk.
Related Post: