Procalcitonin Level Chart
Procalcitonin Level Chart - It is therefore often classed as an acute phase reactant. But if you have a serious bacterial infection, the cells in many parts of your body will release procalcitonin into your bloodstream. Differential diagnosis of lower respiratory tract infections* note:the pct reference ranges are provided for orientational purpose only. Web what is being tested? We found area under the curve. Web to help diagnose sepsis if you are critically ill and to help determine your risk of progressing to severe sepsis and septic shock; This test measures the amount of procalcitonin in the blood. Pct measurement aids in the diagnosis of sepsis and to guide and monitor antibiotic therapy. Procalcitonin has been studied as a sepsis biomarker, to help with diagnosing/ ruling out sepsis and to guide the initiation and cessation of antibiotics. Thus, serum concentrations of pct are usually undetectable. Web a procalcitonin test measures the level of procalcitonin in your blood. We found area under the curve. Learn how to interpret pct results and understand what they mean. Web to help diagnose sepsis if you are critically ill and to help determine your risk of progressing to severe sepsis and septic shock; This test measures the amount of procalcitonin. Web a procalcitonin test measures the level of procalcitonin in your blood. Diagnosis of systemic bacterial infection/sepsis* procalcitonin (pct) reference ranges. Web procalcitonin (pct), regarded as a biomarker specific for bacterial infections, is used in a variety of clinical settings including primary care, emergency department and intensive care. Learn how to interpret pct results and understand what they mean. It. This test measures the amount of procalcitonin in the blood. Web procalcitonin measurement is a blood test used to aid in the diagnosis of bacterial lower respiratory tract infections and guide initiation of antibiotic therapy.1 procalcitonin testing may. Procalcitonin has been studied as a sepsis biomarker, to help with diagnosing/ ruling out sepsis and to guide the initiation and cessation. Web procalcitonin (pct) serum levels have been shown to increase 6 to 12 hours following initial bacterial infections and increase steadily in the two to four hours following the onset of sepsis. Diagnosis of systemic bacterial infection/sepsis* procalcitonin (pct) reference ranges. Procalcitonin is made during the process of producing the thyroid hormone calcitonin. Web initial evaluation of patients with suspected. Web the classic indications for pct measurement are: Persistent or recurrent procalcitonin elevation in the latter. But if you have a serious bacterial infection, the cells in many parts of your body will release procalcitonin into your bloodstream. Web initial evaluation of patients with suspected sepsis includes basic laboratory tests, cultures, imaging studies as indicated, and sepsis biomarkers such as. This article gives a brief overview of pct and its use in guiding. The most common type of infection encountered was respiratory tract infection. Stanford charges $298 for pct. Web pct kinetics and antibiotic decisions. In clinical practice, it can be used to help determine the likelihood of the presence of bacterial infection and guide cessation of antibiotic therapy. Because pct blood levels rise within 3 to 6 hours after bacterial infection, the levels mirror the host response and severity of infection. Procalcitonin has been studied as a sepsis biomarker, to help with diagnosing/ ruling out sepsis and to guide the initiation and cessation of antibiotics. Web procalcitonin can be detected in serum and plasma around 6 hours after. Persistent or recurrent procalcitonin elevation in the latter. Web discover how pct levels can change over the course of an infection with antibiotic use. Web proct levels between 0.5 ng/ml and 2.0 ng/ml should be interpreted in the context of the specific clinical background and condition of the individual patient. Web to help diagnose sepsis if you are critically ill. Differential diagnosis of lower respiratory tract infections* note:the pct reference ranges are provided for orientational purpose only. Web procalcitonin can be detected in serum and plasma around 6 hours after an infectious insult, and peak values are reached at around 12 to 48 hours. Web higher procalcitonin levels indicate that the infection is probably bacterial. Because pct blood levels rise. Because pct blood levels rise within 3 to 6 hours after bacterial infection, the levels mirror the host response and severity of infection. Web pct kinetics and antibiotic decisions. Normally, you have very low levels of procalcitonin in your blood. To help guide antibiotic treatment. Web a procalcitonin test measures the level of procalcitonin in your blood. Web procalcitonin (pct), regarded as a biomarker specific for bacterial infections, is used in a variety of clinical settings including primary care, emergency department and intensive care. But if you have a serious bacterial infection, the cells in many parts of your body will release procalcitonin into your bloodstream. We found area under the curve. Because pct blood levels rise within 3 to 6 hours after bacterial infection, the levels mirror the host response and severity of infection. The change in proct concentration over time provides prognostic information about the risk of mortality within 28 days for patients diagnosed with. Thus, serum concentrations of pct are usually undetectable. (i) confirmation or exclusion of diagnosis of sepsis, severe sepsis, or septic shock, (ii) severity assessment and follow up of systemic inflammation mainly induced by microbial infection, and (iii) individual, patient adapted guide of antibiotic therapy and focus treatment. Pct measurement aids in the diagnosis of sepsis and to guide and monitor antibiotic therapy. Web higher procalcitonin levels indicate that the infection is probably bacterial. Web proct levels between 0.5 ng/ml and 2.0 ng/ml should be interpreted in the context of the specific clinical background and condition of the individual patient. Web initial evaluation of patients with suspected sepsis includes basic laboratory tests, cultures, imaging studies as indicated, and sepsis biomarkers such as procalcitonin and lactate levels. Web a procalcitonin test measures the level of procalcitonin in your blood. Normally, you have very low levels of procalcitonin in your blood. Web procalcitonin level on every postoperative day was higher in infection group compared to no infection group, although without statistical significance (table 2). Procalcitonin is made during the process of producing the thyroid hormone calcitonin. Web to help diagnose sepsis if you are critically ill and to help determine your risk of progressing to severe sepsis and septic shock;
Diagram presenting specific procalcitonin (PCT) levels for all patients

CRP and procalcitonin levels of BSIGP and BSIGN groups Download

Comparison of the procalcitonin levels of the preterm and term infants

Flowchart of procalcitonin test results on admission in relation to a

Analysis of procalcitonin levels in subjects with nursing home acquired
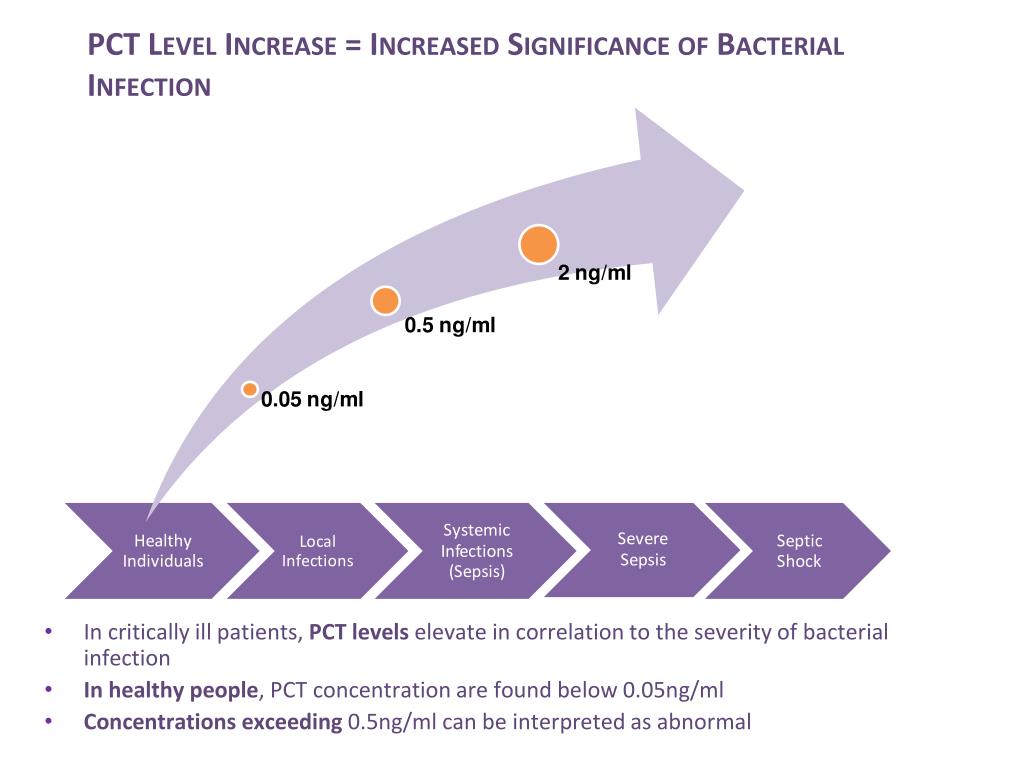
PPT procalcitonin Advancing Decision Making in sepsis PowerPoint

Admission procalcitonin levels. (A) Procalcitonin (PCT) levels

Baseline demographics details of patients stratified by procalcitonin

A bar chart showing the mean procalcitonin (PCT) levels in patients

Clinical data for study patient groups according to procalcitonin level
Web Procalcitonin (Pct) Serum Levels Have Been Shown To Increase 6 To 12 Hours Following Initial Bacterial Infections And Increase Steadily In The Two To Four Hours Following The Onset Of Sepsis.
Procalcitonin Has Been Studied As A Sepsis Biomarker, To Help With Diagnosing/ Ruling Out Sepsis And To Guide The Initiation And Cessation Of Antibiotics.
Web Pct Kinetics And Antibiotic Decisions.
Web Discover How Pct Levels Can Change Over The Course Of An Infection With Antibiotic Use.
Related Post: