Periodontal Disease Chart
Periodontal Disease Chart - P = 0.013) and the number of teeth with pathological mobility ( r = 0.318; Web patient advised of mild/moderate/severe/ very severe / rapidly progressing (aggressive) periodontal disease (periodontitis) which is localised affecting less than 30% of teeth / generalised affecting more than 30% of teeth and progressing at a slow/ moderate/rapid rate and is currently stable/ in remission/ unstable. This form provides a logical method for documenting periodontal findings (as well as other findings). Web this is called periodontal charting, or perio charting, a way for your hygienist to check on the health of your gums. 1 this is due to clinical attachment loss being the gold standard for diagnosis and monitoring of periodontal. Periodontitis is common but can usually be prevented. Hallmark symptoms include red, bleeding and tender gums, loose teeth, bad breath and gum recession. The disease severity was associated with age ( r = 0.241; In addition, radiographic examination is important to verify loss of bone and to show root. The longer plaque and tartar are on teeth, the more harmful they become. This includes good oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings at intervals recommended. Web generalised (81.9%), stage iv (70.1%) and grade c (69.3%) were the most encountered diagnosis. Adults 30 years of age or older have periodontitis. Outline the treatment and management options available for periodontal diseases. Web in 2016, the canadian journal of dental hygiene published an article titled, “current. This form provides a logical method for documenting periodontal findings (as well as other findings). In addition, radiographic examination is important to verify loss of bone and to show root. Describe and summarize the pathophysiology of periodontal diseases. You can’t cure periodontitis, but you can manage the condition with proper care and maintenance. But some people are more prone to. Patients present with a variety of signs including interproximal recession, increased periodontal probing depths, bleeding on probing, mobility of teeth, drifting or loss of teeth and signs of infection with pus on probing. No radiographic bone loss/cal over 5 years. Web generalised (81.9%), stage iv (70.1%) and grade c (69.3%) were the most encountered diagnosis. This form provides a logical. Periodontal (gum) disease is an infection of the tissues that hold your teeth in place. Adults 30 years of age or older have periodontitis. Roughly 42 percent of all dentate u.s. The longer plaque and tartar are on teeth, the more harmful they become. The charts below provide an overview. Web this is called periodontal charting, or perio charting, a way for your hygienist to check on the health of your gums. 1 this is due to clinical attachment loss being the gold standard for diagnosis and monitoring of periodontal. Attachment and bone loss associated with periodontal disease are results of the body’s immune response to plaque biofilm and its. Periodontal (gum) disease is an infection of the tissues that hold your teeth in place. Identify the etiology of periodontal diseases. Web the new worldwide classification was based on interproximal clinical attachment loss. Web patient advised of mild/moderate/severe/ very severe / rapidly progressing (aggressive) periodontal disease (periodontitis) which is localised affecting less than 30% of teeth / generalised affecting more. Web in 2016, the canadian journal of dental hygiene published an article titled, “current status of the classification periodontal diseases”.¹ in this paper, the authors point out that a world workshop in clinical periodontics was planning to meet in november 2017. Web however, detailed periodontal charting is required in all patients with significant levels of disease. Without treatment, periodontitis can. Web periodontitis is characterised by the loss of gingival and periodontal tissues. Outline the treatment and management options available for periodontal diseases. The disease severity was associated with age ( r = 0.241; Without treatment, periodontitis can destroy the bone that supports your teeth. This treatment concept was accordingly implemented in the. The bacteria cause inflammation of the gums that is called “gingivitis.” in gingivitis, the gums become red, swollen and can bleed easily. How common is periodontal disease? Establish stage for mild to moderate periodontitis (typically stage i or stage ii): Attachment and bone loss associated with periodontal disease are results of the body’s immune response to plaque biofilm and its. Describe and summarize the pathophysiology of periodontal diseases. You can’t cure periodontitis, but you can manage the condition with proper care and maintenance. Web generalised (81.9%), stage iv (70.1%) and grade c (69.3%) were the most encountered diagnosis. Web periodontitis is characterised by the loss of gingival and periodontal tissues. This can cause teeth to loosen or lead to tooth. Describe and summarize the pathophysiology of periodontal diseases. This includes good oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings at intervals recommended. Web charting periodontal findings (on a partial reproduction of the form used at the ohio state university college of dentistry). Read on to learn more about perio charting and why it’s such an important part of regular preventative care. Web a recent change to the classification of periodontal disease helps your periodontist express the severity and complexity of the disease (staging) as well as the patient’s risk for progression (grading). Web generalised (81.9%), stage iv (70.1%) and grade c (69.3%) were the most encountered diagnosis. No radiographic bone loss/cal over 5 years. The longer plaque and tartar are on teeth, the more harmful they become. Adults 30 years of age or older have periodontitis. Without treatment, periodontitis can destroy the bone that supports your teeth. Web the new worldwide classification was based on interproximal clinical attachment loss. Roughly 42 percent of all dentate u.s. P < 0.001), bop ( r = 0.230; Web this is called periodontal charting, or perio charting, a way for your hygienist to check on the health of your gums. • full mouth probing depths • full mouth radiographs • missing teeth mild to moderate periodontitis will typically be either stage i or stage ii severe to very severe periodontitis will typically be either stage iii or stage iv step 2: Identify the etiology of periodontal diseases.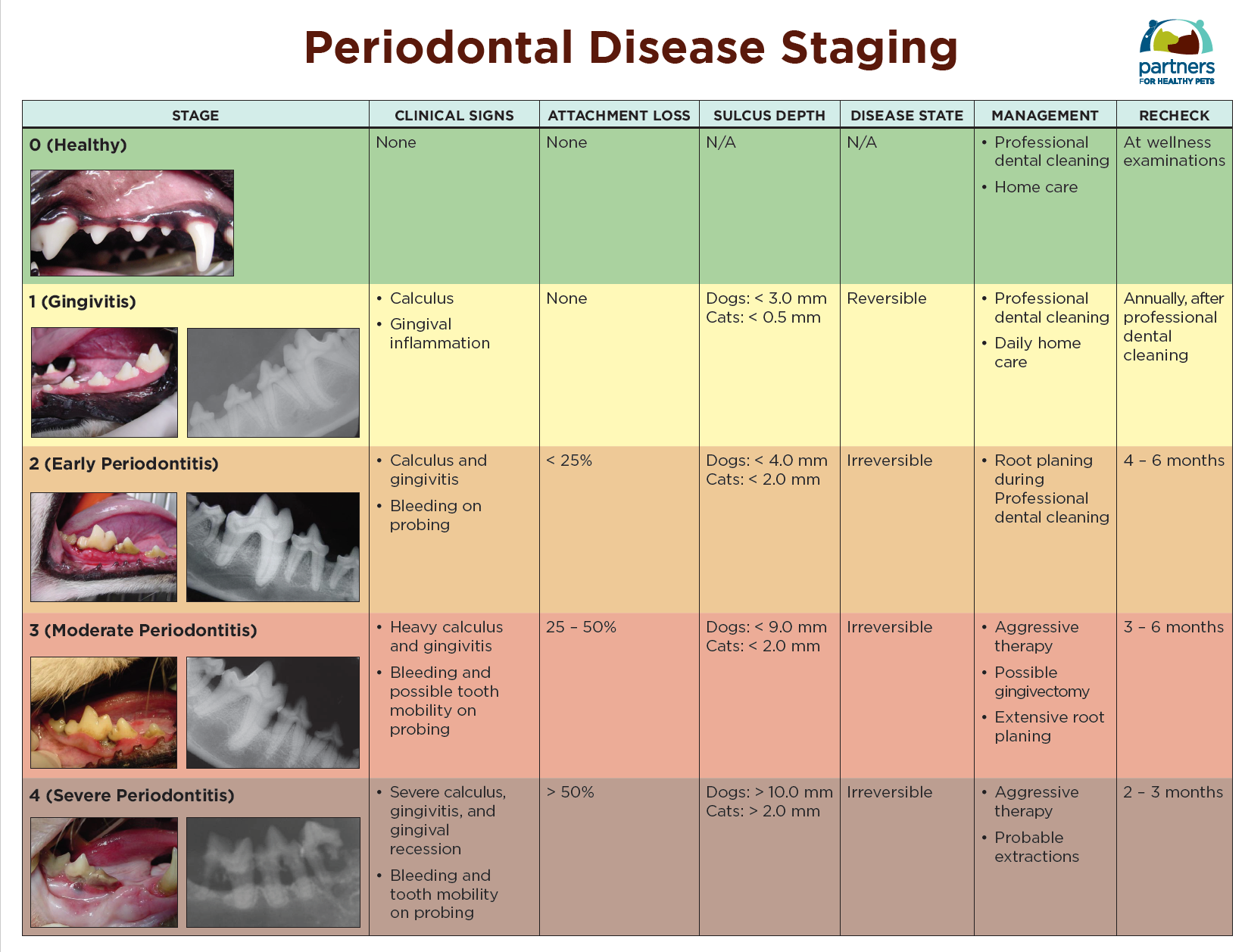
Perio Staging Chart
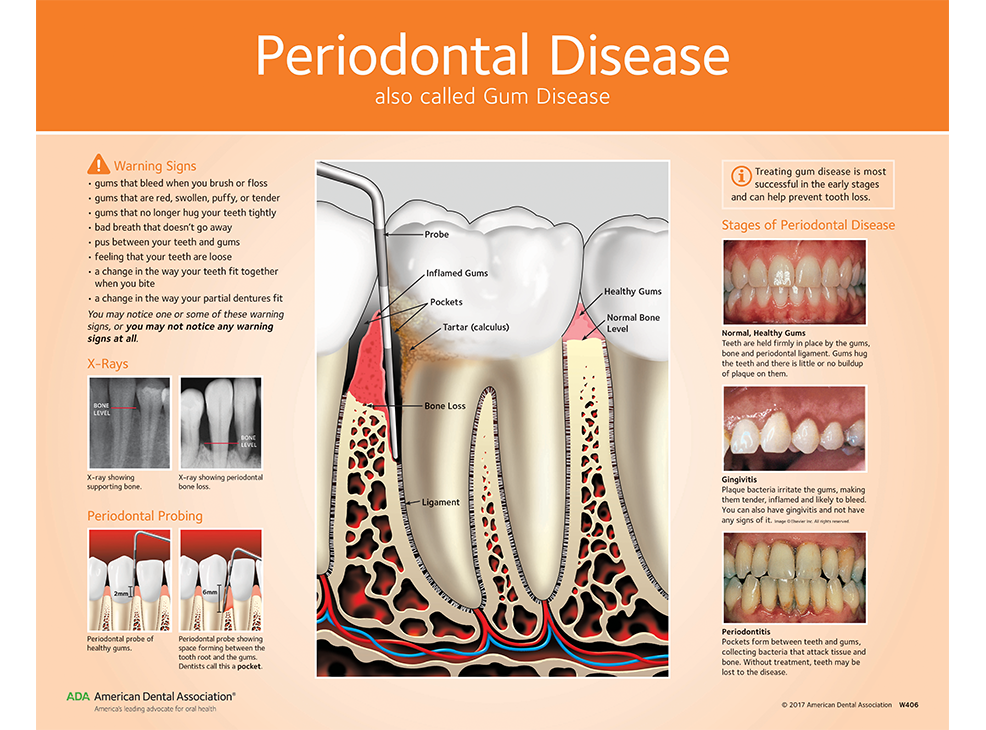
Periodontal (Gum) Disease Chart for Patient Education ADA W406
Top 9 Reasons One Gets Periodontal Disease
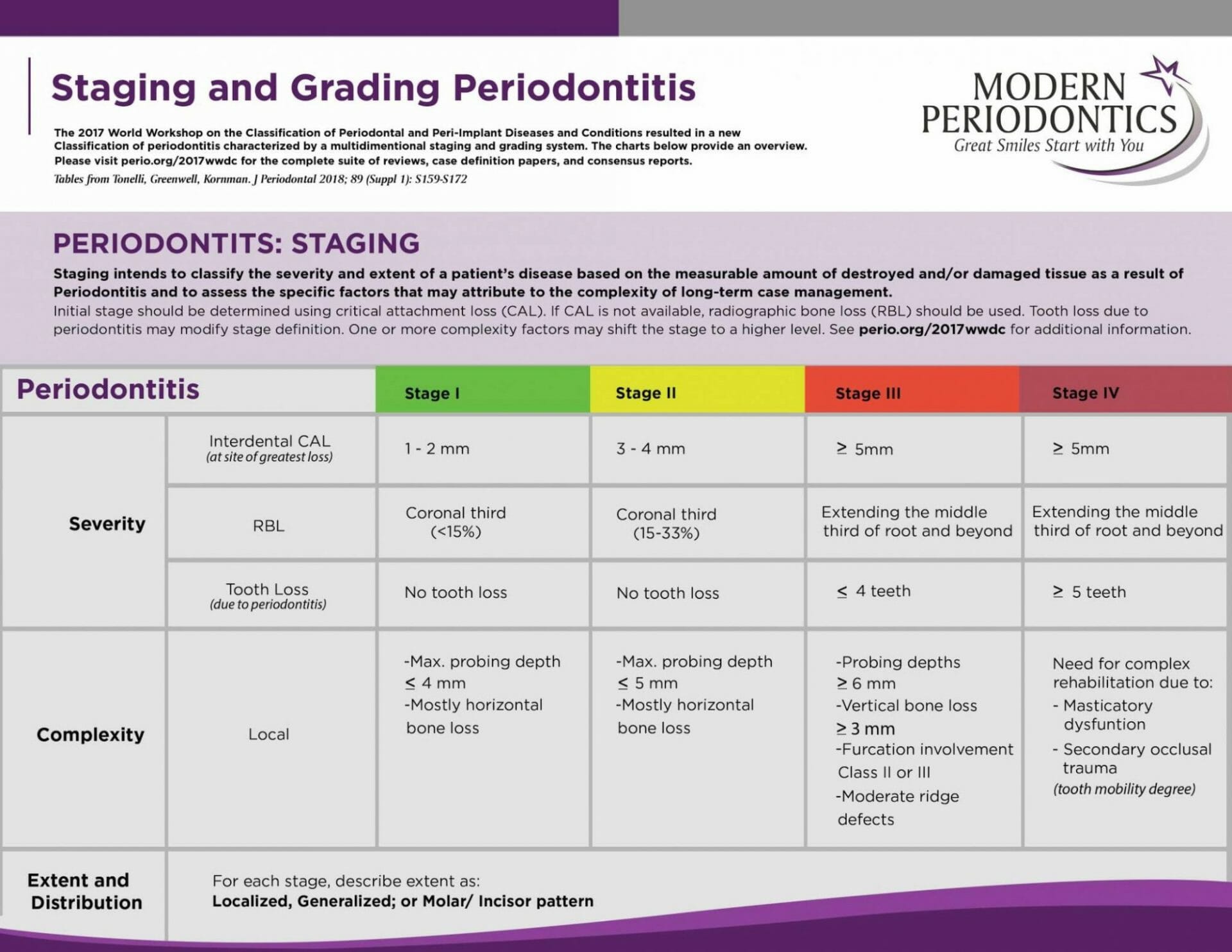
Periodontal Disease Stages Staging and Grading Periodontal Therapy

The Stages Of Periodontal Disease Upper East Side New York, NY The

Periodontal Disease And How it Affects Your Health Victor

Pin on oral health
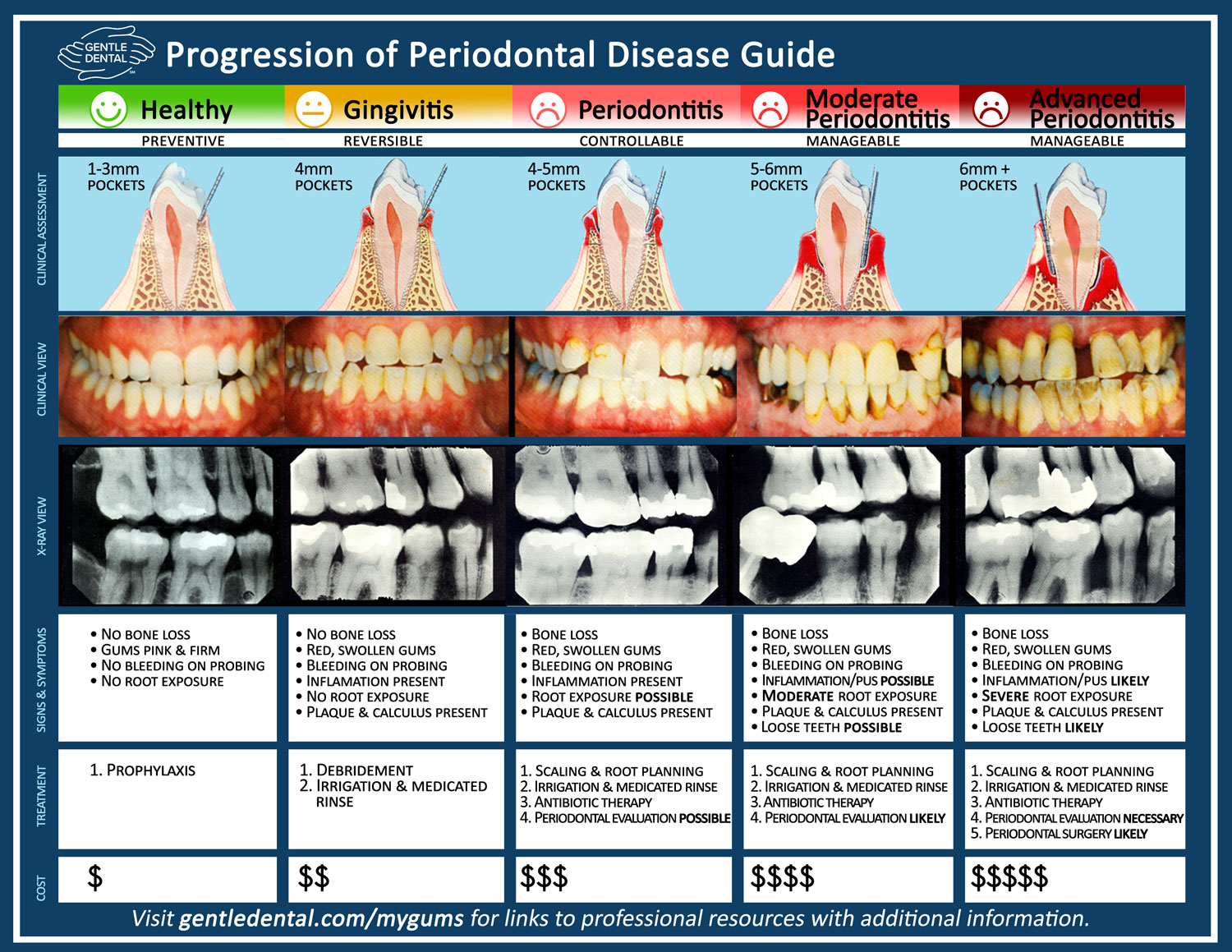
Periodontal Dentistry for Healthy Gums Gentle Dental of New England
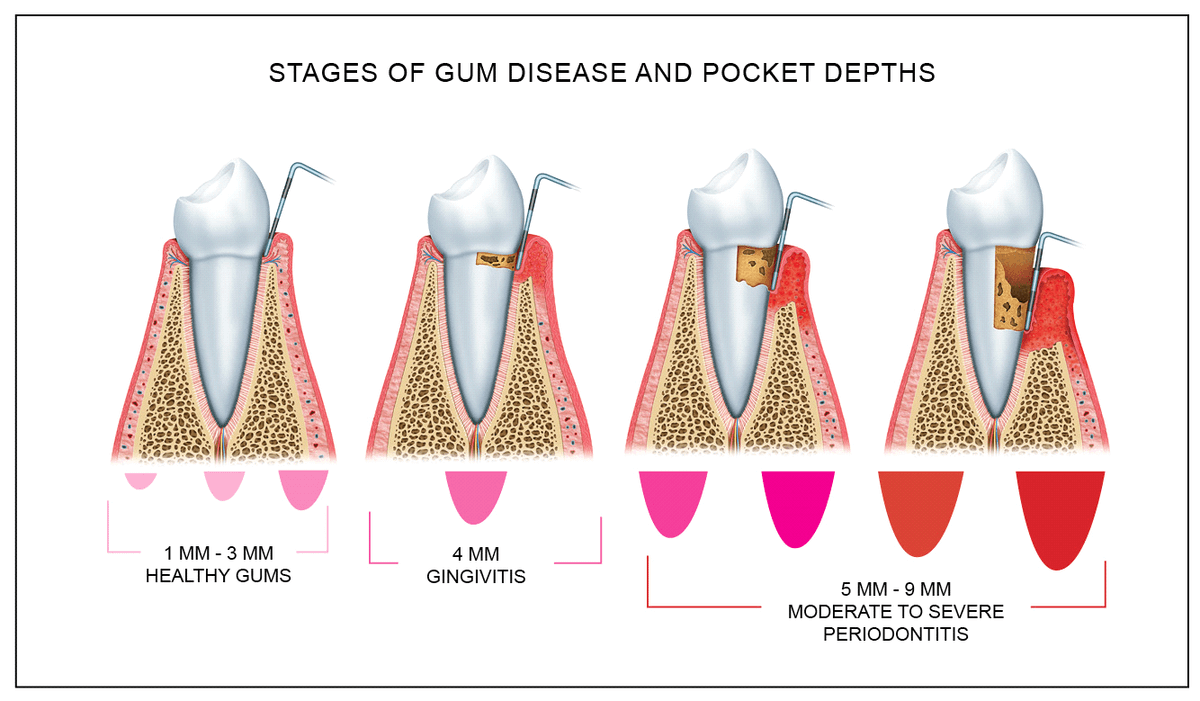
How Gums are Measured Brushwell Dental & Implants
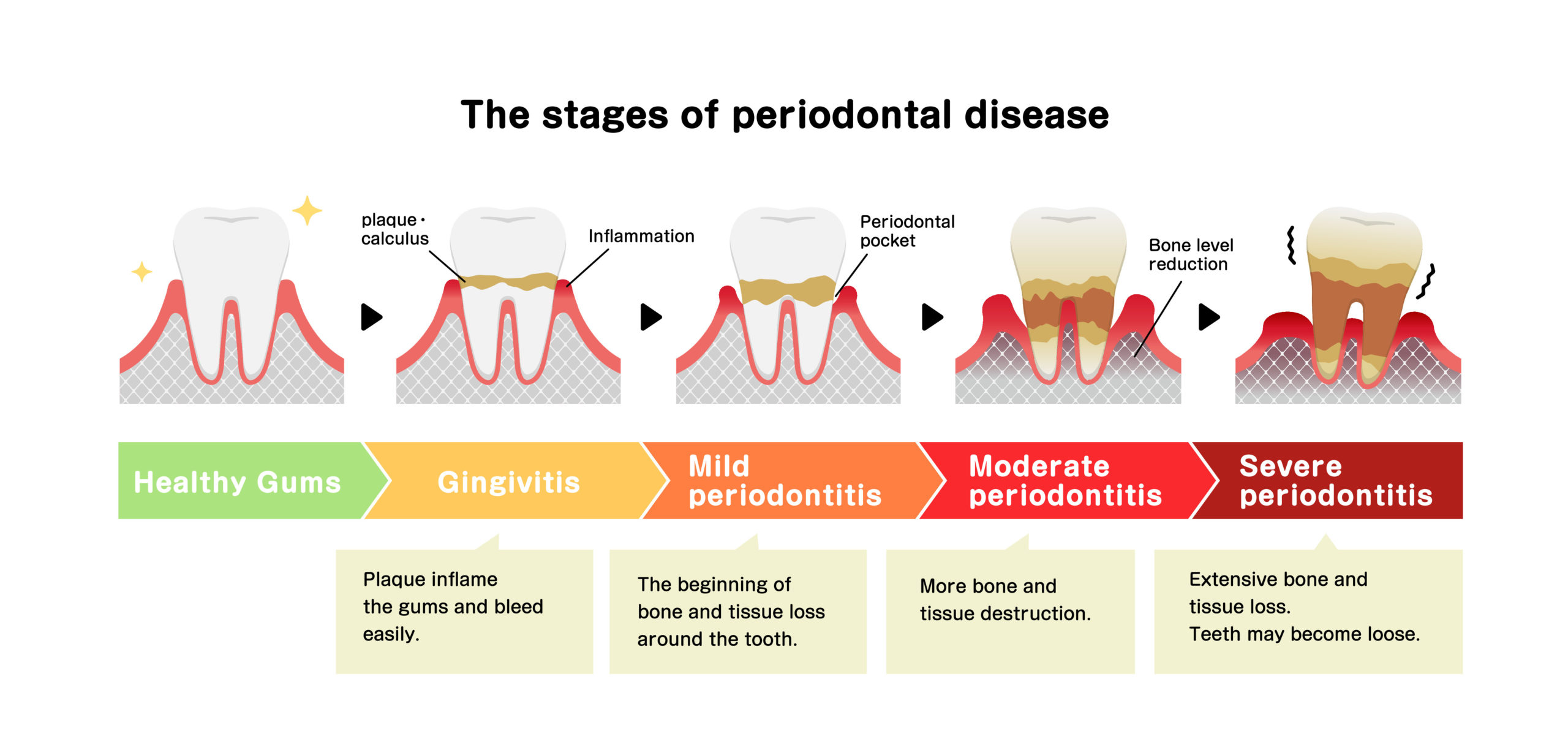
Periodontal Procedures PerioClinik Dr. Freddy Fokam
This Form Provides A Logical Method For Documenting Periodontal Findings (As Well As Other Findings).
P = 0.013) And The Number Of Teeth With Pathological Mobility ( R = 0.318;
The Charts Below Provide An Overview.
Web Periodontitis Is A Severe Form Of Gum Disease.
Related Post: