Non Harmonic Tones Chart
Non Harmonic Tones Chart - Passing tone (pt) the passing tone is a nonchord tone that fills in the space between two chord tones (often a 3rd apart). Suspensions are typically further identified by number. Secondary dominants modulation augmented sixths neapolitan sixth tritone substitution. The second number represents the interval between the note of resolution and the bass. A step is equal to an interval of a generic second. Web a clear understanding of nonharmonic tones is crucial for distinguishing between structural harmonies and what we will call auxiliary sonorities, chords that consist partially or wholly of nonharmonic tones (see chapter 23 ). Web the nonchord tones (ntc) note: Do not use a nct to avoid a part writing error. That point of view looks at them from a melodic perspective rather than a purely harmonic one,. They are defined in western music as the note or tone in a piece of music that does not form part of the chord being played out at the time. The first number represents the interval between the note of suspension and the bass. Web the nonchord tones (ntc) note: Some people call them embellishment tones instead. Web the chart below shows the strong beats or parts of the beat on which an app can be placed and the weaker beats or parts of the beat on which an in. The first number represents the interval between the note of suspension and the bass. Web pedal tone ped common. They are defined in western music as the note or tone in a piece of music that does not form part of the chord being played out at the time. In order to best understand their varying applications, we will group. Web the chart below shows the strong beats or parts of the beat on which an app can be placed and the weaker beats or parts of the beat on which an in can be placed. In this example, the f is a nonharmonic tone because it does not fit into the i chord (which contains c, e, and g).. These notes are present in a piece of music to allow for more melodic movement of each voice, especially the soprano melody. A step is equal to an interval of a generic second. Do not use a nct to avoid a part writing error. Web pedal tone ped common. Suspensions are typically further identified by number. However, they can (and will) occur on a strong beat in some instances. Web the nonchord tones (ntc) note: In the first section we will focus on nonharmonic tones that arise from melodic motion: A step is equal to an interval of a generic second. The second number represents the interval between the note of resolution and the bass. In contrast, a chord tone is a note that is a part of the functional chord. Suspensions are typically further identified by number. The second number represents the interval between the note of resolution and the bass. A skip is equal to an interval of a generic third or more. Web a clear understanding of nonharmonic tones is crucial for. Web a nonchord tone (nct), nonharmonic tone, or embellishing tone is a note in a piece of music or song that is not part of the implied or expressed chord set out by the harmonic framework. The first number represents the interval between the note of suspension and the bass. Web a clear understanding of nonharmonic tones is crucial for. In this example, the f is a nonharmonic tone because it does not fit into the i chord (which contains c, e, and g). Web the nonchord tones (ntc) note: Web pedal tone ped common. These notes are present in a piece of music to allow for more melodic movement of each voice, especially the soprano melody. Web a clear. When part writing with ncts, complete the part writing without ncts first, then look for places to insert ncts. It is approached and left, by step, in the same direction. In contrast, a chord tone is a note that is a part of the functional chord. Some people call them embellishment tones instead. Web pedal tone ped common. In order to best understand their varying applications, we will group them into categories depending on their metrical/rhythmic articulation and the resultant emphasis. Escape tones (et) escape tones are approached by step and left by leap (most often in the opposite direction). Most nct's occur on a weak, or unaccented, beat. Staffs, clefs and ledger lines. The first number represents. Some people call them embellishment tones instead. However, they can (and will) occur on a strong beat in some instances. Staffs, clefs and ledger lines. Most nct's occur on a weak, or unaccented, beat. In this example, the f is a nonharmonic tone because it does not fit into the i chord (which contains c, e, and g). Web a clear understanding of nonharmonic tones is crucial for distinguishing between structural harmonies and what we will call auxiliary sonorities, chords that consist partially or wholly of nonharmonic tones (see chapter 23 ). Passing tone (pt) the passing tone is a nonchord tone that fills in the space between two chord tones (often a 3rd apart). These notes are present in a piece of music to allow for more melodic movement of each voice, especially the soprano melody. Escape tones (et) escape tones are approached by step and left by leap (most often in the opposite direction). The second number represents the interval between the note of resolution and the bass. Do not use a nct to avoid a part writing error. We will then discuss nonharmonic tones that arise from rhythmic action: Check for and resolve errors before inserting ncts. Web a nonchord tone (nct), nonharmonic tone, or embellishing tone is a note in a piece of music or song that is not part of the implied or expressed chord set out by the harmonic framework. In contrast, a chord tone is a note that is a part of the functional chord. Suspensions are typically further identified by number.
NonHarmonic Tones — Kaitlin Bove Music
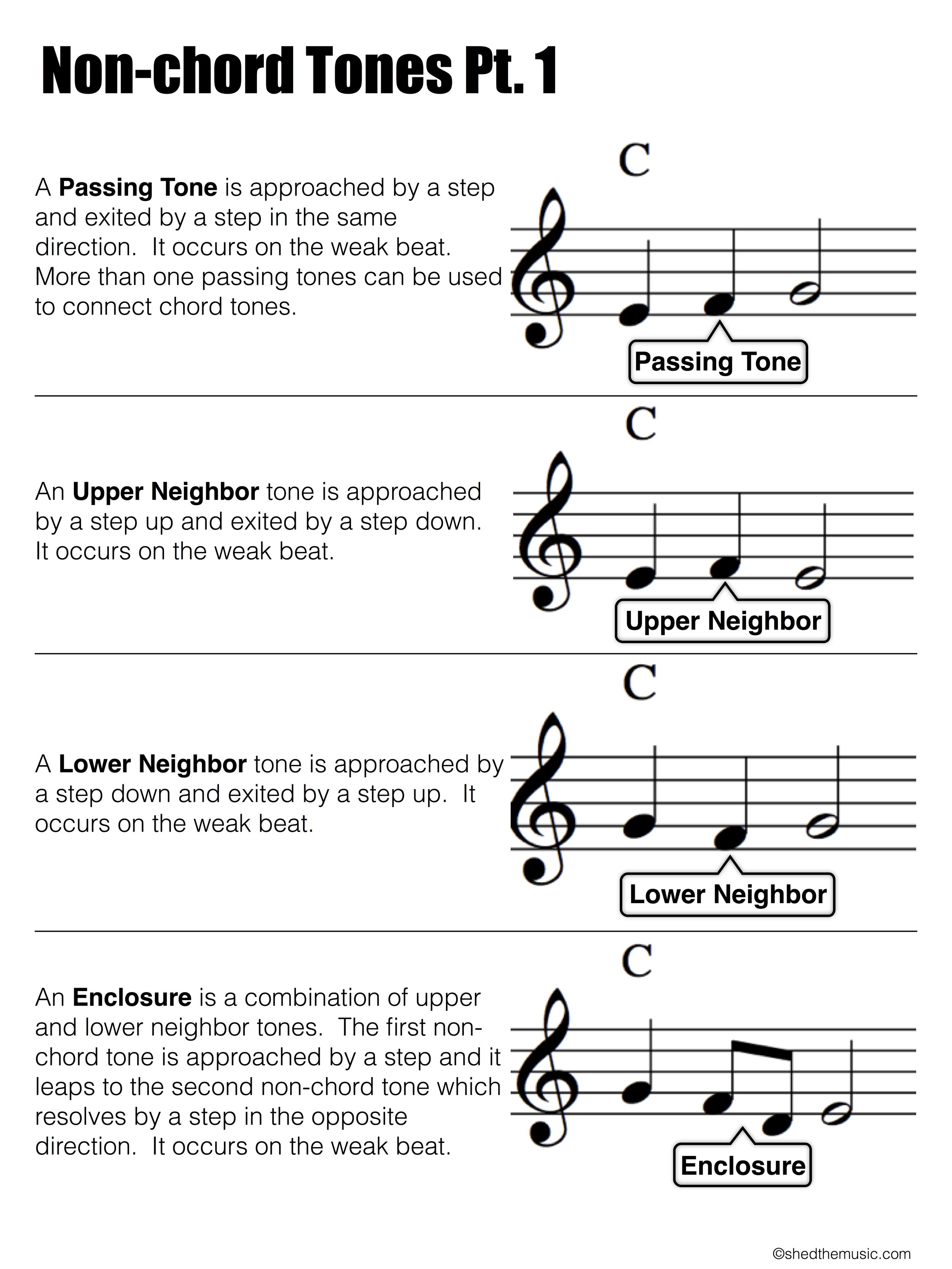
Non Chord Tones — The Shed

list of non harmonic tones
Non Harmonic Tones Chord (Music) Harmony

A description of nonharmonic tones and their use by composers of the

NonHarmonic Tones — Kaitlin Bove Music

NonHarmonic Tones pg1 Discover Guitar Online, Learn to Play Guitar

NonHarmonic Tones — Kaitlin Bove Music

NonHarmonic Tones — Kaitlin Bove Music

NonHarmonic Tone Types Diagram Quizlet
The First Number Represents The Interval Between The Note Of Suspension And The Bass.
In Order To Best Understand Their Varying Applications, We Will Group Them Into Categories Depending On Their Metrical/Rhythmic Articulation And The Resultant Emphasis.
In Order To Best Understand Their Varying Applications, We Will Group Them Into Categories Depending On Their Metrical/Rhythmic Articulation And The Resultant Emphasis.
In The First Section We Will Focus On Nonharmonic Tones That Arise From Melodic Motion:
Related Post:
