Monomer Polymer Chart
Monomer Polymer Chart - Web literature values for the glass transition temperature, (t g ), and melting temperature, (t m) for the more common homopolymers are listed in the table below. Web a polymer is a substance consisting of molecules characterised by the sequence of one or more types of monomer unit. If you think of a monomer as being like a bead, then you can think of a polymer as being like a necklace, a. Web there are two general types of polymerization reactions: Even one kind of monomer can combine in a variety of ways to form several different polymers: Web polymers are very large molecules made from smaller ones. Web a monomer is a type of molecule that has the ability to chemically bond with other molecules in a long chain; A large molecule made of repeating subunits (monomers). Fassen wir noch einmal zusammen: Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like monomer (subunit) of carbohydrates, function of carbohydrates, polymer formed from simple sugars and more. For example, glucose monomers are the constituents of starch, glycogen, and cellulose. Monosaccharides such as glucose make up polysaccharides like starches. For example, a carbohydrate is a polymer that is made of repeating monosaccharides. A large molecule made of repeating subunits (monomers). This single bond is a remnant of the double bond which joined those. Each vinyl chloride monomer molecule contributes a ch 2 group joined to a chcl unit by a single bond. Web a monomer is a type of molecule that has the ability to chemically bond with other molecules in a long chain; Monosaccharides such as glucose make up polysaccharides like starches. Web the monomer is a small molecule, which can undergo. Essentially, monomers are the building blocks of polymers, which are more complex type of molecules. Several important biological polymers include proteins, starch, cellulose, and dna. A relatively large molecule consisting of a chain or network of many identical or similar monomers chemically bonded to each other. Fassen wir noch einmal zusammen: Cells perform repeated dehydration synthesis reactions to build diverse. Polymers are frequently made through the action of an initiator, which gets the monomer units to start attaching to each other. Web different types of monomers can combine in many configurations, giving rise to a diverse group of macromolecules. Das liegt daran, dass monomere reaktionsfreudig sind und sich gerne miteinander verknüpfen. Web most large biological molecules are polymers, long chains. This single bond is a remnant of the double bond which joined those. Meat, poultry, eggs, beans, soy, nuts, peanut butter, enzymes *one of the most important biomolecules *nitrogen makes it different. Web different types of monomers can combine in many configurations, giving rise to a diverse group of macromolecules. Without the initiator, the monomers just sit there. Web polymers. For the purpose of our study, we have chosen linear chains as topological representations. Die „verknüpfungsreaktion“ nennst du polymerisation. Cells perform repeated dehydration synthesis reactions to build diverse polymers, including polysaccharides and polynucleotides (the rna and dna nucleic acids). Addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. Web polymers are long chain, giant organic molecules are assembled from many smaller molecules called monomers. 126 organic molecules, monomers, & polymers. Web a molecule from which a polymer is made is called a monomer. Several important biological polymers include proteins, starch, cellulose, and dna. The word ‘poly’ literally means ‘many’. A large molecule made of repeating subunits (monomers). Each vinyl chloride monomer molecule contributes a ch 2 group joined to a chcl unit by a single bond. Web most large biological molecules are polymers, long chains made up of repeating molecular subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Cells perform repeated dehydration synthesis reactions to build diverse polymers, including polysaccharides and polynucleotides (the rna and dna nucleic acids). Web. A relatively large molecule consisting of a chain or network of many identical or similar monomers chemically bonded to each other. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like monomer (subunit) of carbohydrates, function of carbohydrates, polymer formed from simple sugars and more. Monomers are small molecules that can combine to form larger molecules called polymers. If you. The polymers and corresponding monomers listed are available from us. Web literature values for the glass transition temperature, (t g ), and melting temperature, (t m) for the more common homopolymers are listed in the table below. A polymer is a chain of an unspecified number of monomers. Essentially, monomers are the building blocks of polymers, which are more complex. Fassen wir noch einmal zusammen: Web literature values for the glass transition temperature, (t g ), and melting temperature, (t m) for the more common homopolymers are listed in the table below. Web there are two general types of polymerization reactions: Amino acids make up proteins. Both monomer and polymer are commonly used in the industrial chemistry to relate to different types of material and their constituents. Web to comprehend the full scope of proteins, it is crucial to understand various properties, including the basic biological molecule, peptides, polypeptide chains, amino acids, protein structures, and the processes of protein denaturation. This monomers and polymers chart will help you with monomers and polymers chart, and make your monomers and polymers chart more enjoyable and effective. Monomers are small molecules that can combine to form larger molecules called polymers. The polymers and corresponding monomers listed are available from us. Web you will also discover how to use monomers and polymers chart, such as how to read, compare, and apply the charts. Web in general, polymer properties are determined to a large extent by how the monomer units are interconnected. This single bond is a remnant of the double bond which joined those. Without the initiator, the monomers just sit there. A polymer is a molecule of high molecular weight, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low molecular weight. Web a polymer is a substance consisting of molecules characterised by the sequence of one or more types of monomer unit. Polymers are frequently made through the action of an initiator, which gets the monomer units to start attaching to each other.
Image Gallery Monomers Chart
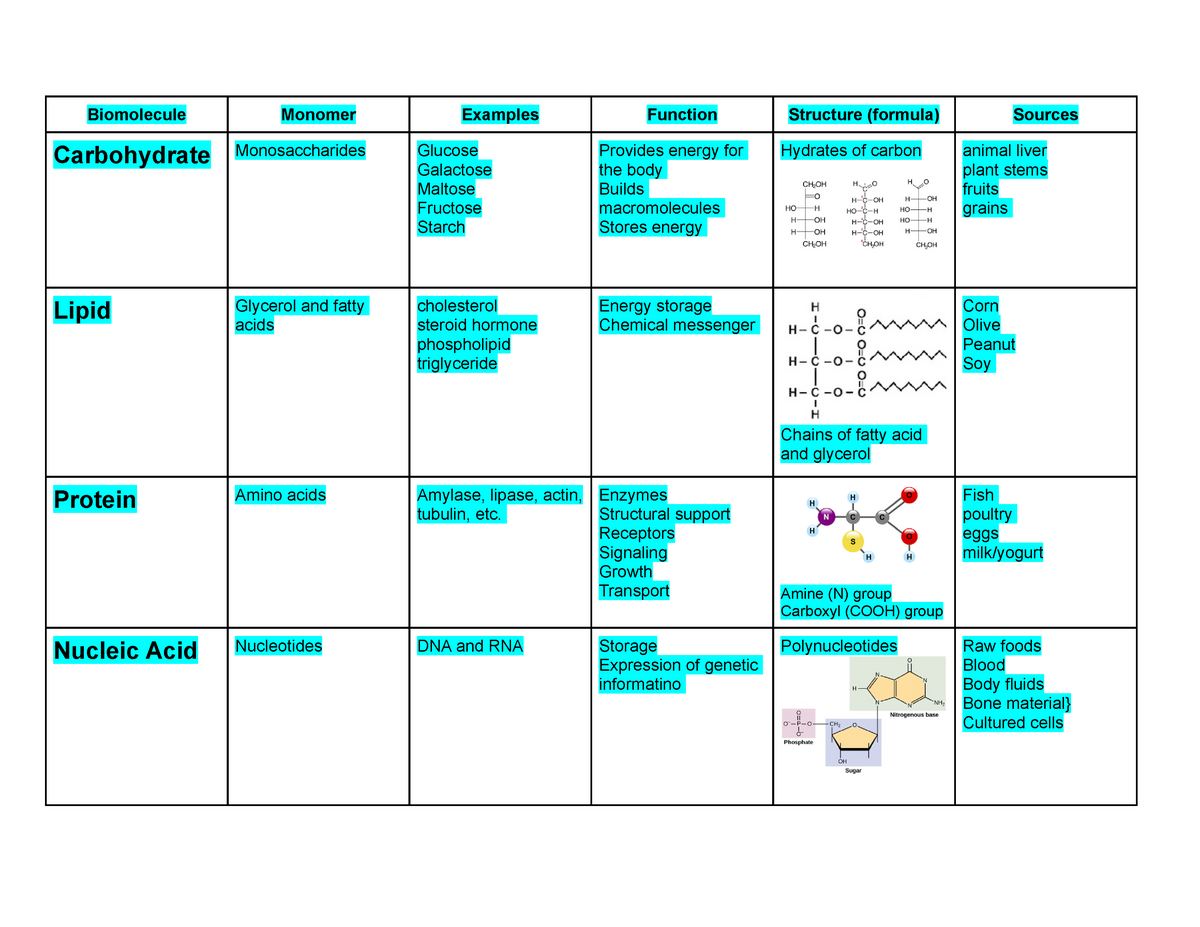
Biomolecule Chart Biomolecule Monomer Examples Function Structure
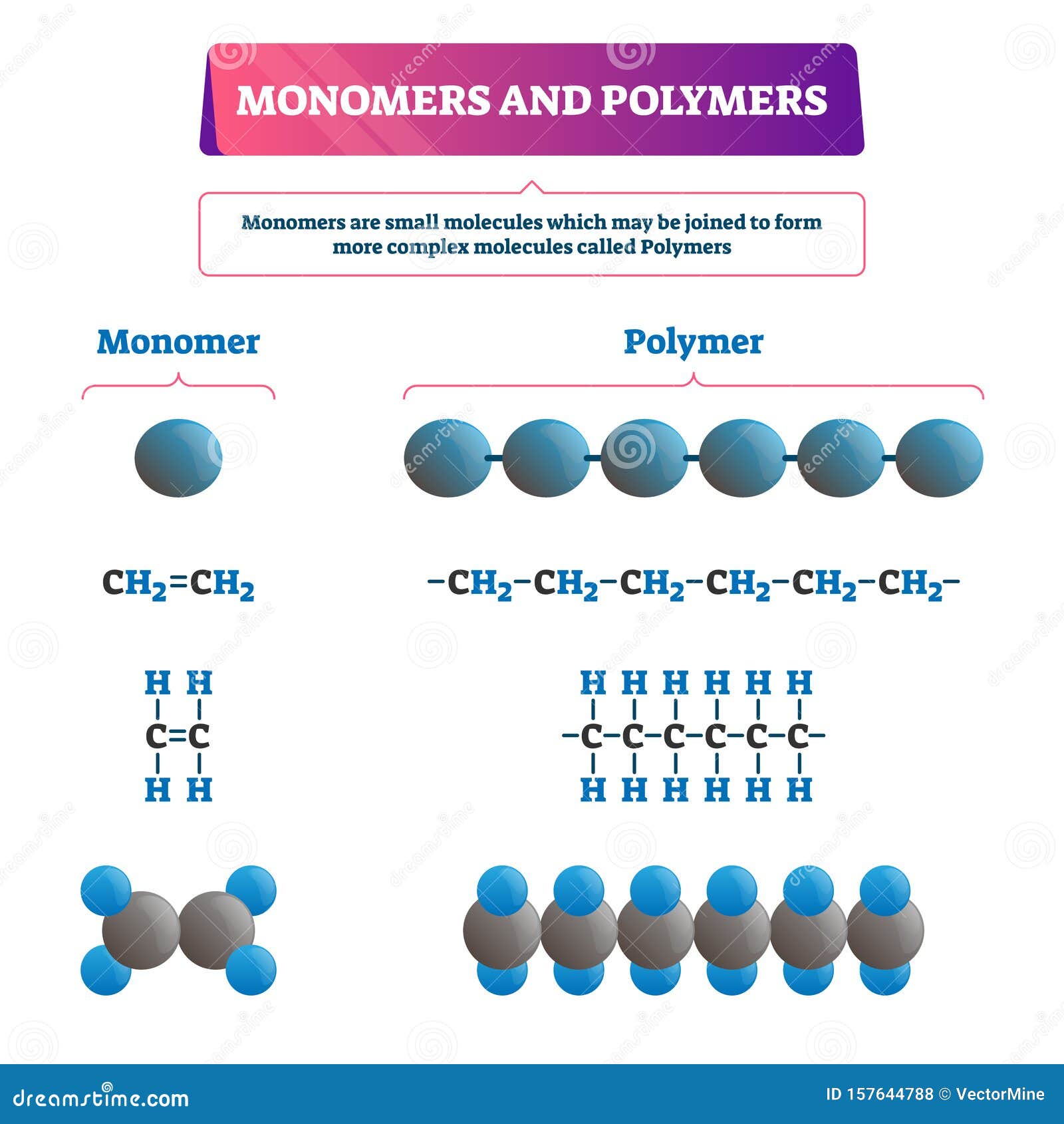
Monomer Or Polymer Vector Illustration Labeled Chemical Educational

What are the MONOMERS of each POLYMER? ppt download
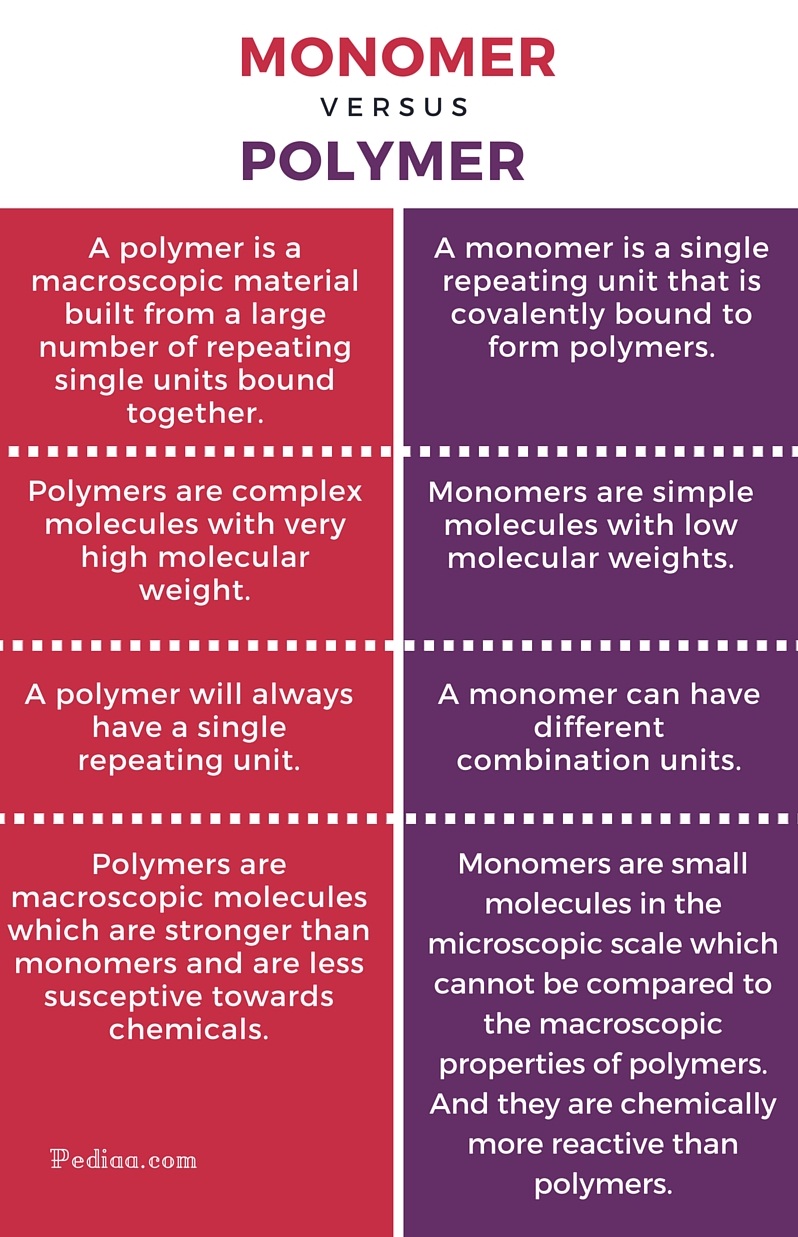
Explain How Monomers and Polymers Are Different From Each Other Azul
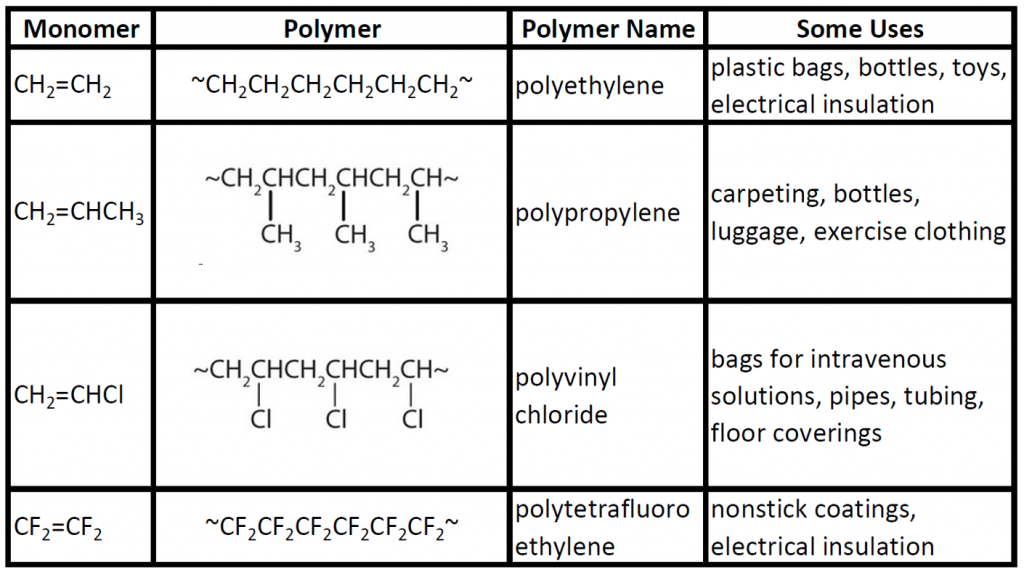
Polymers And Monomers Chart
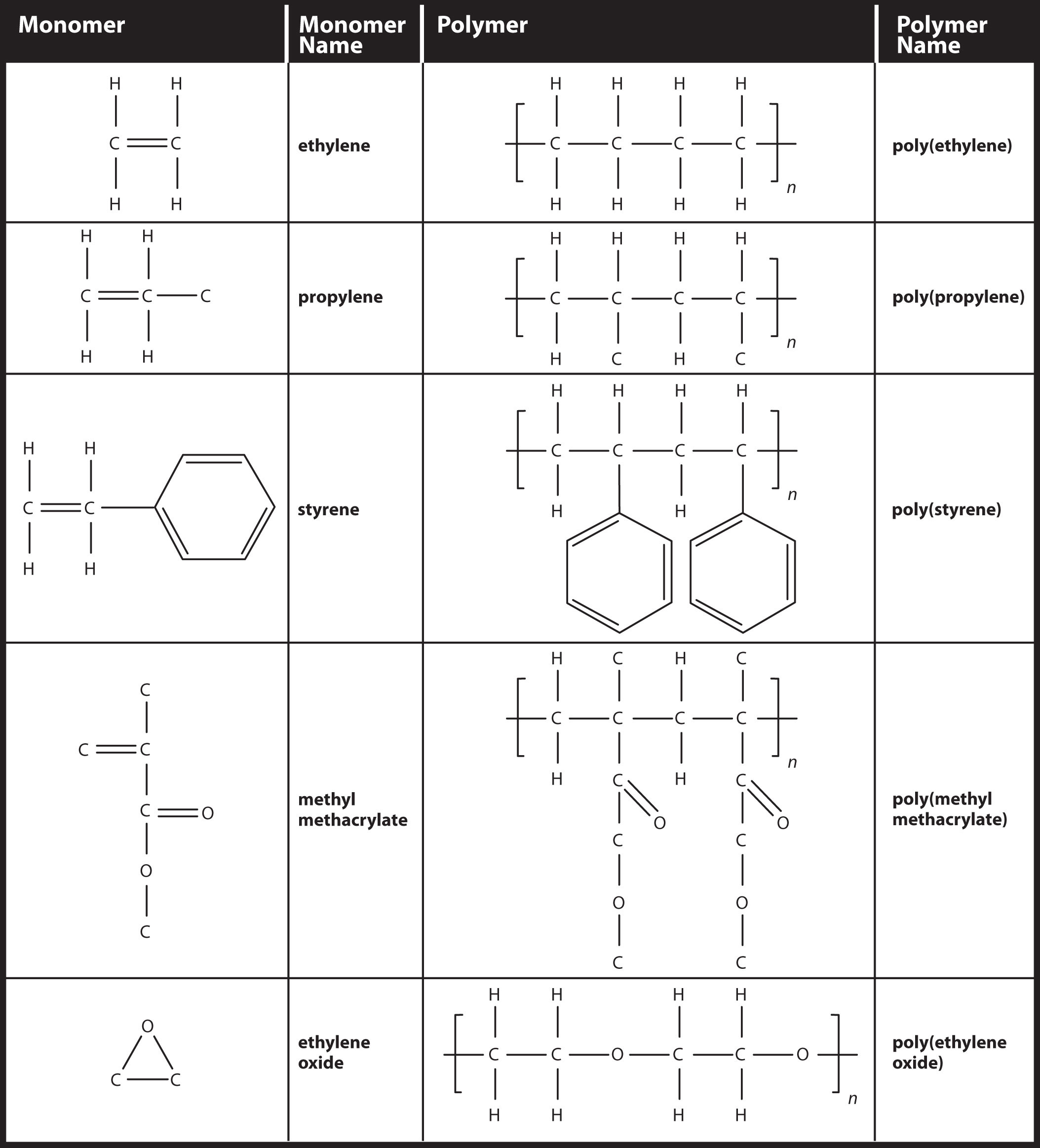
Polymers

BIO101 Biological Macromolecule Monomers & Polymers Diagram Quizlet
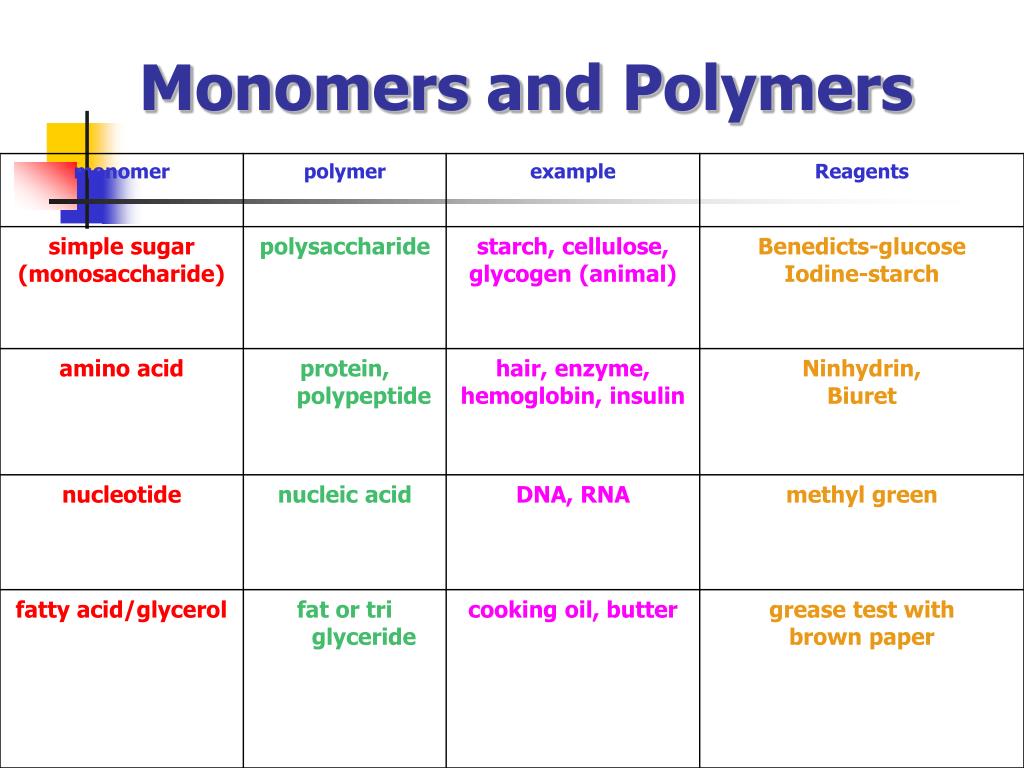
PPT CELL BIOLOGY (C) 2015 PowerPoint Presentation, free download
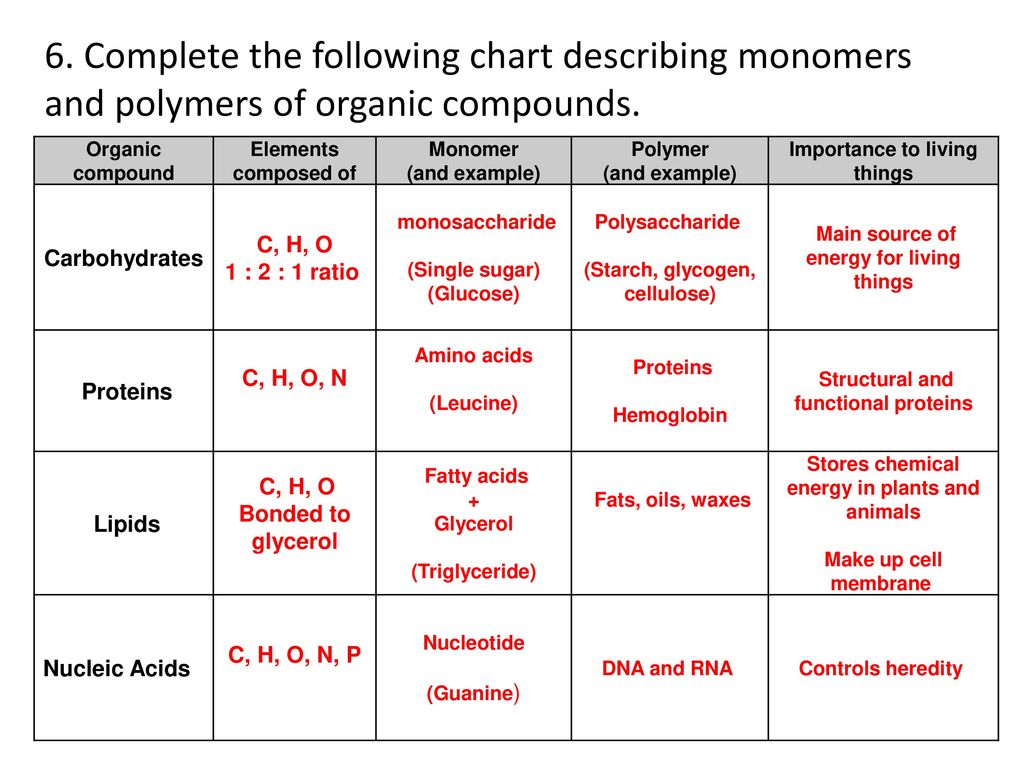
Complete The Following Chart Monomer Polymer Example Function Chart Walls
For Example, A Carbohydrate Is A Polymer That Is Made Of Repeating Monosaccharides.
Web Polymers Are Very Large Molecules Made From Smaller Ones.
Cells Perform Repeated Dehydration Synthesis Reactions To Build Diverse Polymers, Including Polysaccharides And Polynucleotides (The Rna And Dna Nucleic Acids).
Web Polymers Are Long Molecules Composed Of Chains Of Units Called Monomers.
Related Post: