Macromolecule Monomer Polymer Chart
Macromolecule Monomer Polymer Chart - Web most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. These biological macromolecules are essential for life and include proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. There are multiple hydroxyl groups and a carbonyl group. What are the definitions for a monomer and polymer? Draw a starch polymer containing its many monomers. Browse videos, articles, and exercises by topic. Even one kind of monomer can combine in a variety of ways to form several different polymers: Web level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 400 mastery points! Polymers are made of many small molecules linked together. Monosaccharide (simple sugar molcules, condensation reaction) polymer:polysaccharide & dissaccharide (complex carbs) This type of reaction is dehydration synthesis, which means “to put together while losing water.” A relatively small molecule that can form covalent bonds with other molecules of this type to form a polymer. Web macromolecules are large molecules composed of two or more polymers combined together (macro=large). Monosaccharide (simple sugar molcules, condensation reaction) polymer:polysaccharide & dissaccharide (complex carbs) Web. Web most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. If the carbonyl group is at an end, the sugar has an aldehyde and is known as an aldose sugar. For example, an amino acid acts as the building blocks for proteins. Even one kind of monomer can combine in a variety of ways to form several. Even one kind of monomer can combine in a variety of ways to form several different polymers: Web level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 400 mastery points! Monomers are smaller molecules, and when bonded together, make up polymers. Monosaccharide (simple sugar molcules, condensation reaction) polymer:polysaccharide & dissaccharide (complex carbs) This unit is part. A relatively small molecule that can form covalent bonds with other molecules of this type to form a polymer. Monosaccharides have a formula of ( ch 2 o) n , and they typically contain three to seven carbon atoms. Web level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 400 mastery points! Web most macromolecules are. Web most large biological molecules are polymers, long chains made up of repeating molecular subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Web macromolecules are large molecules composed of two or more polymers combined together (macro=large). The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. This unit is part of the biology library. Web monomer. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. Aldoses have a carbonyl group (indicated in green) at the end of the carbon chain, and ketoses have a. Meat, poultry, eggs, beans, soy, nuts, peanut butter, enzymes *one of the most important biomolecules *nitrogen makes it different. Draw a starch polymer containing its many monomers. How is that formula different. Web in biology, macromolecules refer to large organic molecules that form by polymerization, a process that joins smaller units called monomers via covalent bonds. Web monomer = amino acids. Draw a starch polymer containing its many monomers. The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. Web most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Nearly c h 2 o. How is that formula different from carbohydrates in general? If you think of a monomer as being like a bead, then you can think of a polymer as being like. Web macromolecule proteins monomer name and chemical composition and name of bond between adjacent monomers amino acids peptide bonds types of this macromolecule and example(s). Web in biology, macromolecules refer to large organic molecules that form by polymerization, a process that joins smaller units called monomers via covalent bonds. Monosaccharides have a formula of ( ch 2 o) n , and they typically contain three to seven carbon atoms. Use hexagons as a monomer. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form. Meat, poultry, eggs, beans, soy, nuts, peanut butter, enzymes *one of the most important biomolecules *nitrogen makes it different. Monomers are smaller molecules, and when bonded together, make up polymers. Web different types of monomers can combine in many configurations, giving rise to a diverse group of macromolecules. For example, glucose monomers are the constituents of starch, glycogen, and cellulose.. If the carbonyl group is at an end, the sugar has an aldehyde and is known as an aldose sugar. Monomer = _____________________________________________________________ polymer = _____________________________________________________________ 2. For example, a carbohydrate is a polymer that is made of repeating monosaccharides. Web in biology, macromolecules refer to large organic molecules that form by polymerization, a process that joins smaller units called monomers via covalent bonds. How is that formula different from carbohydrates in general? This type of reaction is dehydration synthesis, which means “to put together while losing water.” Therefore, polymer nomenclature is generally based upon a type of a monomer residue comprising a polymer. For example, glucose monomers are the constituents of starch, glycogen, and cellulose. Web macromolecules are large molecules composed of two or more polymers combined together (macro=large). Web most large biological molecules are polymers, long chains made up of repeating molecular subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Web monomer = amino acids. Web monosaccharides are classified based on the position of their carbonyl group and the number of carbons in the backbone. What are the definitions for a monomer and polymer? Meat, poultry, eggs, beans, soy, nuts, peanut butter, enzymes *one of the most important biomolecules *nitrogen makes it different. Nearly c h 2 o. Monosaccharides have a formula of ( ch 2 o) n , and they typically contain three to seven carbon atoms.
Macromolecules Worksheet Chart
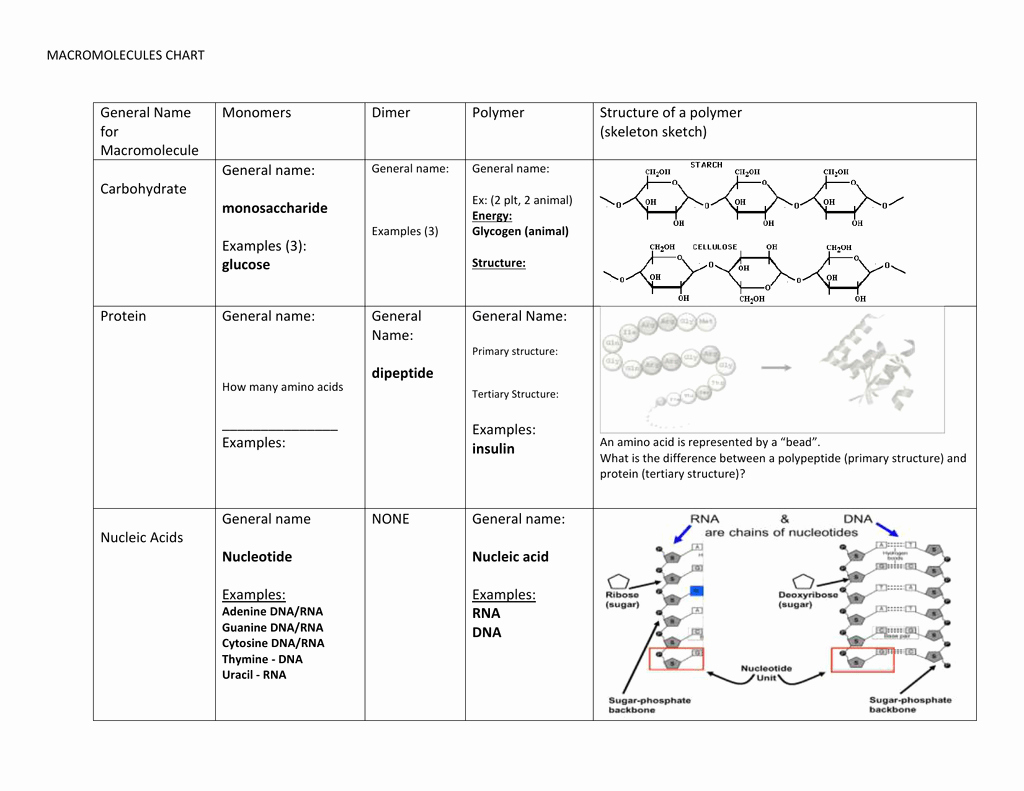
50 Building Macromolecules Worksheet Answers

Macromolecules Monomers And Polymers Monomers and additives used

Difference Between Polymer and Macromolecule Compare the Difference
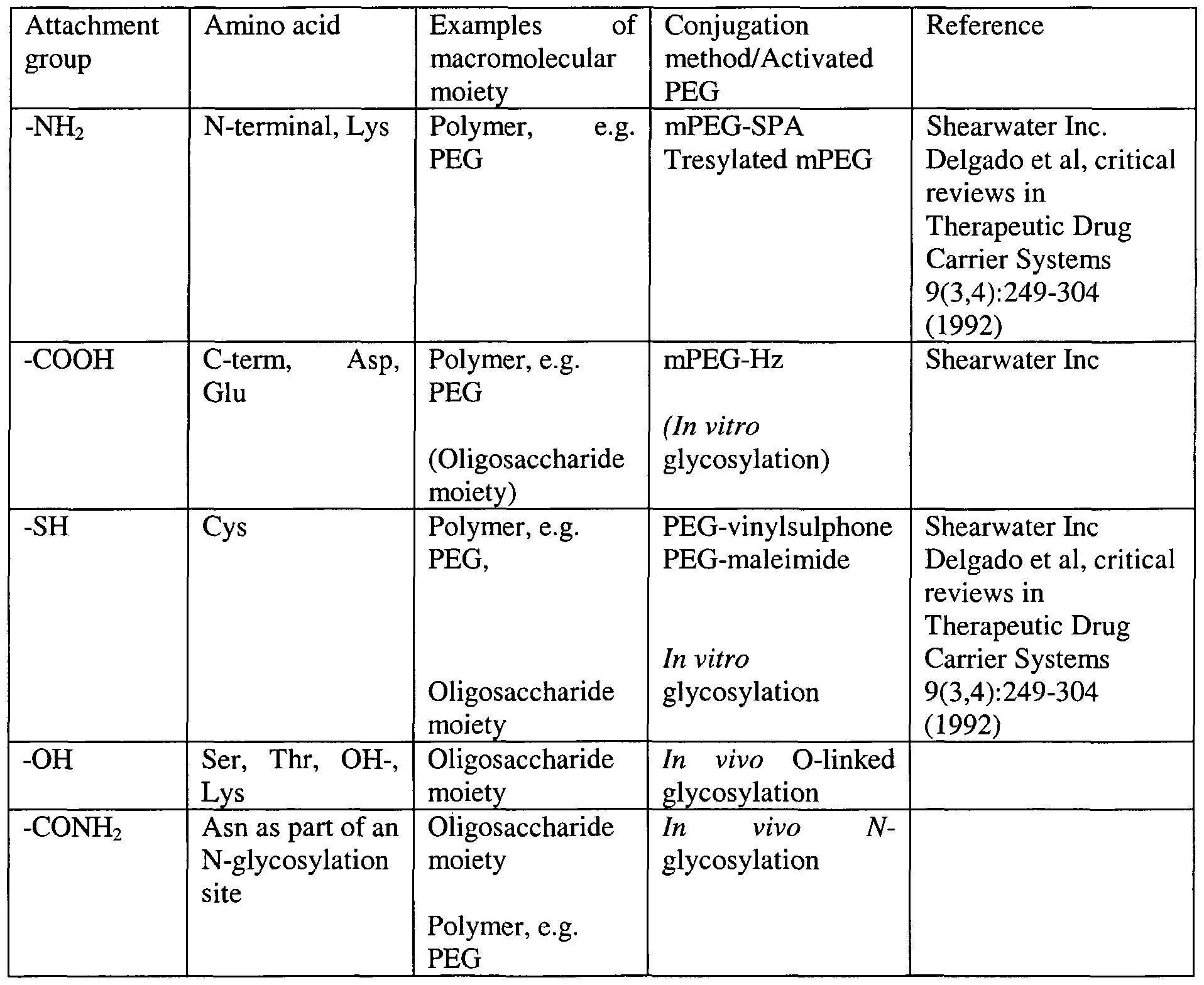
15 Best Images of Macromolecules Coloring Worksheet Macromolecule
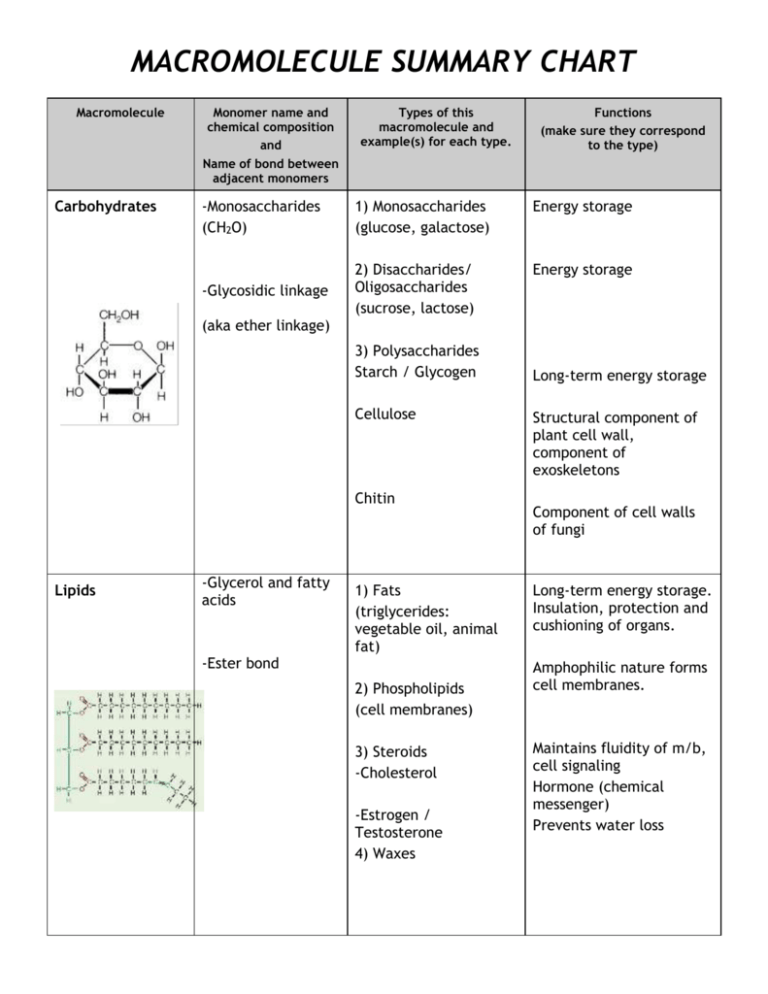
macromolecule summary chart

LabXchange

BIO101 Biological Macromolecule Monomers & Polymers Diagram Quizlet

SOLUTION Macromolecule Chart Studypool

Image Gallery Monomers Chart
The Monomers Combine With Each Other Using Covalent Bonds To Form Larger Molecules Known As Polymers.
Aldoses Have A Carbonyl Group (Indicated In Green) At The End Of The Carbon Chain, And Ketoses Have A.
These Biological Macromolecules Are Essential For Life And Include Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Carbohydrates, And Lipids.
A Relatively Small Molecule That Can Form Covalent Bonds With Other Molecules Of This Type To Form A Polymer.
Related Post: