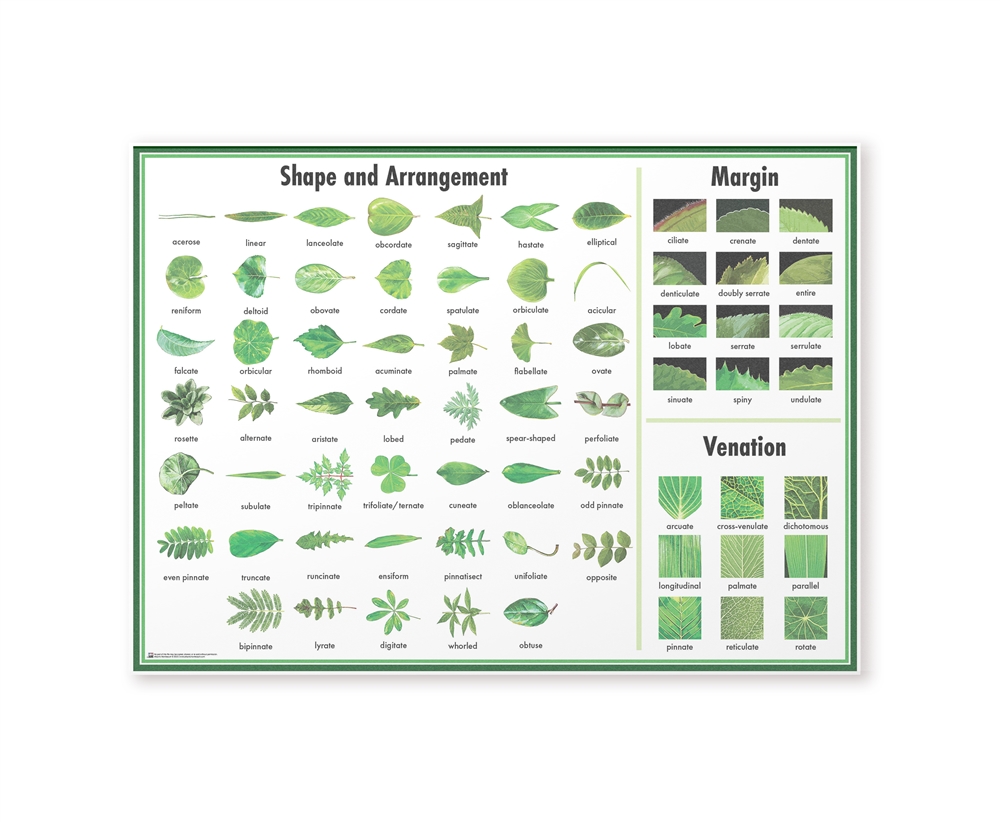
Leaf Morphology Chart
Leaf Morphology Chart - Web leaves are generally composed of a few main parts: The main function of a leaf is. (c) senna reticulata compact spongy parenchyma with only few and. Buds may be lateral or terminal. The following terms are used to describe leaf morphology in the description and taxonomy of plants. Leaves are very important in plant morphology. Compare the adaptations of mesophytic, hydrophytic, and xerophytic leaves. Web figure 14.4 leaf morphology chart with narrow to broad examples. Web higher levels of nutrients, in particular nitrogen, are found in regions of the canopy that receive the highest amounts of solar radiation, and also have the highest sla, i.e., the leaves found at the tops of trees and the upper third of the canopy. In the last decade, however, there has been an increasing interest in the use of modern geometric morphometrics (gmm) to study the form of leaves. Leaves are very important in plant morphology. Leaves differ in their arrangement and whether they are. Web use the leaf morphology chart to describe leaf parts. Web computerized geometric morphometric methods for quantitative shape analysis measure, test and visualize differences in form in a highly effective, reproducible, accurate and statistically powerful way. Web what can you learn from a tree's. Knowing this fundamental difference in leaf type is key to identifying plant specimens. Web leaves are generally composed of a few main parts: Web what can you learn from a tree's leaves? Use morphological descriptors for leaf parts. The main function of a leaf is. Identify the unique features of pine and corn leaves. Web what can you learn from a tree's leaves? The blade is held away from the stem and supported by the petiole. (a) eugenia inundata cross section with large epidermal cells; C) estimate the accuracy o. A) compute size and shape variables using procrustes methods; Leaf shapes | leaf margins | leaf venation: Web leaves are generally composed of a few main parts: Identify the unique features of pine and corn leaves. Web use the leaf morphology chart to describe leaf parts. Web morphology of the leaf. The number of leaves, root diameter,. Leaf shapes | leaf margins | leaf venation: Use morphological descriptors for leaf parts. Leaves may be simple (a single leaf blade or lamina) or compound (with several leaflets ). This illustrated guide shows you what both look like. Leaf shapes | leaf margins | leaf venation: The blade is most frequently the flat, photosynthetic part. Changes in morphology and chlorophyll of c. The space between two nodes is an internode. Web leaves commonly consist of a petiole and lamina (blade). The height of the bar chart represents the numerical value, and a,b,c indicates the significance between treatment groups. The blade and the petiole. Tree leaves come in all sorts and sizes, and knowing the shape of particular leaves can help to quickly identify the tree species. Web use the leaf. The edge of the leaf is called the margin, and the vascular bundles form veins. Web what is the size, shape, texture, and color variation of the leaves? (a) eugenia inundata cross section with large epidermal cells; Click the image hot spots. A) compute size and shape variables using procrustes methods; Web morphology of the leaf. The number of leaves, root diameter,. Web what is the size, shape, texture, and color variation of the leaves? Web higher levels of nutrients, in particular nitrogen, are found in regions of the canopy that receive the highest amounts of solar radiation, and also have the highest sla, i.e., the leaves found at the tops. Knowing this fundamental difference in leaf type is key to identifying plant specimens. Structure of a leaf leaves are thin, flat organs responsible for photosynthesis in the plants. (c) senna reticulata compact spongy parenchyma with only few and. Web use the leaf morphology chart to describe leaf parts. Use morphological descriptors for leaf parts. Web figure 14.4 leaf morphology chart with narrow to broad examples. The ability to describe the leaf is a must even for novices in botany. Changes in morphology and chlorophyll of c. The blade is most frequently the flat, photosynthetic part. Web leaf morphology is central to plant taxonomy and systematics [1] and it has mostly been studied using traditional morphometrics [2], [3]. Web what can you learn from a tree's leaves? The blade and the petiole. An illustrated glossary of leaf terminology. Web using free software and an example dataset from two geographical populations of sessile oak leaves, we describe in detailed but simple terms how to: C) estimate the accuracy o. Learn how to recognize a leaf that has a lobed or divided shape. The main function of a leaf is. Discover how leaf shape, edges, patterns, and more can help you identify a tree in the forest. Web computerized geometric morphometric methods for quantitative shape analysis measure, test and visualize differences in form in a highly effective, reproducible, accurate and statistically powerful way. Morphology means external, well visible structural features whereas anatomy needs tools like a scalpel and/or microscope to study needs tools like a microscope and/or scalpel. The blade is held away from the stem and supported by the petiole.
Leaf Shape Study Chart ETC Montessori
Printable Tree Leaf Identification Chart Printable World Holiday

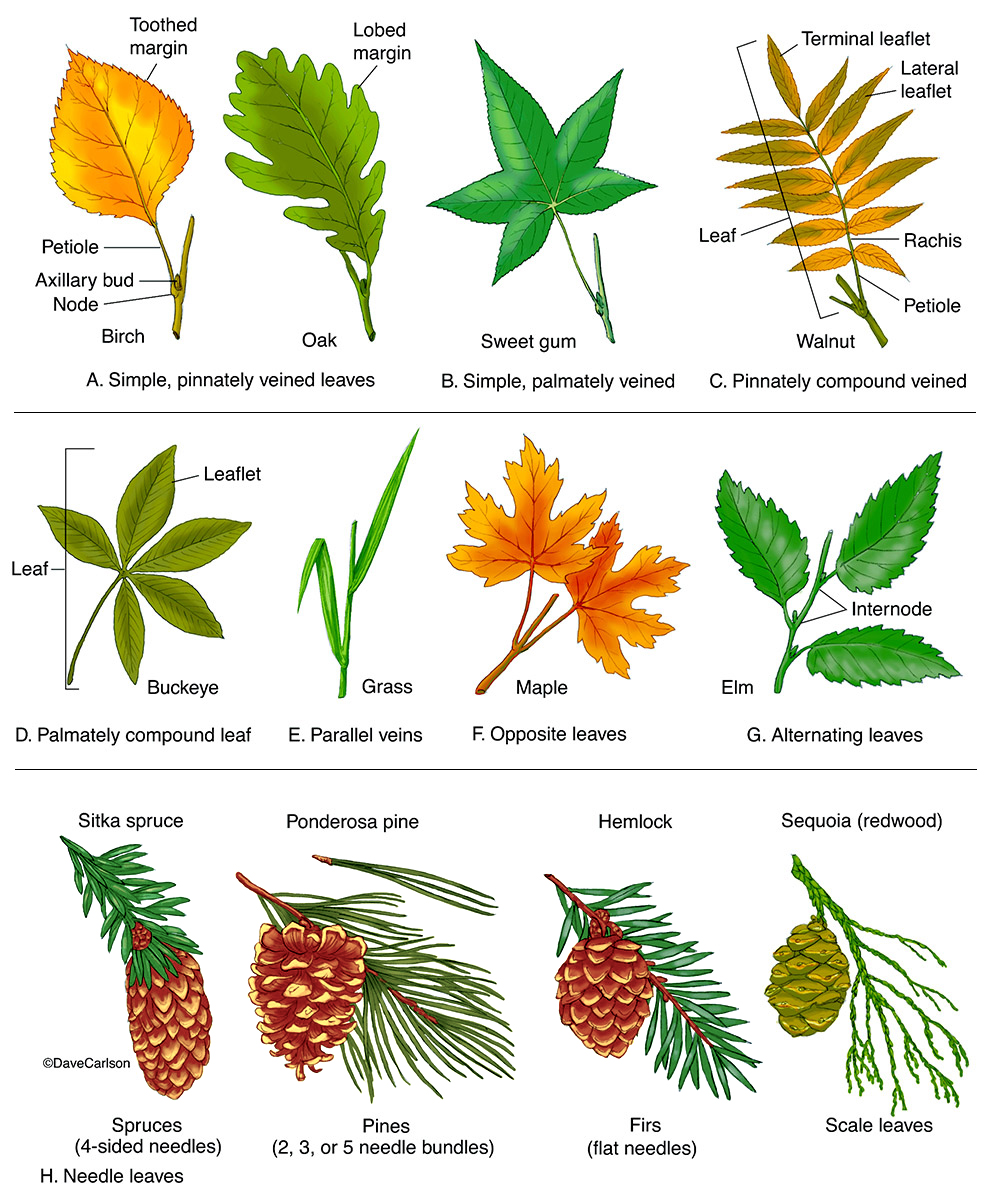
Leaf guide tree identification key copatila

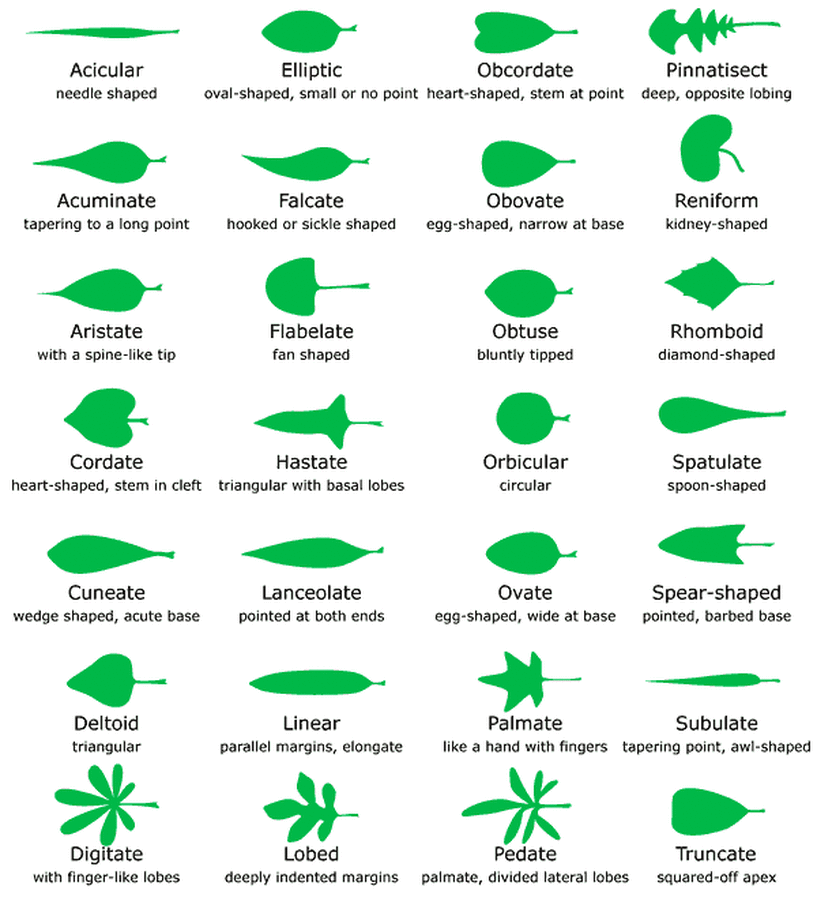
Glossary of leaf morphology Wikipedia

Leaf Shapes Chart Poster Morphology Diagram 5 Sizes Etsy Shape
Leaf Morphology C. Hales Farm
Leaf Types (Morphology) Carlson Stock Art

Leaf Morphology What Is Leaf Morphology is the

Essential Leaf Classification and Morphology Guide Shape, Arrangement

Leaf Shape Study Chart ETC Montessori
Web Understand How A Leaf's Guard Cells, Stomata, Epidermis, And Mesophyll Regulate Transpiration.
Web We Have Looked At Ways Of Identifying Leaves By Looking At The Way They Are Arranged On The Stem And Their Overall Shape.
The Space Between Two Nodes Is An Internode.
Long Lasting Inundations Affect The Physicochemical Conditions In The Soil, With Oxygen Deficiency In The Rhizosphere And Resulting Stresses (Haase And Rätsch 2010) Which Have A Strong Influence On The Whole Metabolism Of The Trees.
Related Post: