Latin Infinitives Chart
Latin Infinitives Chart - Web in latin, infinitives are rarely used to indicate purpose, but rather are most often used to express indirect speech (oratorio obliqua). In english this part of a verb is easily recognised as it is preceded by ‘to’. Next time we’ll look at more infinitives, including those of deponent and irregular verbs. Web conjugation tables of all latin verbs, with passive, participes and translations. A change to the final vowel of the stem, e.g. Web the infinitive is most widely used in latin in indirect speech (oratio obliqua), which combines an accusative subject with an infinitive in subordinate clauses after a verbs of saying, thinking, and perceiving. Web morphological chart of latin infinitives The source is on github. In applying the rule for the sequence of tenses, observe— Laudo instead of laudao, (a): For the verb “to love” ( amo, amare, amavi, amatus) you would look at amare. In accusative + infinitive clauses it is fundamental to take into account the relative time and, of course, practice a lot. The personal ending (see § 163 ). Web participle, infinitive, verb tense summary charts. Web in latin, infinitives are rarely used to indicate purpose,. In complex sentences a primary tense in the main clause is followed by the present or perfect in the dependent clause, and a secondary tense by the imperfect or pluperfect. Laudo instead of laudao, (a): Web in latin, infinitives are rarely used to indicate purpose, but rather are most often used to express indirect speech (oratorio obliqua). The ending, consisting. The personal ending (see § 163 ). Web indirect speech & infinitives the gerund and gerundive the periphrastics the supine ut clauses cum clauses common contractions correlatives numbers full grammar forms bennett's new latin grammar. Web an infinitive is the part of a verb which is unaffected by person or number. But it has in many constructions developed into a. For the verb “to love” ( amo, amare, amavi, amatus) you would look at amare. 2.18) this freedom from pain. This is either the root or a modification or development of it. Web with past tenses of verbs of necessity, propriety, and possibility (as dēbuī, oportuit, potuī), the present infinitive is often used in latin where the english idiom prefers. Every form of the finite verb is made up of two parts: Laudo instead of laudao, (a): Puto eum sapientem esse = i think that he is wise. Web to have been driven. To be about to jump. Perfect participle stem + us/a/um (sg.) In accusative + infinitive clauses it is fundamental to take into account the relative time and, of course, practice a lot. Web with past tenses of verbs of necessity, propriety, and possibility (as dēbuī, oportuit, potuī), the present infinitive is often used in latin where the english idiom prefers the perfect infinitive. 5.33) this. Hence the variety of its use. Next time we’ll look at more infinitives, including those of deponent and irregular verbs. Often, the infinitive can be translated using the preposition “to”, as in “to love” or “to hear”. Web the latin infinitive is the dative or locative case of such a noun 1 and was originally used to denote purpose; Web. In accusative + infinitive clauses it is fundamental to take into account the relative time and, of course, practice a lot. Web there are four forms of the infinitive: Perfect participle stem + us/a/um (sg.) Often, the infinitive can be translated using the preposition “to”, as in “to love” or “to hear”. Web an infinitive is the part of a. The source is on github. Often, the infinitive can be translated using the preposition “to”, as in “to love” or “to hear”. 1.9) our life (to live) scire tuum (id. 5.33) this whole matter of the happy life. Puto eum sapientem esse = i think that he is wise. Web an infinitive is the part of a verb which is unaffected by person or number. Next time we’ll look at more infinitives, including those of deponent and irregular verbs. This video covers not just how latin utilizes the infinitive, the unconjugated form of the verb, but also how the infinitive changes in different tenses and voices. In english this. This is either the root or a modification or development of it. In complex sentences a primary tense in the main clause is followed by the present or perfect in the dependent clause, and a secondary tense by the imperfect or pluperfect. Often, the infinitive can be translated using the preposition “to”, as in “to love” or “to hear”. Hence the variety of its use. Web with past tenses of verbs of necessity, propriety, and possibility (as dēbuī, oportuit, potuī), the present infinitive is often used in latin where the english idiom prefers the perfect infinitive. 1.27) your knowledge (to know) Web there are four forms of the infinitive: In accusative + infinitive clauses it is fundamental to take into account the relative time and, of course, practice a lot. Web the infinitive is most widely used in latin in indirect speech (oratio obliqua), which combines an accusative subject with an infinitive in subordinate clauses after a verbs of saying, thinking, and perceiving. To be about to jump. The personal ending (see § 163 ). Web in latin, infinitives are rarely used to indicate purpose, but rather are most often used to express indirect speech (oratorio obliqua). In english this part of a verb is easily recognised as it is preceded by ‘to’. 5.33) this whole matter of the happy life. Perfect participle stem + us/a/um (sg.) The ending, consisting of— the signs of mood and tense (see § 168 and § 169 ).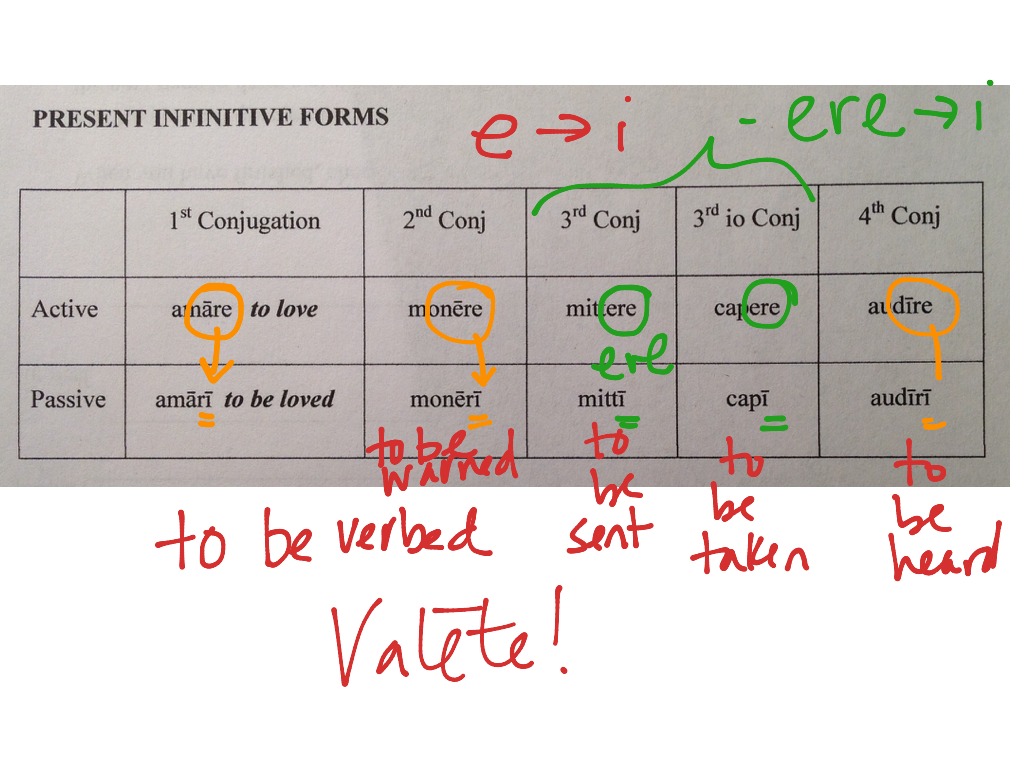
Infinitives Present Tense Language, latin, Latin Grammar ShowMe

latin infinitif présent passif infinitif parfait passif latin 023NLN

Latin Verb Conjugations Chart In 2020 Conjugation Cha vrogue.co

Perfect Active Infinitive Language, latin ShowMe

Oxford Latin Course, Ch. 4 Infinitive YouTube

PPT Latin Infinitives PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4265923
Colorcoded chart 4 Infinitives/Participles/Gerund etc. Latin D

New Latin Grammar

The Latin Infinitive YouTube
Infinitives In Latin Transexual Free Pictures
Web Morphological Chart Of Latin Infinitives
The Stem (See § 24 ).
Web The Infinitive Occasionally Occurs As A Pure Noun Limited By A Demonstrative, A Possessive, Or Some Other Adjective.
See The Chart Below To See All Conjugations.
Related Post: