Laser Wavelengths Chart
Laser Wavelengths Chart - A special section on commercial lasers is an added featured. Brief descriptions of each type of laser are presented, followed by tables listing the laser wavelength, lasing element or medium, host, transition, and primary literature citations. Web the co2 laser produces a beam of infrared light with the principal wavelength bands centering around 9.4 and 10.6 micrometers (as in figure3). In addition, text below the chart describes how divergence (beam spread), power and wavelength (color) affects these hazard distances. The visible colors from shortest to longest wavelength are: Web the laser wavelength is represented by the symbol λ, with units of nm. Raman laser wavelength selection chart. Some lasers emit light in a very narrow spectrum of wavelengths. Figure 3 shows the relative. Also, some frequently used wavelengths from sources with frequency doubling, frequency tripling or frequency quadrupling are listed. Web the laser wavelength is represented by the symbol λ, with units of nm. Web the wavelength of a laser is its most fundamental characteristic, determining its properties, material interactions, and applications. Although there are many candidates for the oscillation wavelength within the resonator length, the laser wavelength at which the most gain is obtained. Brief descriptions of each type. One laser is often not enough. Raman laser wavelength selection chart. Web the laser wavelength is represented by the symbol λ, with units of nm. 2.3 solid state dye lasers. Web the most common are gas lasers, solid state lasers, and fiber lasers. Web in the laser glossary: In detector applications, it is beneficial to use filtering to increase your snr and perhaps utilize a lens to limit field of view. All the lasers with thin lines (i.e. A special section on commercial lasers is an added featured. Thin and thick lines, what do they mean? Blue violet (405nm), blue (445nm, 460nm), pure blue (473nm), green (532nm), yellow (589nm) and red. 2.3 solid state dye lasers. Web the most common are gas lasers, solid state lasers, and fiber lasers. It is determined by the bandgap of the crystal material of the active layer and the resonator length of the chip structure. Consult other sources for classifications. The visible colors from shortest to longest wavelength are: Two, three, four, or even more lasers? Laser types with distinct laser lines are shown above the wavelength bar, while below are shown lasers that can emit in a wavelength range. To order a copy of the latest printed version of the photonics spectrum reference chart, visit our bookstore at www.photonics.com/wallchart.. Web wavelengths of commercially available lasers. Web for visual applications, the closer to 550nm (green) the laser wavelength is, the brighter it will appear. Blue violet (405nm), blue (445nm, 460nm), pure blue (473nm), green (532nm), yellow (589nm) and red. Figure 3 shows the relative. Laser types with distinct laser lines are shown above the wavelength bar, while below are shown. Although there are many candidates for the oscillation wavelength within the resonator length, the laser wavelength at which the most gain is obtained. The visible colors from shortest to longest wavelength are: Laser types with distinct laser lines are shown above the wavelength bar, while below are shown lasers that can emit in a wavelength range. Web the wavelength of. One laser is often not enough. Because of the extremely small beam, small processing and minimal damage are two key components of a uv laser. Two, three, four, or even more lasers? Each wavelength is suitable for marking in specific ways on specific materials. To order a copy of the latest printed version of the photonics spectrum reference chart, visit. Web laser wavelength chart. All the lasers with thin lines (i.e. Some lasers emit light in a very narrow spectrum of wavelengths. Consult other sources for classifications of infrared and ultraviolet lasers,. Web laser wavelength chart shows the colors of visible light spectrum and associated wavelength in nanometers: Each type works in a unique way to create a laser beam at a particular wavelength. Thin and thick lines, what do they mean? There are 426 suppliers of lasers in the photonics marketplace. Web the most common are gas lasers, solid state lasers, and fiber lasers. One laser is often not enough. Each wavelength is suitable for marking in specific ways on specific materials. Web to answer this, we have created a straightforward overview chart for raman laser wavelength selection. Some lasers emit light in a very narrow spectrum of wavelengths. Feel free to save it to your computer! Raman laser wavelength selection chart. It is determined by the bandgap of the crystal material of the active layer and the resonator length of the chip structure. To order a copy of the latest printed version of the photonics spectrum reference chart, visit our bookstore at www.photonics.com/wallchart. Web the wavelength of a laser is its most fundamental characteristic, determining its properties, material interactions, and applications. Also, some frequently used wavelengths from sources with frequency doubling, frequency tripling or frequency quadrupling are listed. Thin and thick lines, what do they mean? All the lasers with thin lines (i.e. There are 426 suppliers of lasers in the photonics marketplace. Brief descriptions of each type of laser are presented, followed by tables listing the laser wavelength, lasing element or medium, host, transition, and primary literature citations. Web the chart below gives hazard distances for selected consumer laser types, and for various parameters such as the beam color, beam spread and power. Web the laser wavelength is represented by the symbol λ, with units of nm. The photonics spectrum reference chart.
laser technician «

Laser Beam Wavelength The Best Picture Of Beam
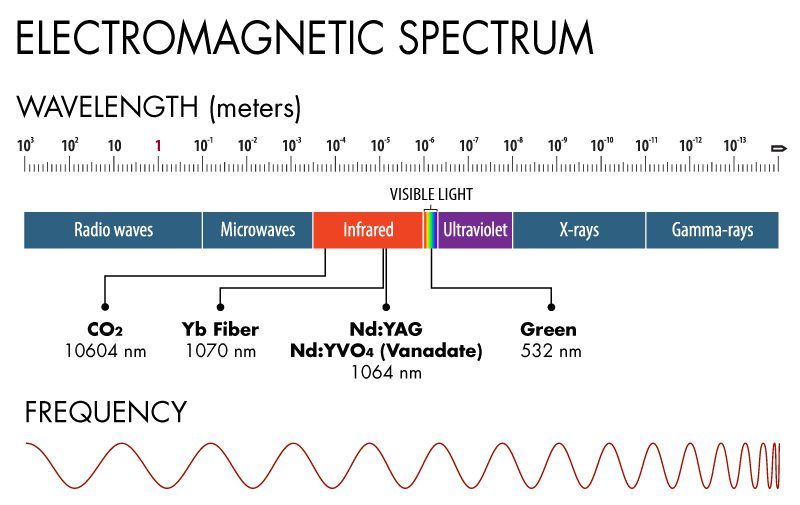
Laser Wavelengths for Specific Materials Pannier Marking Systems
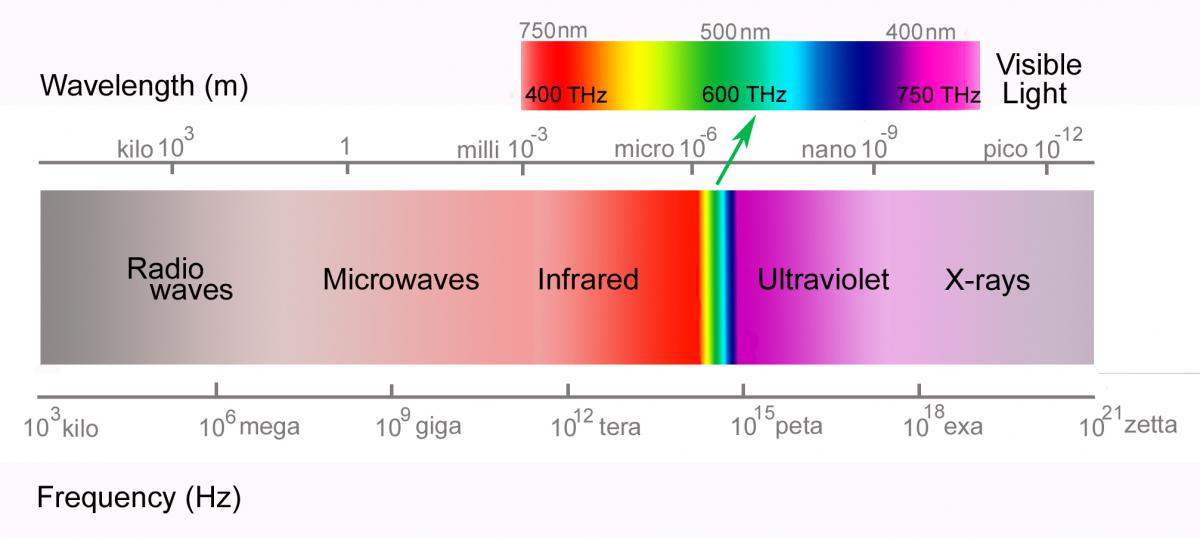
Fiber Lasers Everything You Need to Know Laserax
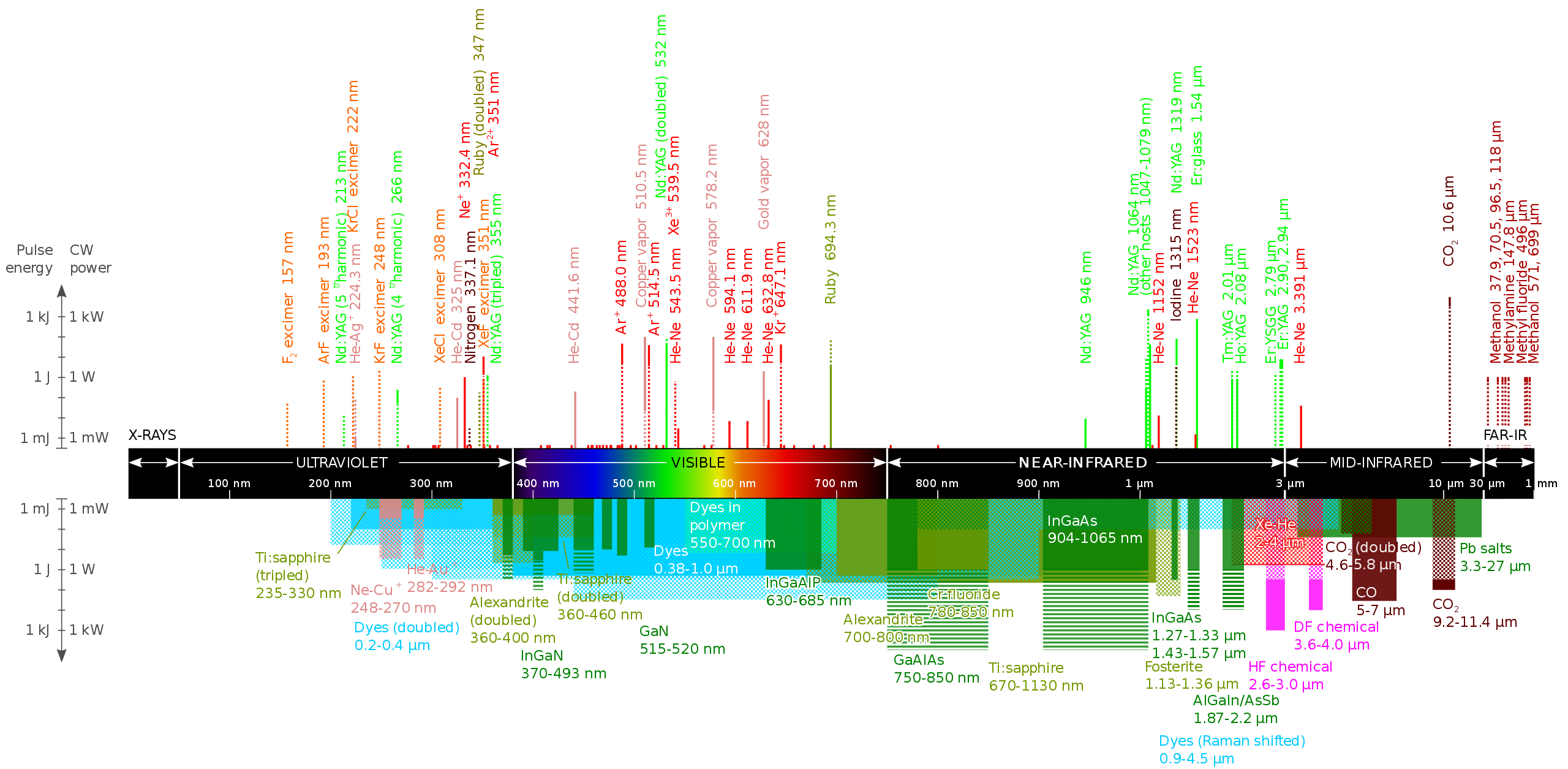
The laser wavelength chart explained
![Typical types of lasers and corresponding wavelengths [69]. Download](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Carl_Magnus/publication/328190911/figure/fig25/AS:680108046163971@1539161802872/Typical-types-of-lasers-and-corresponding-wavelengths-69.png)
Typical types of lasers and corresponding wavelengths [69]. Download

Pin on Astronomy Lasers

Visible Laser Beam Wavelength The Best Picture Of Beam

Chart of the laser wavelengths and pulse durations applied for
Skywise's Lasers & Optics Reference Area
Blue Violet (405Nm), Blue (445Nm, 460Nm), Pure Blue (473Nm), Green (532Nm), Yellow (589Nm) And Red.
In Detector Applications, It Is Beneficial To Use Filtering To Increase Your Snr And Perhaps Utilize A Lens To Limit Field Of View.
Laser Wavelengths Should Be Selected To Best Match A Detector's Responsivity.
Web Figure 1 Shows 23 Of The Most Common Lasers And Their Wavelengths, Modes Of Operation, And Typical Gain Media.
Related Post: