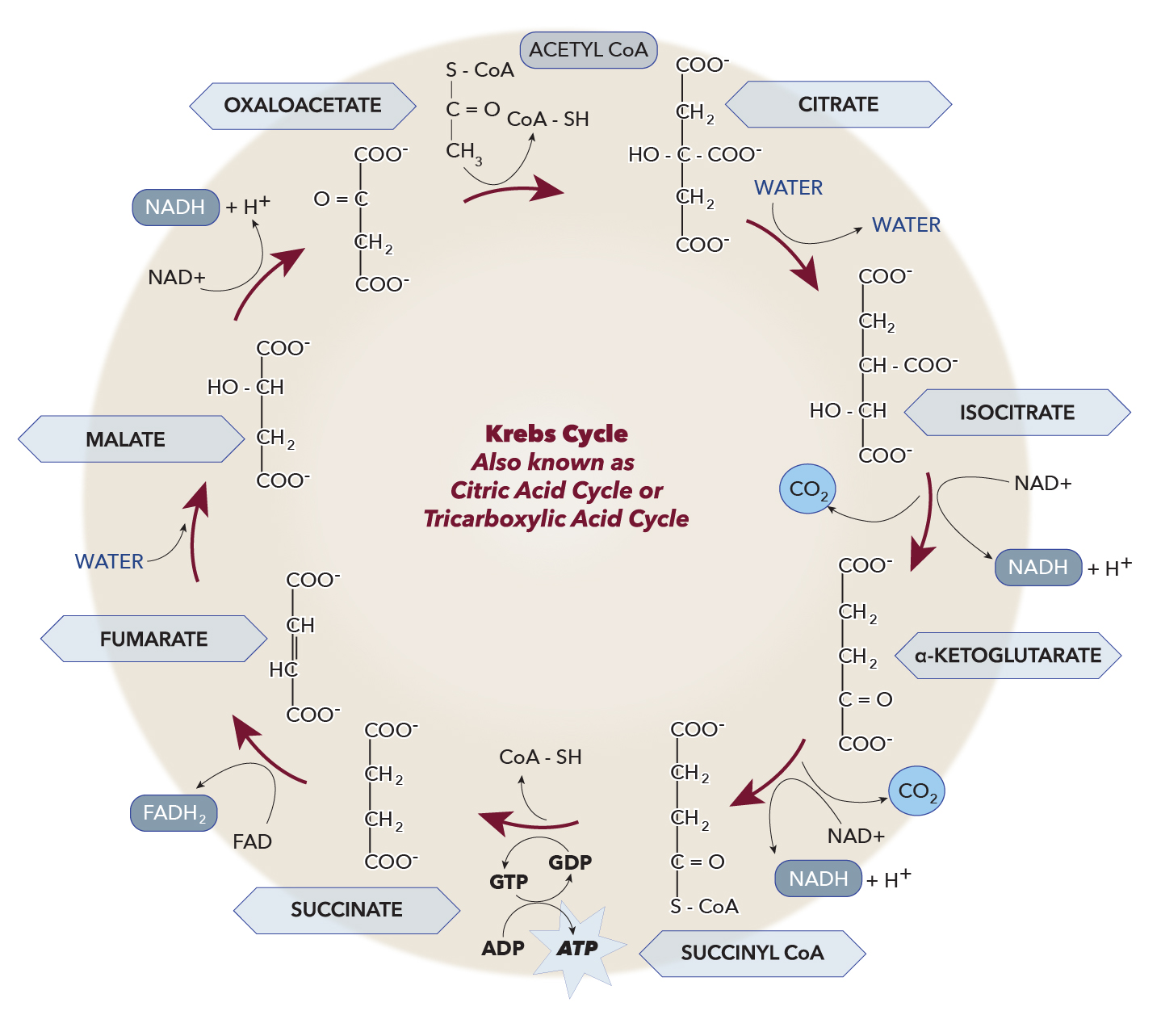
Krebs Cycle Flow Chart
Krebs Cycle Flow Chart - Krebs cycle explains the aerobic phase of respiration. It is also known as citric acid or tricarboxylic acid cycle (tca cycle). How important is the citric acid cycle? Web the four main steps of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, pyruvate decarboxylation (link reaction), the krebs cycle (citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle), and the electron transport chain with oxidative phosphorylation. Overview and steps of the citric acid cycle, also known as the krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid (tca) cycle. This aerobic process takes place in mitochondria where necessary enzymes are present in matrix. In this article, we will outline the steps and regulation of this essential part of cellular physiology. Web the reactions of cellular respiration can be grouped into three main stages and an intermediate stage: The krebs cycle is also commonly called the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid (tca) cycle. Web also known as the citric acid cycle, the krebs cycle or tca cycle is a chain of reactions occurring in the mitochondria, through which almost all living cells produce energy in aerobic respiration. Kreb’s cycle is also called the citric acid cycle or tca (tricarboxylic acid) cycle. Figure \(\pageindex{3}\) gives an overview of these three stages, which are also described in detail below. Web the krebs cycle is the second stage of cellular respiration and it takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. How important is the citric acid cycle? There are. Krebs’ cycle / citric acid cycle /tca cycle. By this cycle, carbon skeleton are got, which are used in process of growth and for maintaining the cells. The link reaction occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. This aerobic process takes place in mitochondria where necessary enzymes are present in matrix. Web the krebs cycle is the second stage of cellular respiration. Electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation. Krebs cycle is a part of aerobic respiration. In this article, we will outline the steps and regulation of this essential part of cellular physiology. The link reaction occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. Fill in the blanks of the summaries. It uses oxygen and gives out water and carbon dioxide as products. The pyruvic acid produced in glycolysis enters into krebs’ cycle for further oxidation. Kreb’s cycle is also called the citric acid cycle or tca (tricarboxylic acid) cycle. By this cycle, carbon skeleton are got, which are used in process of growth and for maintaining the cells. Pyruvate is. The pyruvic acid produced in glycolysis enters into krebs’ cycle for further oxidation. Figure \(\pageindex{3}\) gives an overview of these three stages, which are also described in detail below. Web the pyruvate molecules generated during glycolysis are transported across the mitochondrial membrane into the inner mitochondrial matrix, where they are metabolized by enzymes in a pathway called the krebs cycle. By this cycle, carbon skeleton are got, which are used in process of growth and for maintaining the cells. In this article, we will outline the steps and regulation of this essential part of cellular physiology. Electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation. This aerobic process takes place in mitochondria where necessary enzymes are present in matrix. Krebs cycle is a. If oxygen is present in a cell where respiration is occurring, then glycolysis is followed by a series of reactions that completely oxidize pyruvate (pyruvic acid) and the molecules it gets broken down into. During the krebs cycle, energy stored in pyruvate is transferred to nadh and fadh 2, and some atp is produced. Web the krebs cycle is the. You can see this in. This aerobic process takes place in mitochondria where necessary enzymes are present in matrix. Web cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp. Overview and steps of the citric acid cycle, also known as the krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid (tca) cycle. Fill in the blanks of the summaries. The role of these hydrogen atoms is shown in the electron carrier system. Web the four main steps of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, pyruvate decarboxylation (link reaction), the krebs cycle (citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle), and the electron transport chain with oxidative phosphorylation. Web also known as the citric acid cycle, the krebs cycle or tca cycle is. Web the four main steps of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, pyruvate decarboxylation (link reaction), the krebs cycle (citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle), and the electron transport chain with oxidative phosphorylation. There are a series of cyclic reactions involved in converting pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and water in mitochondria. The pyruvic acid produced in glycolysis enters into krebs’. The energy is used to create atp. The link reaction occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. Pyruvate is broken down into carbon dioxide and energy is released. So important that it has not one, not two, but three different names in common usage today! Fill in the molecules created or released during the krebs cycle. Web the krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tca cycle is a series of reactions that take place in the mitochondria resulting in oxidation of acetyl coa to release carbon dioxide and hydrogen atoms that later lead to the formation of water. Web these electrons come from electron carriers such as nadh and fadh₂, which are produced by the tricarboxylic acid cycle (tca cycle, also known as the kreb’s/citric acid cycle). Krebs’ cycle / citric acid cycle /tca cycle. The krebs cycle is also commonly called the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid (tca) cycle. You can see this in. By this cycle, carbon skeleton are got, which are used in process of growth and for maintaining the cells. Web the flow diagram shows that every time a stage produces two hydrogen atoms, in the presence of oxygen, three atp molecules are produced. Krebs’ cycle is also known as citric acid cycle or tri carboxylic acid (tca) cycle. Web the four main steps of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, pyruvate decarboxylation (link reaction), the krebs cycle (citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle), and the electron transport chain with oxidative phosphorylation. There are a series of cyclic reactions involved in converting pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and water in mitochondria. How important is the citric acid cycle?
Krebs Cycle Definition, Products and Location Biology Dictionary
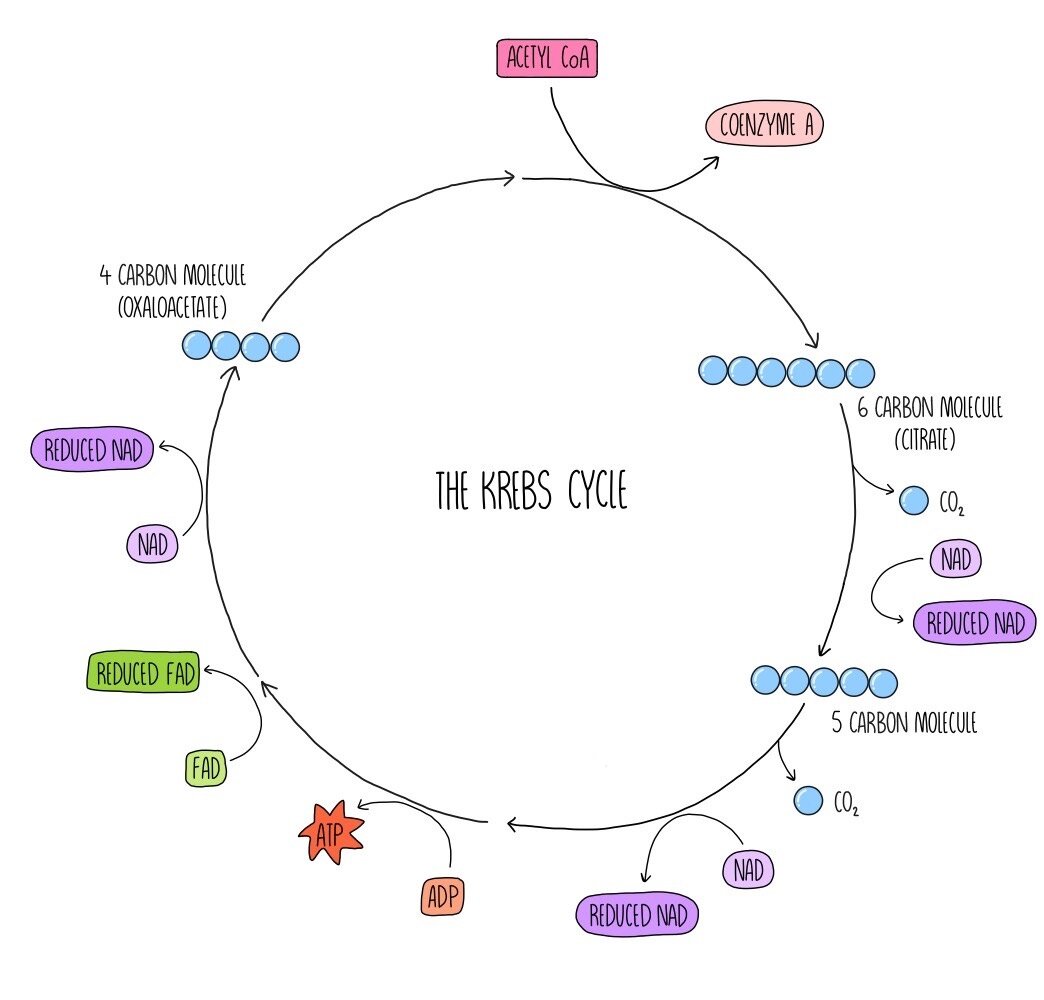
Respiration (A Level) — the science sauce
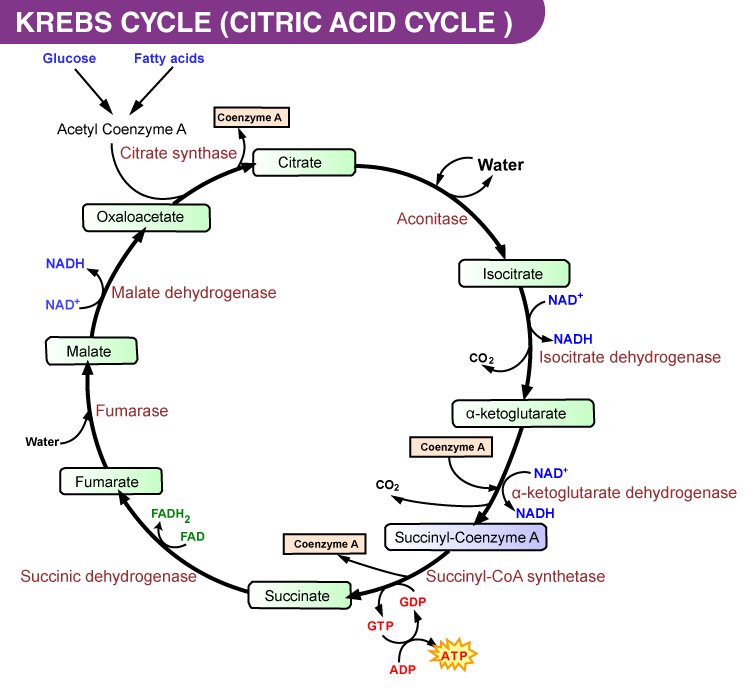
Krebs Cycle or Citric Acid Cycle Steps, Products, Significance

Krebs Cycle Con Academy
Physiology, Krebs Cycle Article

Krebs Cycle/ TCA Cycle Mnemonic Simplified Biology

Pin on Biochemistry
Krebs Cycle ( Read ) Biology CK12 Foundation

8 Steps of Citric acid Cycle (Krebs cycle) and Enzymes involved in each

Krebs Cycle Location, Enzymes, Steps, Products, Diagram
Aerobic Respiration Is The Process Which Occurs In The Presence Of Oxygen To Convert Food Into Carbon Dioxide, Water And Energy.
In This Article, We Will Outline The Steps And Regulation Of This Essential Part Of Cellular Physiology.
Web The Krebs Cycle Is The Second Stage Of Cellular Respiration.
This Aerobic Process Takes Place In Mitochondria Where Necessary Enzymes Are Present In Matrix.
Related Post: