Kingdoms Biology Chart
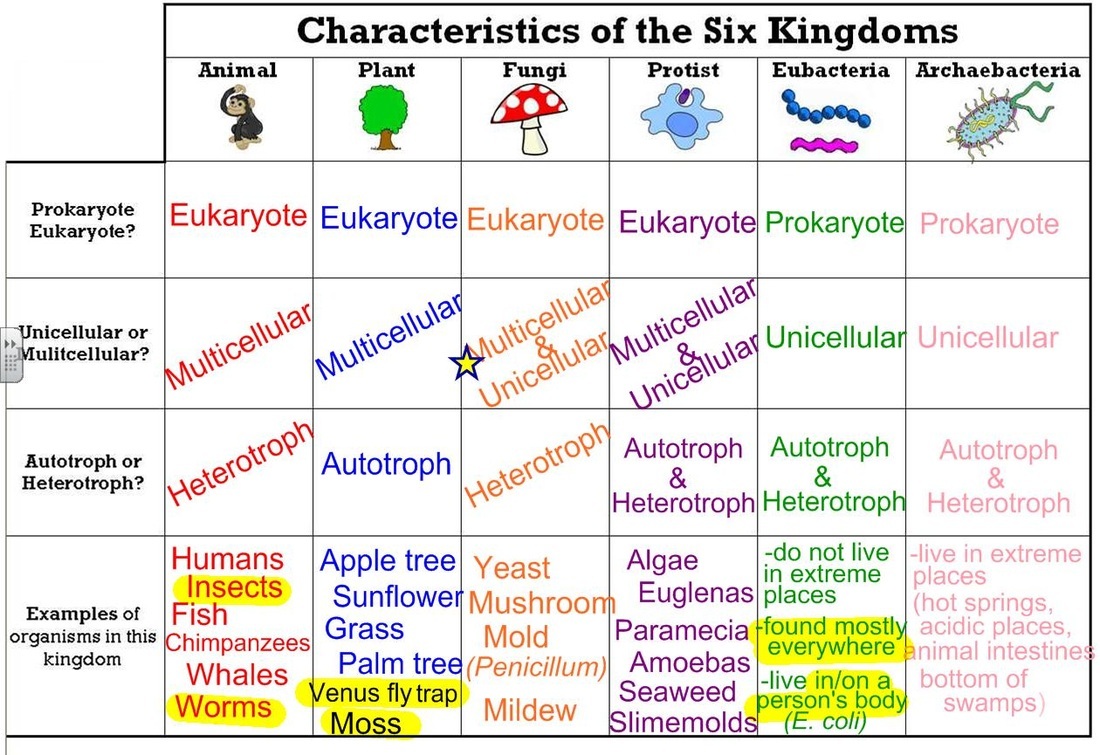
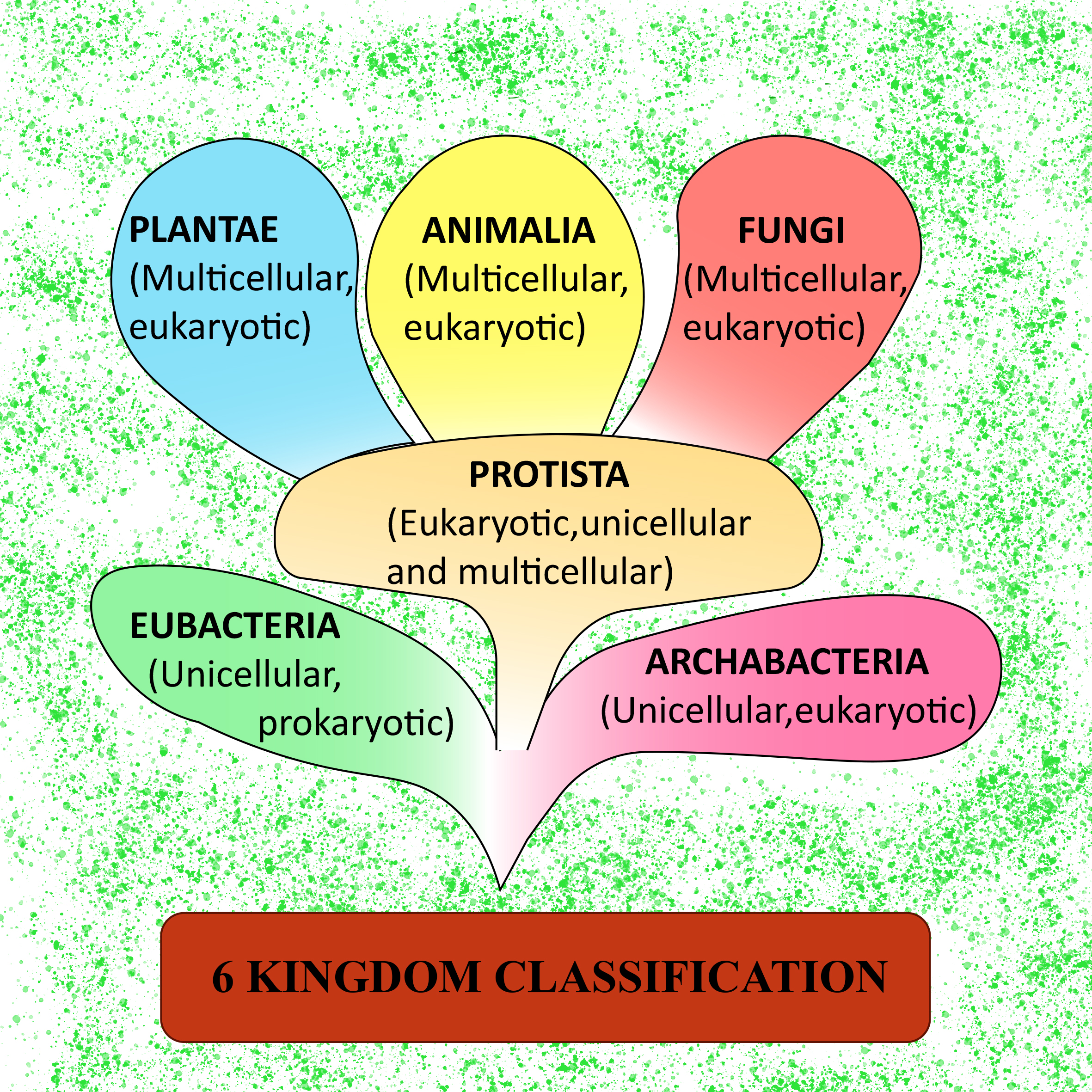
Kingdoms Biology Chart - Students should include the major properties of that kingdom and a short description of the organism they selected. Web the first division of living things in the classification system is to put them into one of five kingdoms. The diversity of the life of earth is bewildering. (cell wall / no cell wall) mobility. Based on the linnaeus method, species are arranged and grouped based on shared characteristics. Web each kingdom includes a set of organisms that share similar characteristics. Animalia , contains general animals and is the largest kingdom with over 1 000 000 species. The protists are predominantly unicellular, microscopic, nonvascular organisms that do not generally form tissues. (autotrophic / heterotrophic) body type. It provides an easy way to investigate many types of organisms or their life forms in an extremely simple way. Taxonomy and the tree of life. Exhibiting all modes of nutrition, protists are frequently motile organisms, primarily using flagella, cilia, or pseudopodia. Web this form of kingdom classification includes five kingdoms monera, protista, fungi, plantae and animalia. Web each kingdom includes a set of organisms that share similar characteristics. Animal kingdom classification is an important system for understanding how all. Web organisms are traditionally classified into six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia) based on characteristics like cell type, nutrient acquisition, and reproduction. This hierarchical approach helps biologists study the relationships and diversity among all living things on earth. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phylum. Web this form of kingdom classification includes five kingdoms monera, protista,. The protists are predominantly unicellular, microscopic, nonvascular organisms that do not generally form tissues. Based on the linnaeus method, species are arranged and grouped based on shared characteristics. Web the currently recognized kingdoms include animalia ( animals ), plantae ( plants ), fungi ( fungi ), protista ( protists ), and monera ( bacteria ). From microorganisms to trees to. Web many biologists now recognize six distinct kingdoms, dividing monera into the eubacteria and archeobacteria. Web this form of kingdom classification includes five kingdoms monera, protista, fungi, plantae and animalia. Web the four commonly recognized kingdoms are protista, animalia, plantae, and fungi. All i can say is that the sytem holds true for this week, at least. Web each kingdom. (cell wall / no cell wall) mobility. Web in biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. It might even hold up for a century or two. Web many biologists now recognize six distinct kingdoms, dividing monera into the eubacteria and archeobacteria. It provides an easy way to investigate many types of organisms or their life. The diversity of the life of earth is bewildering. Based on the linnaeus method, species are arranged and grouped based on shared characteristics. (unicellular / multicellular) cell structure. Web find out what a kingdom is in biology and how living things are classified into 5 kingdoms, as well as their characteristics and different examples of each one. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi,. When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. The organisms in each kingdom are considered biologically distinct from the others. Web kingdoms of life. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi, protista, plants and animals. Animalia , contains general animals and is the largest kingdom with over 1 000 000 species. Web under the three domains are six kingdoms in taxonomy: Web the first division of living things in the classification system is to put them into one of five kingdoms. It provides an easy way to investigate many types of organisms or their life forms in an extremely simple way. (autotrophic / heterotrophic) body type. Web the currently recognized kingdoms. Web find out what a kingdom is in biology and how living things are classified into 5 kingdoms, as well as their characteristics and different examples of each one. Learn the six groups that all organisms are divided into based on similarities. When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. Web fill in the chart below, listing. Web fill in the chart below, listing the distinctive characteristics of each kingdom. Web in this biology boost deep dive, we take a look at the five kingdoms of classification; The bacteria and archaea are sometimes grouped into one kingdom, the monera, and sometimes given their own separate kingdom. Web the four commonly recognized kingdoms are protista, animalia, plantae, and. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phylum. Web each kingdom includes a set of organisms that share similar characteristics. Animal kingdom classification is an important system for understanding how all living organisms are related. Web the four commonly recognized kingdoms are protista, animalia, plantae, and fungi. Web in biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. Web find out what a kingdom is in biology and how living things are classified into 5 kingdoms, as well as their characteristics and different examples of each one. Plantae , contains all plants on earth. (unicellular / multicellular) cell structure. Web evolution & classification link. Organisms can be in the kingdoms of animal, plant, bacteria, fungi, protist or archaea. It provides an easy way to investigate many types of organisms or their life forms in an extremely simple way. Web fill in the chart below, listing the distinctive characteristics of each kingdom. (autotrophic / heterotrophic) body type. Web the currently recognized kingdoms include animalia ( animals ), plantae ( plants ), fungi ( fungi ), protista ( protists ), and monera ( bacteria ). Animalia , contains general animals and is the largest kingdom with over 1 000 000 species.
biological classification Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
biologyKINGDOMS OF LIFE PROJECT Home

Biology Kingdoms Comprehensive Chart Activity
Science poster of six kingdoms of life 2906732 Vector Art at Vecteezy

Characteristics and Classification of Living Organisms HowForKids
Six kingdom classification was suggested by?

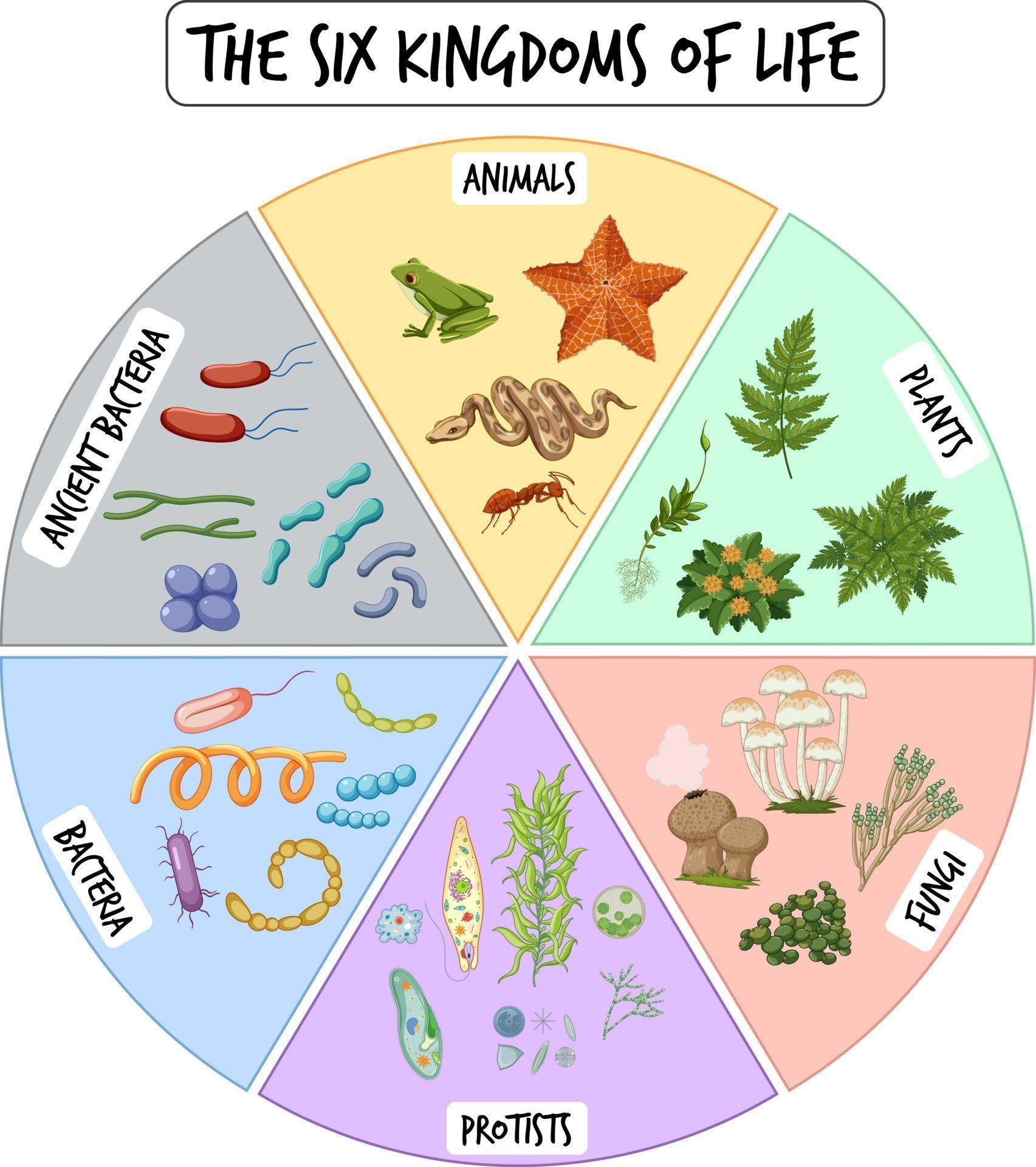
The 6 Kingdoms of Life Simple Explanation for Kids WeHaveKids
Information poster of six kingdoms of life 2906704 Vector Art at Vecteezy
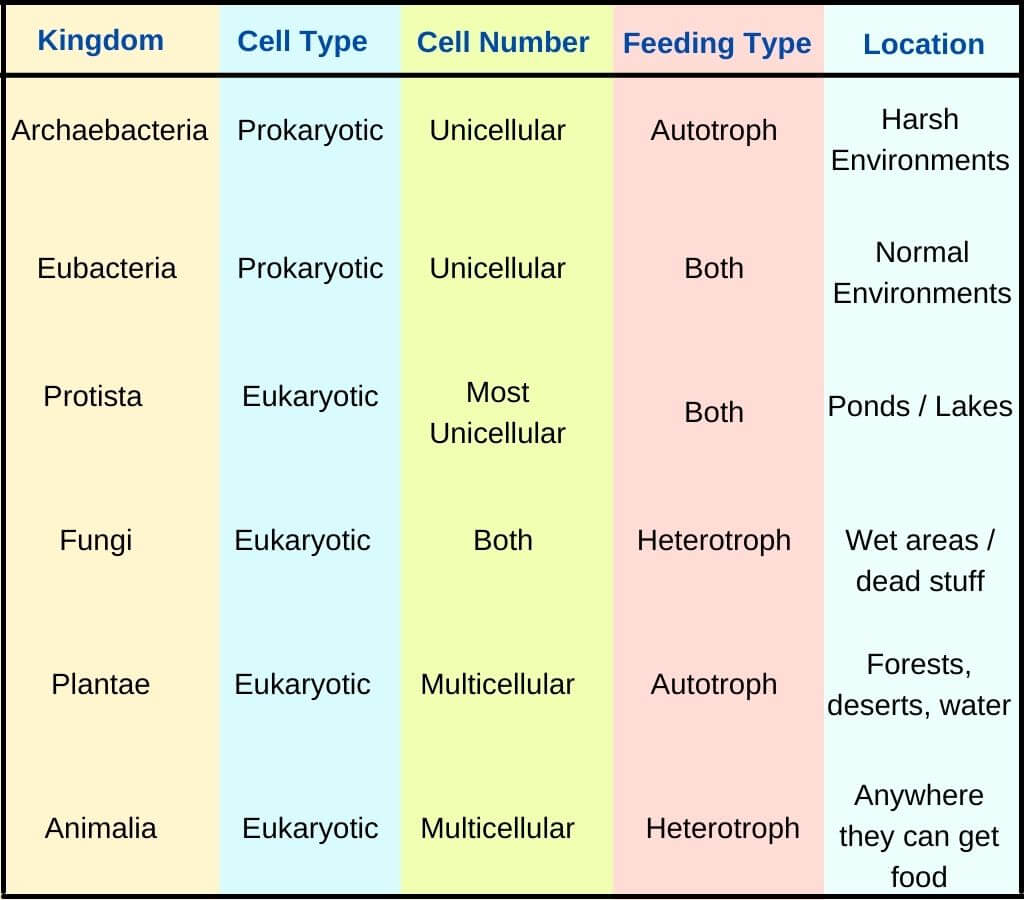
A Simple Explanation of the 6 Kingdoms of Life

biological classification Students Britannica Kids Homework Help
From Microorganisms To Trees To Animals To Fungi, Life Has Evolved Through Time Down Countless Pathways To Provide Us With The Present Day Contingent Of Species.
Exhibiting All Modes Of Nutrition, Protists Are Frequently Motile Organisms, Primarily Using Flagella, Cilia, Or Pseudopodia.
The Following Kingdoms Were Included In The Classification Of Living Things :
Based On The Linnaeus Method, Species Are Arranged And Grouped Based On Shared Characteristics.
Related Post: