In The Chart The Recessive Trait Is
In The Chart The Recessive Trait Is - Exploring their association with 15% of phenotypically detailed genetic disorders But where did our knowledge of dominance and recessivity first. Web if the trait is recessive, neither parent is required to have the trait since they can be heterozygous. Web recessive alleles are only expressed when no dominant allele is present. The allele for albinism, expressed here in humans, is recessive. There is not enough information to determine the genotype of individuals 5, 6, 8, and 9. From this pedigree, we can infer that individuals 1, 2, 3, 4, and 11 are carriers. This pair of alleles is called a genotype and determines the organism's appearance, or phenotype. The right answer is c)small teeth. By scrutinizing genotypes and utilizing a punnett square, the probability of color blindness in offspring can be calculated. Dominant allele + recessive allele = dominant phenotype; The right answer is c)small teeth. There is not enough information to determine the genotype of individuals 5, 6, 8, and 9. Laws of segregation and independent assortment. Dominant traits are always expressed when the connected allele is dominant, even if only one copy of the dominant trait exists. Web mendel postulated that genes (characteristics) are inherited as pairs of alleles (traits) that behave in a dominant and recessive pattern. Web the information from a pedigree makes it possible to determine how certain alleles are inherited: An example of a simple phenotype is the flower colour in mendel’s peas. Benefits of using a pedigree chart. They will be either. Recessive allele + recessive allele = recessive phenotype If the trait is dominant, the trait must be one of the parents'. Dominant allele + recessive allele = dominant phenotype; Web mendel postulated that genes (characteristics) are inherited as pairs of alleles (traits) that behave in a dominant and recessive pattern. Web what is the difference between dominant and recessive traits? If the trait is dominant, the trait must be one of the parents'. An example of a simple phenotype is the flower colour in mendel’s peas. Dominant allele + recessive allele = dominant phenotype; They will be either homozygous dominant or heterozygous. Web recessive alleles are only expressed when no dominant allele is present. Web if the trait is recessive, neither parent is required to have the trait since they can be heterozygous. Benefits of using a pedigree chart. Dominant allele + dominant allele = dominant phenotype; But where did our knowledge of dominance and recessivity first. Web however, sometimes the heterozygote displays a phenotype that is an intermediate between the phenotypes of both. Alleles segregate into gametes such that each gamete is equally likely to receive either one of the two alleles present in a diploid individual. If the phenotype is recessive, because they may be heterozygous, no parent is expected to have the phenotype. Web if the trait is recessive, neither parent is required to have the trait since they can be. Web mendel postulated that genes (characteristics) are inherited as pairs of alleles (traits) that behave in a dominant and recessive pattern. The answer can not be d because it already correspond to the t. In most sexually reproducing organisms, each individual has two alleles for each gene (one from each parent). Dominant allele + recessive allele = dominant phenotype; Intersex/differences. So, no they are not just used for autosomal dominant traits. Many human diseases are genetically inherited. The allele for albinism, expressed here in humans, is recessive. A pedigree shows how a trait is passed from generation to generation within a family. Dominant allele + recessive allele = dominant phenotype; By scrutinizing genotypes and utilizing a punnett square, the probability of color blindness in offspring can be calculated. Benefits of using a pedigree chart. Web the dominant/recessive character is a relationship between two alleles and must be determined by observation of the heterozygous phenotype. The answer can not be b because, according to the table, the transmission is autosomal (the. Web mendel postulated that genes (characteristics) are inherited as pairs of alleles (traits) that behave in a dominant and recessive pattern. In most sexually reproducing organisms, each individual has two alleles for each gene (one from each parent). Pedigrees show relationships and identify individuals with a given trait. An example of a simple phenotype is the flower colour in mendel’s. A pedigree shows how a trait is passed from generation to generation within a family. Web with dominant inheritance, all affected individuals will have at least one dominant allele. Dominant allele + recessive allele = dominant phenotype; Benefits of using a pedigree chart. Web mendel postulated that genes (characteristics) are inherited as pairs of alleles (traits) that behave in a dominant and recessive pattern. Many human diseases are genetically inherited. Web the information from a pedigree makes it possible to determine how certain alleles are inherited: Web the dominant/recessive character is a relationship between two alleles and must be determined by observation of the heterozygous phenotype. The right answer is c)small teeth. Web recessive alleles are only expressed when no dominant allele is present. The answer can not be b because, according to the table, the transmission is autosomal (the male and the female have two alleles). Intersex/differences of sex development (i/dsd) traits: But where did our knowledge of dominance and recessivity first. Web dominant phenotypes are not always more common than recessive phenotypes. Dominant allele + dominant allele = dominant phenotype; Web what is the difference between dominant and recessive traits?
Mendel's Law of Dominance Interactive Biology, with Leslie Samuel

What are dominant and recessive alleles? Facts
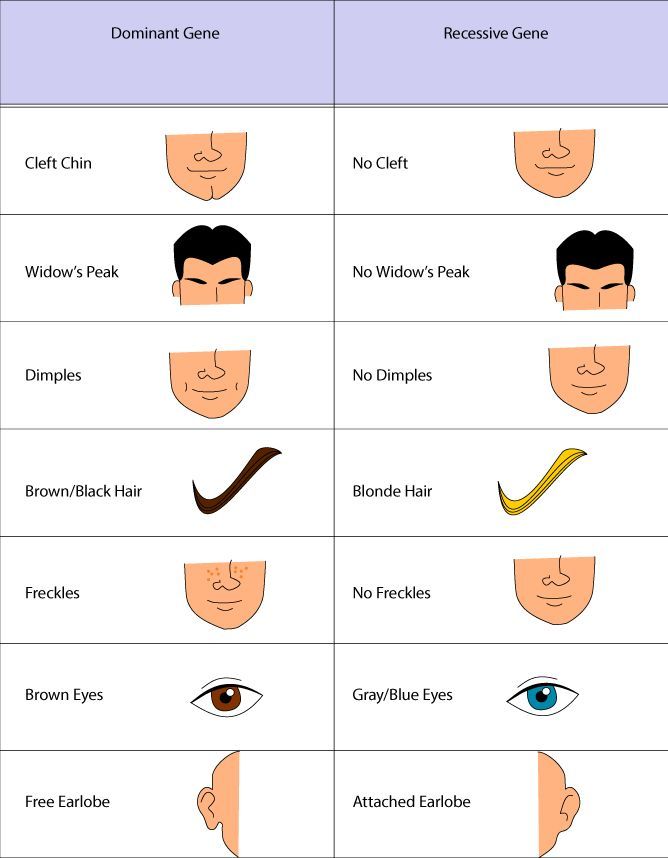
Dominant and Recessive Traits Introduction Examples
Trait Chart

PPT Pedigree Charts PowerPoint Presentation ID340435

XLinked Recessive Traits in a Pedigree YouTube
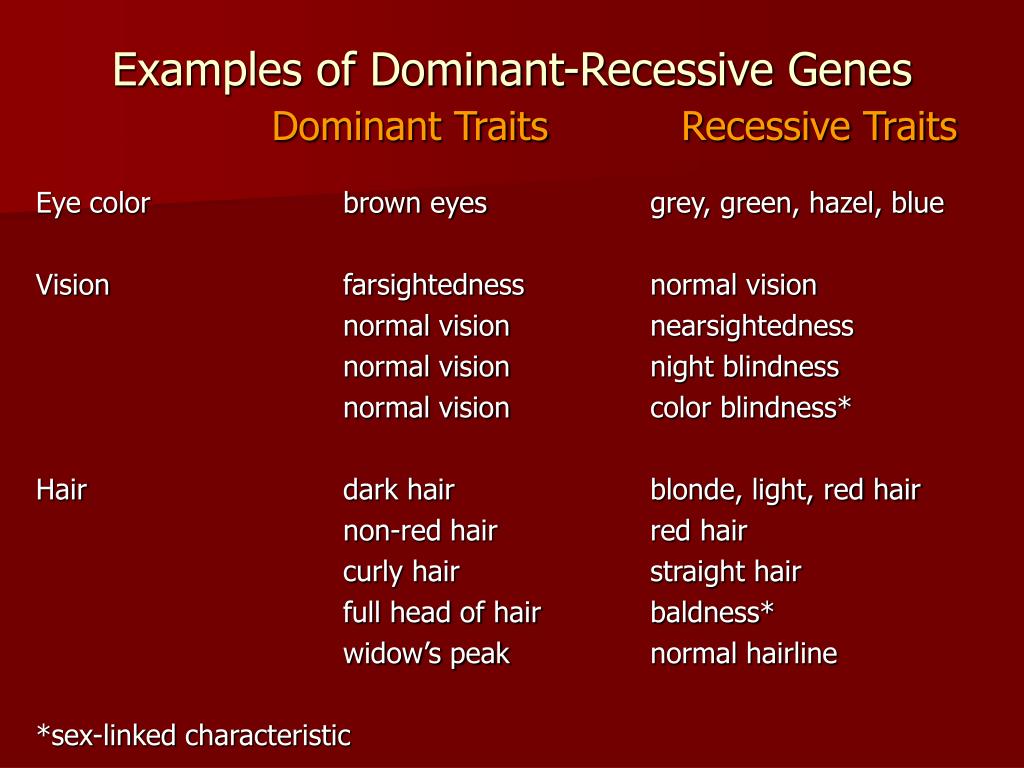
Recessive Trait Definition

Autosomal Recessive Traits and Disorders Tutorial Sophia Learning

Looking At This Pedigree How Can You Tell That Blue Skin Is A Recessive
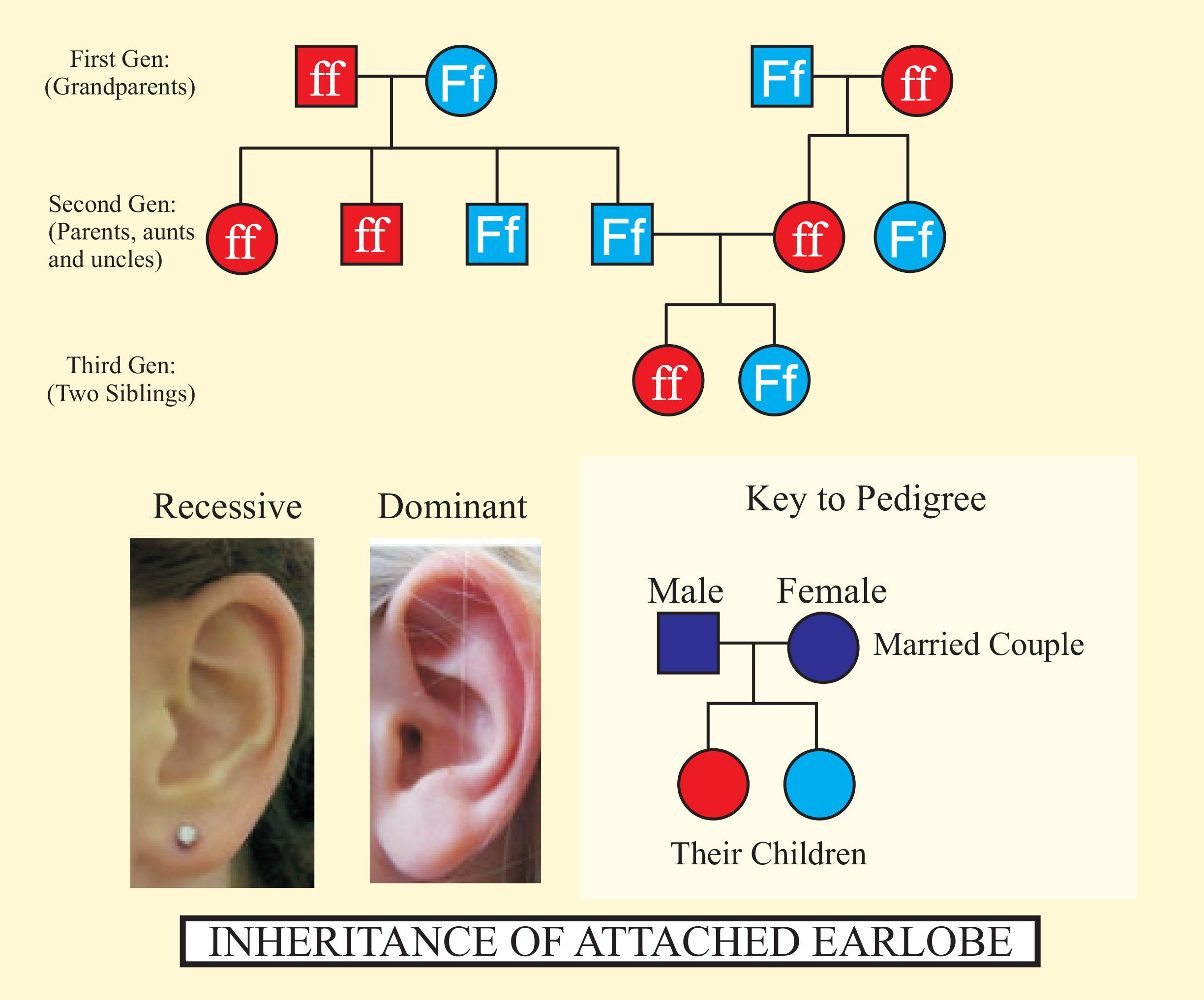
Attached ear lobe in humans is(a)Recessive trait(b)Dominant trait(c
Recessive Allele + Recessive Allele = Recessive Phenotype
Laws Of Segregation And Independent Assortment.
They Will Be Either Homozygous Dominant Or Heterozygous.
Web An Example Of A Pedigree Chart For An Autosomal Recessive Condition.
Related Post: