Hybridization Geometry Chart
Hybridization Geometry Chart - The geometrical arrangements characteristic of the various sets of hybrid orbitals are shown in figure 8.21. Web hybridization is the idea that atomic orbitals fuse to form newly hybridized orbitals, which in turn, influences molecular geometry and bonding properties. Hybrid orbitals have very different shape from original atomic orbitals. Web learn the definition of orbital hybridization and the characteristics and geometries of sp, sp2, sp3, sp3d1, and sp3d2 hybridization. This 109.5 o arrangement gives tetrahedral geometry (figure 4). Web summary vsepr and hybridization table. Predicted bond angle(s) hybridization of central atom. Web molecular geometry van koppen/offen procedure: Valence electrons repel one another because they are negatively charged and like charges repel. Want to join the conversation? Web hybridization increases the overlap of bonding orbitals and explains the molecular geometries of many species whose geometry cannot be explained using a vsepr approach. An atom has a given hybridization depending on the number of bonds extending from it. Web learn the definition of orbital hybridization and the characteristics and geometries of sp, sp2, sp3, sp3d1, and sp3d2 hybridization.. Ways carbon can bond to others. Two electron groups are involved resulting in sp hybridization; If it’s 4, your atom is sp3. Number of hybrid orbitals is equal to number of pure atomic orbitals used in the hybridization process. Web we can find the hybridization of an atom in a molecule by either looking at the types of bonds surrounding. Here is a chart that sums this up: Web hybridization of an s orbital with two p orbitals (p x and p y) results in three sp 2 hybrid orbitals that are oriented at 120 o angle to each other (figure 3). Two electron groups are involved resulting in sp hybridization; An atom has a given hybridization depending on the. Reactions involve making and breaking of bonds! Web hybridization of an s orbital with two p orbitals (p x and p y) results in three sp 2 hybrid orbitals that are oriented at 120 o angle to each other (figure 3). Two electron groups are involved resulting in sp hybridization; Web the hybridization of an atom is determined based on. Web hybridization of an s orbital with all three p orbitals (p x, p y, and p z) results in four sp 3 hybrid orbitals. Hybridisation and geometry of molecules play a vital role in their reactivity. Web we can find the hybridization of an atom in a molecule by either looking at the types of bonds surrounding the atom. The geometrical arrangements characteristic of the various sets of hybrid orbitals are shown in figure 8.21. Predicted bond angle(s) hybridization of central atom. Two electron groups are involved resulting in sp hybridization; The angle between the orbitals is 180°. Furthermore, the bond angles formed are important. Web we can find the hybridization of an atom in a molecule by either looking at the types of bonds surrounding the atom or by calculating its steric number. Web hybridization increases the overlap of bonding orbitals and explains the molecular geometries of many species whose geometry cannot be explained using a vsepr approach. Web the five basic shapes of. There is also an implicit geometric shape associated with the hybridization. This type of hybridization is required whenever an atom is surrounded by two groups of electrons. Reactions involve making and breaking of bonds! Web hybridization increases the overlap of bonding orbitals and explains the molecular geometries of many species whose geometry cannot be explained using a vsepr approach. Want. Web the hybridization of an atom is determined based on the number of regions of electron density that surround it. Valence electrons repel one another because they are negatively charged and like charges repel. The angle between the orbitals is 180°. Lewis structures provide us with the number and types of bonds around a central atom, as well as any. This 109.5 o arrangement gives tetrahedral geometry (figure 4). So, before we start with organic chemistry, let's revise a few things about bonding in organic molecules. Web so how do we explain this? Find out by adding single, double or triple bonds and lone pairs to the central atom. Draw lewis structure, determine steric number (sn), molecular geometry and hybridization. If it’s 4, your atom is sp3. Sp 3 hybrid orbitals are oriented at bond angle of 109.5 o from each other. Web learn the definition of orbital hybridization and the characteristics and geometries of sp, sp2, sp3, sp3d1, and sp3d2 hybridization. Valence electrons repel one another because they are negatively charged and like charges repel. This type of hybridization is required whenever an atom is surrounded by two groups of electrons. Furthermore, the bond angles formed are important. Draw lewis structure, determine steric number (sn), molecular geometry and hybridization sn = # of atoms bonded to the central atom plus # of lone pairs on the central atom (sn = the effective number of electron pairs surrounding a central atom). The geometry of the orbital arrangement is as follows: Want to join the conversation? Send feedback | visit wolfram|alpha. Explore molecule shapes by building molecules in 3d! Hybridisation and geometry of molecules play a vital role in their reactivity. Then, compare the model to real molecules! Mix at least 2 nonequivalent atomic orbitals (e.g.s and p). Web hybridization increases the overlap of bonding orbitals and explains the molecular geometries of many species whose geometry cannot be explained using a vsepr approach. Lewis structures provide us with the number and types of bonds around a central atom, as well as any nb electron pairs.
Hybridization and Hybrid Orbitals ChemTalk

Hybridization Wize University Chemistry Textbook Wizeprep
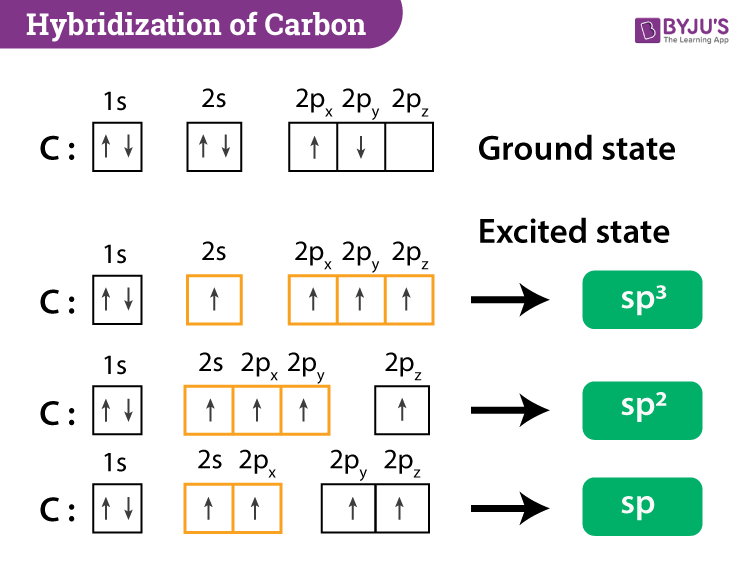
MariePreAPChem Hybridization

XeCl4 Lewis Structure, Geometry, Hybridization, and Polarity

Molecular Geometry Chart With Hybridization carthopde
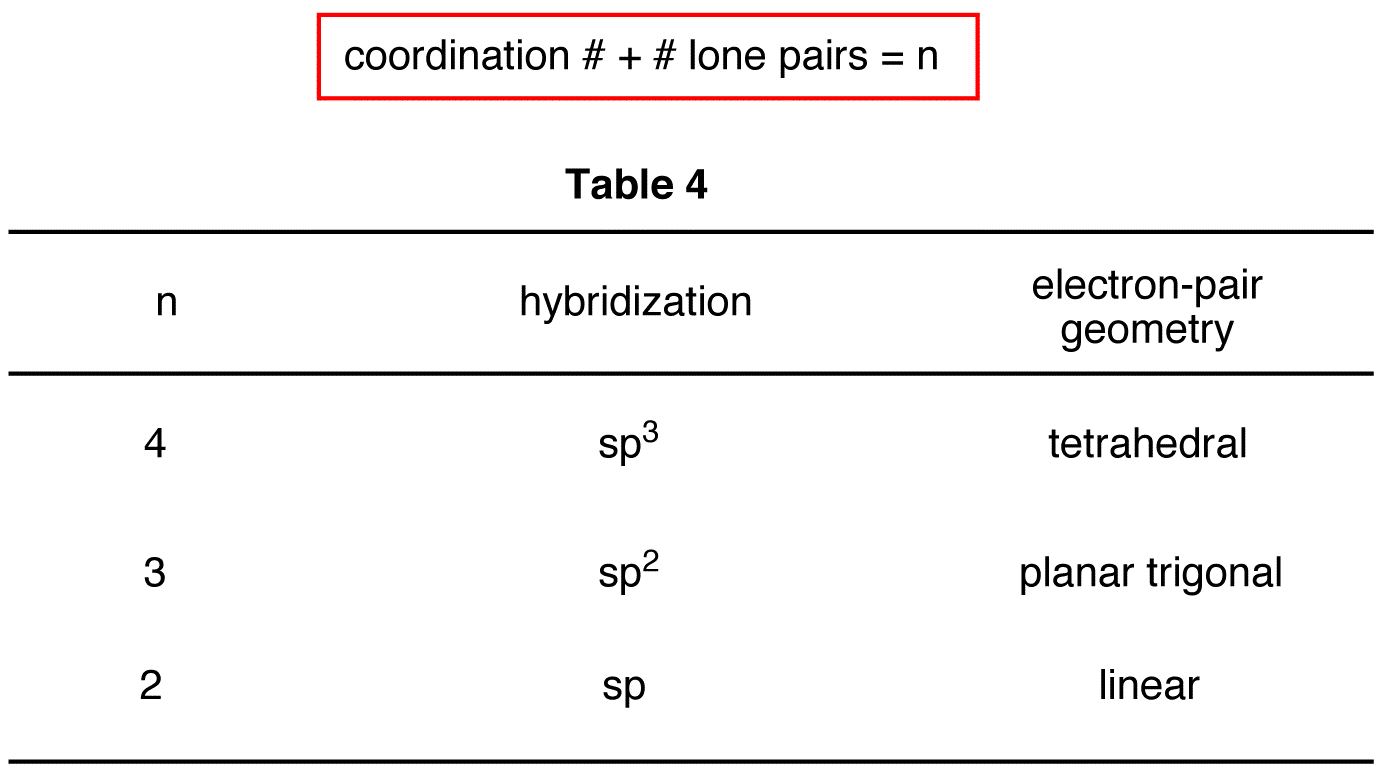
Hybridization Orbitals Chart
.jpg)
Types of Hybridization Definitions, Examples, Key Features, Steps to

Molecular Geometry Chart With Hybridization
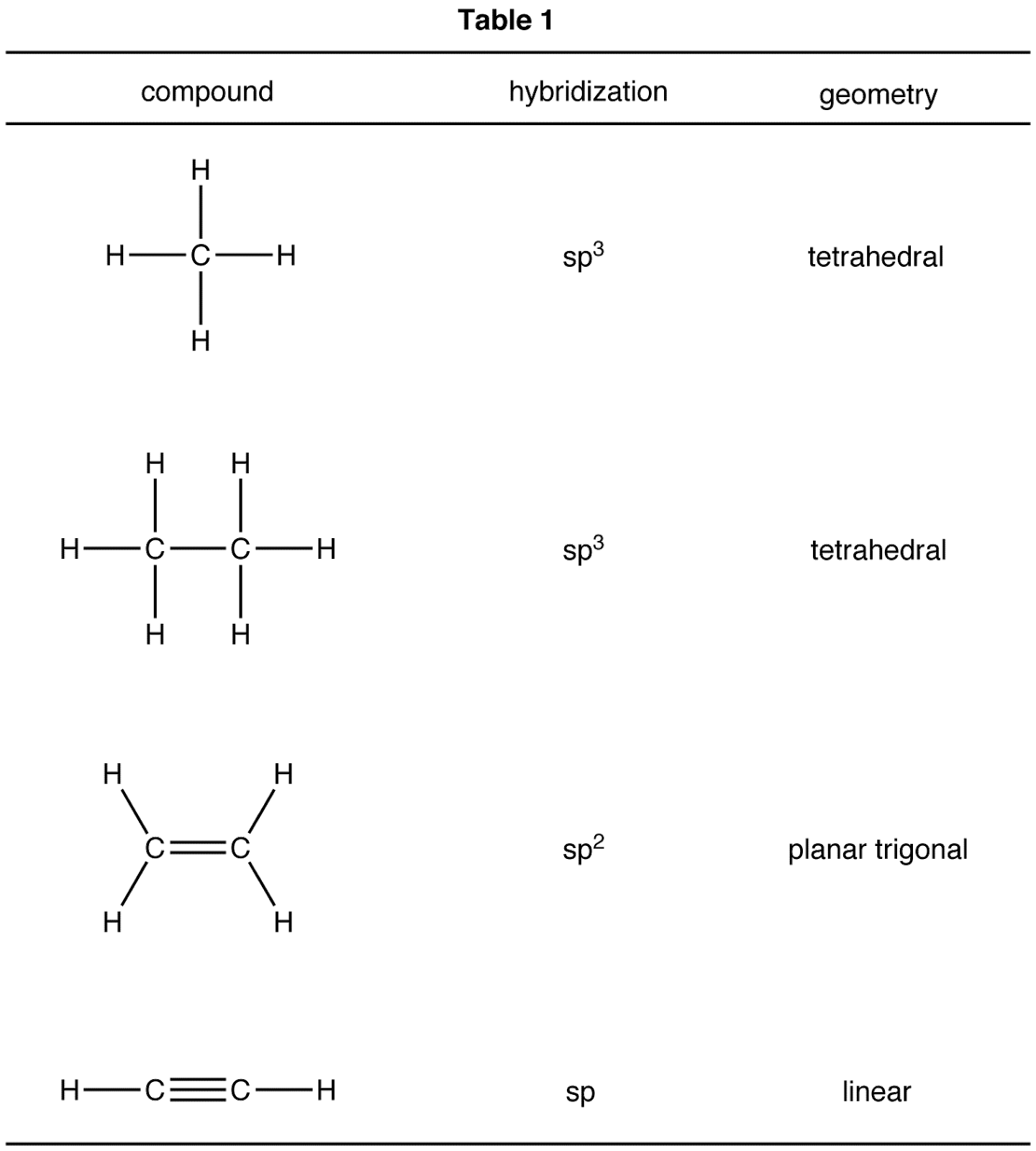
Molecular Geometry And Hybridization Chart

What is Hybridization? sp3, sp2, Examples and Formula
Web 10.4 Hybridization Of Atomic Orbitals 1.
Web Hybridization Increases The Overlap Of Bonding Orbitals And Explains The Molecular Geometries Of Many Species Whose Geometry Cannot Be Explained Using A Vsepr Approach.
Web Hybridization Is The Idea That Atomic Orbitals Fuse To Form Newly Hybridized Orbitals, Which In Turn, Influences Molecular Geometry And Bonding Properties.
So, Before We Start With Organic Chemistry, Let's Revise A Few Things About Bonding In Organic Molecules.
Related Post: