Header Beam Span Chart
Header Beam Span Chart - Web span length (feet): How to use a header sizing calculator: Web calculate the size needed for a beam, girder, or header made from no. These tables provide maximum spans for the #2 grades of four common. Web the header and beam tables provided below have been computed using allowable stress design and standard engineering design equations for simple span beams with. It also shows the maximum that the beam. Web therefore, a double 2×6 carries 2 x 347 = 694 pounds per lineal foot. Determine your wood beam's modulus of elasticity (e). Web simply put, a header (in this case) is a horizontal member that spans a wall opening such as a door or window to transfer loads from above down and around that. Click on the appropriate beam, this will take you to the calculation table for. Web although calculating the maximum rough opening a door header can span is very easy, here is the door header size chart we can use for convenience: How to use a header sizing calculator: It also shows the maximum that the beam. Determine your wood beam's modulus of elasticity (e). Web headers & beams : Web therefore, a double 2×6 carries 2 x 347 = 694 pounds per lineal foot. Web determine the beam / header span (length) and the span carried (supported) by the beam / header. Covers any span and every load with pin point accuracy. Web span length (feet): Web simply put, a header (in this case) is a horizontal member that. Web although calculating the maximum rough opening a door header can span is very easy, here is the door header size chart we can use for convenience: The full table shows more lumber sizes. It also shows the maximum that the beam. Web find span charts and 2012 irc building codes for girders and headers in floor and wall systems.. Covers any span and every load with pin point accuracy. See span tables for different load bearing locations, number of plies and jacks,. These tables provide maximum spans for the #2 grades of four common. Web calculate the size needed for a beam, girder, or header made from no. Sfpa provides size selection tables for various beam spans and loading. Determine your wood beam's modulus of elasticity (e). Web to find the span of a wood beam, let's say a 2×8 beam (with actual measurements of 1.5×7.5 ): Web in the 2012 irc and earlier versions, the header span table for exterior bearing walls (r502.6 [1]) was published in chapter 5, “floors”—hardly a logical spot—and the table. It also shows. Web although calculating the maximum rough opening a door header can span is very easy, here is the door header size chart we can use for convenience: These tables provide maximum spans for the #2 grades of four common. Web the header and beam tables provided below have been computed using allowable stress design and standard engineering design equations for. How to use a header sizing calculator: These tables provide maximum spans for the #2 grades of four common. Determine your wood beam's modulus of elasticity (e). Click on the appropriate beam, this will take you to the calculation table for. Web therefore, a double 2×6 carries 2 x 347 = 694 pounds per lineal foot. Web although calculating the maximum rough opening a door header can span is very easy, here is the door header size chart we can use for convenience: Web determine the beam / header span (length) and the span carried (supported) by the beam / header. Web simply put, a header (in this case) is a horizontal member that spans a. Web determine the beam / header span (length) and the span carried (supported) by the beam / header. Web use the span tables in the links below to determine the maximum allowable lengths of joists and rafters. Determine your wood beam's modulus of elasticity (e). Covers any span and every load with pin point accuracy. Click on the appropriate beam,. Web headers & beams : Click on the appropriate beam, this will take you to the calculation table for. These tables provide maximum spans for the #2 grades of four common. How to use a header sizing calculator: Determine your wood beam's modulus of elasticity (e). Web to find the span of a wood beam, let's say a 2×8 beam (with actual measurements of 1.5×7.5 ): Web headers & beams : Web therefore, a double 2×6 carries 2 x 347 = 694 pounds per lineal foot. Covers any span and every load with pin point accuracy. How to use a header sizing calculator: Web find span charts and 2012 irc building codes for girders and headers in floor and wall systems. See span tables for different load bearing locations, number of plies and jacks,. Web simply put, a header (in this case) is a horizontal member that spans a wall opening such as a door or window to transfer loads from above down and around that. Determine your wood beam's modulus of elasticity (e). Web span length (feet): Web the header and beam tables provided below have been computed using allowable stress design and standard engineering design equations for simple span beams with. It also shows the maximum that the beam. Web determine the beam / header span (length) and the span carried (supported) by the beam / header. Sfpa provides size selection tables for various beam spans and loading combinations. Web calculate the size needed for a beam, girder, or header made from no. Web use the span tables in the links below to determine the maximum allowable lengths of joists and rafters.
Glulam Beam Header Span Table Elcho Table

2x10 Header Span Chart
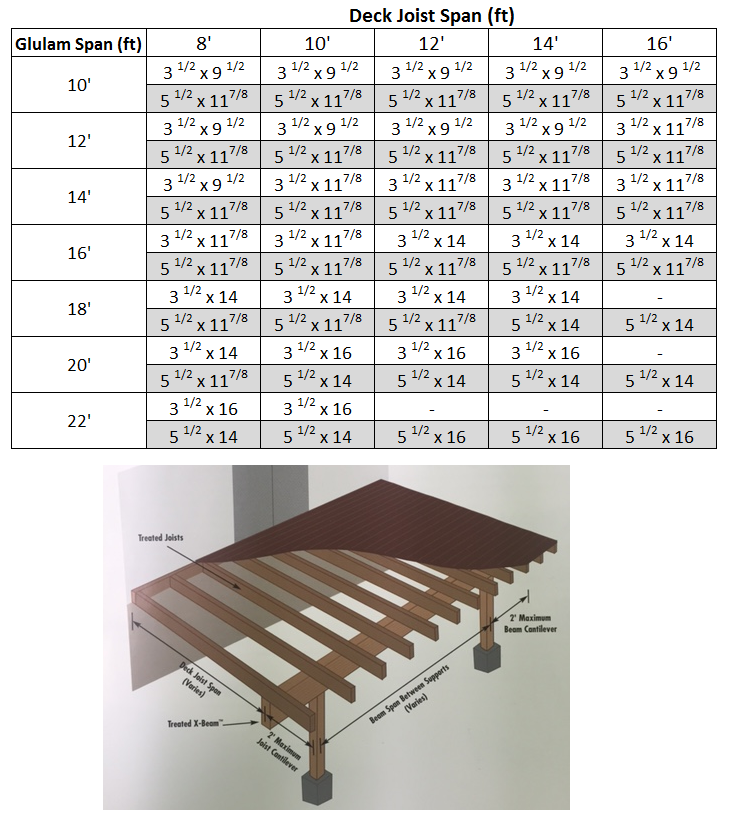
Installing Wall Switch Laminated beam span tables
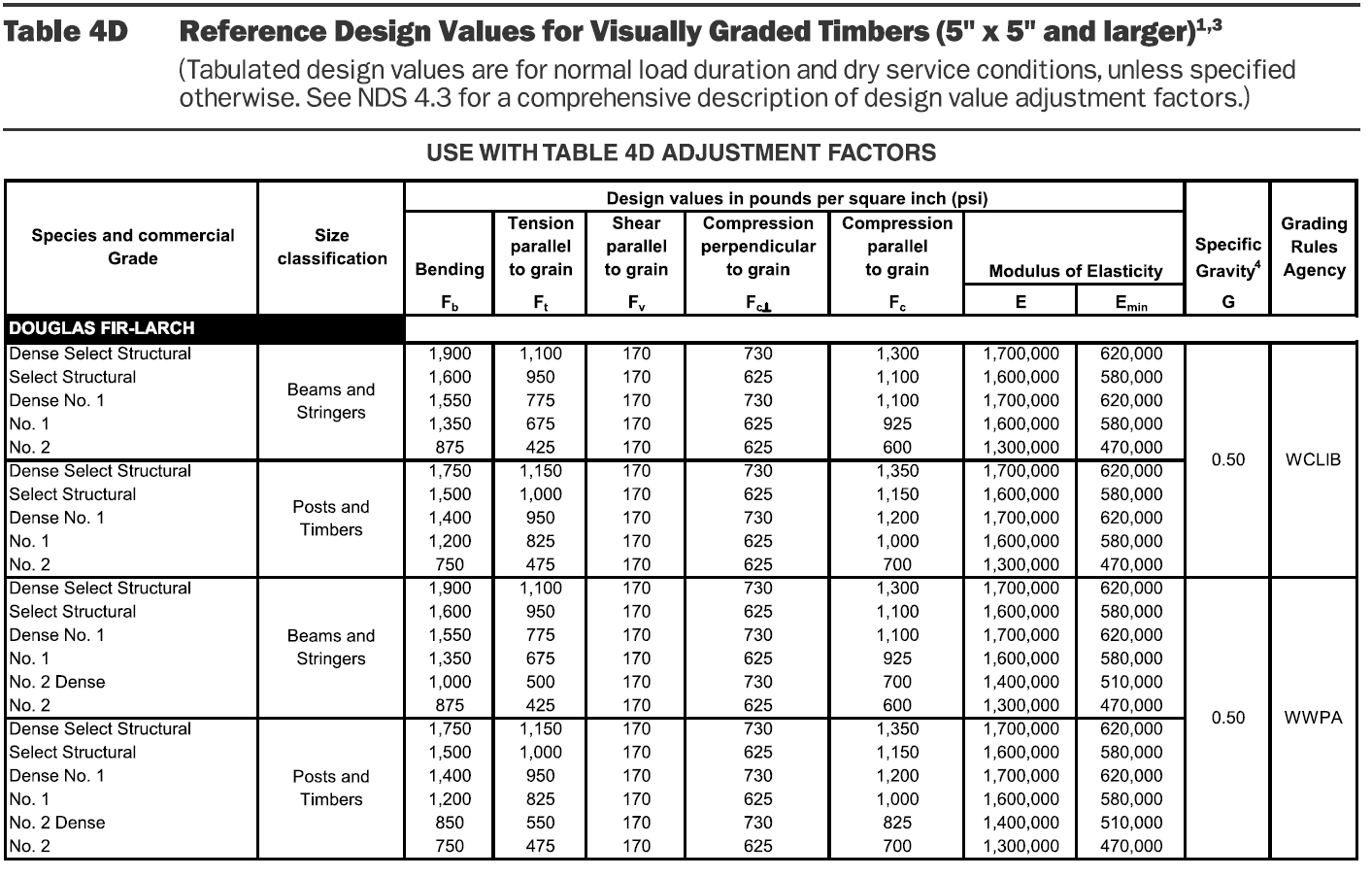
Douglas Fir Header Beam Span Tables Home Interior Design
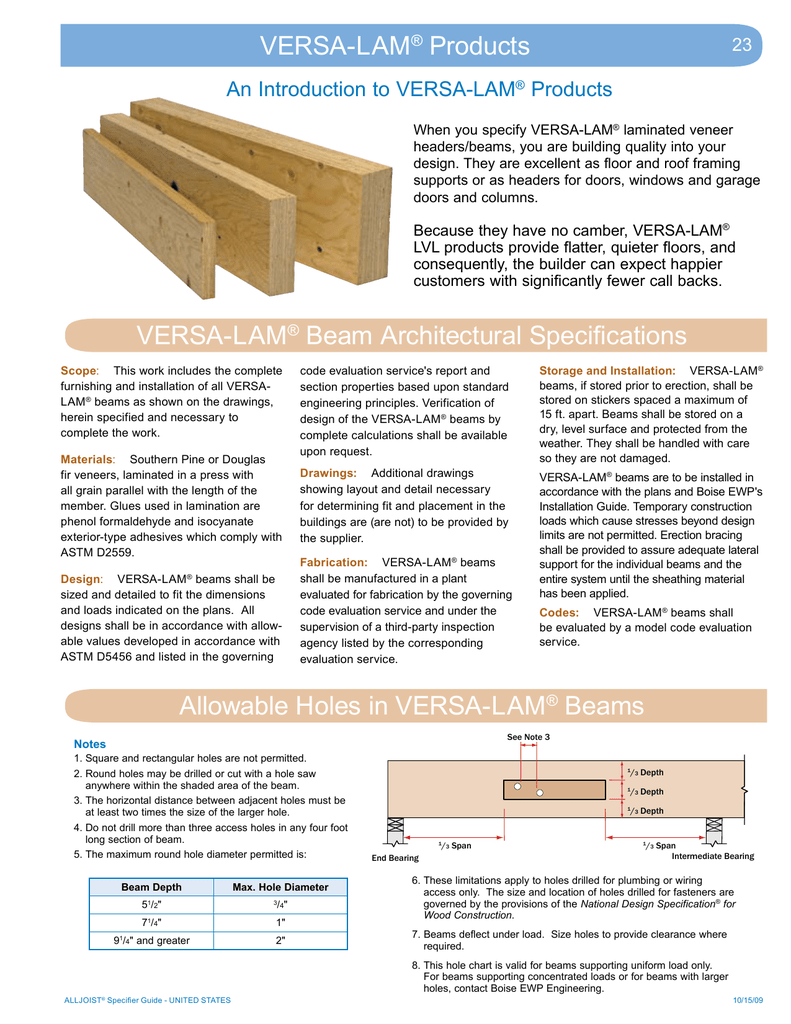
VERSALAM LVL Beams, Headers, Columns Guide

Douglas Fir Header Beam Span Tables

Header Span Table Irc
lvl span chart Sundayid

Lumber Span Tables Canada

Douglas Fir Header Beam Span Tables
Web Although Calculating The Maximum Rough Opening A Door Header Can Span Is Very Easy, Here Is The Door Header Size Chart We Can Use For Convenience:
These Tables Provide Maximum Spans For The #2 Grades Of Four Common.
Click On The Appropriate Beam, This Will Take You To The Calculation Table For.
Web In The 2012 Irc And Earlier Versions, The Header Span Table For Exterior Bearing Walls (R502.6 [1]) Was Published In Chapter 5, “Floors”—Hardly A Logical Spot—And The Table.
Related Post: