Grub Life Cycle Chart
Grub Life Cycle Chart - During this 4 stage process, the white grub transforms itself in shape, size, colour and feeding habits. Pupae are present in the soil for a week in mid june to mid july; Early symptoms include gradual thinning, yellowing, and weakening of the grass stand followed by the appearance of scattered, irregular dead patches. Web white grubs are the larvae of certain beetles, like june beetles and chafers. And adults emerge early the following summer to complete the cycle). Web among native white grub species, the most important and widespread include the masked chafer ( cyclocephala ), may beetle ( phyllophaga ), black turfgrass ataenius ( ataenius spretulus ), and green june beetle ( cotinis nitida ). Web the life cycle of the white grub consists of 4 stages, egg, larvae, pupa, and adult. Heavy infestations of white grubs may kill grass or attract mammals, such as skunks, that damage grass when digging to feed on grubs. Web here you will find information on white grubs and how they damage turf, their life cycle and solutions for controlling them. While grub preventatives can be applied in late spring or early summer to target eggs prior to hatching, the optimal time for when to apply grub control will be in mid to late summer, when larvae are most actively feeding, and thus vulnerable to control applications. Web white grubs are the larvae of certain beetles, like june beetles and chafers. White grubs are best controlled with insecticides when eggs are beginning to hatch. Web life cycle european chafers lay their eggs in late june; Web here you will find information on white grubs and how they damage turf, their life cycle and solutions for controlling them.. Adult beetles tend to lay their eggs in holes around your lawn between june and august every year. Web quick facts… billbugs and white grubs are insects that damage turf grasses by feeding on the roots. By considering a grub’s life cycle, you can anticipate problems before your lawn is ruined—not just by root damage, but by hungry birds and. Web the life cycle of the white grub consists of 4 stages, egg, larvae, pupa, and adult. And adults emerge early the following summer to complete the cycle). Knowing the life cycle of grubs is the key to determining whether you have a problem, what to do about it, and when to do it. Web among native white grub species,. Japanese beetles in july and august. Web among native white grub species, the most important and widespread include the masked chafer ( cyclocephala ), may beetle ( phyllophaga ), black turfgrass ataenius ( ataenius spretulus ), and green june beetle ( cotinis nitida ). During this 4 stage process, the white grub transforms itself in shape, size, colour and feeding. In healthy, warm conditions, these eggs will hatch within two weeks. During the first year, true white grub feeding causes no observable injury. Sometimes called grub worms, though not technically worms at all, the white grubs you’ll find in your garden and lawn are scarabaeidae larvae, spanning several genera. Web the short answer: Web among native white grub species, the. In healthy, warm conditions, these eggs will hatch within two weeks. Sometimes called grub worms, though not technically worms at all, the white grubs you’ll find in your garden and lawn are scarabaeidae larvae, spanning several genera. Annual grubs stop feeding in the spring, and may be avoided by adjusting planting time, but a field infested with june beetle may. It also changes where it lives during its life cycle. Web the short answer: Egg, larvae, pupa, and adult. Web here you will find information on white grubs and how they damage turf, their life cycle and solutions for controlling them. Web white grubs are the larvae of certain beetles, like june beetles and chafers. Web this publication will help you understand the white grub life cycle and how to identify and control these pests. Japanese beetles in july and august. Web a grub life cycle chart provides a visual representation of the different stages a grub goes through, from egg to adult beetle. During this 4 stage process, the white grub transforms itself in. Web quick facts… billbugs and white grubs are insects that damage turf grasses by feeding on the roots. There are over 100 species of may/june beetles in texas, but only a few species cause damage to turfgrass. In healthy, warm conditions, these eggs will hatch within two weeks. Web white grubs are the larvae of certain beetles, like june beetles. Knowing the life cycle of grubs is the key to determining whether you have a problem, what to do about it, and when to do it. Larvae feed on turf roots from early july through mid autumn and again in the spring; Once the egg hatches, the grubs will go through three larval stages or instars during their development. Web. Once the egg hatches, the grubs will go through three larval stages or instars during their development. In healthy, warm conditions, these eggs will hatch within two weeks. Web among native white grub species, the most important and widespread include the masked chafer ( cyclocephala ), may beetle ( phyllophaga ), black turfgrass ataenius ( ataenius spretulus ), and green june beetle ( cotinis nitida ). During the first year, true white grub feeding causes no observable injury. After the white grub eggs hatch, white grub larvae emerge and start munching on the root system of your turfgrass and plants including potted plants and ornamental plants. Web white grubs are the larvae of certain beetles, like june beetles and chafers. By considering a grub’s life cycle, you can anticipate problems before your lawn is ruined—not just by root damage, but by hungry birds and rodents as well. Larvae feed on turf roots from early july through mid autumn and again in the spring; Pupae are present in the soil for a week in mid june to mid july; Japanese beetles in july and august. Several factors create the prime environment for grubs, including the health of your lawn, moisture, and food sources available. Web insect pest management on turfrass. While grub preventatives can be applied in late spring or early summer to target eggs prior to hatching, the optimal time for when to apply grub control will be in mid to late summer, when larvae are most actively feeding, and thus vulnerable to control applications. Egg, grub (larva), pupa, and adult. Web the short answer: Web the life cycle of the white grub consists of 4 stages:
Grub worm cycle Science Camp, Summer Science, Garden Bugs, Backyard
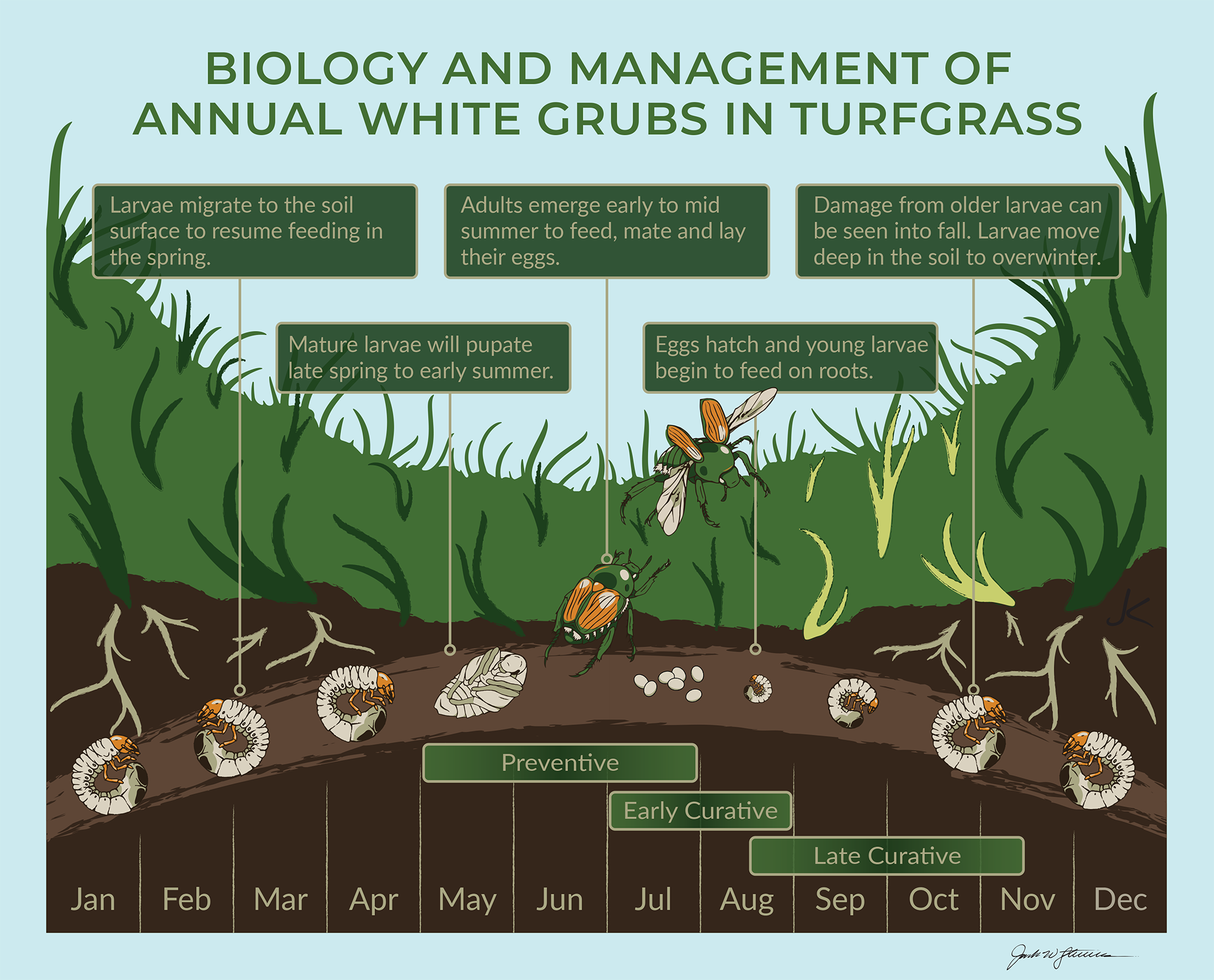
Grub Life Cycle

Chafer grub life cycle diagram The Lawn Man
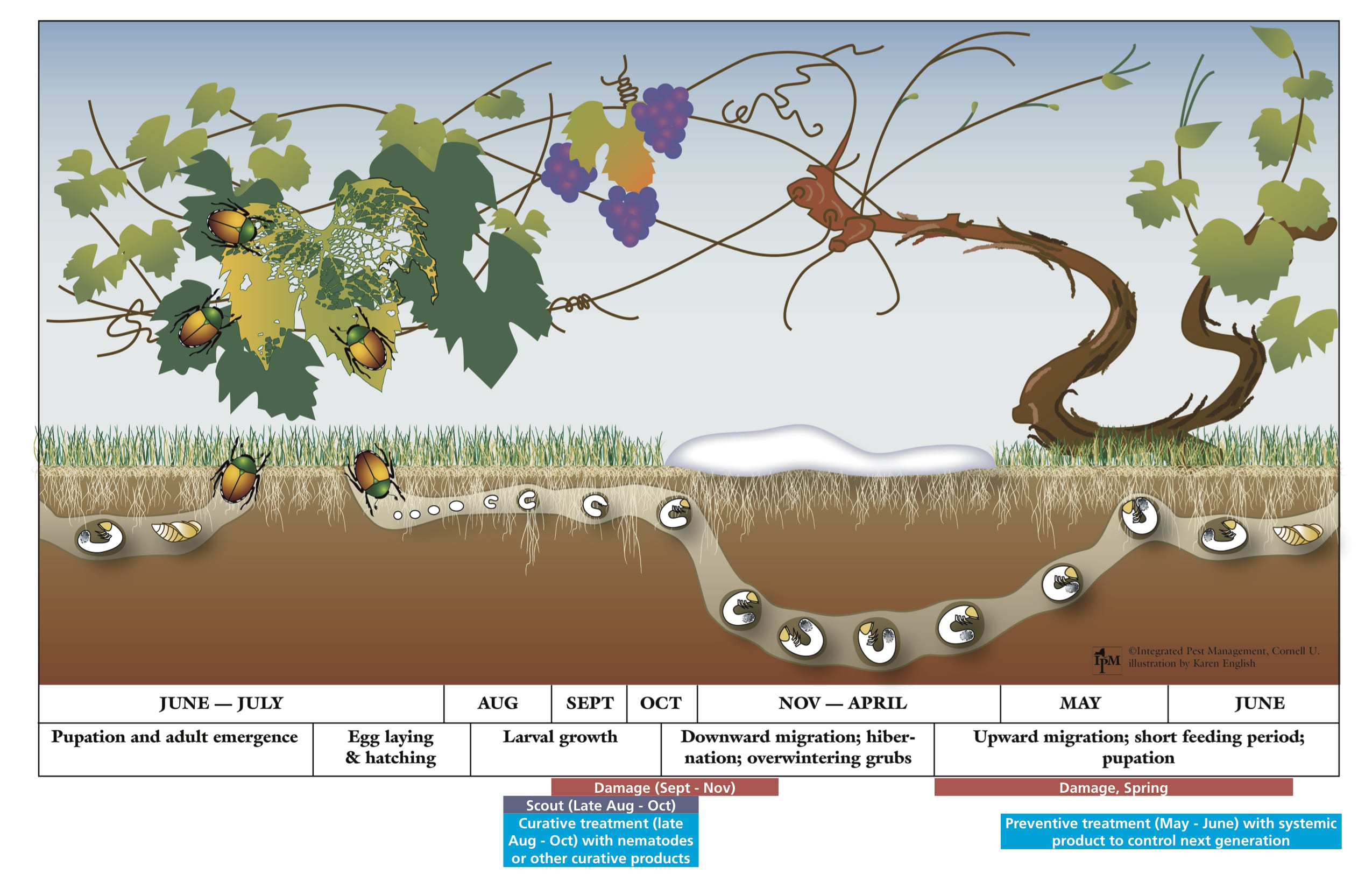
grub Biocontrol Bytes
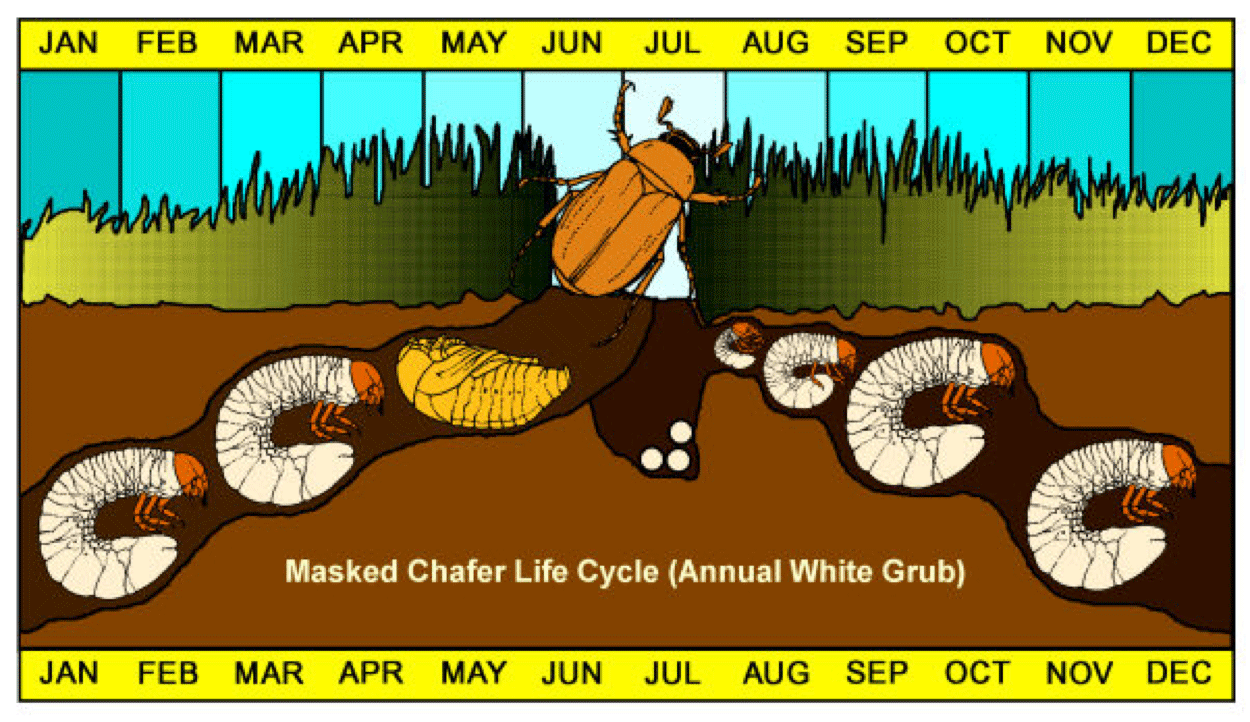
Bird Feeding and Mushroom Growth in Lawns NOT Reasons to Apply

White Grub Control Ford's Hometown Services
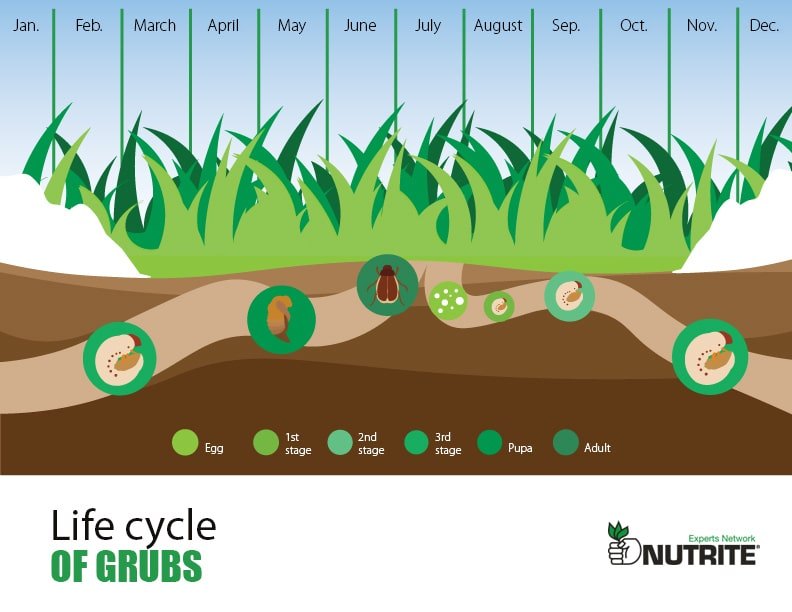
Grub Control Nutrite Expert Network

Grubs CALS

What Are White Grubs & How To Identify Them
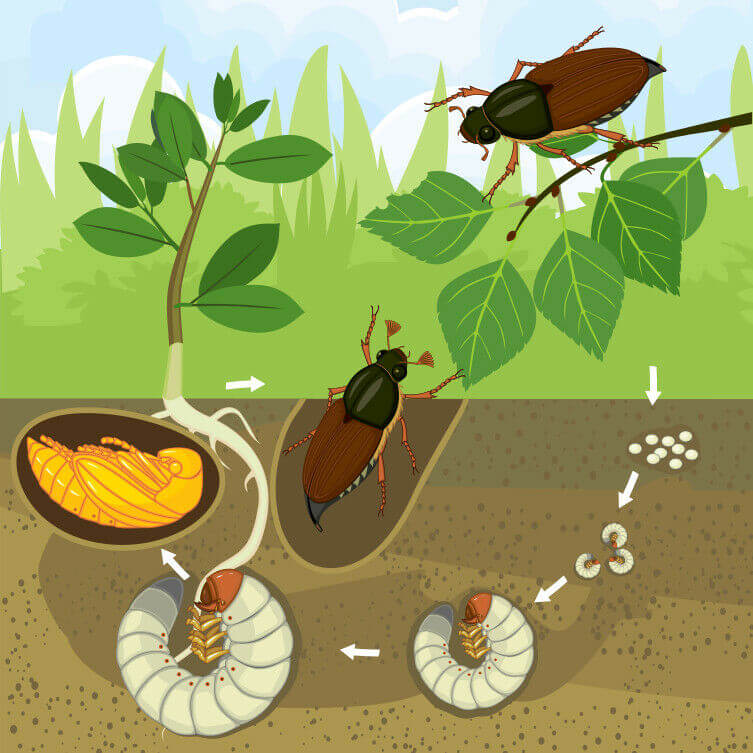

Grub Life Cycle Chart
Web Insect Life Cycle All Of These Beetles Go Through Four Distinct Forms During Their Life Cycle:
Web Life Cycle European Chafers Lay Their Eggs In Late June;
White Grubs Are Best Controlled With Insecticides When Eggs Are Beginning To Hatch.
Knowing The Life Cycle Of Grubs Is The Key To Determining Whether You Have A Problem, What To Do About It, And When To Do It.
Related Post: