Generalized Compressibility Chart
Generalized Compressibility Chart - Web this chapter covers the fundamental concepts of thermodynamics, including thermodynamic properties and their units (sect. That is the purpose of the example that appears on the following page. On the next page and you can see all three in the chapter 2 first aid kit. The best way to teach you to read these charts is to show you ! The compressibility factor chart plots the compressibility factor \(z\), equal to. For example, see the following figures: 13.3 ), specific heats of gases (sect. Web with the reduced temperature and specific volume, we can refer to a generalized compressibility chart (or function), which specifies the compressiblity factor as a function of reduced temperature, reduced pressure, and/or reduced specific volume for general gas mixtures. The reduced pressure and temperature are defined by and , respectively, where is the critical pressure and is the critical temperature. 13.4 ), and compressibility chart for nonideal behavior of gases (sect. For example, see the following figures: It is valid for many substances, especially those that have simple molecular structures. Web properties of common gases. The solid lines represent the best curves fitted to the data. Web the compressibility factor chart plots the compressibility factor , equal to , where is the volume per mole, versus the reduced pressure for several. The deviation of a gas from ideal gas behavior is greatest in the area of the critical point. It is valid for many substances, especially those that have simple molecular structures. Web the key parameter is the compressibility factor, z, which can be estimated using a generalised chart. This chart brings the following information: The solid lines represent the best. 13.2 ), concept of mole, ideal gas law (sect. Web a generalized compressibility chart z=f(p r, t r) is presented in fig. Reduced temperature and reduced pressure.more. The solid lines represent the best curves fitted to the data. Below is the procedure of how to use the generalized compressibility chart, followed by examples. Web figure 1 shows the essential features of a generalized compressibility factor chart. The ideal gas equation (eqs. Bloch copyright © 2006 john wiley & sons, inc. If we only know the temperature and pressure, we can still calculate it using a compressibility chart. Web download chapter pdf. Web this chapter covers the fundamental concepts of thermodynamics, including thermodynamic properties and their units (sect. Web download chapter pdf. Reduced temperature and reduced pressure.more. Web properties of common gases. Web reading the generalized compressibility charts and using them to solve problems are two different things ! At very low pressure (pr << 1), gases behave as an ideal gas regardless of temperature. 2.1 and 2.3) is modified for use for real gases by introducing the generalized compressibility factor, which is represented. 13.4 ), and compressibility chart for nonideal behavior of gases (sect. Web properties of common gases. Bloch copyright © 2006 john wiley & sons, inc. The deviation of a gas from ideal gas behavior is greatest in the area of the critical point. On the next page and you can see all three in the chapter 2 first aid kit. At high temperatures (tr > 2), ideal gas behavior can be assumed with good accuracy. The ideal gas equation (eqs. The reduced pressure and temperature. Web the generalized compressibility chart can be viewed as a graphical representation of the gas behaviour over a wide range of pressures and temperatures. 2.1 and 2.3) is modified for use for real gases by introducing the generalized compressibility factor, which is represented. Web reading the generalized compressibility charts and using them to solve problems are two different things !. Web the generalized compressibility chart can be viewed as a graphical representation of the gas behaviour over a wide range of pressures and temperatures. The deviation of a gas from ideal gas behavior is greatest in the area of the critical point. Web with the reduced temperature and specific volume, we can refer to a generalized compressibility chart (or function),. If we only know the temperature and pressure, we can still calculate it using a compressibility chart. As seen in the figure, at all temperatures z tends to 1 as p r tends to 0. Web figure 1 shows the essential features of a generalized compressibility factor chart. Web a generalized compressibility chart z=f(p r, t r) is presented in. Web if neither tool is available, the generalized compressibility chart may be used instead as a fast and reasonably accurate tool, especially for substances with simple molecular structures. For example, see the following figures: It is valid for many substances, especially those that have simple molecular structures. At very low pressure (pr << 1), gases behave as an ideal gas regardless of temperature. Web reading the generalized compressibility charts and using them to solve problems are two different things ! The reduced pressure and temperature are defined by and , respectively, where is the critical pressure and is the critical temperature. \(\frac{pv}{rt}\), where \(v\) is the volume per mole, versus the reduced pressure \(p_r\) for. If we only know the temperature and pressure, we can still calculate it using a compressibility chart. 13.4 ), and compressibility chart for nonideal behavior of gases (sect. Vapor pressure curves for common pure gases. Web with the reduced temperature and specific volume, we can refer to a generalized compressibility chart (or function), which specifies the compressiblity factor as a function of reduced temperature, reduced pressure, and/or reduced specific volume for general gas mixtures. Web a generalized compressibility chart z=f(p r, t r) is presented in fig. The ideal gas equation (eqs. Figure 2.21 shows the chart for sweet natural gases as prepared by standing and katz [ 62 ]. This chart brings the following information: This means that the behavior of the actual gas closely approaches ideal gas behavior, as the pressure approaches zero.
physical chemistry How to understand NelsonObert charts? Chemistry

Generalized Compressibility Chart
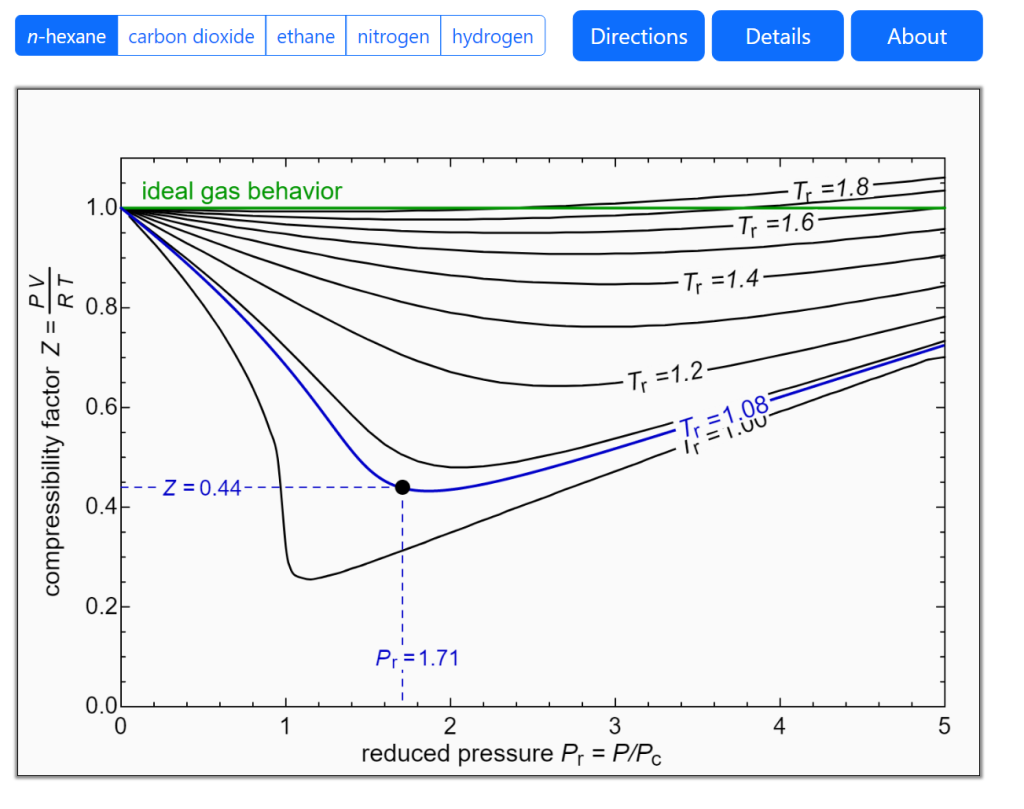
compressibilityfactorcharts LearnChemE

Introduction to the Generalized Compressibility Chart Engineering
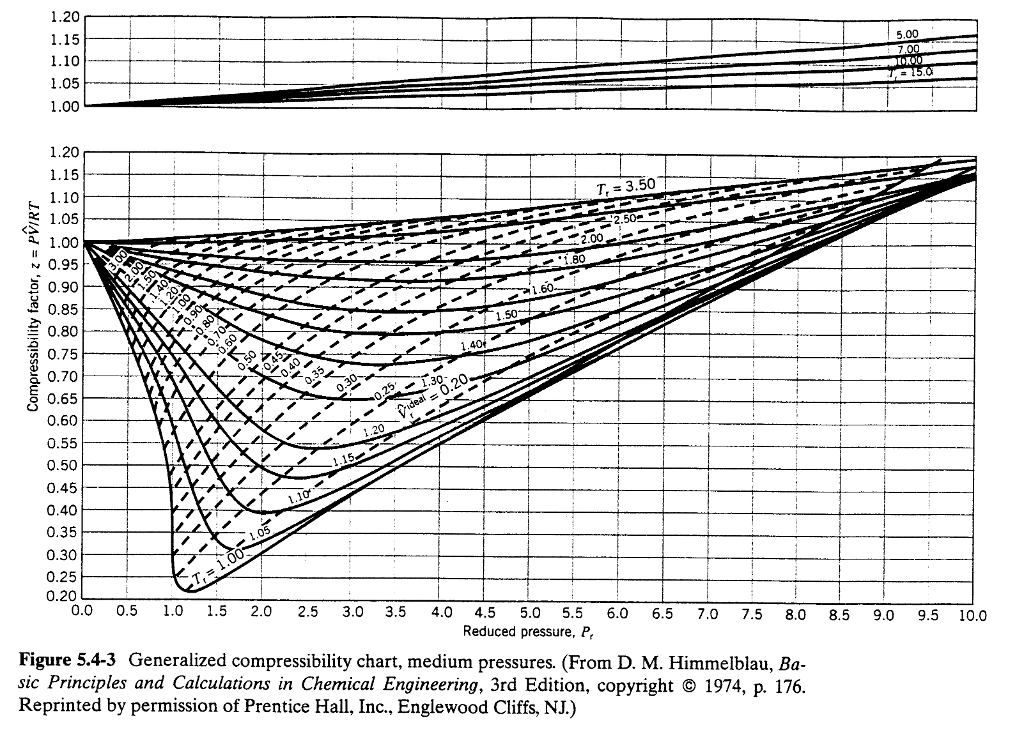
Solved Use the generalised compressibility chart to estimate
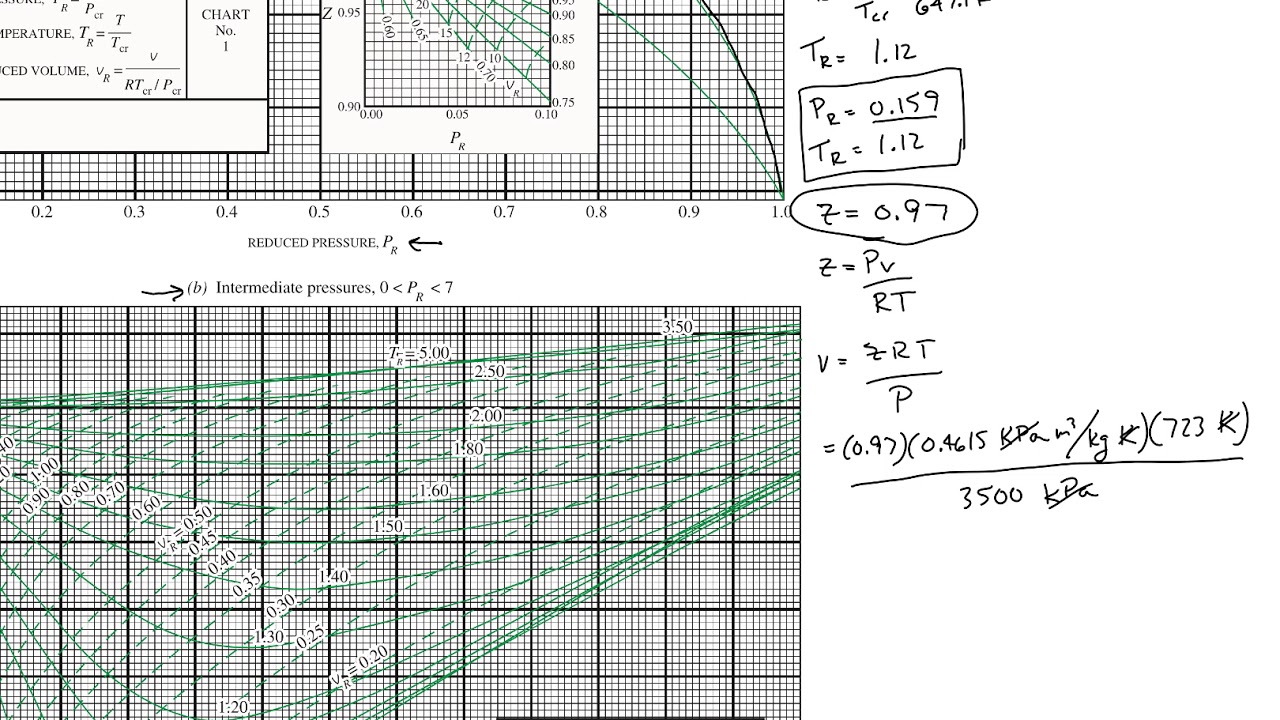
Thermodynamics Generalized Compressibility Chart YouTube

Generalized compressibility charts Big Chemical Encyclopedia
Generalized Compressibility Chart PDF Thermodynamics

Generalized Compressibility Chart

Generalized Compressibility Chart, Reduced Pressure & Reduced
At High Temperatures (Tr > 2), Ideal Gas Behavior Can Be Assumed With Good Accuracy.
Web The Compressibility Factor Chart Plots The Compressibility Factor , Equal To , Where Is The Volume Per Mole, Versus The Reduced Pressure For Several Values Of The Reduced Temperature.
That Is The Purpose Of The Example That Appears On The Following Page.
Reduced Temperature And Reduced Pressure.more.
Related Post:
