Gas Laws Chart
Gas Laws Chart - Web the behavior of gases can be modeled with gas laws. Suppose p is the pressure and v is the volume, then. At constant temperature and pressure, the volume of a sample of gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas in the sample. Boyle’s law describes the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a fixed amount of gas at a constant temperature. Boyle's law, charles' law, the combined gas law, avogadro's law, and the ideal. Web the five gas laws are listed below: Web a gas law is a simple mathematical formula that allows you to model, or predict, the behavior of a gas. Boyle’s law states the relation between volume and pressure at constant temperature and mass. These laws show how a change in one of these properties affects the others. He observed that the volume of a given mass of a gas is inversely proportional to. · head back to the helpdesk. And is the ideal gas constant. How do you fill up a hot air balloon? Web p1v1 = p2v2 = constant. · try some practice worksheets. It can also be derived from the microscopic kinetic theory, as was achieved (apparently independently) by august krönig in 1856 [2] and rudolf clausius in 1857. Each law is titled by its discoverer. Web as the temperature is raised, the fraction of molecules that can break away into the gas phase grows and vapor pressure increases. Web the behavior of. Suppose p is the pressure and v is the volume, then. Web the ideal gas law relates the pressure, temperature, volume and moles of a gas through the gas constant “r.”. He observed that the volume of a given mass of a gas is inversely proportional to. Charles's law relates a gas's volume and temperature at constant pressure and amount.. Is the amount of substance; Web the ideal gas law relates the pressure, temperature, volume and moles of a gas through the gas constant “r.”. Web the ideal gas law relates the four independent physical properties of a gas at any time. Principle that warm air is less dense than cooler air. Web there are 4 general laws that relate. In gas laws, temperatures must always be expressed in kelvins. Web there are 4 general laws that relate the 4 basic characteristic properties of gases to each other. Charles' law, boyle's law and avogadro's law (all of which will later combine into the general gas equation and ideal gas law). Web the ideal gas law relates the pressure, temperature, volume. Web european union countries approved a law on monday to impose methane emissions limits on europe's oil and gas imports from 2030, pressuring international suppliers to cut leaks of the potent. Suppose p is the pressure and v is the volume, then. A hot air balloon works on the. Web the gas laws consist of three primary laws: It provides. Web as the temperature is raised, the fraction of molecules that can break away into the gas phase grows and vapor pressure increases. And is the ideal gas constant. In gas laws, temperatures must always be expressed in kelvins. Web the gas laws are empirical laws that describe the properties of gases and typically include avogadro's law, boyle's law, and. It provides a relationship between the volume occupied by a gas and the absolute temperature. Boyle's law relates a gas's pressure and volume at constant temperature and amount. The ideal gas law can be used in stoichiometry problems whose chemical reactions involve gases. Include units on your work, and write your final answers in the tables. Web european union countries. Web p1v1 = p2v2 = constant. Web the five gas laws are listed below: Web • in chemistry, the relationships between gas physical properties are described as gas laws. Include units on your work, and write your final answers in the tables. Charles's law relates a gas's volume and temperature at constant pressure and amount. Is the amount of substance; And is the ideal gas constant. Suppose p is the pressure and v is the volume, then. Web as the temperature is raised, the fraction of molecules that can break away into the gas phase grows and vapor pressure increases. At stp, gases have a volume of 22.4 l per. Web the gas laws consist of three primary laws: However, a number of rates available to. Boyle’s law establishes a relationship between pressure and volume, keeping temperature and the number of moles constant. Principle that warm air is less dense than cooler air. Web the ideal gas law relates the pressure, temperature, volume and moles of a gas through the gas constant “r.”. It states that under a constant temperature when the pressure on a gas increases its volume decreases. Web the ideal gas law relates the four independent physical properties of a gas at any time. According to it, the pressure is inversely proportional to the volume. These laws show how a change in one of these properties affects the others. The ideal gas law reduces to the other gas laws when you start holding different variables constant. The ideal gas law can be used in stoichiometry problems whose chemical reactions involve gases. Some of these properties are pressure, volume, and temperature. · head back to the helpdesk. Web as the temperature is raised, the fraction of molecules that can break away into the gas phase grows and vapor pressure increases. Each law is titled by its discoverer. Web a gas law is a simple mathematical formula that allows you to model, or predict, the behavior of a gas.
The Theories and Behavior of Gas Owlcation
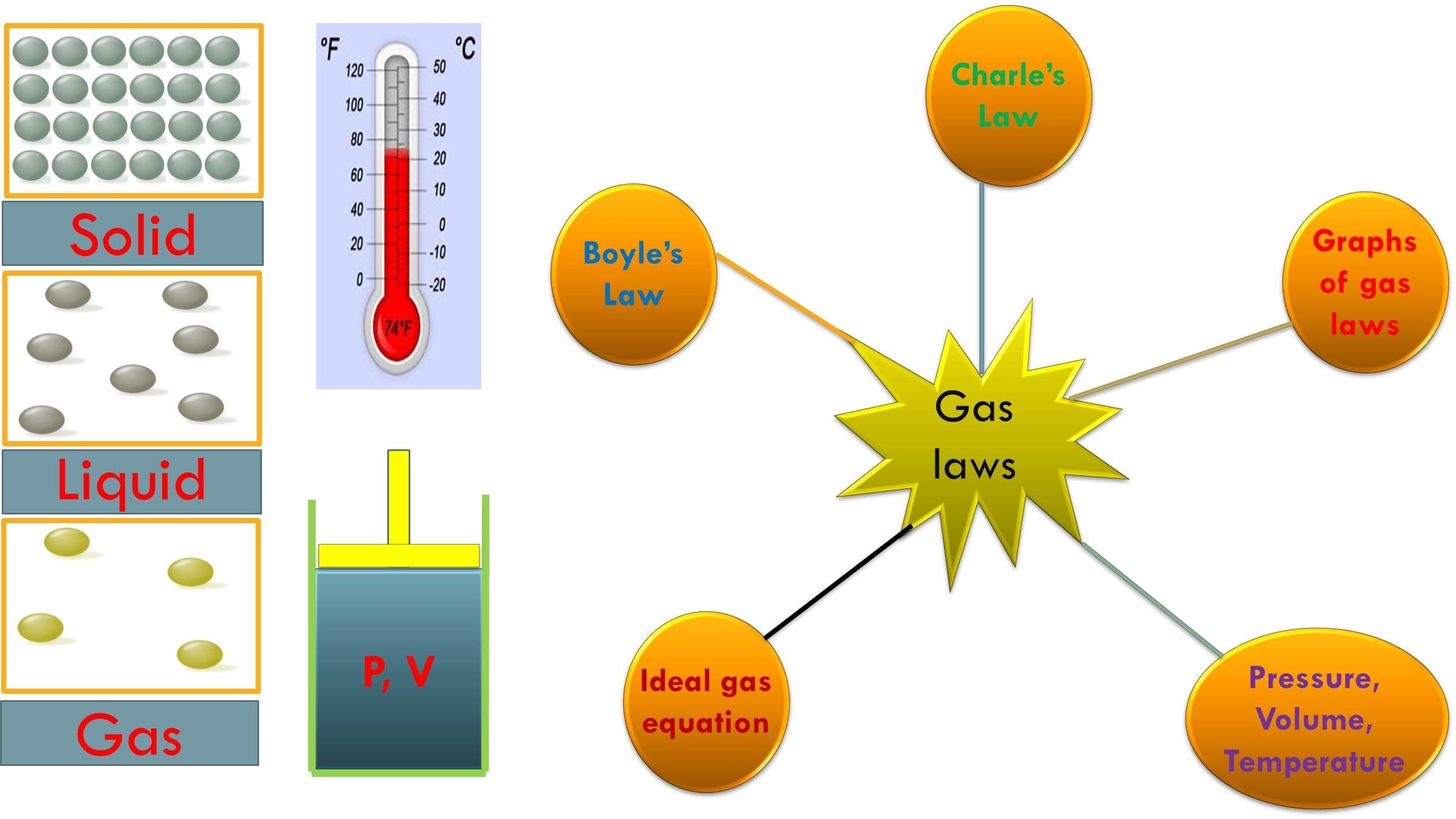
The Gas Laws Definition, Formula & Examples StudiousGuy

Gas Laws Environmental Chemistry

OCR A2 Physics Gas Laws Andrew PoverAndrew Pover
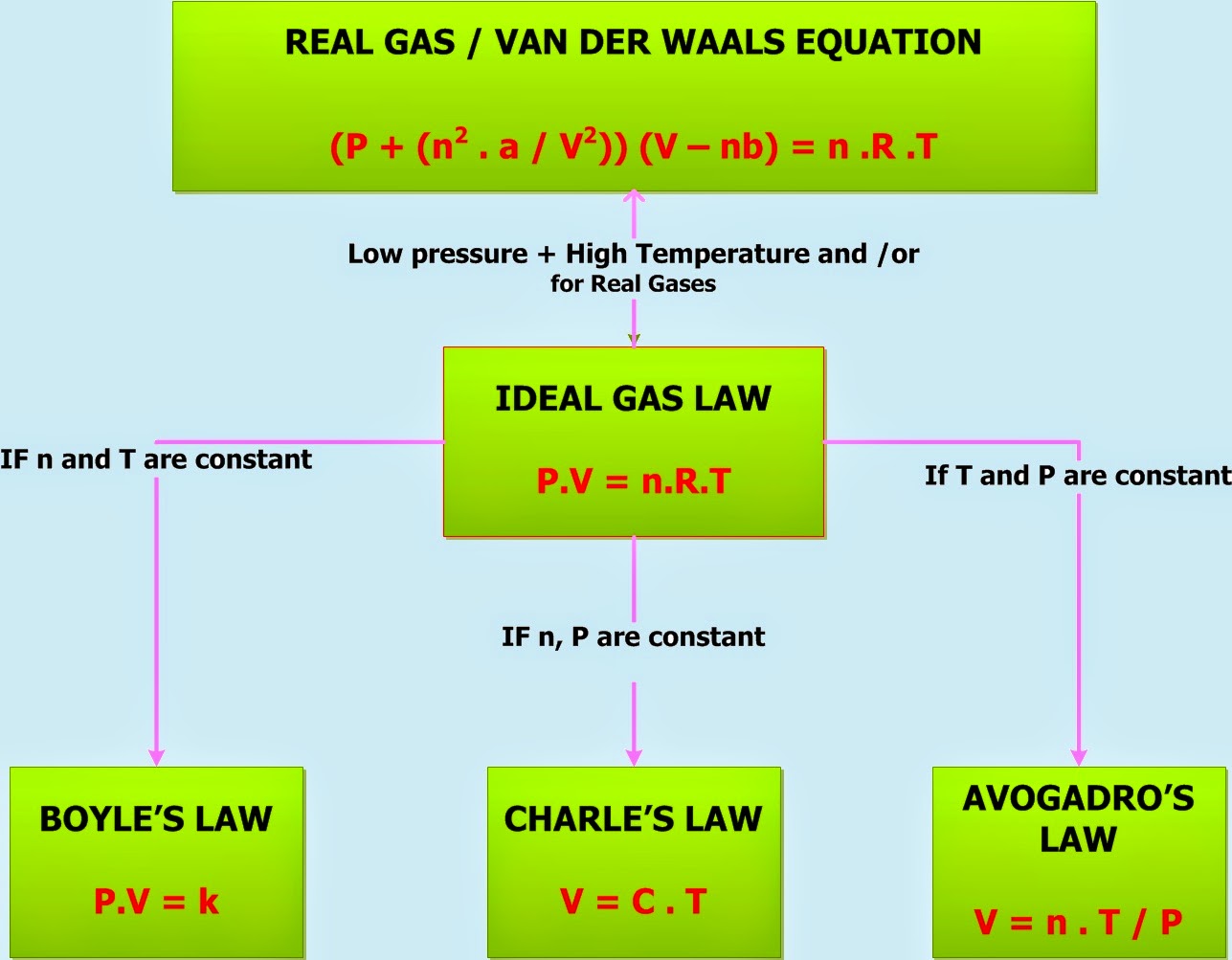
Gas Laws Ideal Gas Law Chemistry Net

Combined Gas Law — Overview & Calculations Expii

Charle’s vs Boyle’s Gas Laws anchor chart Chemistry classroom

Pin by Joni Loomis on Chemistry (With images) Ideal gas law, Gas laws
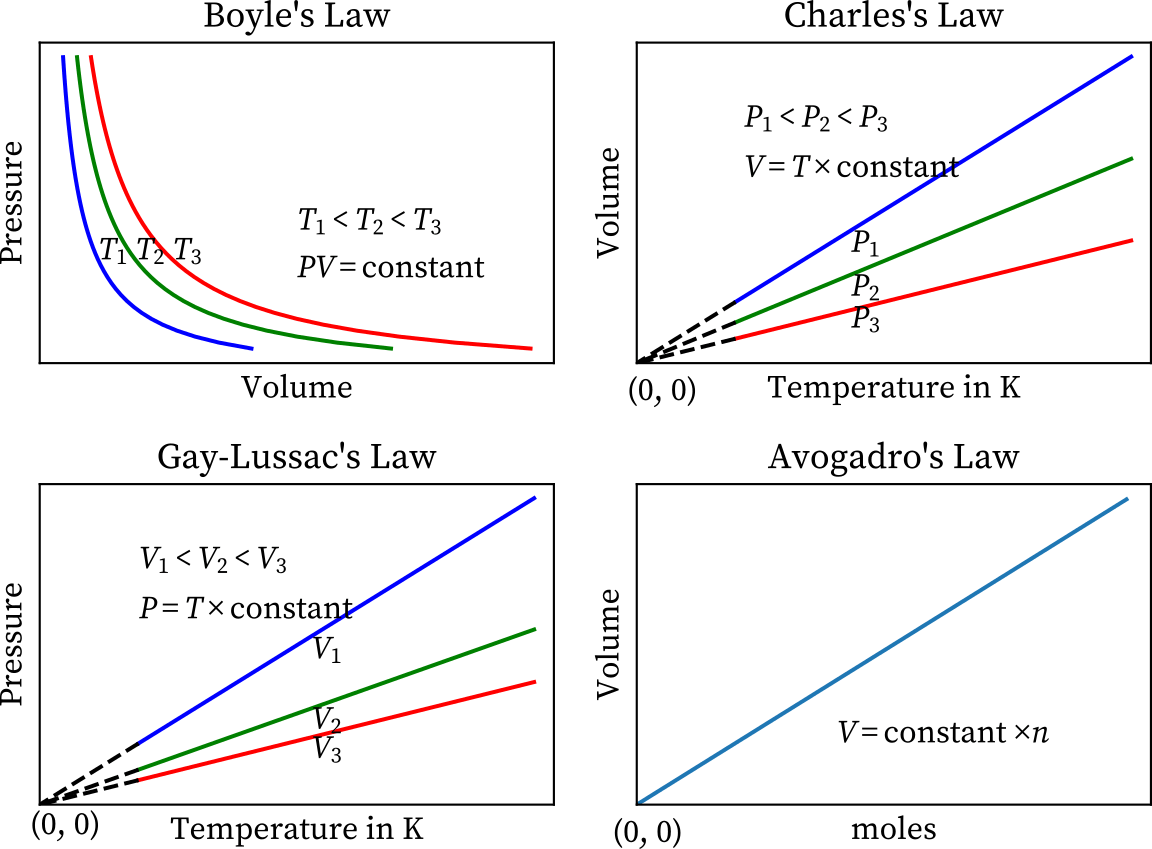
Universal Gas Law Study Guide Inspirit Learning Inc
Gas Laws CK12 Foundation
Complete The Following Tables, Showing Your Work For Each Lettered Box Beside The Corresponding Letter Below.
Boyle’s Law Describes The Inverse Relationship Between The Pressure And Volume Of A Fixed Amount Of Gas At A Constant Temperature.
It Provides A Relationship Between The Pressure And The Volume Of A Gas.
In 1662, Robert Boyle Systematically Studied The Relationship Between The Volume And Pressure Of A Fixed Amount Of Gas At A Constant Temperature.
Related Post:
