Garden Crop Rotation Chart
Garden Crop Rotation Chart - Learn the basics in this factsheet. Web one approach to crop rotation is to divide your plants into these four basic groups: How to rotate crops to aid growth and prevent disease, including a no fuss guide with david hurrion. Imagine your garden separated into four areas, as shown in the chart at the top of the page. Web garden crop rotation describes a simple system for rotating crops in your garden to minimize pests and ensure the highest yields. Creating a crop rotation chart either on paper or electronically will help you keep tabs on which crop is planted where each year. Companion planting chart and guide for vegetable gardens. Vegetable crops in the same botanical family are often susceptible to the same diseases and insects. This page is optimized for printing. Some plants are high feeders, some are low feeders and then some are givers!!! Web crop rotation is the practice of changing or switching the crops that are grown in a particular location (e.g. Vegetable crops in the same botanical family are often susceptible to the same diseases and insects. Learn the basics in this factsheet. However, if you have a long enough season to do some succession planting, rotating crops may happen more. Leafy greens (spinach, chard, kale, cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli, spinach); The basic idea is that we do not (usually) want to grow only one crop in a bed. They also really appreciate added phosphorus (p) and potassium (k). A field, plot or garden bed) every season. Web my crop rotation guide will help you have a successful and healthy gardening season. Green sand improves the soil structure. Web plan your crop rotation direction. Each successive year, you would move each group one spot clockwise. Vegetable crops in the same botanical family are often susceptible to the same diseases and insects. They also really appreciate added phosphorus (p) and potassium (k). Web my crop rotation guide will help you have a successful and healthy gardening season. They also really appreciate added phosphorus (p) and potassium (k). Reduce disease and insect pests. Web crop rotation can be carried out in a four season cyle. Web it recommends that you divide crops into four main groups as follows: So if you grow tomatoes in one bed this year, next year, you don’t grow them in the same bed. Blood meal for added nitrogen. Web crop rotation can be carried out in a four season cyle. Some plants are high feeders, some are low feeders and then some are givers!!! These tips will ensure that your crops help balance. Legumes (bush beans, peas, pole beans, broad beans); Includes peas, beans and broad beans; Legumes, root crops, fruit crops, and leaf crops. Leafy greens (spinach, chard, kale, cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli, spinach); Learn the basics in this factsheet. Large groups of the same crop make an easy target for pests. Web garden crop rotation describes a simple system for rotating crops in your garden to minimize pests and ensure the highest yields. A simple garden map showing where each crop is planted will help you plan and plant a different crop in that spot next year. Blood meal. Crop rotation involves changing the planting location of vegetables each season to reduce damage from insect pests, limit diseases, and manage soil fertility. Green sand improves the soil structure. Web my crop rotation guide will help you have a successful and healthy gardening season. Vegetable crops in the same botanical family are often susceptible to the same diseases and insects.. Follow these rotation guides, based on your initial categorization of them. Legumes, root crops, fruit crops, and leaf crops. Web one approach to crop rotation is to divide your plants into these four basic groups: Using a cyclical system of crop rotation for growing edible crops is easy and creates a vegetable plot that is cheaper and easier to manage.. Large groups of the same crop make an easy target for pests. Some plants are high feeders, some are low feeders and then some are givers!!! The basic idea is that we do not (usually) want to grow only one crop in a bed. Imagine your garden separated into four areas, as shown in the chart at the top of. A full crop rotation cycle lasts three to four years. Legumes, root crops, fruit crops, and leaf crops. Benefits of crop rotation include: Each successive year, you would move each group one spot clockwise. Includes peas, beans and broad beans; Web one approach to crop rotation is to divide your plants into these four basic groups: Crop rotation involves changing the planting location of vegetables each season to reduce damage from insect pests, limit diseases, and manage soil fertility. Follow these rotation guides, based on your initial categorization of them. Plants require varying amounts of minerals and nutrients to grow. Web when planning crop rotations, keep a garden log, draw a map, create a diagram, or take a photo to help you remember where vegetables are planted each year and your plans for upcoming years. Web plan your crop rotation direction. Some plants are high feeders, some are low feeders and then some are givers!!! Learn the basics in this factsheet. Root vegetables (radish, carrot, potato, onion, garlic, beet, rutabaga, sweet potato, shallots); Legumes (bush beans, peas, pole beans, broad beans); Web vegetable crop rotation chart.
How to Practice Crop Rotation (Benefits Explained) Homestead and Chill
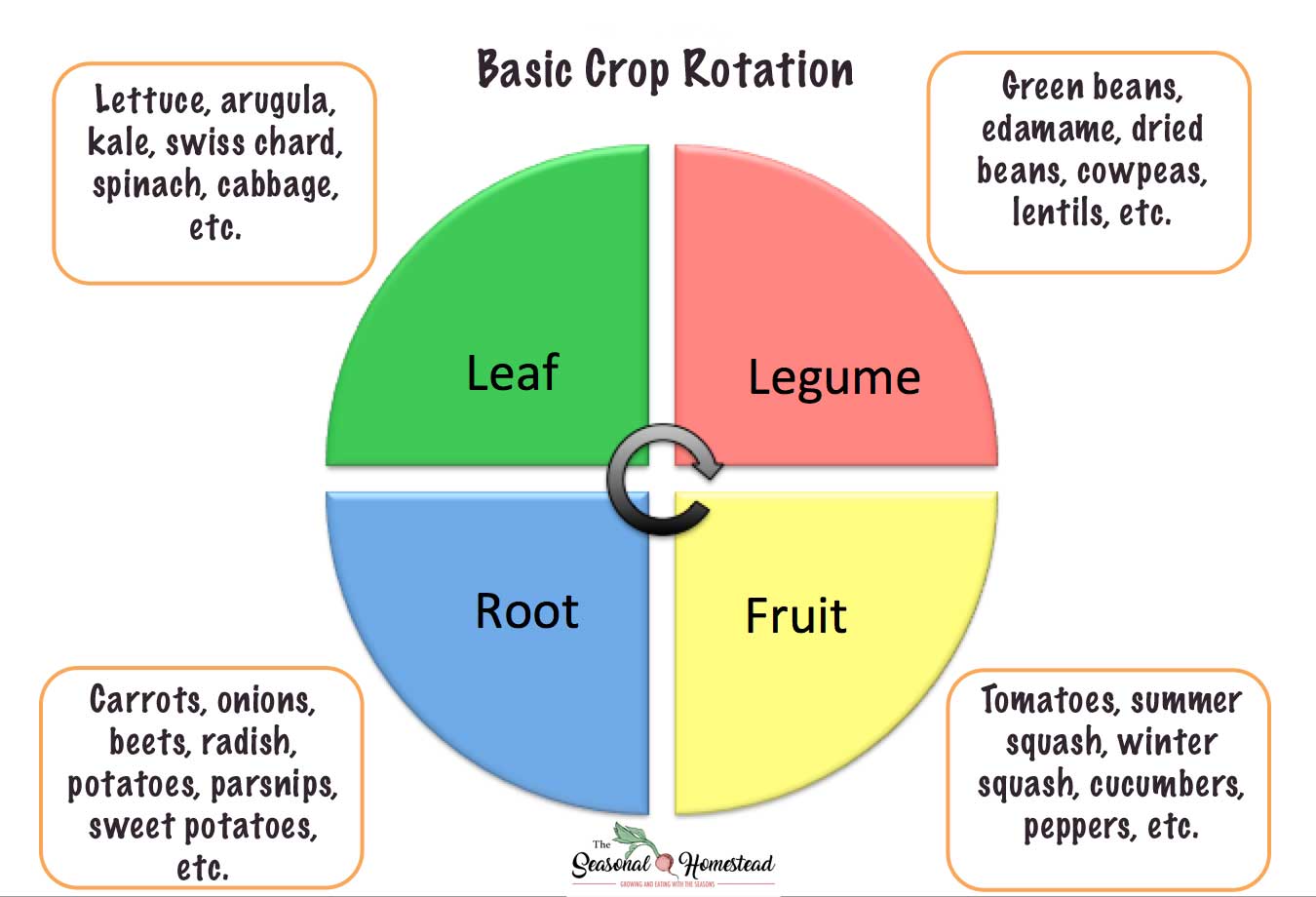
Crop Rotation Ideas for an Organic Vegetable Garden The Seasonal
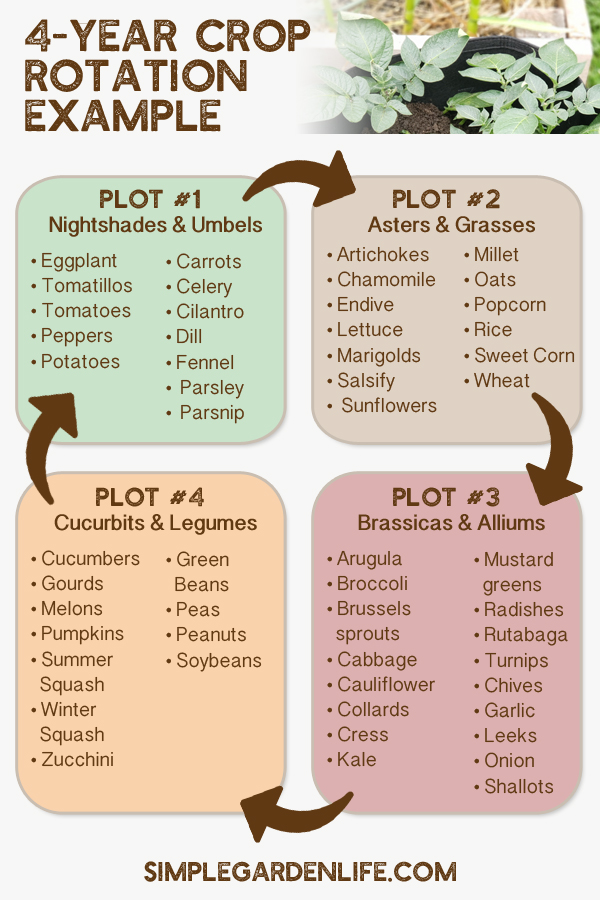
How To Rotate Garden Crops And Why It's So Important For Your Plants!

Crop Rotation Ideas for an Organic Vegetable Garden The Seasonal

Crop Rotation Chart (peace love and vegetables veggie gardens) Crop
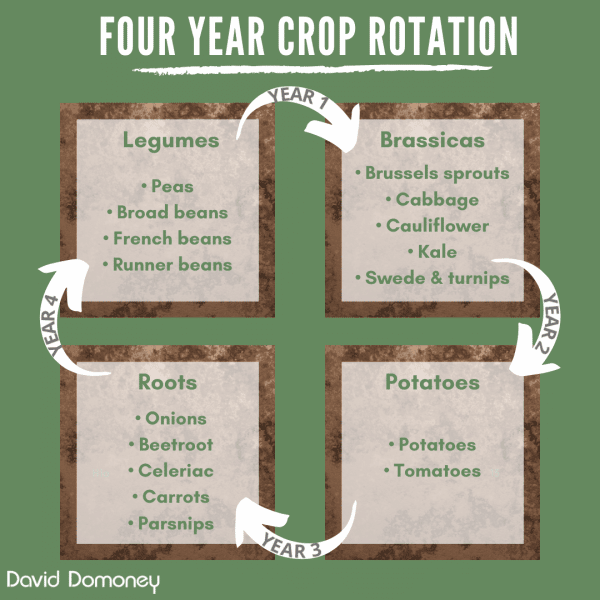
rotation

Crop Rotation The Garden Academy
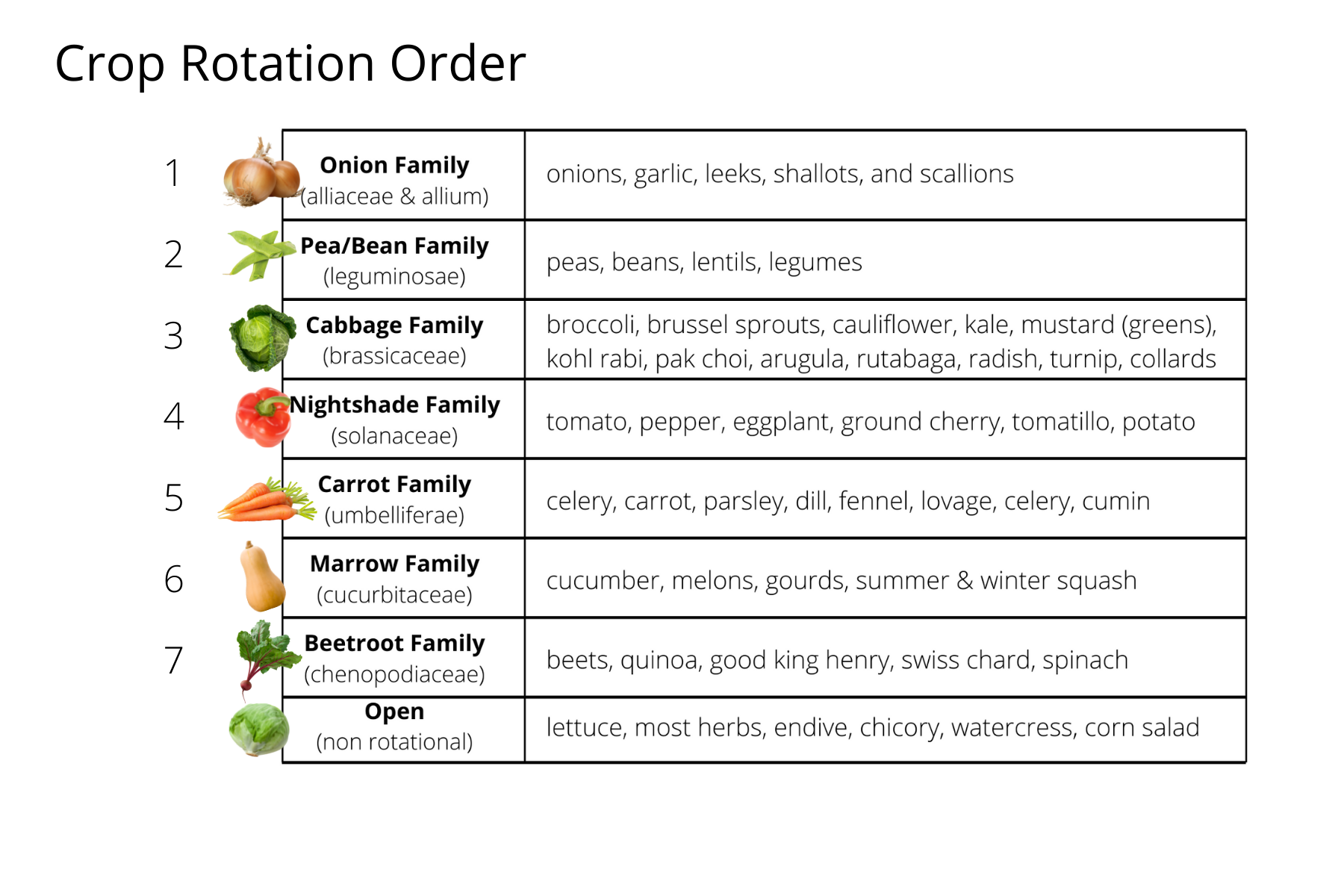
Vegetable crop rotation complete guide — Living Wyld

The Basics of Crop Rotation Hook's Greenhouse
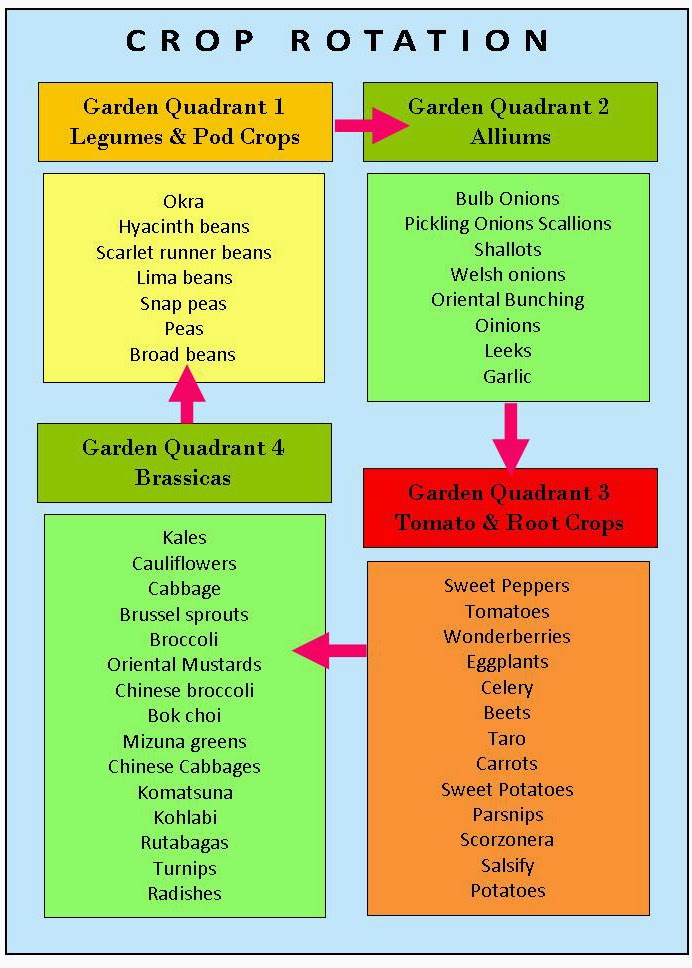
Durham Council of Garden Clubs Vegetable Crop Rotation Healthier Soil
Vegetable Crops In The Same Botanical Family Are Often Susceptible To The Same Diseases And Insects.
Common Vegetables And Their Plant Family Classifications.
Web Crop Rotation Is The Practice Of Changing Or Switching The Crops That Are Grown In A Particular Location (E.g.
A Field, Plot Or Garden Bed) Every Season.
Related Post: