Galvanic Chart Of Metals
Galvanic Chart Of Metals - Below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. To minimize galvanic corrosion, select fasteners based on their material compatibility with the. Web table 1 gives the galvanic series for various metals, as determined in seawater. The closer a metal or an alloy is in the galvanic series, the less are the effects of galvanic corrosion compared to those metals far. The metals are ordered from the most reactive at the bottom of the table to the least reactive at the top. Enter keyword or document title. Web the galvanic series chart below shows metals and their electrochemical voltage range (relative activity in flowing sea water). The chart can be used to determine the likelihood of a galvanic reaction, and galvanic corrosion or bimetallic corrosion, between two different metals in a seawater environment. The list begins with the more active (anodic) metal and proceeds down the to the least active (cathodic) metal of the galvanic series. When is stainless steel passive or active. Galvanic voltage relative to standard electrode. The closer together the material are on the chart to the right, the less galvanic action will. There are three conditions that must exist for galvanic corrosion to occur. To minimize galvanic corrosion, select fasteners based on their material compatibility with the. Web table 1 gives the galvanic series for various metals, as determined. Galvanic voltages relative to gold. To minimize galvanic corrosion, select fasteners based on their material compatibility with the. The environment generally used is seawater. Web the following galvanic table lists metals in the order of their relative activity in seawater environment. Web view this chart of galvanic compatibility. First there must be two electrochemically dissimilar metals present. Web galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, in the presence of an electrolyte. The metals are ordered from the most reactive at the bottom of the table to the. The metals are ordered from the most reactive at the bottom of the table to the least reactive at the top. Web a chart depicting the galvanic series for some common metals in a frequently encountered conducting solution, seawater, is included in figure 1. Metals nearer the top of the table are less noble metals and have a greater tendency. The chart can be used to determine the likelihood of a galvanic reaction, and galvanic corrosion or bimetallic corrosion, between two different metals in a seawater environment. Below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. Although graphite is not a metal, its conductivity is high enough that it can cause galvanic corrosion, so it is also included in table. The following galvanic table lists metals in the order of their relative activity in seawater environment. The metals are ordered from the most reactive at the bottom of the table to the least reactive at the top. (noble metals are those that are resistant to corrosion and oxidation.) when two metals are immersed in an electrolyte, while also being connected. There are three conditions that must exist for galvanic corrosion to occur. Enter keyword or document title. Web galvanic series of metals in seawater. A typical rule of thumb is that voltage differences of 0.2 volts or more suggest a galvanic corrosion risk. Galvanic voltages relative to gold. Web below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming into contact with another metal. The closer together the material are on the chart to the right, the less galvanic action will. The list begins with the more active (anodic). Galvanic series in seawater at 25 o c (77 o f) are indicated below with the most noble at top. We also provide other helpful methods for avoiding galvanic corrosion. Web table 1 gives the galvanic series for various metals, as determined in seawater. The closer a metal or an alloy is in the galvanic series, the less are the. Web the following galvanic table lists metals in the order of their relative activity in seawater environment. Galvanic voltage relative to standard electrode. Metals nearer the top of the table are less noble metals and have a greater tendency to lose electrons than the more noble metals found lower on the list. Web a chart depicting the galvanic series for. Web galvanic corrosion (some times called dissimilar metal corrosion) is the process by which the materials in contact with each other oxidizes or corrodes. Web the galvanic series of metals (right) lists metals and alloys in decreasing order of electrical activity. To minimize galvanic corrosion, select fasteners based on their material compatibility with the. Web the following galvanic table lists metals in the order of their relative activity in seawater environment. Below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. No literature found with entered search criteria. Though the order of metals in a galvanic series remains the same in most conducting solutions, some. Web below, we give a brief overview of galvanic corrosion and provide a galvanic corrosion chart to help fabricators and machinists avoid using the wrong metal combinations. Web galvanic series it is a list of metal and alloys based on their relative potentials in a specified environment. The environment generally used is seawater. Galvanic voltage relative to standard electrode. Web the galvanic series chart below shows metals and their electrochemical voltage range (relative activity in flowing sea water). When is stainless steel passive or active. (noble metals are those that are resistant to corrosion and oxidation.) when two metals are immersed in an electrolyte, while also being connected externally by a conductor, the less noble metal experiences galvanic corrosion. The closer a metal or an alloy is in the galvanic series, the less are the effects of galvanic corrosion compared to those metals far. Although graphite is not a metal, its conductivity is high enough that it can cause galvanic corrosion, so it is also included in table 1.
Galvanic Chart Of Metals
![Galvanic Corrosion [with Chart] EngineerExcel](https://engineerexcel.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/galvanic-corrosion-chart.png)
Galvanic Corrosion [with Chart] EngineerExcel

Galvanic Chart Of Metals
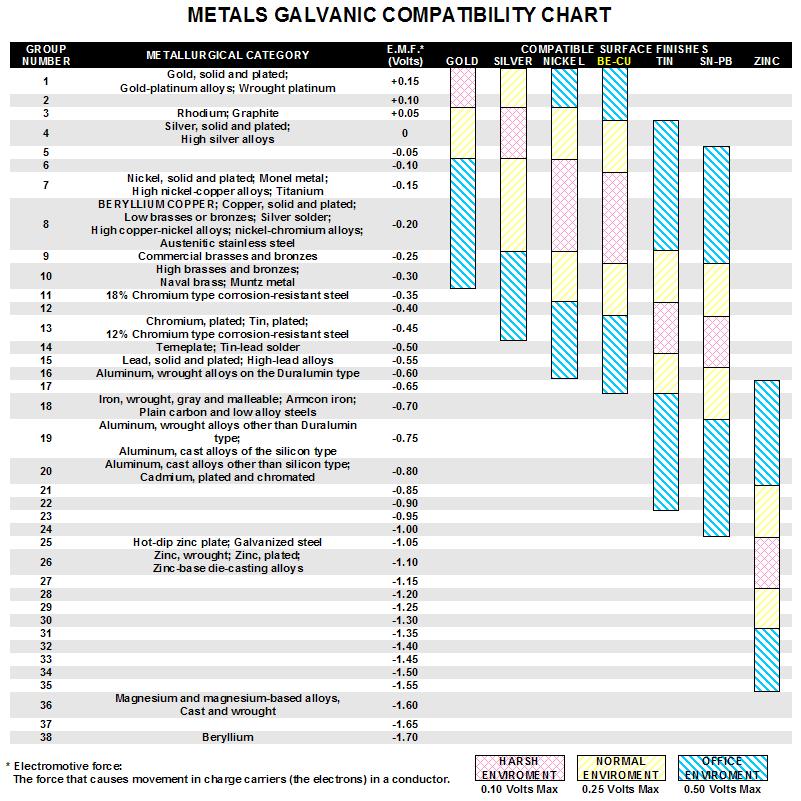
Omega Shielding Products Metals Galvanic Compatibility Chart

An Introduction to the Galvanic Series Galvanic Compatibility and
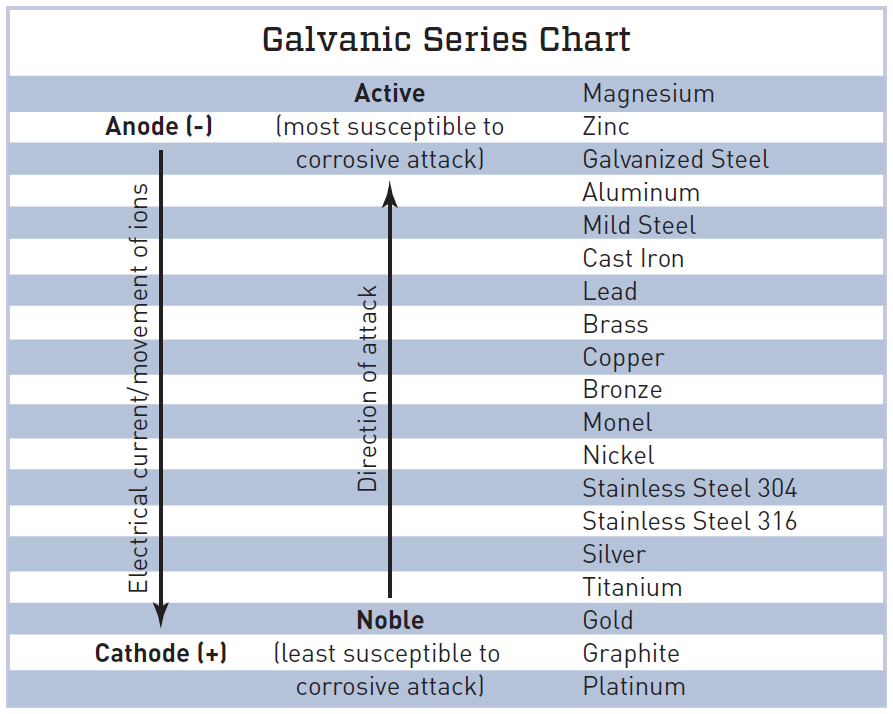
Separating Galvanic Metals JLC Online
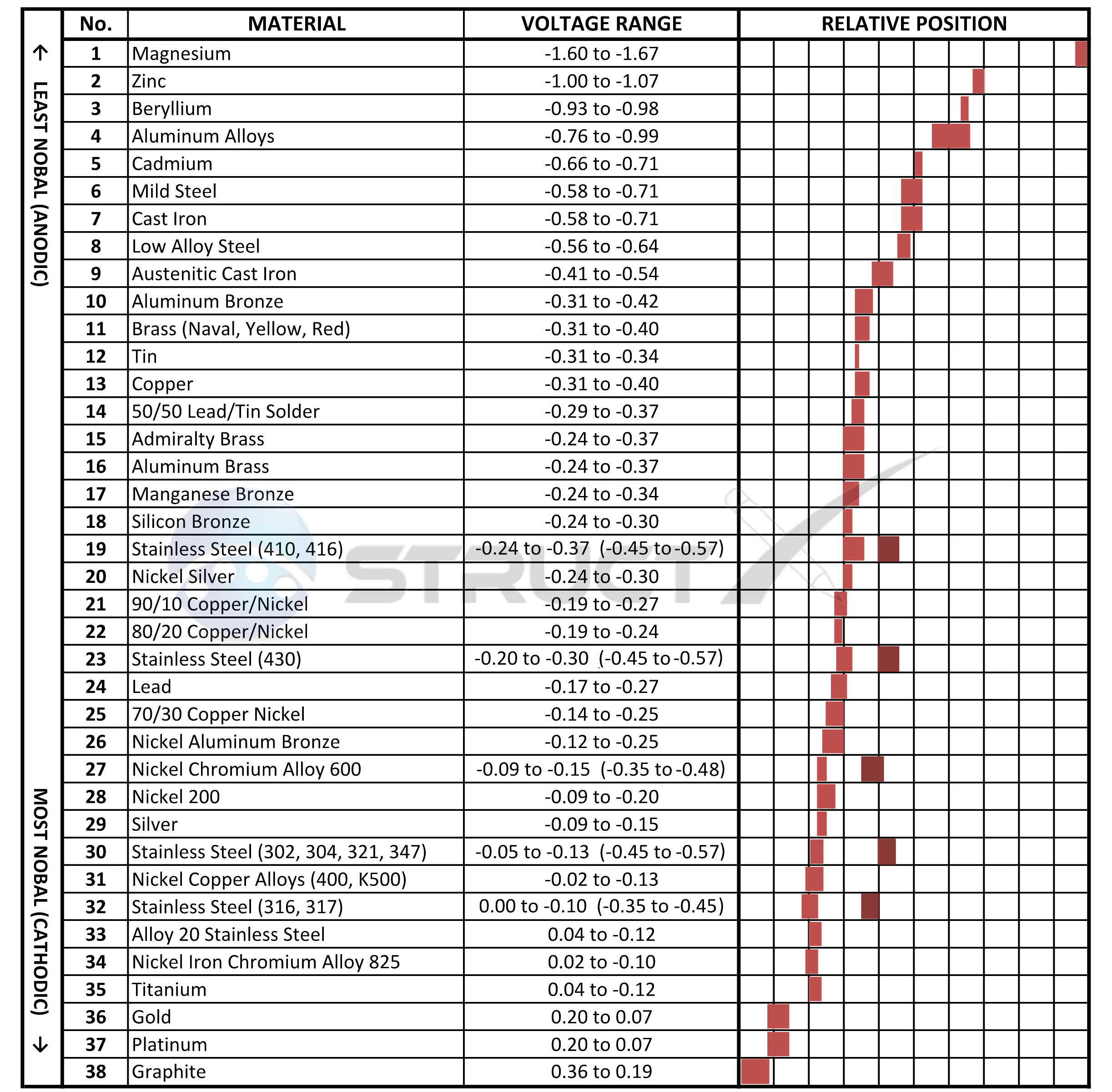
Galvanic Series (electrochemical series)
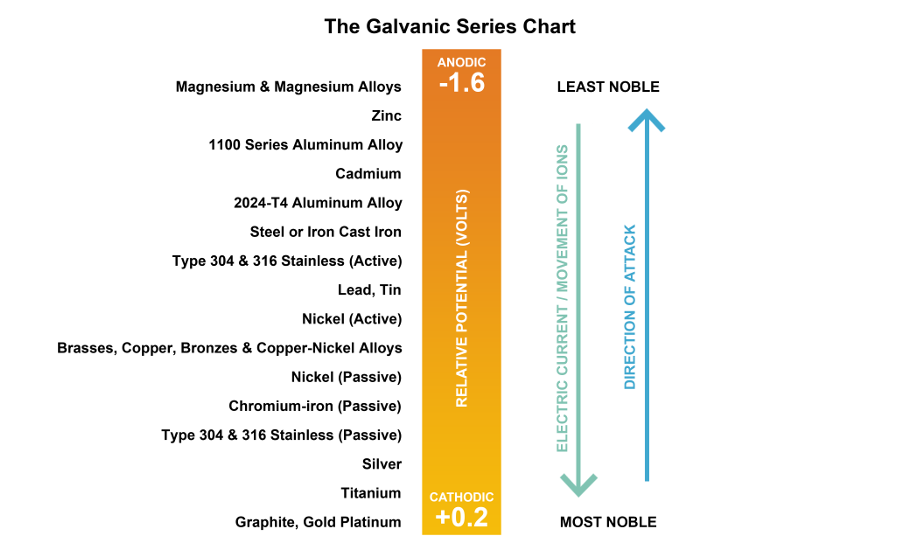
Galvanic Chart Of Metals

Galvanic Corrosion Chart Metals

Metals Galvanic Compatibility Chart Online Shopping
The Closer Together The Material Are On The Chart To The Right, The Less Galvanic Action Will.
There Are Three Conditions That Must Exist For Galvanic Corrosion To Occur.
Below Is A Galvanic Reaction Chart For Dissimilar Metals.
Web Simply Speaking, Galvanic Corrosion Is The Damage Or Deterioration Of Metal That Takes Place Between Dissimilar Metals Because Of An Electrochemical Reaction.
Related Post: