First Derivative Sign Chart
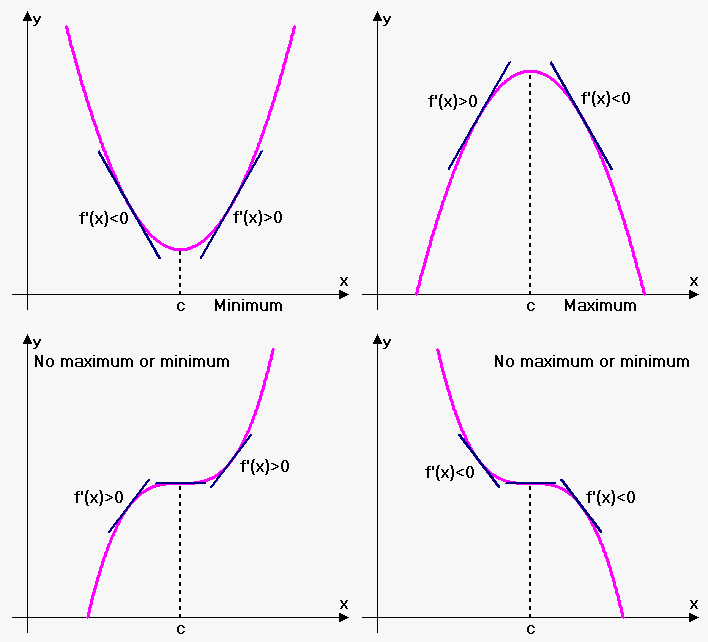
First Derivative Sign Chart - Web how does the first derivative of a function reveal important information about the behavior of the function? Web the top graph is the original function, f (x), and the bottom graph is the derivative, f’ (x). The stationary points are written on the sign diagram. Here, it’s important to keep your head in the game. Every order of derivative after is just the derivative of the function before that. Web 4.5.1 explain how the sign of the first derivative affects the shape of a function’s graph. You’re looking to say something about the function f ( x) based on its derivative f ′ ( x). State the first derivative test for critical points. Web we create a first derivative sign chart to summarize the sign of f' on the relevant intervals along with the corresponding behavior of f. They help you find maxima, minima and saddle points. 4.5.2 state the first derivative test for critical points. The stationary points are written on the sign diagram. Web explain how the sign of the first derivative affects the shape of a function’s graph. Web the graph of the derivative 𝑓 ′ of a function 𝑓 is shown. Use concavity and inflection points to explain how the sign of the. Web what information does the first derivative tell you? This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the first derivative test. State the first derivative test for critical points. Consider the graph of the function. State the first derivative test for critical points. Web we create a first derivative sign chart to summarize the sign of f' on the relevant intervals along with the corresponding behavior of f. To establish a sign chart (number lines) for f ' , first set f ' equal to zero and then solve for x. Get a grid of sign charts for a function and its first. This is the sign chart for our function: Web explain how the sign of the first derivative affects the shape of a function’s graph. Web here are instruction for establishing sign charts (number line) for the first and second derivatives. In this question, we are given the curve of 𝑦 = 𝑓 ′ ( 𝑥) and asked to find the. This is how you do it: State the first derivative test for critical points. What do you notice about each pair? Explain the concavity test for a function over an open interval. Web we create a first derivative sign chart to summarize the sign of f' on the relevant intervals along with the corresponding behavior of f. In the regions between these points, a positive sign is written when the function is increasing and a negative sign is written when the function is decreasing. This is the sign chart for our function: Web 493k views 6 years ago new calculus video playlist. Graph of derivative to original function. Web 4.5.1 explain how the sign of the first. In the regions between these points, a positive sign is written when the function is increasing and a negative sign is written when the function is decreasing. Graph of derivative to original function. Web we create a first derivative sign chart to summarize the sign of f' on the relevant intervals along with the corresponding behavior of f. Web what. To establish a sign chart (number lines) for f ' , first set f ' equal to zero and then solve for x. Web derivativesigncharts | wolfram function repository. Here, it’s important to keep your head in the game. This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the first derivative test. Use concavity and inflection points to explain how. The stationary points are written on the sign diagram. 4.5.2 state the first derivative test for critical points. See the adjoining sign chart for the first derivative, f '. Web we create a first derivative sign chart to summarize the sign of \(f'\) on the relevant intervals, along with the corresponding behavior of \(f\text{.}\) figure \(\pageindex{4}\). Web 493k views 6. Web f' is the derivative of f, and f'' is the second derivative of f, which is the first derivative of f'. Web 493k views 6 years ago new calculus video playlist. In this question, we are given the curve of 𝑦 = 𝑓 ′ ( 𝑥) and asked to find the intervals on which 𝑓 ( 𝑥) is increasing.. Web what follows is the first derivative sign chart for a function which has a positive derivative to the left of x = 0 , a negative derivative to the right of x = 0, and zero derivative at x = 0. Now determine a sign chart for the first derivative, f ' : Consider the graph of the function. Web how does the first derivative of a function reveal important information about the behavior of the function? Every order of derivative after is just the derivative of the function before that. Graph of derivative to original function. Now determine a sign chart for the second derivative, f '' : Web the graph of the derivative 𝑓 ′ of a function 𝑓 is shown. Resourcefunction [ derivativesigncharts] [ f, x] creates a grid of sign charts for f(x), f' (x) and f'' (x). This is the sign chart for our function: Web what information does the first derivative tell you? Web this can be done in many ways, but we like using a sign chart. Web the top graph is the original function, f (x), and the bottom graph is the derivative, f’ (x). Web explain how the sign of the first derivative affects the shape of a function’s graph. State the first derivative test for critical points. They help you find maxima, minima and saddle points.
3.3 First Derivative Test / Slope Shuford's Site
First Derivative Test eMathHelp
![[Math] How to identify the graph of a function and the graphs of its](https://i.stack.imgur.com/vze2T.png)
[Math] How to identify the graph of a function and the graphs of its

next well construct a first derivative sign chart for f the 1 all
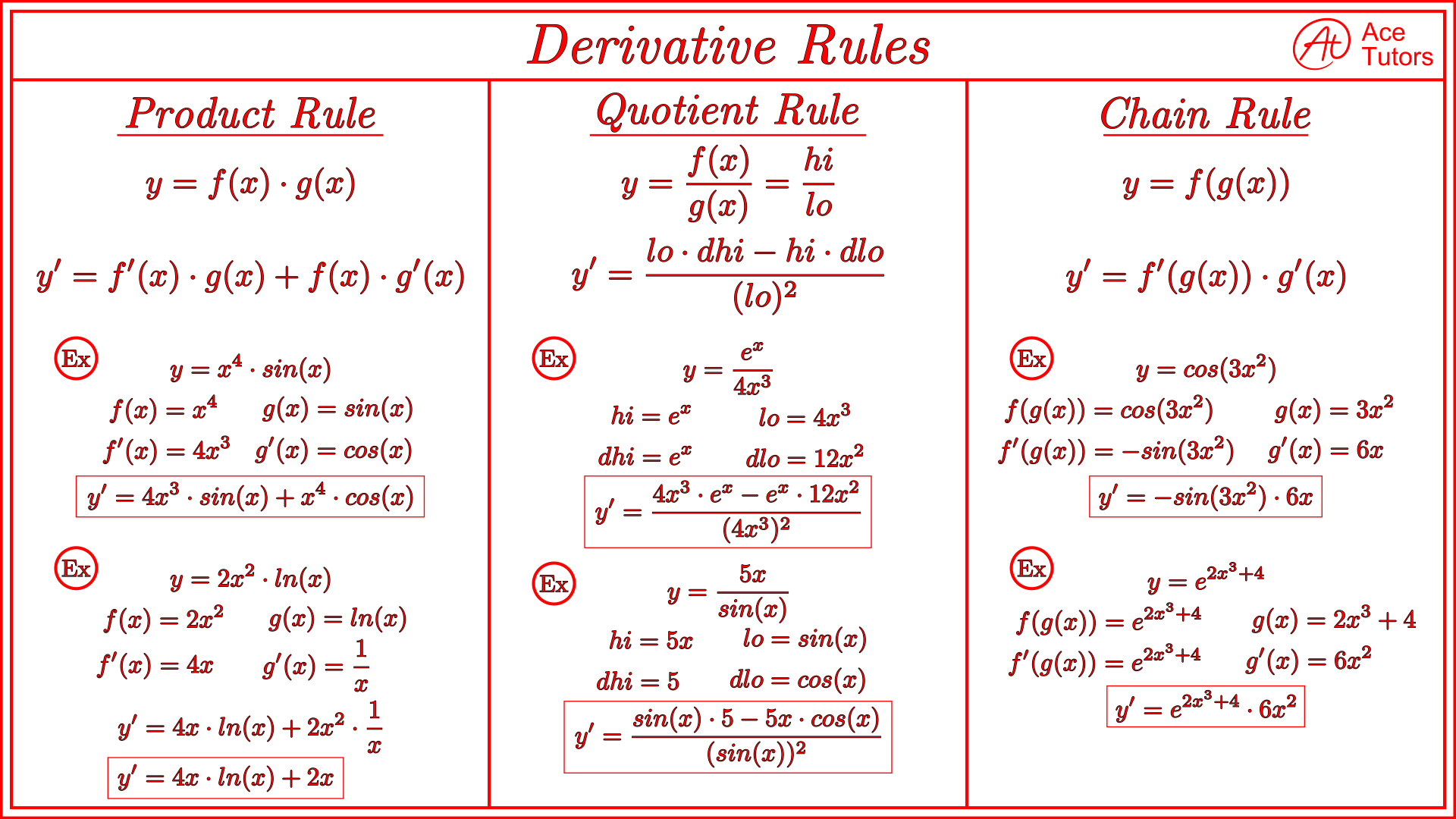
Derivative Rules Cheat Sheet Calculus Ace Tutors Blog
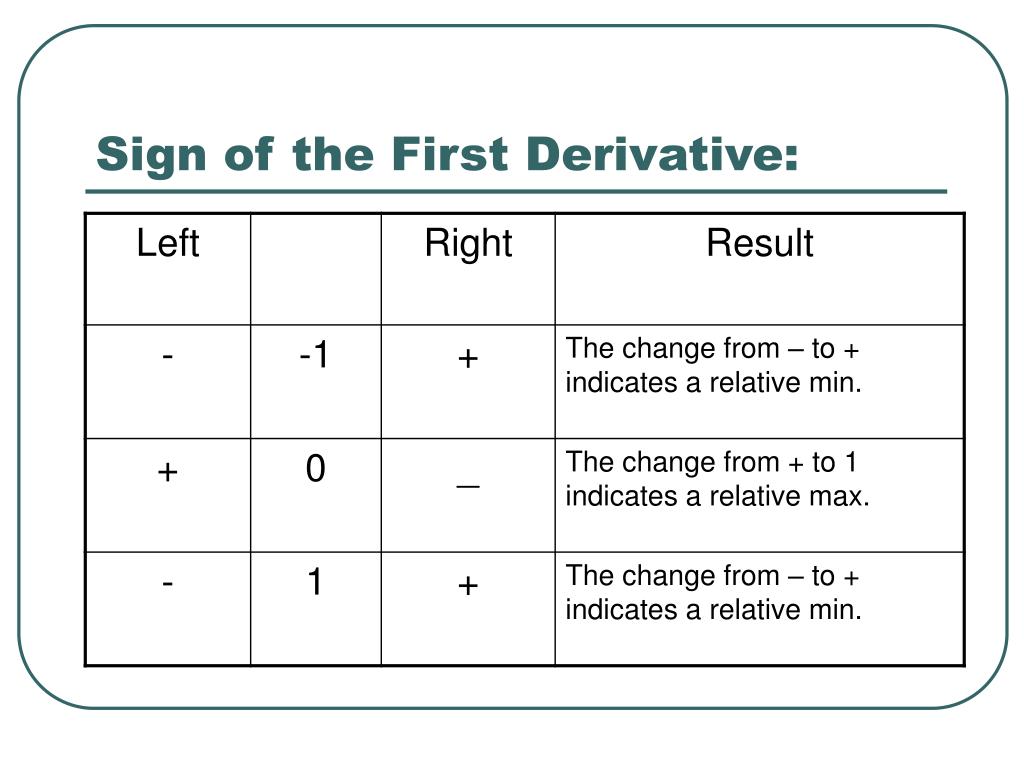
PPT Applications of Derivatives PowerPoint Presentation, free

Making and Interpreting Sign Charts (First and Second Derivatives

How to Understand Sign Diagrams

Chart Of Derivatives
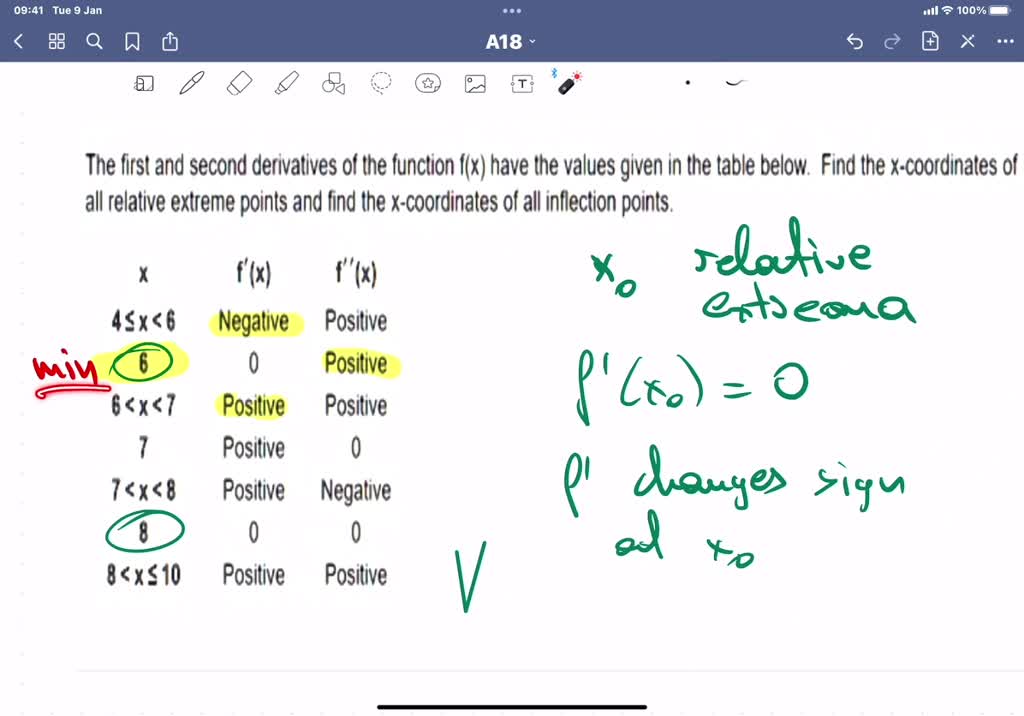
SOLVED Below you see the first derivative sign chart (the sign chart
4.5.3 Use Concavity And Inflection Points To Explain How The Sign Of The Second Derivative Affects The Shape Of.
How Do You Find The Interval In Which The Function F (X) = 2X3 + 3X2 + 180X Is Increasing Or Decreasing?
In A Sign Chart, We Pick A Test Value At Each Interval That Is Bounded By The Points We Found In Step 2 And Check The Derivative's Sign On That Value.
Web The First Derivative Of The Function F(X), Which We Write As F0(X) Or As Df Dx, Is The Slope Of The Tangent Line To The Function At The Point X.
Related Post: