Exothermic Reaction Chart
Exothermic Reaction Chart - In an exothermic reaction or process, energy is released into the environment, usually in the form of heat, but also electricity, sound, or light. An energy diagram represents this change. If δh is negative, the process releases heat to the surroundings and is said to be exothermic. Web updated on september 12, 2019. In simple terms, the endothermic reactions absorb energy from the surrounding that is in the form of heat. This information can be shown as. Next, students explore the relationship between an observed change in temperature and the classification of a change as. Chemical reactions can result in energy being released (exothermic) or energy being absorbed (endothermic). Exothermic reactions are reactions that release energy into the environment in the form of heat. Many chemical reactions release energy in the form of heat, light, or sound. Web if δh is positive, the process absorbs heat from the surroundings and is said to be endothermic. Specifically, the combustion of 1 mol 1 mol of methane releases 890.4 kilojoules of heat energy. We can use the law of conservation of energy to determine how that energy is transferred between a system and its surroundings. Web in chemical reactions,. Web an exothermic reaction is a reaction in which energy is released in the form of light or heat. There is usually a temperature change. When methane gas is combusted, heat is released, making the reaction exothermic. Thus in an exothermic reaction, energy is transferred into the surroundings rather than taking energy from the surroundings as in an endothermic reaction.. An explanation of this graph is as follows. The opposite is the case for a reaction that consumes heat when it occurs. Web this graph shows the change in energy as the reaction progresses from reactants to products. This is represented as dh on the diagram. In an exothermic reaction or process, energy is released into the environment, usually in. In a reaction, any reaction, the same general trend occurs. When a reaction absorbs or emits heat at constant pressure, the enthalpy changes. Specifically, the combustion of 1 mol 1 mol of methane releases 890.4 kilojoules of heat energy. Web in thermochemistry, an exothermic reaction is a reaction for which the overall standard enthalpy change δ h ⚬ is negative.. The difference in energy between the reactants and products is the amount of heat energy transferred to the surroundings. An endothermic reaction or process takes place when the system absorbs heat energy from the surrounding environment. In a reaction, any reaction, the same general trend occurs. The beaker now contains sodium chloride and. When methane gas is combusted, heat is. Web an exothermic reaction is defined as a reaction that releases heat and has a net negative standard enthalpy change. Chemical reactions can result in energy being released (exothermic) or energy being absorbed (endothermic). Web e x o t h e r m i c p r o c e s s. Examples include any combustion process, rusting of iron,. Next, students explore the relationship between an observed change in temperature and the classification of a change as. Web e x o t h e r m i c p r o c e s s. An explanation of this graph is as follows. What is an endothermic reaction? Web in chemical reactions, bond breaking requires an input of energy. Web if δh is positive, the process absorbs heat from the surroundings and is said to be endothermic. Exothermic, endothermic, & chemical change. What is an endothermic reaction? Thus in an exothermic reaction, energy is transferred into the surroundings rather than taking energy from the surroundings as in an endothermic reaction. Such a reaction is said to be endothermic. A reaction for which the overall standard gibbs energy change δ g ⚬ is negative. [2]. Examples include any combustion process, rusting of iron, and freezing of water. The beaker now contains sodium chloride and. Web the peaks in energy diagrams for both endothermic and exothermic reaction energy diagrams are known as the transition state or the activation complex. On. The substances involved in the reaction are the system, and the engine and. Many chemical reactions release energy in the form of heat, light, or sound. In an exothermic reaction, the change in enthalpy ( δh) will be negative. The energy diagram of endothermic and exothermic reactions. Specifically, the combustion of 1 mol 1 mol of methane releases 890.4 kilojoules. Exothermic, endothermic, & chemical change. Web the typical energy level diagram for an exothermic reaction is shown below: When methane gas is combusted, heat is released, making the reaction exothermic. The thermometer shows the initial temperature, which is room temperature. The beaker now contains sodium chloride and. Thus in an exothermic reaction, energy is transferred into the surroundings rather than taking energy from the surroundings as in an endothermic reaction. In a reaction, any reaction, the same general trend occurs. Specifically, the combustion of 1 mol 1 mol of methane releases 890.4 kilojoules of heat energy. A reaction for which the overall standard gibbs energy change δ g ⚬ is negative. [2]. Web this graph shows the change in energy as the reaction progresses from reactants to products. Examples include any combustion process, rusting of iron, and freezing of water. Web the reaction of gasoline and oxygen is exothermic. The term is often confused with exergonic reaction, which iupac defines as . Web exothermic reactions transfer energy to the surroundings and the temperature of the surroundings increases. The substances involved in the reaction are the system, and the engine and. Sodium hydroxide solution is poured into a beaker of hydrochloric acid.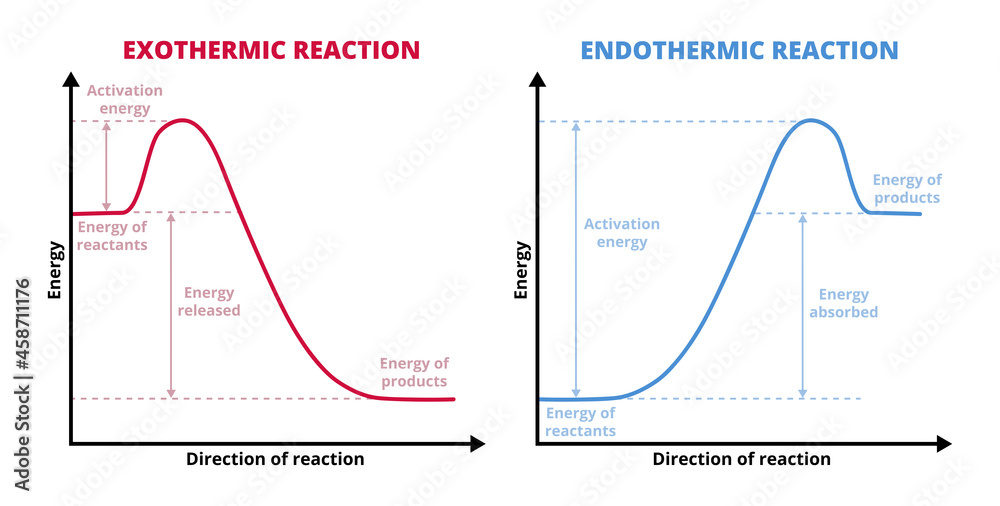
Vector graphs or charts of endothermic and exothermic reactions
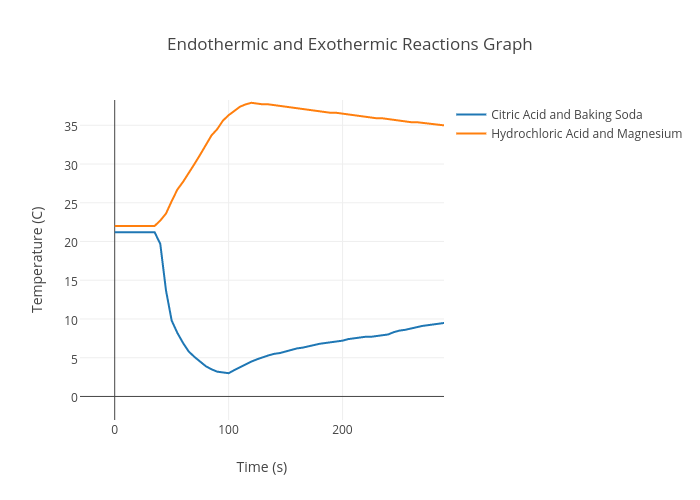
Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions Graph scatter chart made by
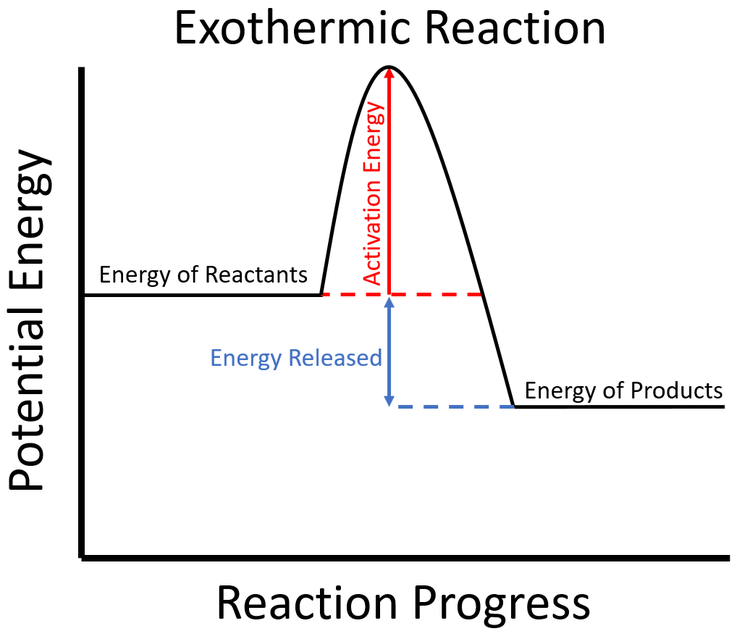
Exothermic Key Stage Wiki
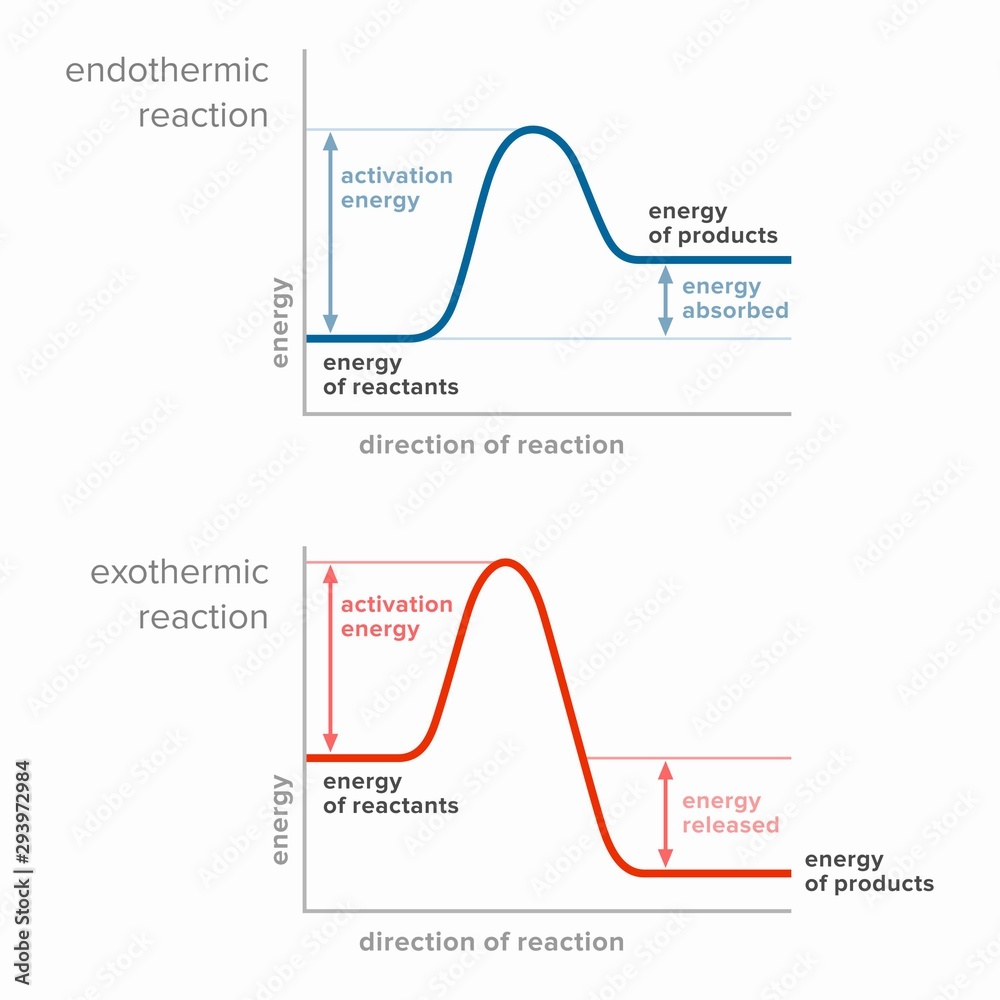
Activation energy in endothermic and exothermic reactions. Stock
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/endothermic-and-exothermic-reactions-602105_final-c4fdc462eb654ed09b542da86fd447e2.png)
Endothermic and Exothermic Chemical Reactions

Exothermic energy diagram. MCAT Pinterest Diagram, Chemistry and
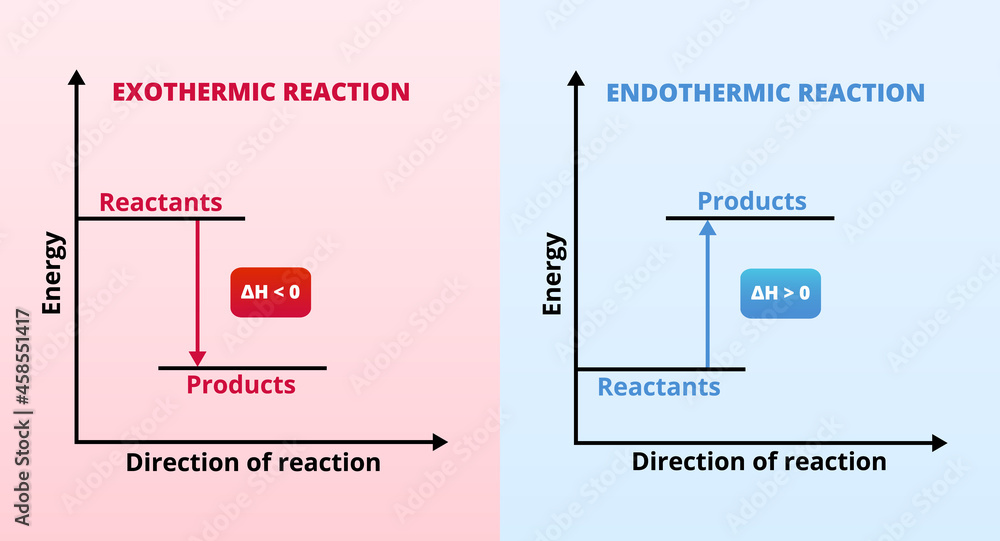
Vecteur Stock Vector graphs or charts of endothermic and exothermic

(A) An exothermic reaction system during normal operation. (B
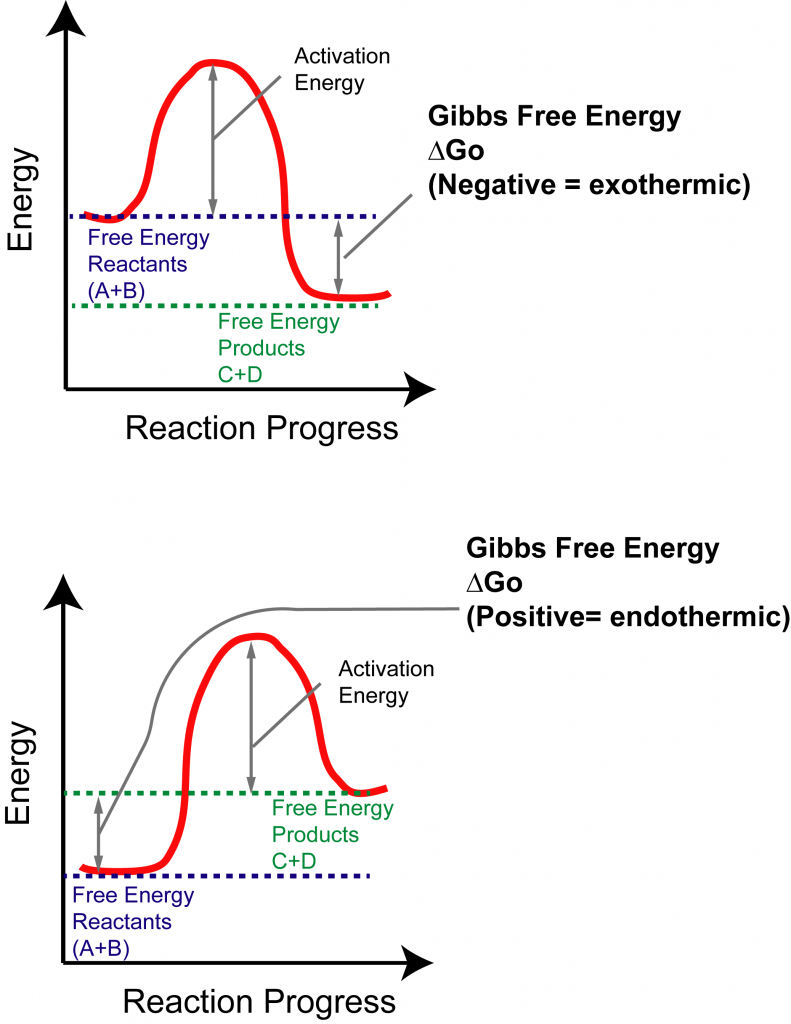
How to Interpret Thermodynamics of Reactions

Exothermic and Endothermic Processes Introduction to Chemistry
Web E X O T H E R M I C P R O C E S S.
Endothermic Reactions Take In Energy And The Temperature Of The Surroundings.
A Chemical Reaction Always Involves A Change In Energy.
Chemical Reactions Can Result In Energy Being Released (Exothermic) Or Energy Being Absorbed (Endothermic).
Related Post: