Excitationcontraction Coupling Flow Chart
Excitationcontraction Coupling Flow Chart - Web excitation contraction (ec) coupling electrical event action potential generated in muscle fiber memb. Web the mechanism of muscle contraction: Due to depolarization of motor end plate ap. It involves a steeply voltage. Medically reviewed by anatomy team. Release of neurotransmitter from acetylcholine. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like action potential, acetylcholine (ach), synaptic cleft and more. Specifically, it is the process by which the action potential causes a sufficient increase in. Web ec coupling results in the sequential contraction of the heart muscles that allows blood to be pumped, first to the lungs (pulmonary circulation) and then around the rest of the. In the heart, the mechanism. Sarcoendoplasmic reticulum ca 2+ adenosine. Release of neurotransmitter from acetylcholine. Sarcomeres, action potential, and the neuromuscular junction Web ec coupling results in the sequential contraction of the heart muscles that allows blood to be pumped, first to the lungs (pulmonary circulation) and then around the rest of the. Medically reviewed by anatomy team. Sarcomeres, action potential, and the neuromuscular junction Web excitation contraction (ec) coupling electrical event action potential generated in muscle fiber memb. Specifically, it is the process by which the action potential causes a sufficient increase in. Web the mechanism of muscle contraction: In the heart, the mechanism. Sarcoendoplasmic reticulum ca 2+ adenosine. Web key to the figure: Web excitation contraction (ec) coupling electrical event action potential generated in muscle fiber memb. Release of neurotransmitter from acetylcholine. In the heart, the mechanism. Medically reviewed by anatomy team. Web key to the figure: Due to depolarization of motor end plate ap. Web the mechanism of muscle contraction: Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like action potential, acetylcholine (ach), synaptic cleft and more. Study material bio 315_davis t_sp22 flow chart skeletal muscle excitation, coupling, contraction action potential (voltage change). In the heart, the mechanism. It involves a steeply voltage. Web excitation contraction (ec) coupling electrical event action potential generated in muscle fiber memb. Sarcomeres, action potential, and the neuromuscular junction Web excitation contraction (ec) coupling electrical event action potential generated in muscle fiber memb. Web key to the figure: Due to depolarization of motor end plate ap. Specifically, it is the process by which the action potential causes a sufficient increase in. Sarcoendoplasmic reticulum ca 2+ adenosine. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like action potential, acetylcholine (ach), synaptic cleft and more. Web excitation contraction (ec) coupling electrical event action potential generated in muscle fiber memb. Sarcomeres, action potential, and the neuromuscular junction Medically reviewed by anatomy team. Web key to the figure: Web ec coupling results in the sequential contraction of the heart muscles that allows blood to be pumped, first to the lungs (pulmonary circulation) and then around the rest of the. Due to depolarization of motor end plate ap. Sarcomeres, action potential, and the neuromuscular junction Medically reviewed by anatomy team. Web excitation contraction (ec) coupling electrical event action potential. Release of neurotransmitter from acetylcholine. Web key to the figure: Study material bio 315_davis t_sp22 flow chart skeletal muscle excitation, coupling, contraction action potential (voltage change). In the heart, the mechanism. Sarcoendoplasmic reticulum ca 2+ adenosine. Study material bio 315_davis t_sp22 flow chart skeletal muscle excitation, coupling, contraction action potential (voltage change). Due to depolarization of motor end plate ap. Web the mechanism of muscle contraction: Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like action potential, acetylcholine (ach), synaptic cleft and more. Web ec coupling results in the sequential contraction of the heart muscles that. Sarcomeres, action potential, and the neuromuscular junction Web key to the figure: Sarcoendoplasmic reticulum ca 2+ adenosine. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like action potential, acetylcholine (ach), synaptic cleft and more. It involves a steeply voltage. Release of neurotransmitter from acetylcholine. In the heart, the mechanism. Web ec coupling results in the sequential contraction of the heart muscles that allows blood to be pumped, first to the lungs (pulmonary circulation) and then around the rest of the. Web excitation signalling of action potentials from the motor neuron are coupled with calcium release. Study material bio 315_davis t_sp22 flow chart skeletal muscle excitation, coupling, contraction action potential (voltage change). Web the mechanism of muscle contraction: Specifically, it is the process by which the action potential causes a sufficient increase in.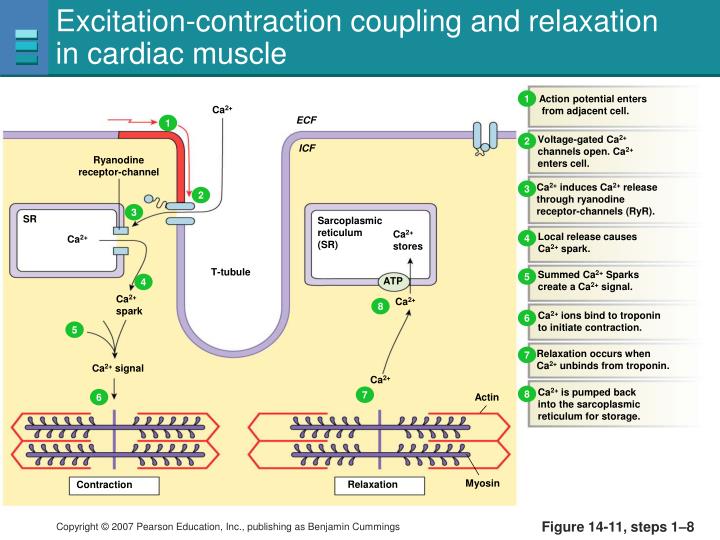
PPT Cardiovascular Physiology PowerPoint Presentation ID6592110
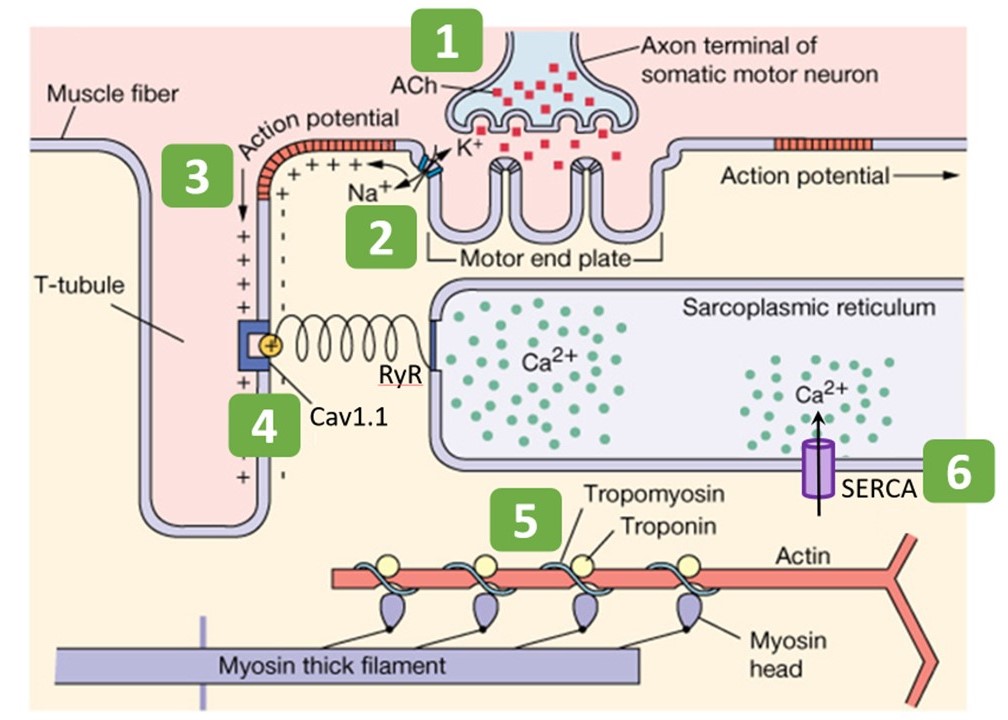
Muscle Physiology Muscle Physiology

38.19 Muscle Contraction and ExcitationContraction
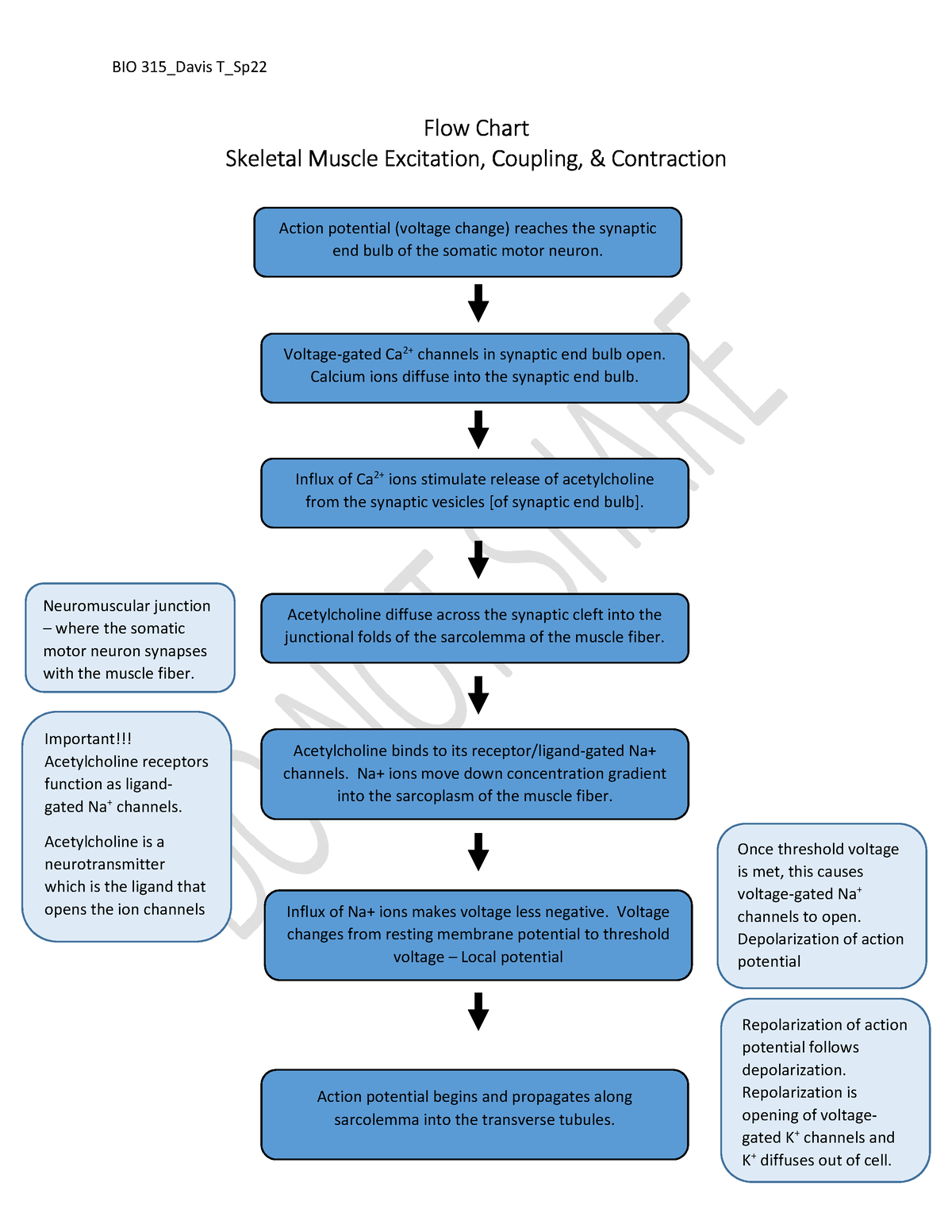
Flow Chart muscle excitation coupling contraction BIO 315_Davis T_Sp

Muscle Contraction Flow Chart

Diagram showing the process of excitationcontraction coupling in the
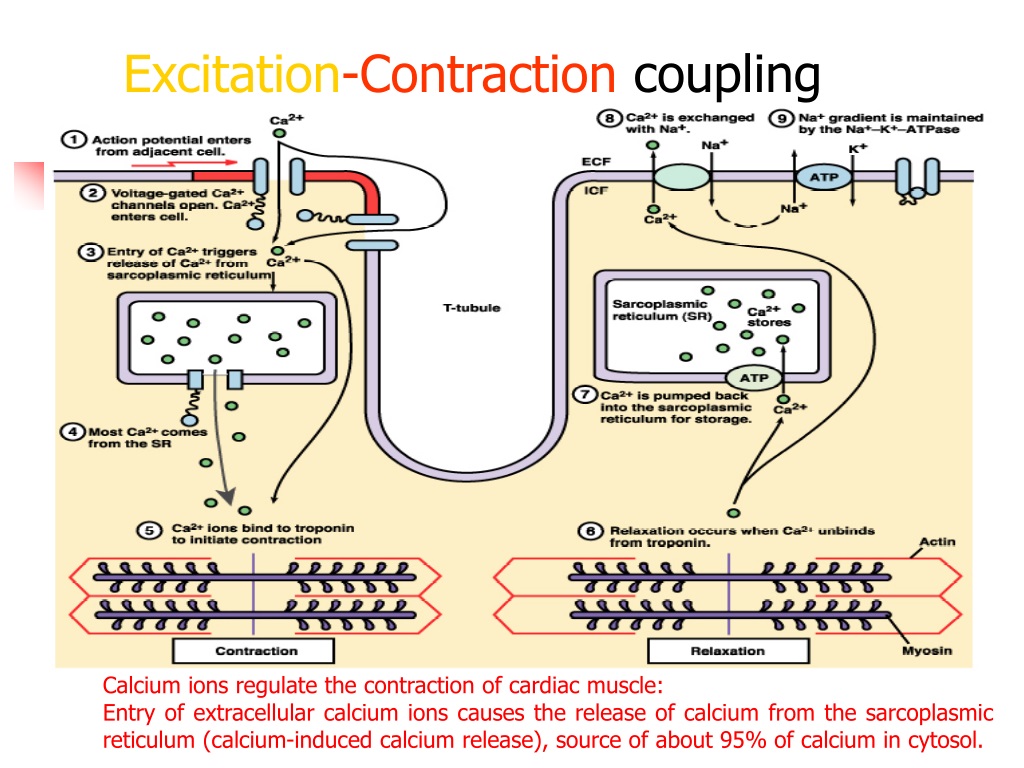
PPT CARDIAC MUSCLE CONTRACTILE MECHANISM OF CARDIAC MUSCLE
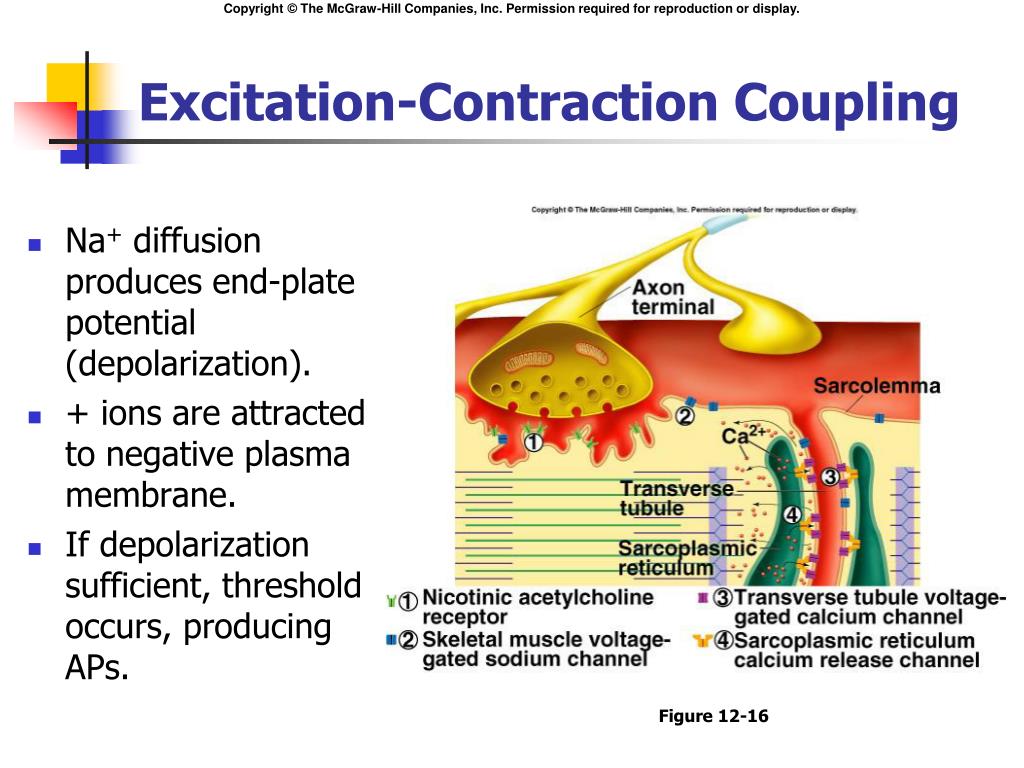
Excitationcontraction Coupling Flow Chart

Cardiac Muscle Berne and Levy Physiology, 6th ed
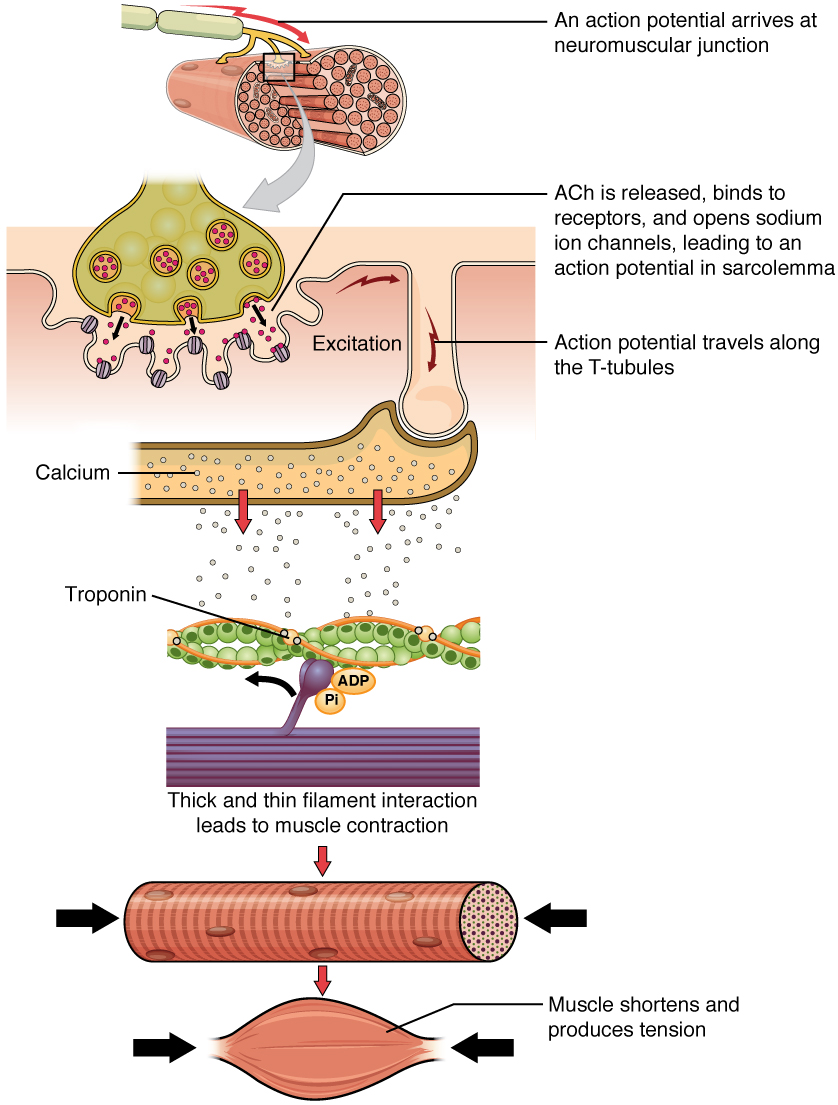
Excitationcontraction coupling BioSerendipity
Medically Reviewed By Anatomy Team.
Web Excitation Contraction (Ec) Coupling Electrical Event Action Potential Generated In Muscle Fiber Memb.
Due To Depolarization Of Motor End Plate Ap.
Related Post: