Endometrial Polyp Size Chart In Cm
Endometrial Polyp Size Chart In Cm - Web endometrial polyps are localized hyperplastic overgrowths of endometrial glands and stroma around a vascular core that form a sessile or pedunculated projection from the surface of the endometrium ( picture 1) [. Web an endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is a mass in the inner lining of the uterus. These polyps usually stay within the uterus but can sometimes grow into the cervix (opening of the uterus) and. Web the prevalence of endometrial polyps was 7.8% (48/619; Web an endometrial polyp is defined as a localized hyperplastic overgrowth of endometrial glands and stroma that projects from the endometrial surface (kim). They may have a large flat base or be attached to the uterus by an elongated pedicle (pedunculated). Web endometrial polyps are localized intrauterine overgrowths of endometrial glands and stroma covered by a surface epithelium. Can range in size from millimeters (about the size of a sesame seed) to centimeters (about the size of a golf ball and even larger). Web polyps may be round or oval and range in size from a few millimeters (the size of a sesame seed) to a few centimeters (the size of a golf ball) or larger. Endometrial polyps are common findings, both in women with and without gynaecological symptoms. Polyps may be found as a single lesion or multiple lesions filling the entire endometrial cavity. In women below the age of 30 years, the prevalence was 0.9%. On average, these polyps are typically less than 1 cm. Web polyps may be round or oval and range in size from a few millimeters (the size of a sesame seed) to. Polyps may be found as a single lesion or multiple lesions filling the entire endometrial cavity. Age, htn, obesity, tamoxifen use (salim). Web a uterine (endometrial) polyp is a small, fleshy growth that can develop along the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium). Endometrial polyps form from an overgrowth of cells within the uterine lining. Diagnostic et prise en charge. Can range in size from millimeters (about the size of a sesame seed) to centimeters (about the size of a golf ball and even larger). Web endometrial polyps are localized intrauterine overgrowths of endometrial glands and stroma covered by a surface epithelium. They may have a large flat base or be attached to the uterus by an elongated pedicle (pedunculated).. They can grow to be several centimeters in size. Giant endometrial polyps occur with increased frequency secondary to unbalanced oestrogen levels or tamoxifen exposure after breast cancer [ 1 ]. A mostly benign pathology finding. Endometrial polyps are localized tumors within the mucosa of the uterine cavity. Can range in size from millimeters (about the size of a sesame seed). The prevalence was influenced significantly by age ( p < 0.005); Web uterine polyps attach to the uterus by a large base or a thin stalk. Uterine polyps can cause irregular menstrual bleeding, bleeding after menopause, very heavy menstrual flow. Web the prevalence of endometrial polyps was 7.8% (48/619; Giant endometrial polyps occur with increased frequency secondary to unbalanced oestrogen. The exact cause is unknown, however identified risk factors include: These are usually less than 1 cm in diameter, which often flatten to fit the cavity of the uterus. Polyps may be found as a single lesion or multiple lesions filling the entire endometrial cavity. Web polyps may be round or oval and range in size from a few millimeters. In women below the age of 30 years, the prevalence was 0.9%. They range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters. The exact cause is unknown, however identified risk factors include: Pedunculated polyps are more common than sessile ones. Web the most common size of polyp is less than 2 cm, and those greater than 4 cm are. Web an endometrial polyp represents the extreme end of macroscopic hyperplasia of the endometrium when tissue grows so fast that parts of the endometrium are pushed into the cavity of the uterus. Web endometrial polyps are localized hyperplastic overgrowths of endometrial glands and stroma around a vascular core that form a sessile or pedunculated projection from the surface of the. The lesions may contain blood vessels and cause irregular menstrual bleeding, spotting, menorrhagia, and postmenopausal bleeding. Web an endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is a mass in the inner lining of the uterus. Abnormal cell changes are often associated with malignancy, but the vast majority of endometrial polyps do not cause cancer. Diagnosis and management of endometrial polyps. Polyps may. Abnormal cell changes are often associated with malignancy, but the vast majority of endometrial polyps do not cause cancer. Web uterine polyps attach to the uterus by a large base or a thin stalk. The prevalence was influenced significantly by age ( p < 0.005); Web the most common size of polyp is less than 2 cm, and those greater. Web polyps may be round or oval and range in size from a few millimeters (the size of a sesame seed) to a few centimeters (the size of a golf ball) or larger. Endometrial polyps greater than 15 mm showed a hyperplasia rate of 14.8%, compared with 7.7% in the group with smaller polyps ( p < 0.05). Endometrial polyps form from an overgrowth of cells within the uterine lining. In women below the age of 30 years, the prevalence was 0.9%. Diagnosis and management of endometrial polyps. They may be a cause of menorrhagia and of post menopausal bleeding. Endometrial polyps measuring more than 15 mm were associated with hyperplasia. Endometrial polyps are localized tumors within the mucosa of the uterine cavity. Uterine polyps are soft fleshy outgrowths from the lining of the uterus (also called the endometrium). Diagnostic et prise en charge du vasa prævia) the english document is the original version; Web an endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is an abnormal growth containing glands, stroma and blood vessels projecting from the lining of the uterus (endometrium) that occupies spaces small or large enough to fill the uterine cavity. Web an endometrial polyp is defined as a localized hyperplastic overgrowth of endometrial glands and stroma that projects from the endometrial surface (kim). Overgrowth of localized endometrial tissue that may be pedunculated or sessile, single or multiple, and up to many centimeters in size. The exact cause is unknown, however identified risk factors include: These polyps usually stay within the uterus but can sometimes grow into the cervix (opening of the uterus) and. Web the most common size of polyp is less than 2 cm, and those greater than 4 cm are called giant polyps.
Endometrial & Uterine Polyps Canberra Deakin, ACT
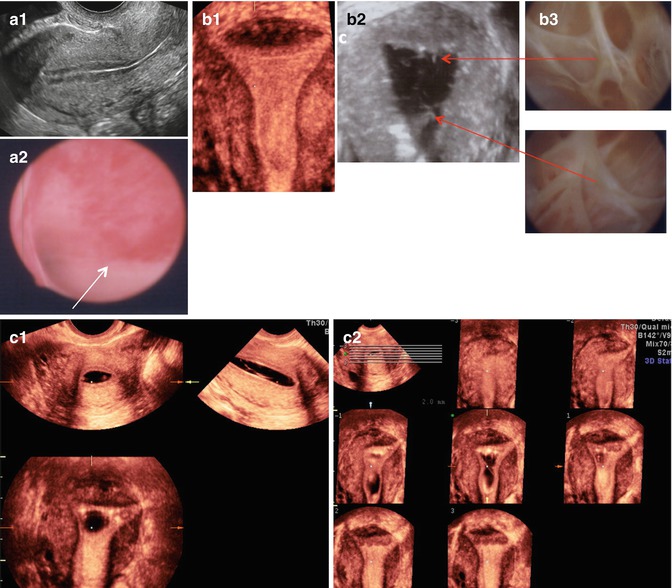
Representative size measurement and appearance of endometrial polyps

Endometrial polyps Pathogenesis, sequelae and treatment Njume Peter

Uterine Polyp Size Chart
Endometrial Polyp Size Chart
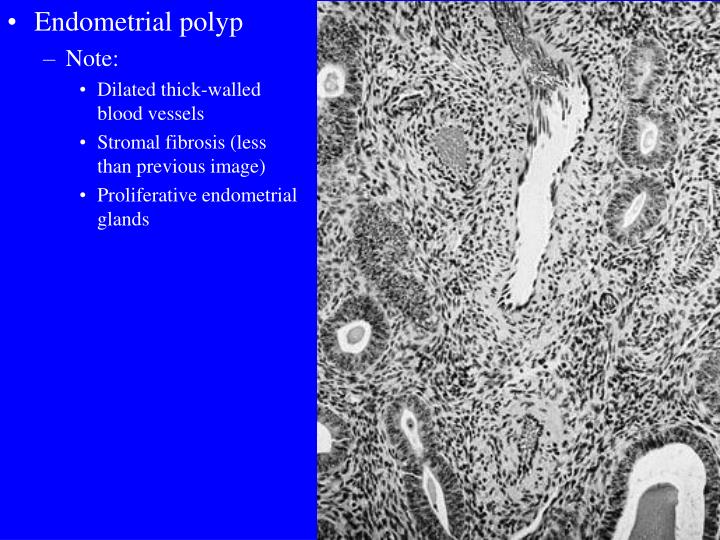
Dra. Joana Faria Uterine polyp Lisbon, Portugal
![[PDF] Giant endometrial polyp protruding from the external cervical os](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/8ee776e2c239fe8f6fe5bef07581c99c4de87bae/5-Figure4-1.png)
[PDF] Giant endometrial polyp protruding from the external cervical os
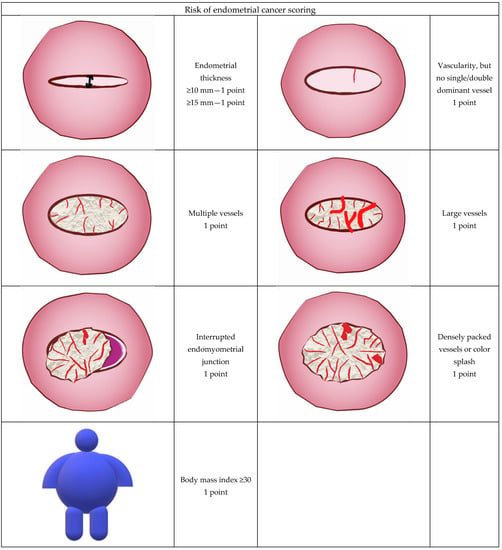
Diagnostics Free FullText Risk Assessment of Endometrial
Endometrial Polyp Size Chart

Polyp size and malignancy Download Table
Web A Committee Of Six Expert Researchers Draw The Recommendations According To Agree Ii Reporting Guideline.
A Mostly Benign Pathology Finding.
Web An Endometrial Polyp Represents The Extreme End Of Macroscopic Hyperplasia Of The Endometrium When Tissue Grows So Fast That Parts Of The Endometrium Are Pushed Into The Cavity Of The Uterus.
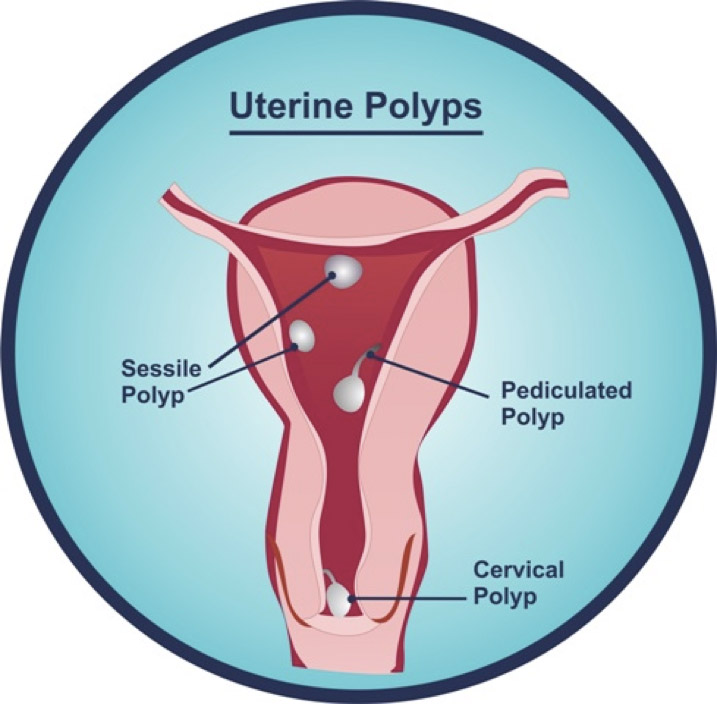
Pedunculated Polyps Are More Common Than Sessile Ones.
Related Post: