Domains And Kingdoms Chart
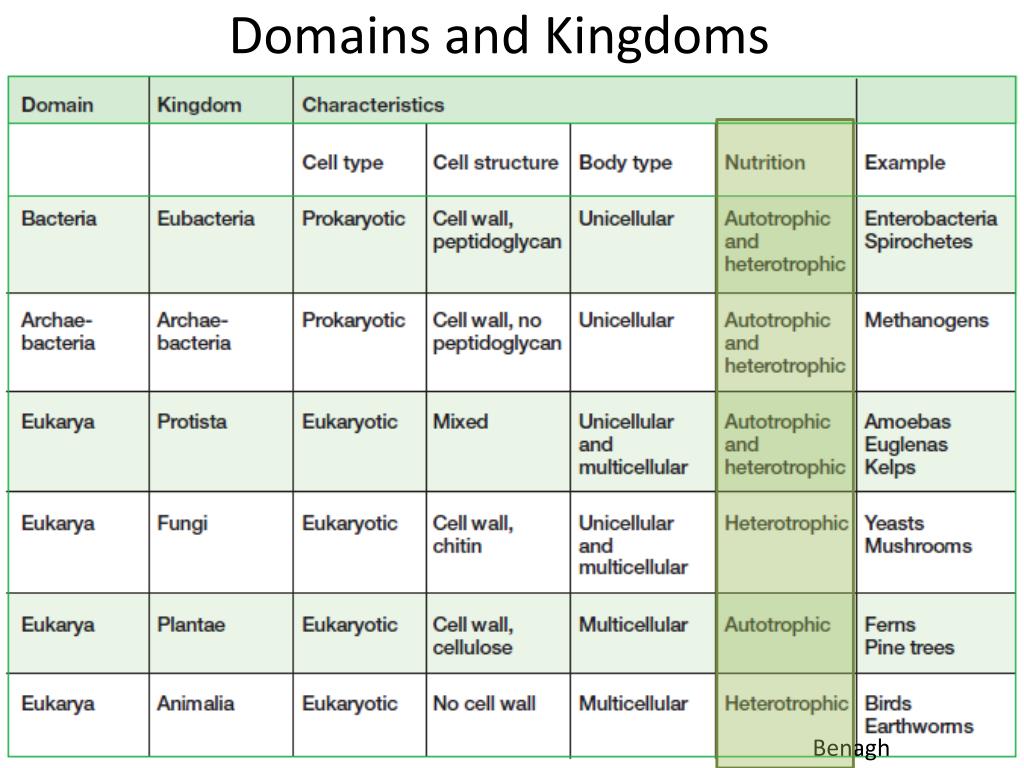
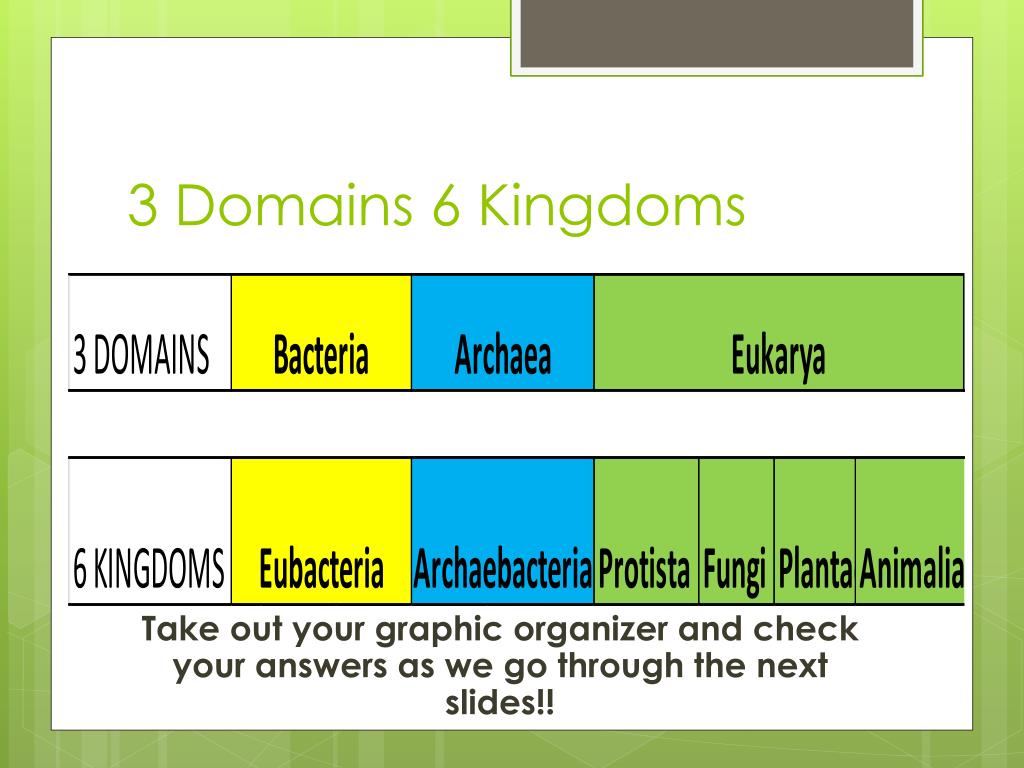
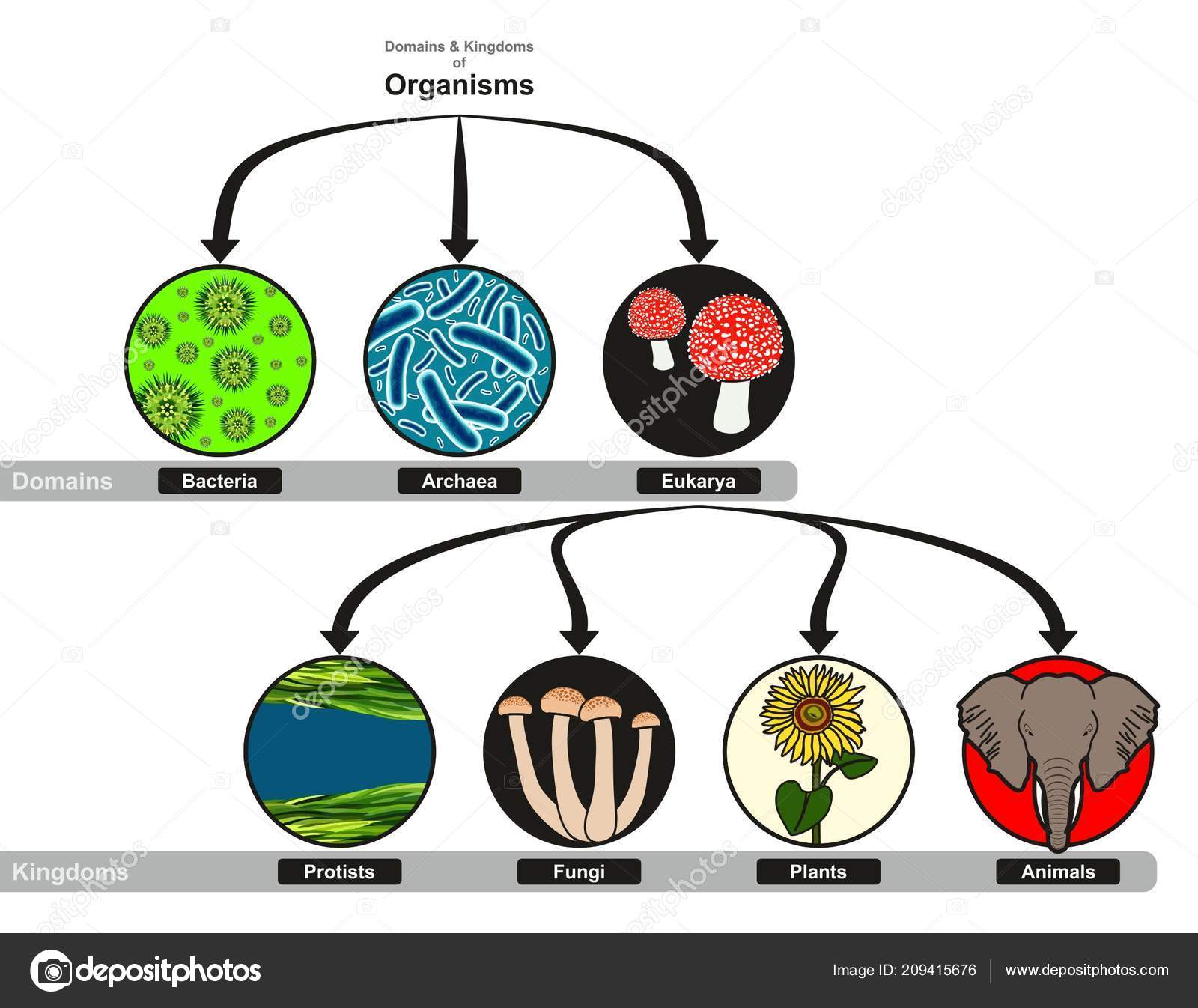
Domains And Kingdoms Chart - After kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: Web the chart below shows how the kingdoms have changed over time. Plantae (the plant kingdom) and animalia (the animal kingdom). Web classify organisms into their domain and kingdom by sorting cards with various organisms into the proper category. Web in biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. Web there are millions and millions of species, so classifying organisms into proper categories can be a difficult task. It’s even more general than asking whether an organism is a plant or an animal. After kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: Web today organisms are grouped into three domains and six kingdoms based on their cell type, ability to make food, and the number of cells that make up their bodies. As scientists began to understand more about dna, evolutionary biologists established a new taxonomic category—the domain. Web organisms are traditionally classified into six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia) based on characteristics like cell type, nutrient acquisition, and reproduction. Linnaeus established two kingdoms of organisms in his classification system: In other words, it is a broad classification of. Dominium), introduced by moore in 1974. Domains are used to distinguish between the cell types and, in the case of prokaryotes, where they are found and what the cell walls are made of. Web the chart below shows how the kingdoms have changed over time. It’s even more general than asking whether an organism is a plant or an animal.. Web there are millions and millions of species, so classifying organisms into proper categories can be a difficult task. After kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: Web linnaeus invented binomial nomenclature, the system of giving each type of organism a genus and species name. Here is a look at how many kingdoms there are, their main properties, and. Here is a look at how many kingdoms there are, their main properties, and examples of organisms from each kingdom. Phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species (figure 1). Web the chart below shows how the kingdoms have changed over time. Web today organisms are grouped into three domains and six kingdoms based on their cell type, ability to make. He also developed a classification system called the taxonomic hierarchy, which today has eight ranks from general to specific: Plantae , contains all plants on earth. Web in biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. Linnaeus established two kingdoms of organisms in his classification system: In a final surprise, the sequences. Web for example, after the common beginning of all life, scientists divide organisms into three large categories called a domain: As scientists began to understand more about dna, evolutionary biologists established a new taxonomic category—the domain. Web linnaeus invented binomial nomenclature, the system of giving each type of organism a genus and species name. Plantae, animalia, fungi, protoctista and prokaryotae.. In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. After kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: Within each domain is a second category called a kingdom. Web in biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla (singular phylum). Here is a look at how many kingdoms there are, their main properties, and examples of organisms from each kingdom. Web there are millions and millions of species, so classifying organisms into proper categories can be a difficult task. He also developed a classification system called the taxonomic hierarchy, which today has eight ranks from general to specific: Complete a. Complete a semantic feature map to display the results of the card sort. Web in biological taxonomy, a domain (/ d ə ˈ m eɪ n / or / d oʊ ˈ m eɪ n /) (latin: Web classify organisms into their domain and kingdom by sorting cards with various organisms into the proper category. This is because their cells. Phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species (figure 1). It’s even more general than asking whether an organism is a plant or an animal. Web in biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. Web in biological taxonomy, a domain (/ d ə ˈ m eɪ n / or / d oʊ. Web for example, after the common beginning of all life, scientists divide organisms into three large categories called a domain: Domains are used to distinguish between the cell types and, in the case of prokaryotes, where they are found and what the cell walls are made of. To make it easier for all scientists to do, a classification system had to be. Web for example, after the common beginning of all life, scientists divide organisms into three large categories called a domain: Include basic characteristics, such as cell structure, the manner in which food is synthesized, and the mode of reproduction. Web the three domains of life ( archaea, eubacteria and eukarya) quickly supplanted the older division of living things into five kingdoms, the monera (prokaryotes), protista, fungi, plants, and animals (all eukaryotes!). From the most general to the most specific, these are domain, kingdom, phylum (plural, phyla), class, order, family, genus (plural, genera), and species. Web the domain is the highest ranking of biological classification at this time* and includes 3 domains: Within each domain is a second category called a kingdom. Plantae , contains all plants on earth. Within each domain is a second category called a kingdom. Linnaeus established two kingdoms of organisms in his classification system: For example, protists, fungi, plants, and animals are part of the eukarya domain. A domain is the most inclusive of the levels (meaning it has the most number of individuals in the group). Web there are seven main taxonomic ranks: After kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: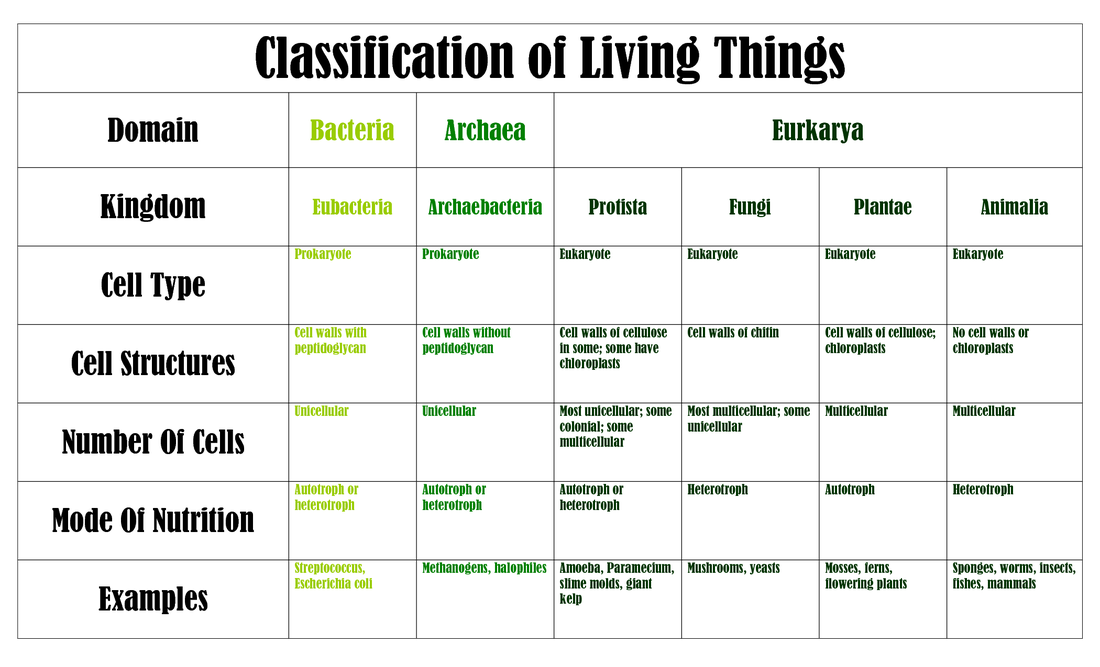
Classification of Living Things michelleburden
PPT Kingdoms, Classification, and Plants PowerPoint Presentation
PPT Domains and Kingdoms PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Domain Kingdoms Organisms Classification Chart Infographic Diagram
Domains & Kingdoms 177 plays Quizizz
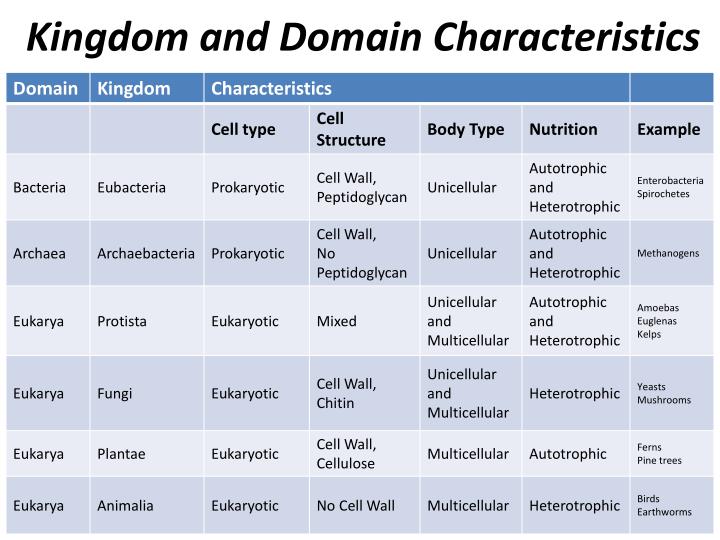
PPT Kingdoms and Domains PowerPoint Presentation ID5353746

️ Kingdom and domain characteristics. Mnemonic taxonomy / biology
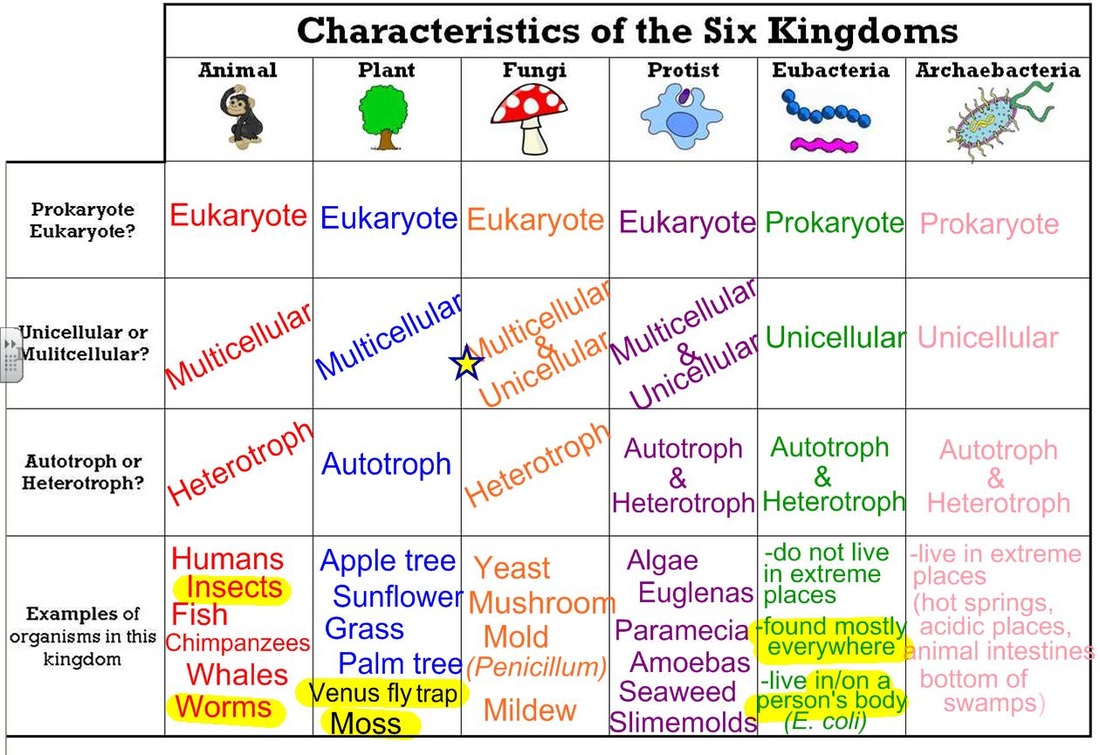
Classification of Organisms Rumney Marsh Academy Science Revere
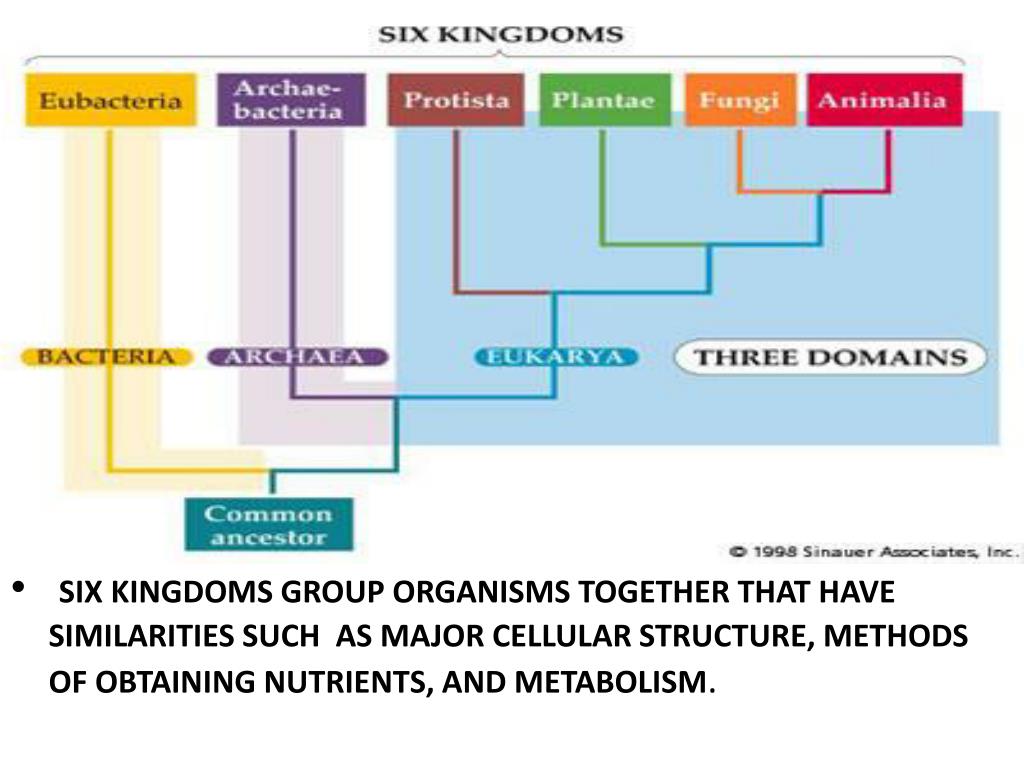
PPT Classification Chapter 17 Taxonomy 6 Kingdoms Dissection notes

What are the 3 domains of life and their characteristics? Three Domain
After Kingdoms, The Subsequent Categories Of Increasing Specificity Are:
Web Today Organisms Are Grouped Into Three Domains And Six Kingdoms Based On Their Cell Type, Ability To Make Food, And The Number Of Cells That Make Up Their Bodies.
A Domain Is A Larger And More Inclusive Category Than A Kingdom.
Plantae (The Plant Kingdom) And Animalia (The Animal Kingdom).
Related Post:
