Dissimilar Metals Corrosion Chart
Dissimilar Metals Corrosion Chart - Web the common factors are dissimilar metals, electrical contact, and a conductive electrolyte in contact with them. So, for example, choosing zinc on zinc would have the lowest. When dissimilar metals are used together in the presence of an electrolyte,. If any of these factors is absent, galvanic corrosion cannot occur. Contact a corrosion specialist to determine the best. Web metals are rated in their ability to resist electrochemical corrosion on the scale of nobility and on the galvanic series chart, which shows their electrical potential in seawater. Web below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. Web galvanic corrosion (also called ' dissimilar metal corrosion' or wrongly 'electrolysis') refers to corrosion damage induced when two dissimilar materials are coupled in a corrosive. Metals close to one another on the chart. Web the larger the separation distance in the electromotive chart between the two metals in contact, the higher the contact potential and chances for corrosion. Web galvanic/dissimilar metal or bimetallic corrosion is a type of electrochemical corrosion, where a material corrodes if it comes in contact with another material in the presence of. So, for example, choosing zinc on zinc would have the lowest. Galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when. Dissimilar metals used in conjunction; Web the galvanic series chart below shows metals and their electrochemical voltage range (relative activity in flowing sea water). Web the following three factors often contribute to a higher risk of galvanic corrosion: Metals close to one another on the chart. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion. Dissimilar metals used in conjunction; When dissimilar metals are used together in the presence of an electrolyte,. Web below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. Web the following three factors often contribute to a higher risk of galvanic corrosion: Web the common factors are dissimilar metals, electrical contact, and a conductive electrolyte in contact with them. Web the larger the separation distance in the electromotive chart between the two metals in contact, the higher the contact potential and chances for corrosion. Web however, you can completely avoid galvanic corrosion by choosing matching metal anchors. Web galvanic corrosion (also called ' dissimilar metal corrosion' or wrongly 'electrolysis') refers to corrosion damage induced when two dissimilar materials are. A similar galvanic reaction is exploited in primary cells to generate a useful electrical voltage to power portable devices. Web galvanic corrosion is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially to another when both metals are in electrical contact, in the. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a. Web galvanic corrosion (also called ' dissimilar metal corrosion' or wrongly 'electrolysis') refers to corrosion damage induced when two dissimilar materials are coupled in a corrosive. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming. Obviously galvanic corrosion is more. Web galvanic corrosion may be experienced when two dissimilar. Web the larger the separation distance in the electromotive chart between the two metals in contact, the higher the contact potential and chances for corrosion. Galvanic corrosion happens when dissimilar metals rub against one. In the case of galvanic corrosion, the combination of two dissimilar metals with an electrolyte is all that is needed to form a. Web this slide. Web this slide includes a chart of galvanic corrosion potential between common construction metals. Galvanic corrosion happens when dissimilar metals rub against one. Web the larger the separation distance in the electromotive chart between the two metals in contact, the higher the contact potential and chances for corrosion. Web galvanic corrosion (also called ' dissimilar metal corrosion' or wrongly 'electrolysis'). Web when two different metals are in contact and exposed to a common electrolyte, one of the metals experiences accelerated corrosion while the other is. Web below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. Web however, you can completely avoid galvanic corrosion by choosing matching metal anchors. Web the following three factors often contribute to a higher risk of. Web galvanic corrosion (also called ' dissimilar metal corrosion' or wrongly 'electrolysis') refers to corrosion damage induced when two dissimilar materials are coupled in a corrosive. Web galvanic corrosion may be experienced when two dissimilar metals or alloys, not in direct contact, are nevertheless connected electrically. Web this slide includes a chart of galvanic corrosion potential between common construction metals.. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming. When dissimilar metals are used together in the presence of an electrolyte,. A typical rule of thumb is that voltage differences. If any of these factors is absent, galvanic corrosion cannot occur. Web the larger the separation distance in the electromotive chart between the two metals in contact, the higher the contact potential and chances for corrosion. Dissimilar metals used in conjunction; Web when two different metals are in contact and exposed to a common electrolyte, one of the metals experiences accelerated corrosion while the other is. A similar galvanic reaction is exploited in primary cells to generate a useful electrical voltage to power portable devices. Web metals are rated in their ability to resist electrochemical corrosion on the scale of nobility and on the galvanic series chart, which shows their electrical potential in seawater. Obviously galvanic corrosion is more. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming. Web metals listed on the top of the chart (anodic) will corrode faster than the metals on the bottom of the chart (cathodic). Contact a corrosion specialist to determine the best. Web the most important type of corrosion for understanding dissimilar metals is galvanic corrosion. Web the following three factors often contribute to a higher risk of galvanic corrosion: Web below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals.
21 Lovely Galvanic Corrosion Chart Dissimilar Metals Chart Gallery

Protection of Dissimilar Metal Contacts and Corrosion Limits

Stainless Steel Galvanic Corrosion Chart
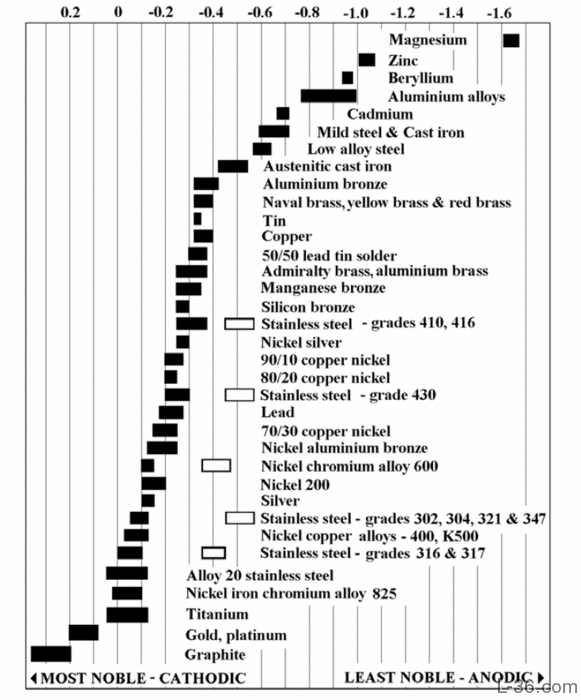
Dissimilar Corrosion Materials Tables

FAQ 1 Galvanic/Dissimilar Metal Corrosion

Metals Galvanic Compatibility Chart A Visual Reference of Charts
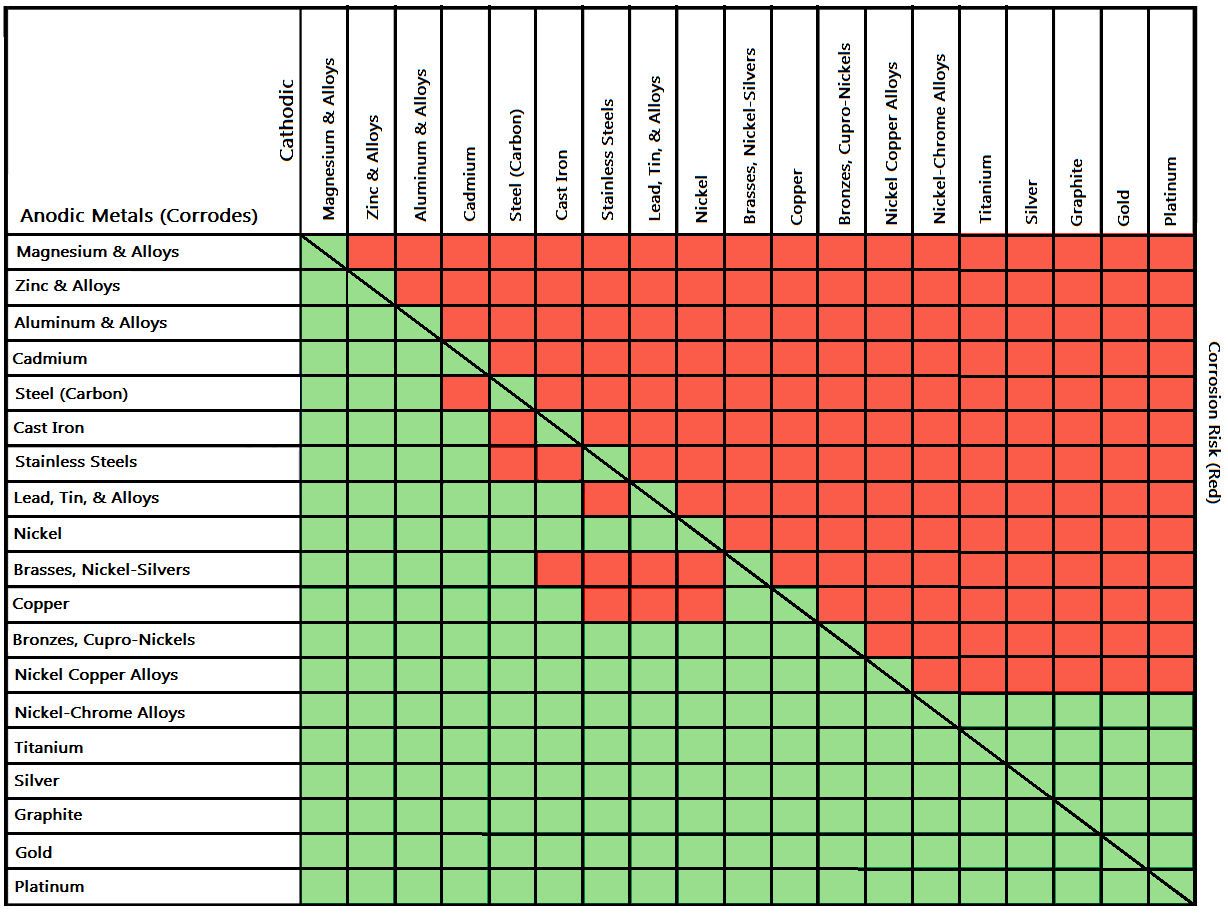
Galvanic Corrosion Common Questions Answered
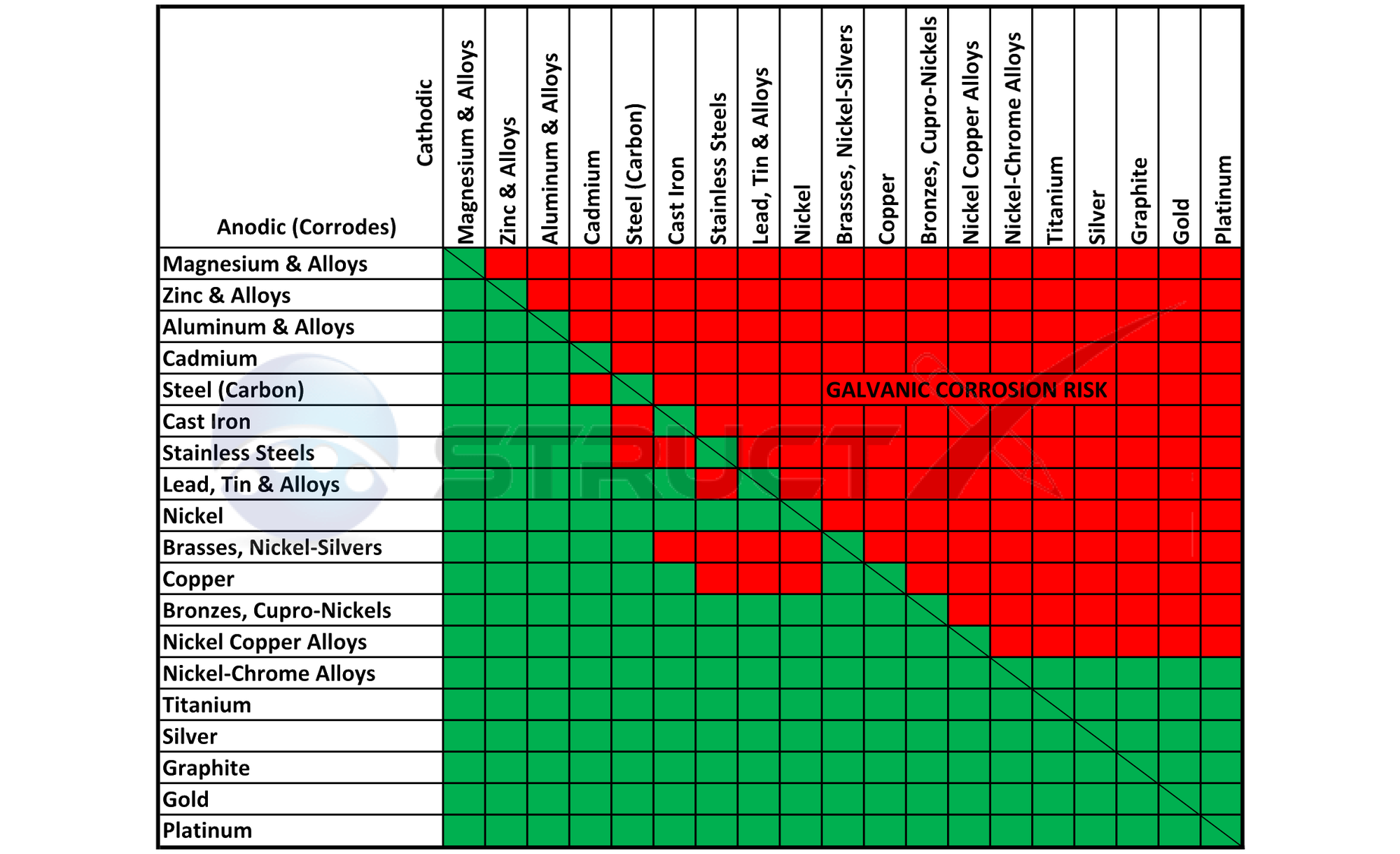
Aluminum Corrosion Resistance Chart
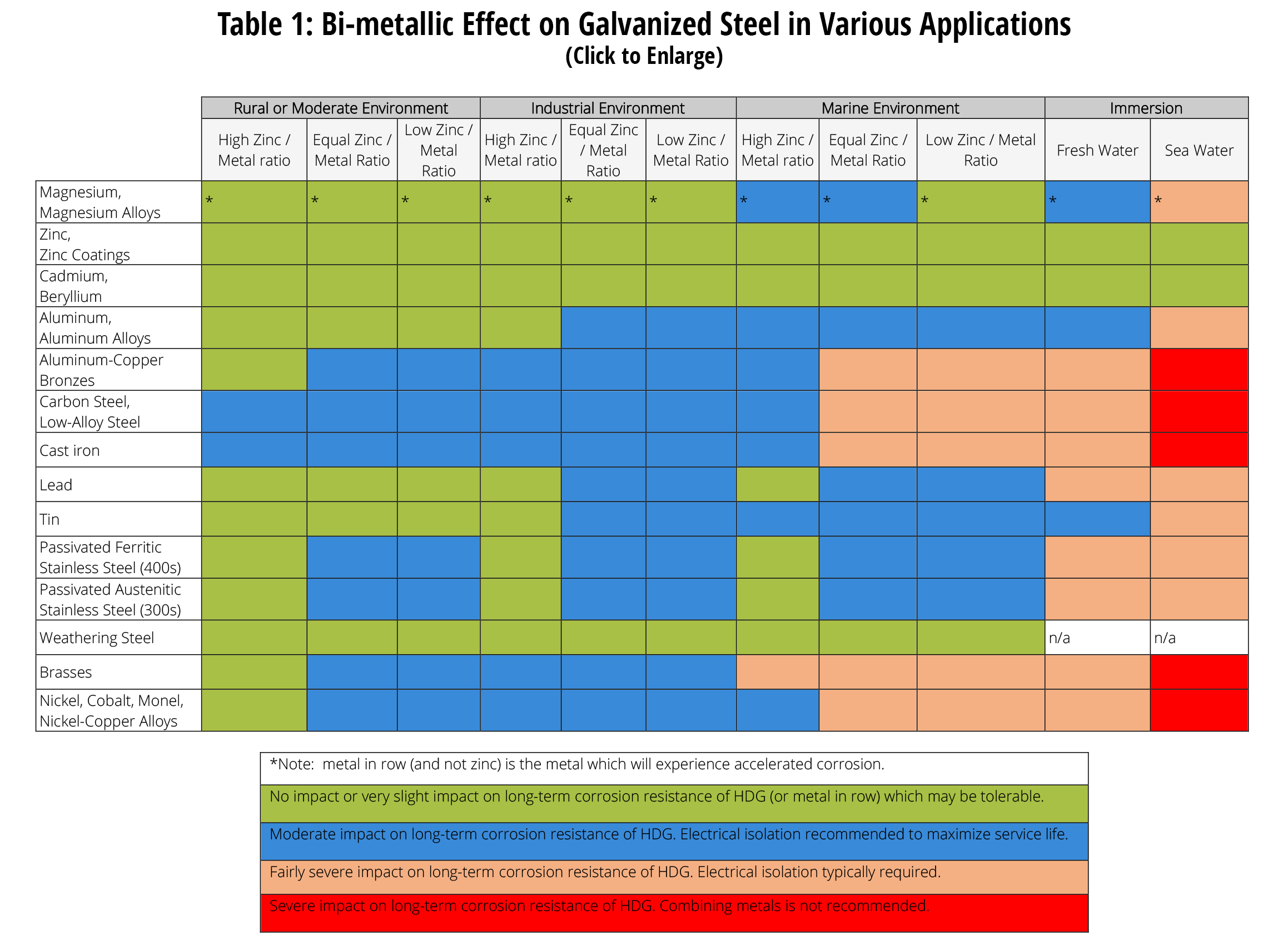
Dissimilar Metal Corrosion with… American Galvanizers Association

Galvanic Corrosion Chart Dissimilar Metals Video Bokep Ngentot
So, For Example, Choosing Zinc On Zinc Would Have The Lowest.
This Phenomenon Is Named After Italian Ph…
Web Below Is A Galvanic Reaction Chart For Dissimilar Metals.
Web Galvanic Corrosion Potential Is A Measure Of How Dissimilar Metals Will Corrode When Placed Against Each Other In An Assembly.
Related Post: