Diesel Fuel Gel Chart
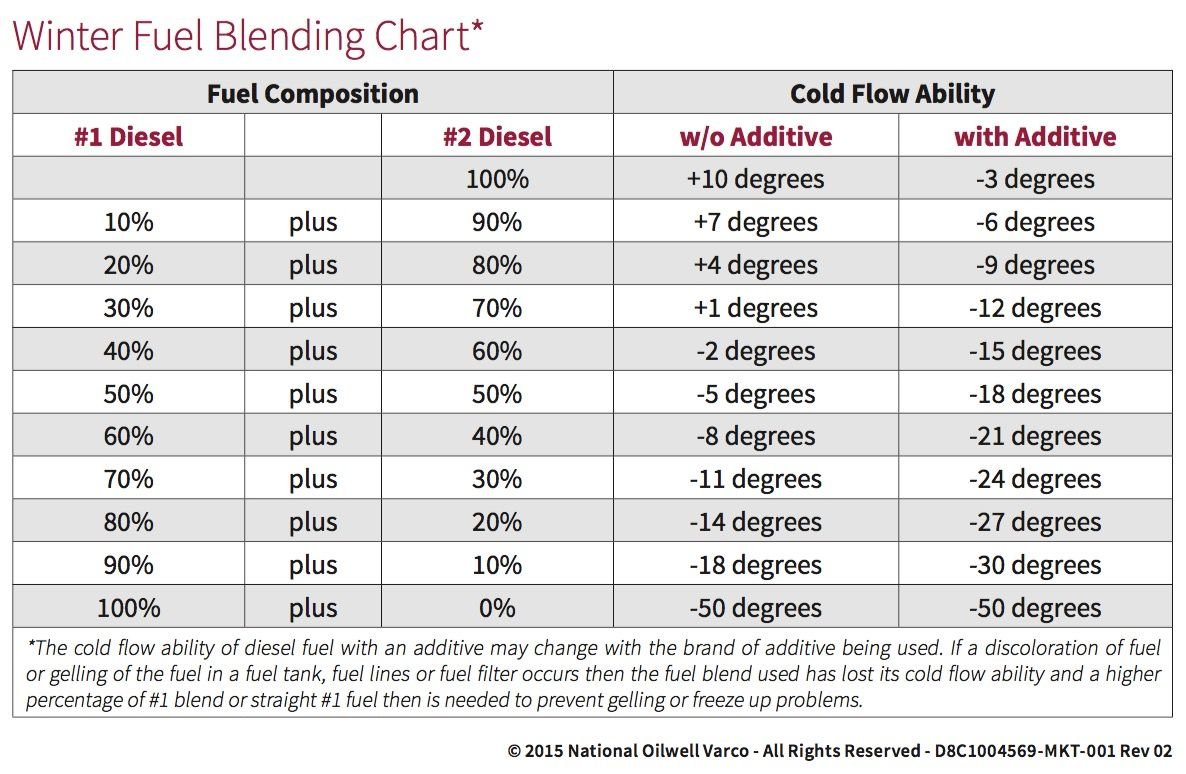
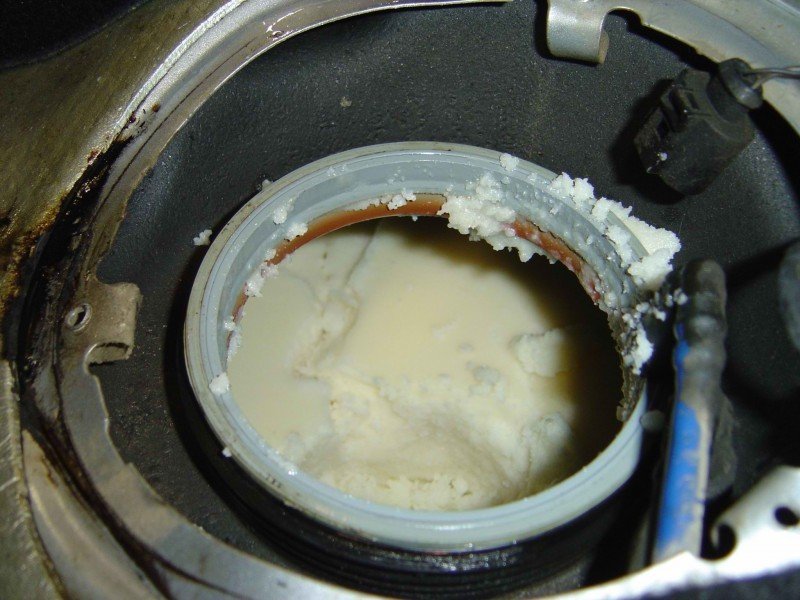
Diesel Fuel Gel Chart - Web gelling happens when the paraffin wax in diesel solidifies due to a drop in temperature, and the fuel’s temperature must be kept below minus 10 degrees f for extended periods of time, such as 48 to 72 hours. Below we list some ways you can prevent diesel gelling from occurring in your truck. Web understanding the nature of diesel fuel and how temperature changes can impact its composition is the first step towards prevention. Web typically, a blend of 80/20 (80% no. Fuel gelling happens in cold weather when the wax in diesel fuel crystalizes and prevents the flow to the engine or clogs fuel lines and/or filters. These will help prevent gelling in the fuel lines and filters. Temperature for this to occur. Web diesel fuel is prone to “gelling”, a term used to describe the crystallization of waxes in diesel fuel in extremely cold weather. 1 diesel) works best for extreme low temperatures in our areas. Biodiesels are more prone to cold filter plug point/cloud point/gel point. The bio part can seperate out of suspension in ulsd more prone than lsd. This gelling can prevent fuel flow to the engine or clog fuel lines/filters, making it impossible for diesel engines to run. The exact gelling point may vary with different diesel components. Web diesel typically transitions into a gel when consistently subjected to low temperatures ranging from. At this stage, the fuel solidifies so completely that it can no longer flow at all (what we refer to as pour point). Below we list some ways you can prevent diesel gelling from occurring in your truck. 2 diesel and 30% no. Web gelling happens when the paraffin wax in diesel solidifies due to a drop in temperature, and. Knowing the difference between gelling and icing will help you determine which issue you may be facing and how to combat the situation. By 15°f, it gets worse and full on gelling has got you, which will block filters and stop you on the spot. Let’s take a minute and get down to the basics of diesel fuel gelling. Rated. By 15°f, it gets worse and full on gelling has got you, which will block filters and stop you on the spot. The cloud point refers to the crystallization of wax materials in the fuel. At this stage, the fuel solidifies so completely that it can no longer flow at all (what we refer to as pour point). The bio. The exact gelling point may vary with different diesel components. The cloud point refers to the crystallization of wax materials in the fuel. Check the fuel filter and lines for signs of waxy, thickened fuel. At the end of the day, one of the easiest ways to prevent diesel fuel from gelling is by using a quality diesel fuel additive.. Paraffin waxes are combustible and help power the engine when burned, but they solidify when temperatures drop. Difficulty in starting the engine, loss of power, or stalling can indicate such problem. 1 diesel) or 70/30 (70% no. It is a common practice for truckers to mix #1 diesel which has a blend of kerosene with diesel #2 which is used. Difficulty in starting the engine, loss of power, or stalling can indicate such problem. Kerosene helps in lowering the plug point temperature of the fuel and reduces its viscosity, therefore making diesel less likely to gel even during low temperatures. Web winter can be rough on diesel equipment. As these crystals form, the substance begins to appear cloudy. This gelling. Rated 4.99 out of 5. 2 diesel and 30% no. Web how to know if diesel is gelling. However, it’s important to note that some diesel fuels may have lower gel points, especially those specifically formulated for cold weather conditions. Biodiesels are more prone to cold filter plug point/cloud point/gel point. These wax crystals hinder the fuel flow, making it hard to start the engine. 1 diesel) or 70/30 (70% no. This gelling can prevent fuel flow to the engine or clog fuel lines/filters, making it impossible for diesel engines to run. How you can tell your fuel gelled. Web understanding the nature of diesel fuel and how temperature changes can. The cloud point refers to the crystallization of wax materials in the fuel. 1 diesel) or 70/30 (70% no. Biodiesels are more prone to cold filter plug point/cloud point/gel point. The crystallization worsens as the temperatures drop. Web how to know if diesel is gelling. Rated 4.99 out of 5. Web typically, a blend of 80/20 (80% no. By 15°f, it gets worse and full on gelling has got you, which will block filters and stop you on the spot. Check the fuel filter and lines for signs of waxy, thickened fuel. 2 diesel and 30% no. 1 diesel) works best for extreme low temperatures in our areas. The cloud point refers to the crystallization of wax materials in the fuel. Web how to know if diesel is gelling. Web gelling happens when the paraffin wax in diesel solidifies due to a drop in temperature, and the fuel’s temperature must be kept below minus 10 degrees f for extended periods of time, such as 48 to 72 hours. When diesel is cold soaked, the paraffin wax in the fuel hardens, giving it a hazy look. Kerosene helps in lowering the plug point temperature of the fuel and reduces its viscosity, therefore making diesel less likely to gel even during low temperatures. They can plug faster, they absorb water more redably. Web at 34°f, you begin to see the start of the gelling process and fuel starts to get cloudy. These wax crystals hinder the fuel flow, making it hard to start the engine. Web when does diesel gel? Let’s take a minute and get down to the basics of diesel fuel gelling.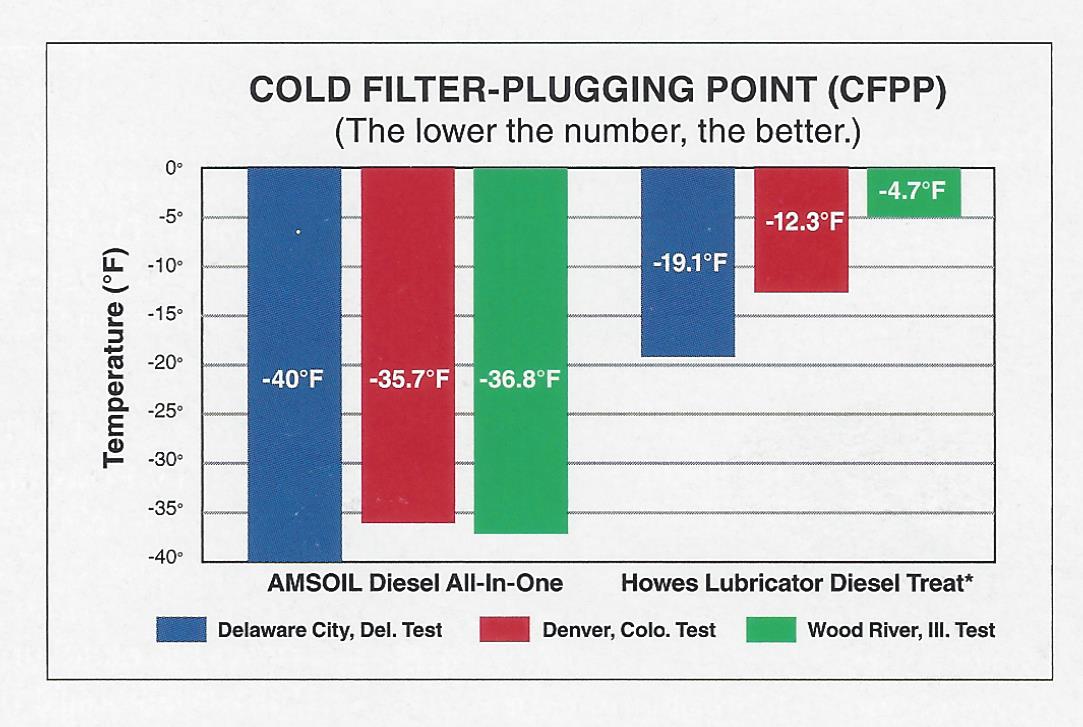
202001PreventDieselFuelGelling1 SLS Associates
Diesel kleen white bottle? Page 2 Ford Truck Enthusiasts Forums

What To Do If Your Diesel Fuel Gels Hot Shot's Secret

Diesel Fuel Gel test Pwr Srvc, Howe's, Schaeffer Page 4 Ford

2 stroke fuel mixture chart

Manalox 730™ FedChem
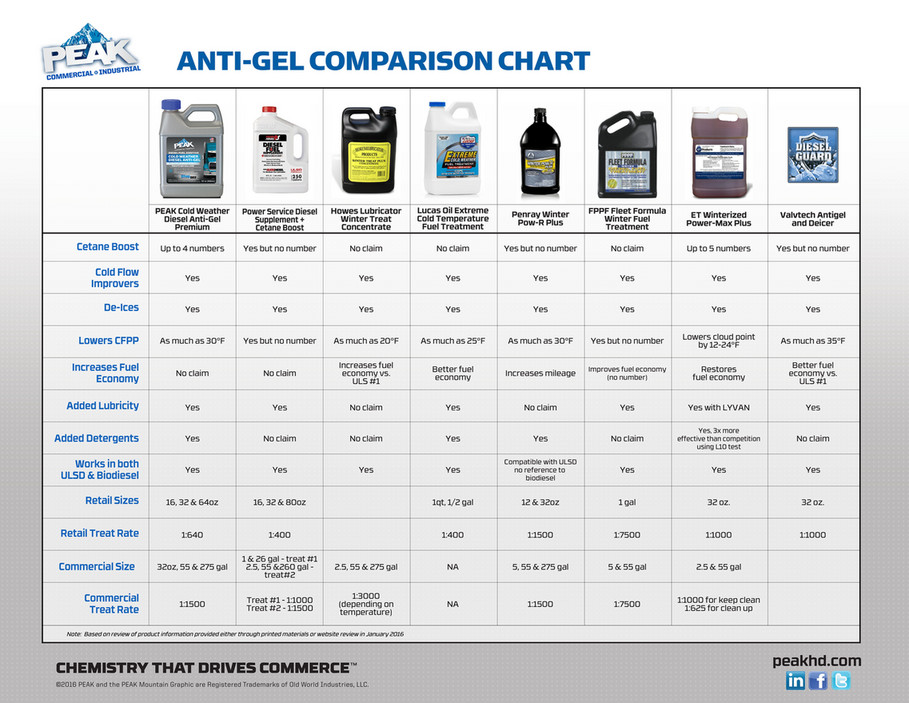
PEAK C&I Diesel Fuel Additive Comparison Chart With All Page 1

What Temp Does Diesel Fuel Gel? How to Ungel Diesel Fuel
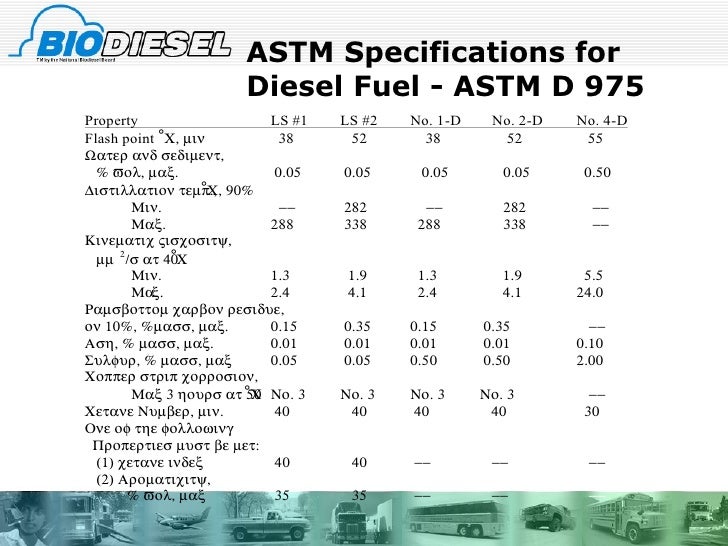
Understanding Diesel Fuel

Discover 8 Types of Fuel Additives from Fuel & Friction
The Rate At Which Your Fuel Gels And The Temperature At Which It Occurs Depend On The Origin And Quality Of The Fuel.
Web In General, Neat Diesel (Ulsd#2) Will Give You Trouble Somewhere South Of 20*F, My Experience Is You Need To Modify Ulsd#2 At Temps Below 15*F.
The Crystallization Worsens As The Temperatures Drop.
It Is A Common Practice For Truckers To Mix #1 Diesel Which Has A Blend Of Kerosene With Diesel #2 Which Is Used On Road Applications.
Related Post: