Diatonic Half Step Chart
Diatonic Half Step Chart - An accidental changes the pitch of a note. E and f are two different letter names and so are b and c. Web at its core, the diatonic scale consists of seven distinct pitches arranged in a specific sequence of whole and half steps. Web the diatonic scale is the backbone of the seven notes, which have been the foundation of western music since the middle ages. Web the basic building blocks of chromatic and diatonic scales are half steps and whole steps, the two smallest intervals between notes in western music. In a chromatic half step, the notes have the same name. Take a look at the musical staff. You can use this formula of whole steps and half steps to form a major scale starting on any note. A half step is diatonic when the two notes names of the interval have not the same name, example: Similarly, b to c is a half step. The second note in each of these examples is a semitone higher. D and eb or e and f. This is a whole step. Here are a few examples, just to help the concept sink in. Web typically, you would call the half step between c and d a c sharp if there is a c sharp in the key. Here is a ascending chromatic scale played by an oboe: A whole step above is two keys to its right, while a whole step below is two keys to its left. Web you just need to understand two things to write out all twelve diatonic major scales: Web for instance, c and c#, eb and e, and g and g#. On a piano, a semitone would be the distance in pitch between e. This sequence forms the basis of the major and natural minor scales, which are the most common manifestations of diatonic. A half step is diatonic when the two notes names of the interval have not the same name, example: Web typically, you would call the half step. In a diatonic half step, the notes have different names: A half step is the distance from one piano key to the next closest (whether it happens to be white or black). A sharp raises a note by a half step, while a flat lowers a note by a half step. 1) the space pattern between notes (structure) and. The. A whole step above is two keys to its right, while a whole step below is two keys to its left. Web a whole step is two half steps. Get free weekly lessons, practice tips, and downloadable resources to your inbox! Web the distance between each note in the chromatic scale is one half step. Email* chords are a key. This is a whole step. Web a diatonic scale will consist only of letters in the musical alphabet with the occasional sharp or flat sign. Web chromatic and diatonic half steps. Web the basic building blocks of chromatic and diatonic scales are half steps and whole steps, the two smallest intervals between notes in western music. You can use this. It’s the smallest interval in western music. E and f, f# and g, and a and bb are pairs of. Remember that the naturally occuring half steps are between b & c and e & f. Web the distance between each note in the chromatic scale is one half step. D and eb or e and f. In a diatonic half step, the notes have different names: Similarly, b to c is a half step. A whole step above is two keys to its right, while a whole step below is two keys to its left. Web in pythagorean tuning, seven semitones out of twelve are diatonic, with ratio 256:243 or 90.2 cents ( pythagorean limma ),. Web for instance, c and c#, eb and e, and g and g# are all pairs of chromatic half steps. On a piano, a semitone would be the distance in pitch between e. E and f are two different letter names and so are b and c. Or in whole steps and half steps, it would be: E to f. “let me tell you why Get free weekly lessons, practice tips, and downloadable resources to your inbox! Church modes originated in the medieval era, and are classified by their use of the diatonic collection, their final, the relationships of other pitches to that final, and their range. Web you just need to understand two things to write out all twelve. The frequency of the vibrations causes a sense of “highness” or “lowness” of the sound, and is measures in cycles per second (cps, also called hertz, hz). 1) the space pattern between notes (structure) and. E to f is a half step, because e and f are next to one another. Web in music theory, a diatonic scale is any heptatonic scale that includes five whole steps (whole tones) and two half steps (semitones) in each octave, in which the two half steps are separated from each other by either two or three whole steps, depending on their position in the scale. Web the distance between each note in the chromatic scale is one half step. A half step is diatonic when the two notes names of the interval have not the same name, example: Here are a few examples, just to help the concept sink in. You can use this formula of whole steps and half steps to form a major scale starting on any note. Web you just need to understand two things to write out all twelve diatonic major scales: Or in whole steps and half steps, it would be: Web at its core, the diatonic scale consists of seven distinct pitches arranged in a specific sequence of whole and half steps. This is a whole step. See reading music in the tutorials section. Web in pythagorean tuning, seven semitones out of twelve are diatonic, with ratio 256:243 or 90.2 cents ( pythagorean limma ), and the other five are chromatic, with ratio 2187:2048 or 113.7 cents ( pythagorean apotome ); They differ by the pythagorean comma of ratio 531441:524288 or 23.5 cents. 2) how sharps (#) and flats (b) control those spaces.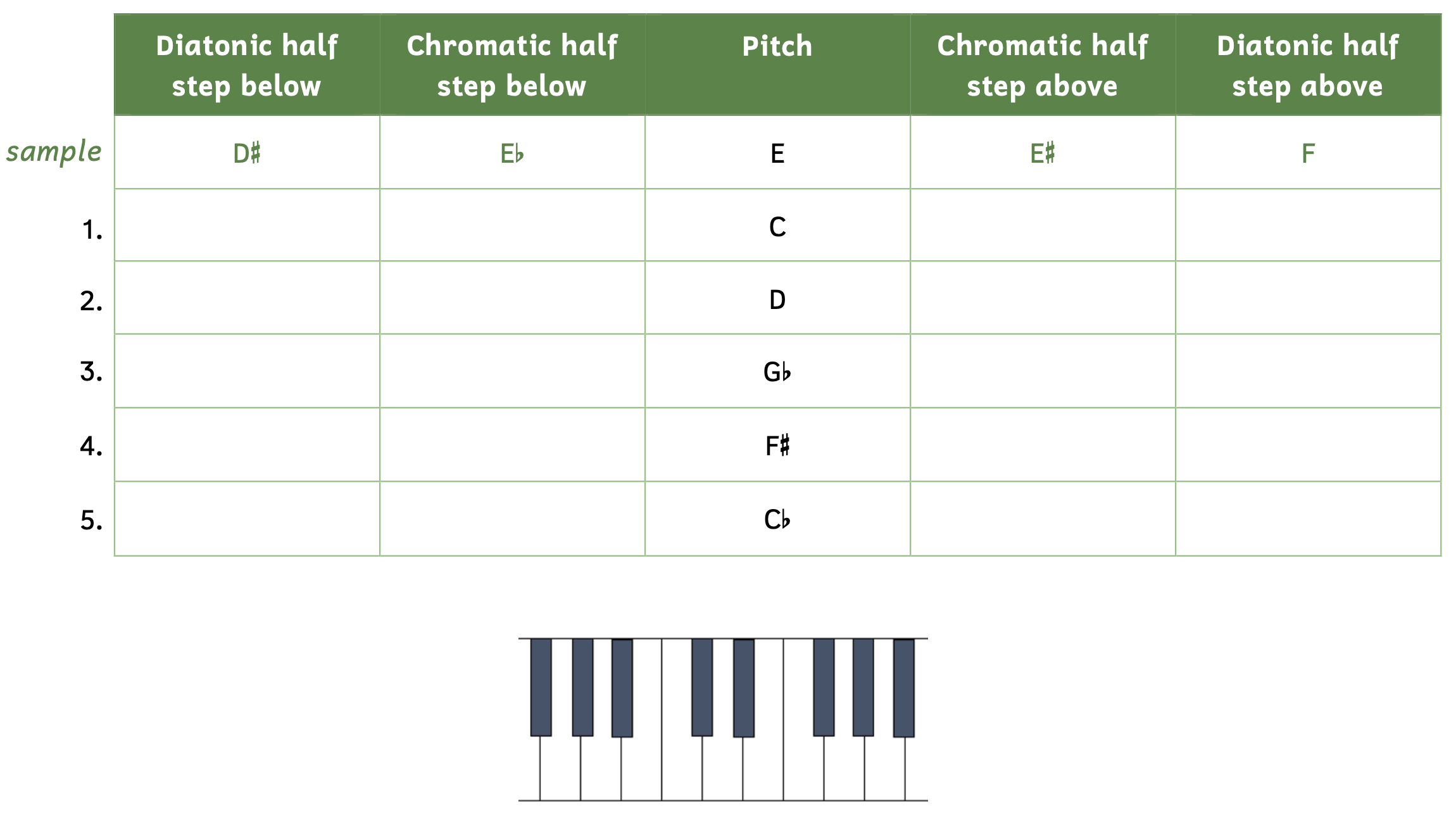
More Basics Steps to Music Theory
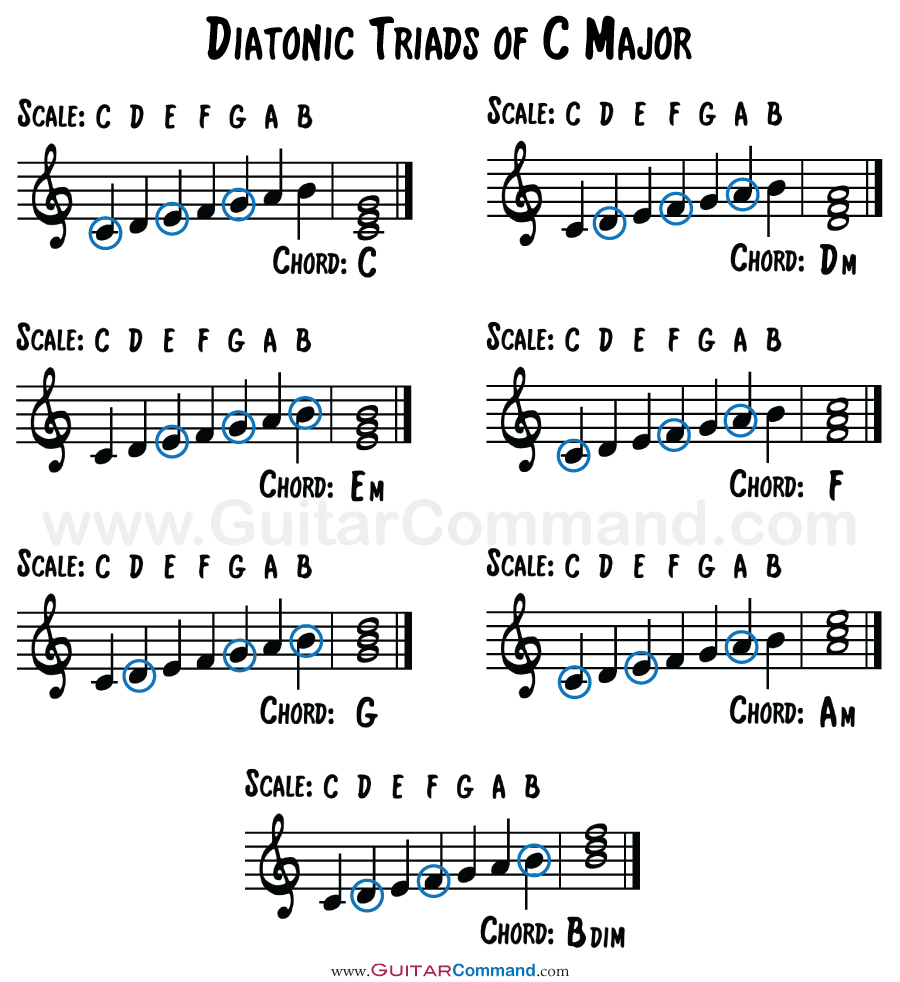
Diatonic Chord Progression Chart
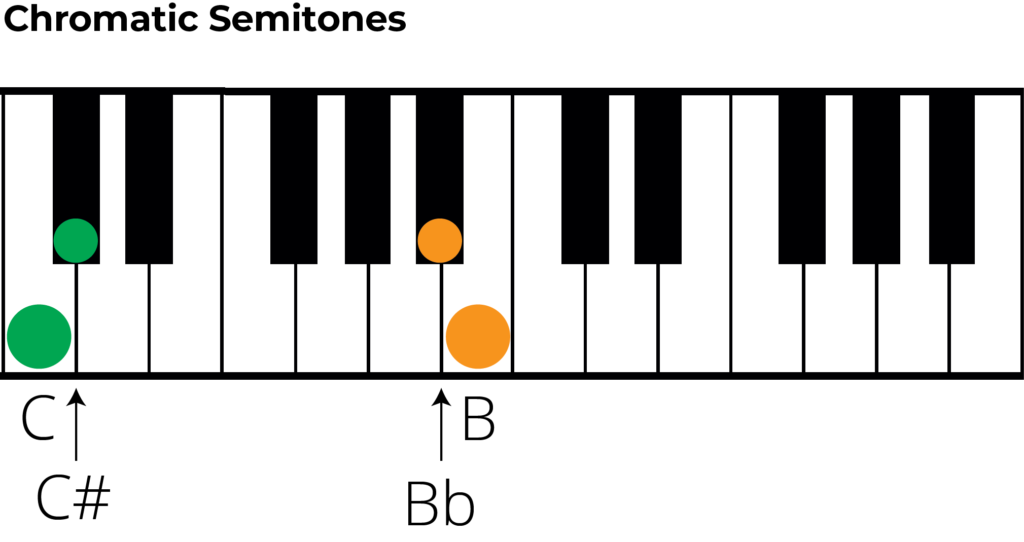
Tones and Semitones (Whole And Half Steps) A Musical Guide

Diatonic Half Step Chart

Diatonic half and whole steps Music, Music Theory ShowMe
Major Guitar Scales TrueFire
[Solved] How do I write the notes?. 3. Half Steps Write a diatonic

How to play the full chromatic scale on a diatonic harmonica Custom

Two HalfStep Types Diatonic HalfStep and Chromatic HalfStep Hear

Diatonic Half Step Music Theory Lesson 3
In A Chromatic Half Step, The Notes Have The Same Name.
Web The Diatonic Scale Is The Backbone Of The Seven Notes, Which Have Been The Foundation Of Western Music Since The Middle Ages.
Web A Diatonic Scale Will Consist Only Of Letters In The Musical Alphabet With The Occasional Sharp Or Flat Sign.
The Second Note In Each Of These Examples Is A Semitone Higher.
Related Post: