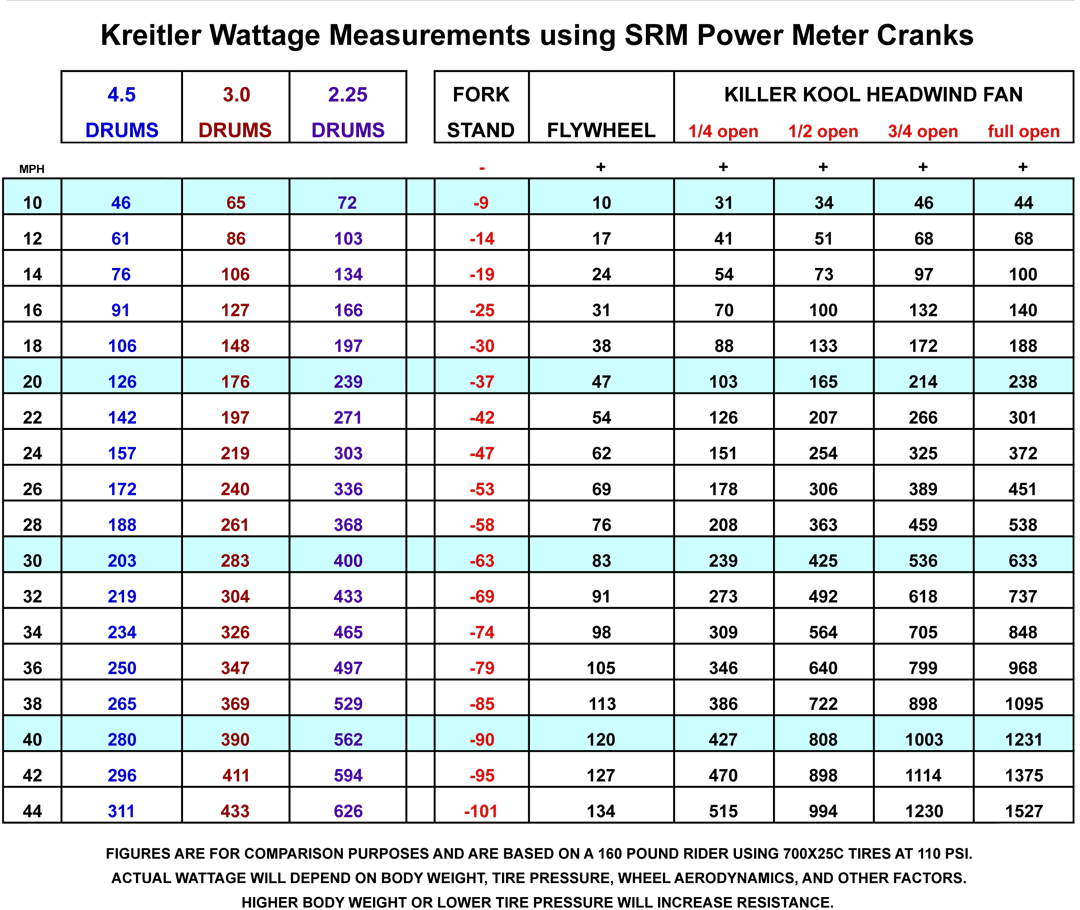
Cyclist Wattage Chart
Cyclist Wattage Chart - Here you will find three (3) graphs for watts vs. Web a much more accurate way to look at it is this chart from data cranker, which shows the average watts per kilogram (w/kg) that cyclists at different abilities typically can. Web typically measured in watts per kg (w/kg), it is a measure of the power a cyclist can generate relative to their body weight. What follows is this table overlaid with coloured lines. Quite intuitively, a rider who can put out 300 watts as their functional. Clothes & gear) 80.0 kg. Modify the fields below and. Web professional cyclists have an ftp of around 410 watts, while amateurs record between 250 and 300 watts. Move your cursor over the graph, or tap on it, to explore specific points. A quick guide to understanding your power. What is the average cycling power? Web a much more accurate way to look at it is this chart from data cranker, which shows the average watts per kilogram (w/kg) that cyclists at different abilities typically can. Web this ratio is calculated by dividing a rider’s power in watts by their weight in kilos (w/kg). Here you will find three. Web use our online cycling ftp calculator to find out what is your current ftp and how it compares with some of the best cyclists in the world. It’s expressed as watts of cycling power produced per. Web think of cycling wattage charts as your road map to competition phase. Web a much more accurate way to look at it. Web for a beginner cyclist, the average maximum watts is 2.11 per kilogram over 5 minutes. Clothes & gear) 80.0 kg. It’s expressed as watts of cycling power produced per. Here you will find three (3) graphs for watts vs. What follows is this table overlaid with coloured lines. Clothes & gear) 80.0 kg. A quick guide to understanding your power. Here you will find three (3) graphs for watts vs. The higher the number, the more. Web professional cyclists have an ftp of around 410 watts, while amateurs record between 250 and 300 watts. The higher the number, the more. However, power is related to weight. Move your cursor over the graph, or tap on it, to explore specific points. Why w/kg is important and how to improve yours | bikeradar. It’s expressed as watts of cycling power produced per. Web we’ll explore how wattage varies for different cycling levels, what factors influence it, how to improve your average power output, and more. Why w/kg is important and how to improve yours | bikeradar. Speed plus calculator for watts to speed plus race category per power to weight measurements. Web think of cycling wattage charts as your road map to. Web this ratio is calculated by dividing a rider’s power in watts by their weight in kilos (w/kg). What you need to know about this metric and how you compare to the competition. Why w/kg is important and how to improve yours | bikeradar. Speed plus calculator for watts to speed plus race category per power to weight measurements. Web. However, power is related to weight. Web typically measured in watts per kg (w/kg), it is a measure of the power a cyclist can generate relative to their body weight. Quite intuitively, a rider who can put out 300 watts as their functional. Why w/kg is important and how to improve yours | bikeradar. It’s expressed as watts of cycling. Web this ratio is calculated by dividing a rider’s power in watts by their weight in kilos (w/kg). An amateur cyclist is likely to have a ratio of 3.5 watts/kg over 5 minutes. You assess where you want to go, then you can figure out exactly what kind of intervals,. Web use our online cycling ftp calculator to find out. However, power is related to weight. Modify the fields below and. Web typically measured in watts per kg (w/kg), it is a measure of the power a cyclist can generate relative to their body weight. Web this ratio is calculated by dividing a rider’s power in watts by their weight in kilos (w/kg). What is the average cycling power? Here you will find three (3) graphs for watts vs. Web use our online cycling ftp calculator to find out what is your current ftp and how it compares with some of the best cyclists in the world. Web professional cyclists have an ftp of around 410 watts, while amateurs record between 250 and 300 watts. Quite intuitively, a rider who can put out 300 watts as their functional. Web explore the relationship between your cycling power (wattage) and speed. Web think of cycling wattage charts as your road map to competition phase. The higher the number, the more. Web typically measured in watts per kg (w/kg), it is a measure of the power a cyclist can generate relative to their body weight. Web for a beginner cyclist, the average maximum watts is 2.11 per kilogram over 5 minutes. What you need to know about this metric and how you compare to the competition. Move your cursor over the graph, or tap on it, to explore specific points. An amateur cyclist is likely to have a ratio of 3.5 watts/kg over 5 minutes. A quick guide to understanding your power. Why w/kg is important and how to improve yours | bikeradar. Generally, untrained riders have an ftp below 2.0 w/kg for men and 1.5 w/kg for women, while professional racers may be. What is the average cycling power?
Table 1 Powertoweight ratio (W/kg) for a range of rider weights and

séance vélo > mesurer sa PMA et pourquoi.
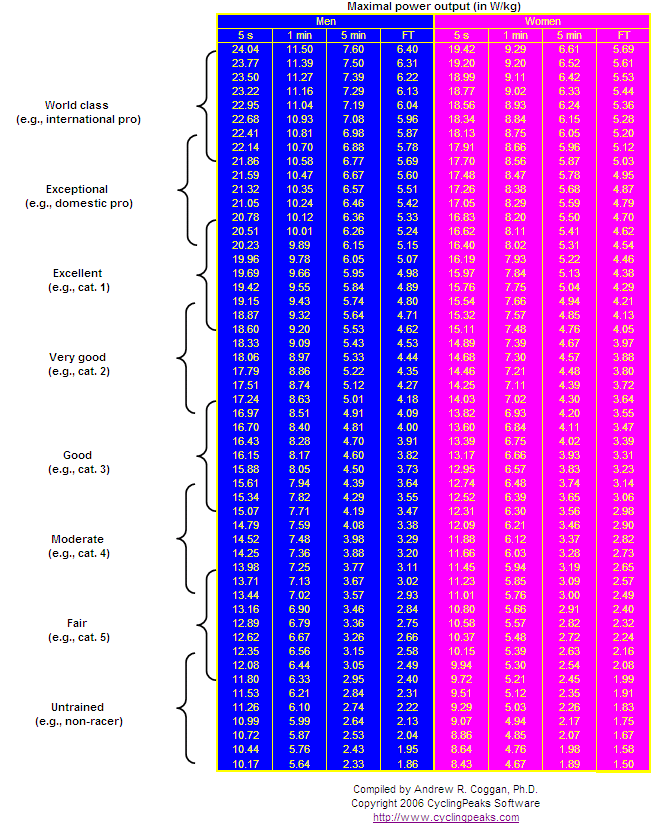
GitHub pulmark/cyclingpowerprofile Power profile calculator for
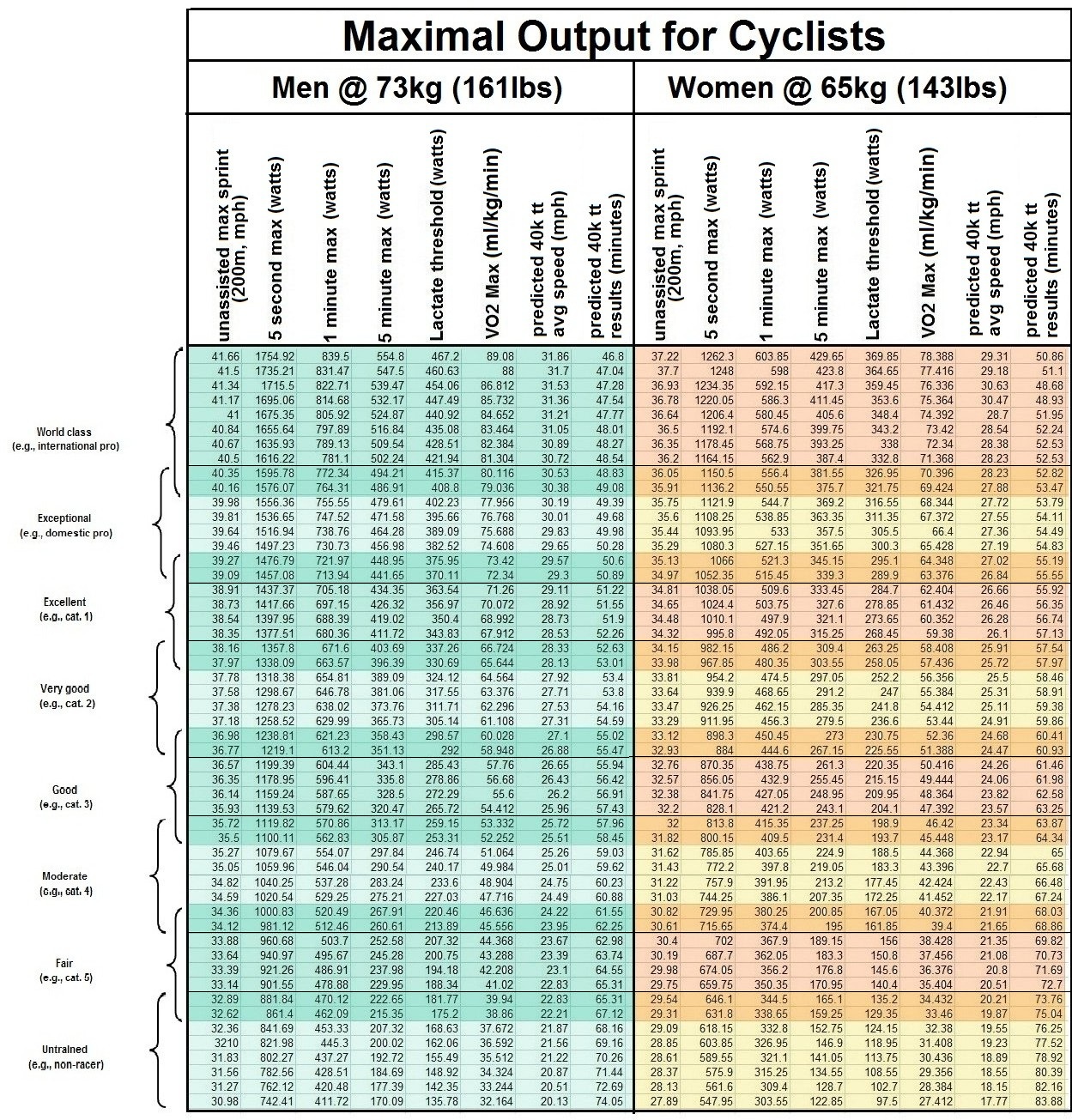
My World From a Bicycle Comparative Measurements of Maximal Outputs
Cycling Watts Chart My XXX Hot Girl

What is the Wattage of a Pro Cyclist With Comprehensive Chart for 2023
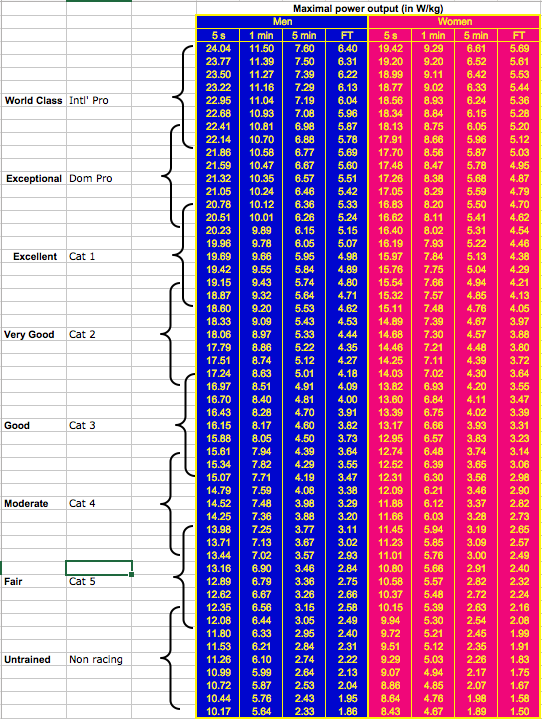
Why Do Watts Per Kilogram Matter in Cycling? Coaching and Training

Watts Per Kg Cycling Chart
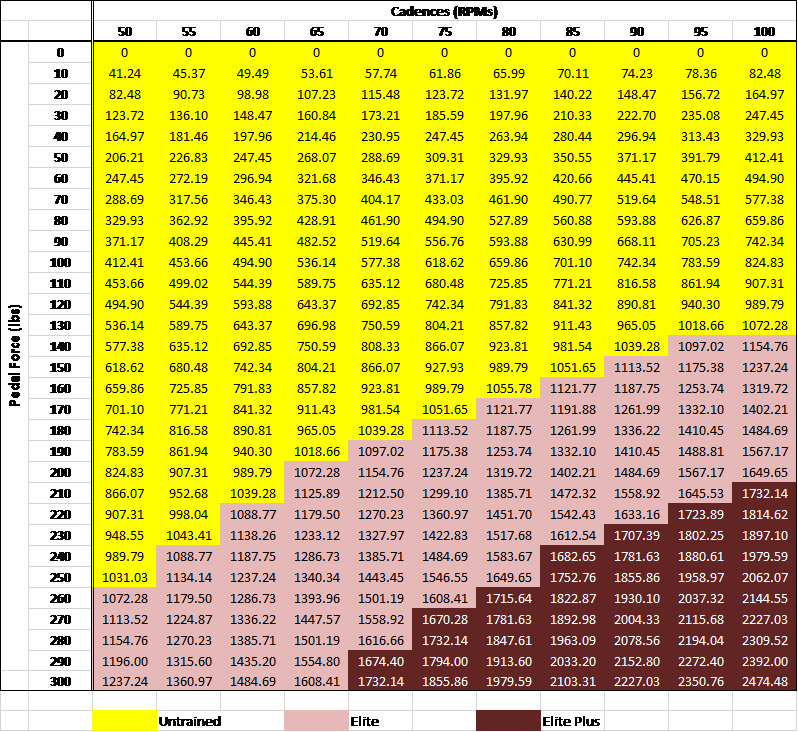
Cyclist Power Generators Physical Cycling
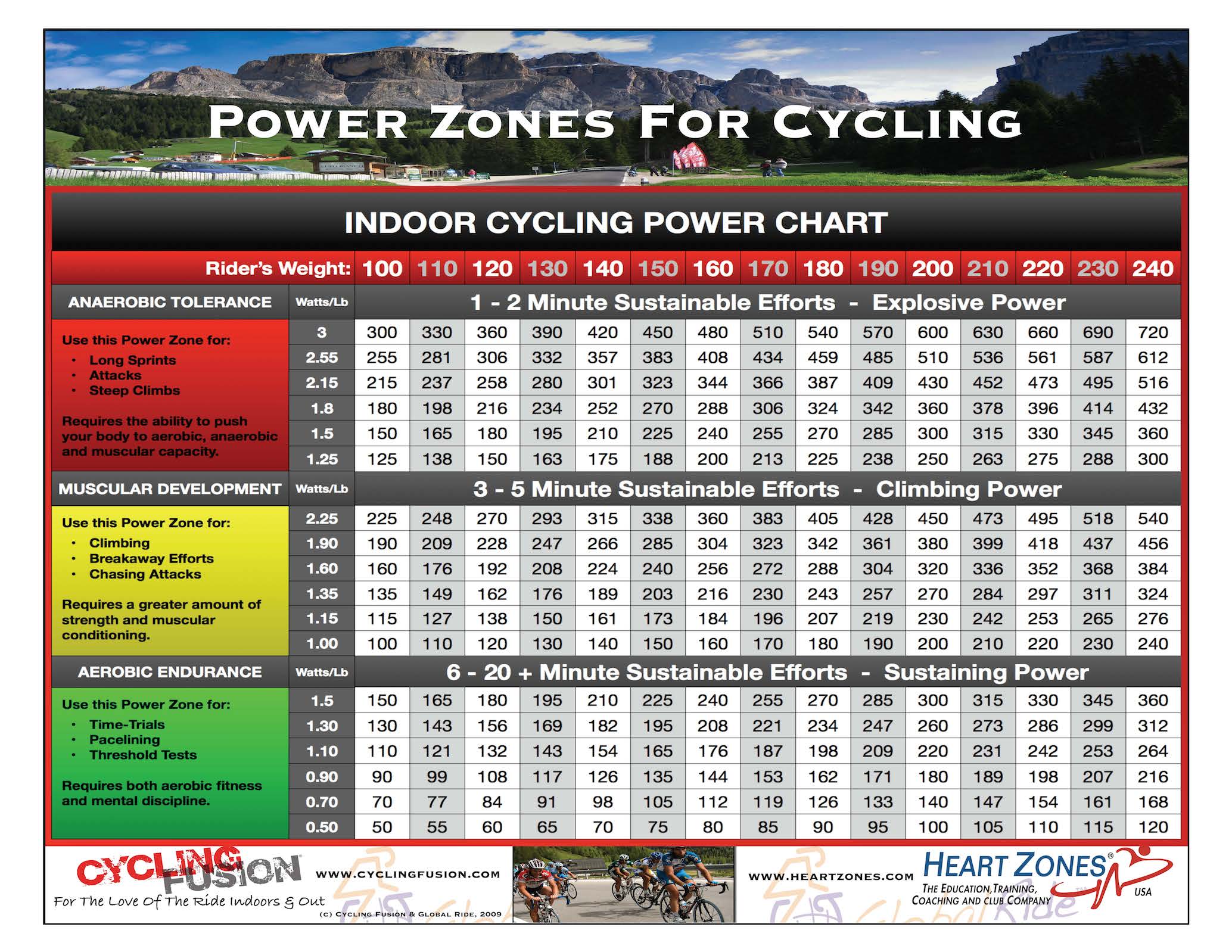
Power Training Cycling Power Training Zones
It’s Expressed As Watts Of Cycling Power Produced Per.
Web We’ll Explore How Wattage Varies For Different Cycling Levels, What Factors Influence It, How To Improve Your Average Power Output, And More.
You Assess Where You Want To Go, Then You Can Figure Out Exactly What Kind Of Intervals,.
However, Power Is Related To Weight.
Related Post: