Covalent Radius Chart
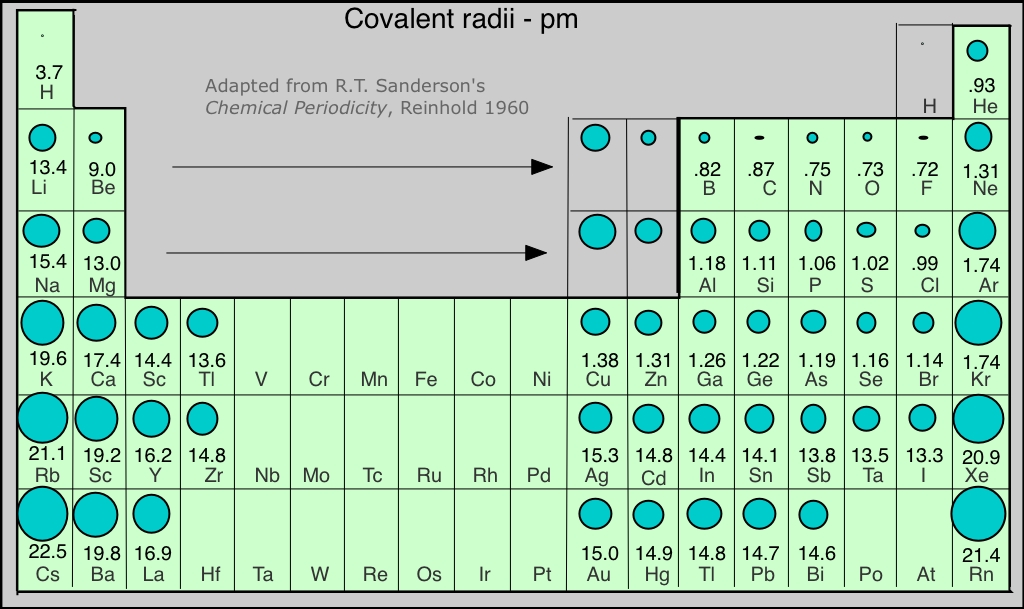
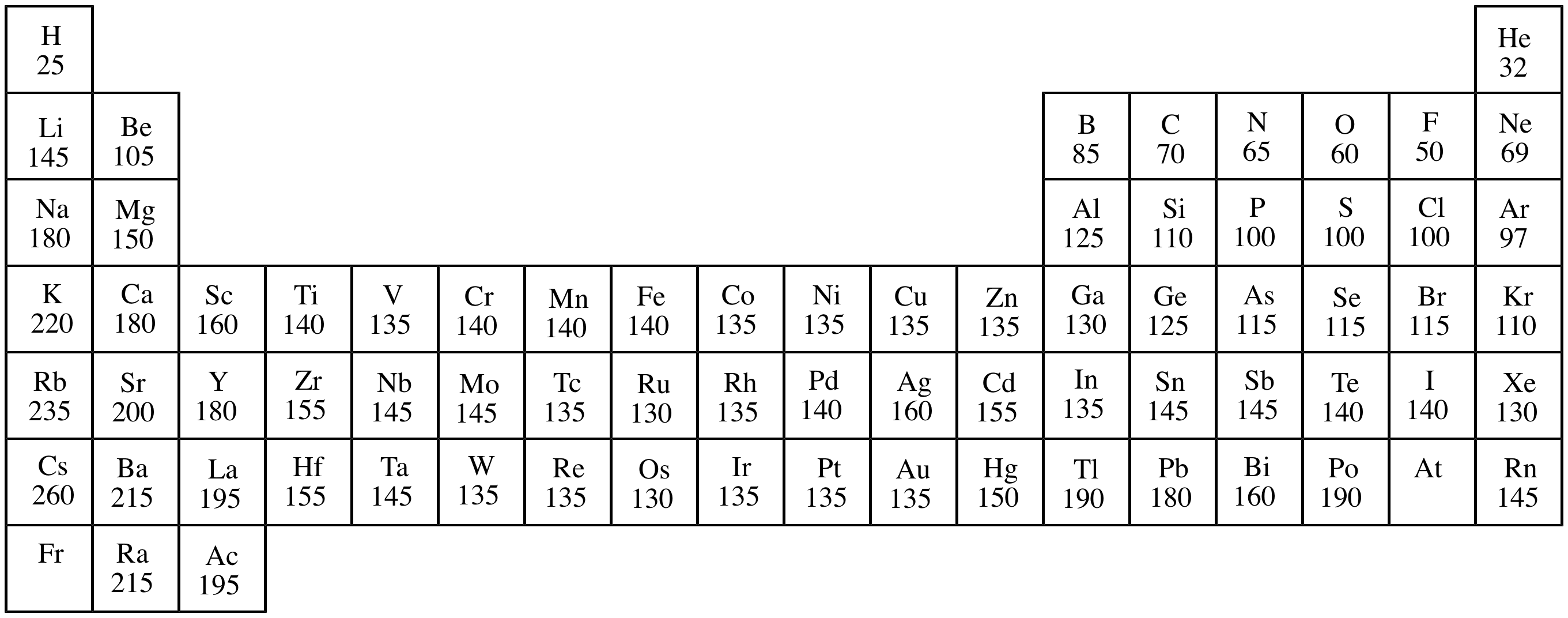
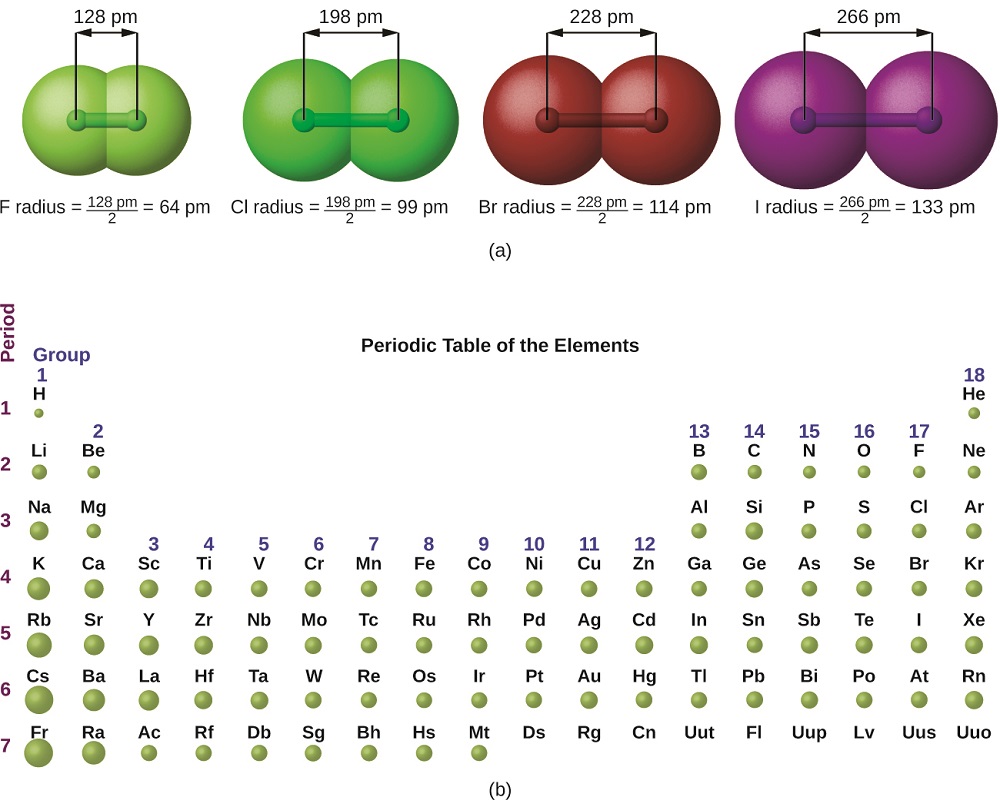
Covalent Radius Chart - Web the covalent radius, r cov, is a measure of the size of an atom that forms part of one covalent bond. Don't let static charges disrupt your weighing accuracy. For example the average covalent radius for hydrogen is 31 pm and the average neon covalent radius is 58 pm. Usually, you see covalent radius in units of picometers (pm) or angstroms (å), where 1 å = 100 pm. When two atoms of the same element are covalently bonded, the radius of each atom will be half the distance between. Point to the graph to see details, or click for full data on that element. Web the covalent radius of an atom is the radius of an atom under the covalent bond with another atom (s) of a similar element. When two atoms of the same kind are bonded through a single bond in a neutral molecule, then one half of the bond length is referred to as the covalent radius. It is usually measured either in picometres (pm) or angstroms (å), with 1 å = 100 pm. [1], and pyykkö and atsumi [2]. Web atomic radius of all the elements are mentioned in the chart below. Complete and detailed technical data about the element $$$elementname$$$ in the periodic table. Web half of the single bond length between two similar atoms covalently bonded in a molecule is called the covalent radius. Thus, in cl 2 the internuclear distance is 0.198 nm so the covalent. When two atoms of the same element are covalently bonded, the radius of each atom will be half the distance between. Web covalent radius is expressed in terms of picometers (pm) or angstroms (å). [1], and pyykkö and atsumi [2]. Below mentioned radii are the van der waals radius in picometer (pm)). Wells, structural inorganic chemistry, 5th ed., clarendon press,. Web half of the single bond length between two similar atoms covalently bonded in a molecule is called the covalent radius. Wells, structural inorganic chemistry, 5th ed., clarendon press, oxford, 1984, p. Click here to buy a book, photographic periodic table poster, card deck, or 3d print based on the images you see here! Web the covalent radius is half. Thus, in cl 2 the internuclear distance is 0.198 nm so the covalent radius is taken to be 0.099 nm. Web the covalent atomic radius (r cov) is half the internuclear distance in a molecule with two identical atoms bonded to each other, whereas the metallic atomic radius (r met) is defined as half the distance between the nuclei of. [1], and pyykkö and atsumi [2]. It depends on the type of bond (single, double,.) and the electronegativity of the bonding partners. Don't let static charges disrupt your weighing accuracy. Click here to buy a book, photographic periodic table poster, card deck, or 3d print based on the images you see here! Web covalent radius is expressed in terms of. Atomic radius in the periodic table of elements. If the two atoms are of the same kind, then the covalent radius is simply one half of the bond length. In theory, the sum of two covalent radii should equal the covalent bond length between two atoms, but in practice the length of the bond depends on the chemical environment. Web. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the size of its atom, usually, the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost isolated electron. Web the covalent radius is half the distance between two atoms that share a covalent bond. The radius of an atom is derived from the bond lengths within nonpolar molecules;. Complete and detailed technical data about the element $$$elementname$$$ in the periodic table. Web the values of table 3 show the covalent radii from the two recent original determinations by cordero et al. Thus, in cl 2 the internuclear distance is 0.198 nm so the covalent radius is taken to be 0.099 nm. Web atomic radius of all the elements. Hence, the values of atomic radii given here in picometers can be converted to atomic units by dividing by 53, to the level of accuracy of the data given in this table. Web the covalent radius is half the distance between two atoms that share a covalent bond. Usually, you see covalent radius in units of picometers (pm) or angstroms. Web covalent radius when a covalent bond is present between two atoms, the covalent radius can be determined. Web it is often denoted by a0 and is approximately 53 pm. 292 (covalent radii for nonmetals); Web half of the single bond length between two similar atoms covalently bonded in a molecule is called the covalent radius. The radius of an. In theory, the sum of two covalent radii should equal the covalent bond length between two atoms, but in practice the length of the bond depends on the chemical environment. There are several methods that can be used to determine radii of atoms and ions: An effective radius assigned to an atom in a covalent compound. In principle, the sum of the two covalent radii should equal the covalent bond length between two atoms, r (ab) = r (a) + r (b). Web the covalent radius of an atom is the radius of an atom under the covalent bond with another atom (s) of a similar element. Web covalent radius when a covalent bond is present between two atoms, the covalent radius can be determined. Web it is often denoted by a0 and is approximately 53 pm. Usually, you see covalent radius in units of picometers (pm) or angstroms (å), where 1 å = 100 pm. The radius of an atom is derived from the bond lengths within nonpolar molecules; It is usually measured either in picometres (pm) or angstroms (å), with 1 å = 100 pm. Web for facts, physical properties, chemical properties, structure and atomic properties of the specific element, click on the element symbol in the below periodic table. Web the covalent radius, rcov, is a measure of the size of atom which forms part of a covalent bond. Web the values of table 3 show the covalent radii from the two recent original determinations by cordero et al. Web complete and detailed technical data about the element $$$elementname$$$ in the periodic table. Web the covalent radius is defined as half the distance between two atoms of the same element that are covalently bonded. Web the covalent radius is half the distance between two atoms that share a covalent bond.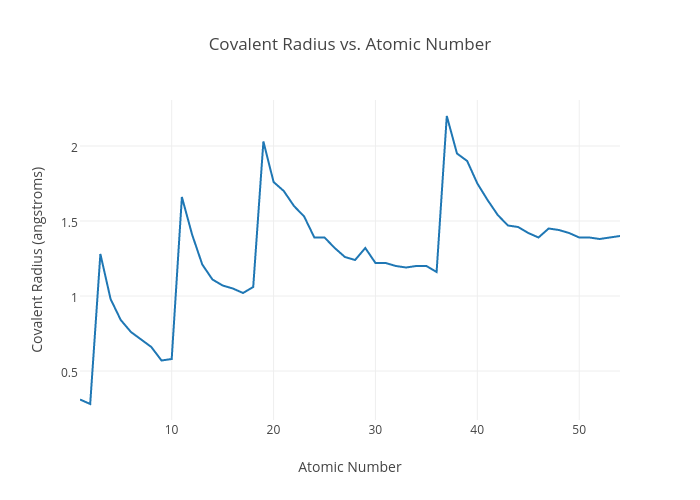
Covalent Radius Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
2.10 Periodic Properties of the Elements Chemistry LibreTexts
Periodic Table Atomic Radius Elcho Table

Smallest to largest atomic radius fleetlokasin

What is the Atomic Radius? EnthuZiastic
7.4 Electron Configurations, Valence Electrons, and the Periodic Table
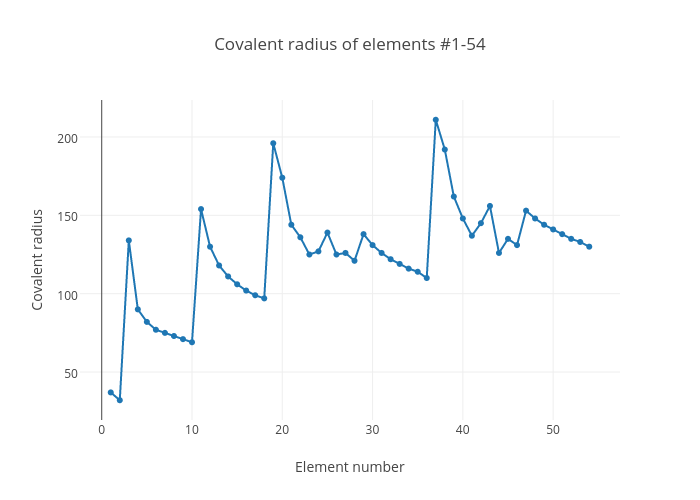
Covalent Radius Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master

Covalent Radius Definition and Trend
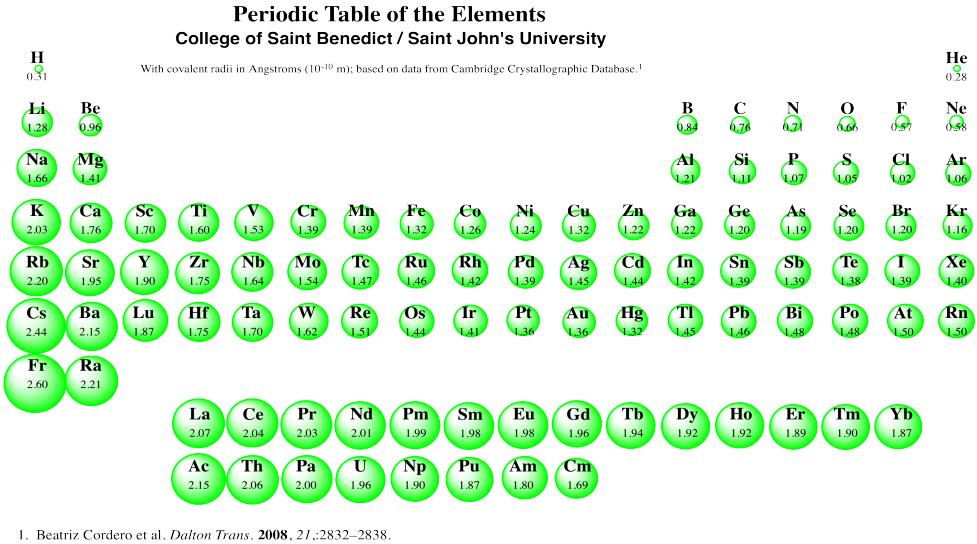
Covalent Radius
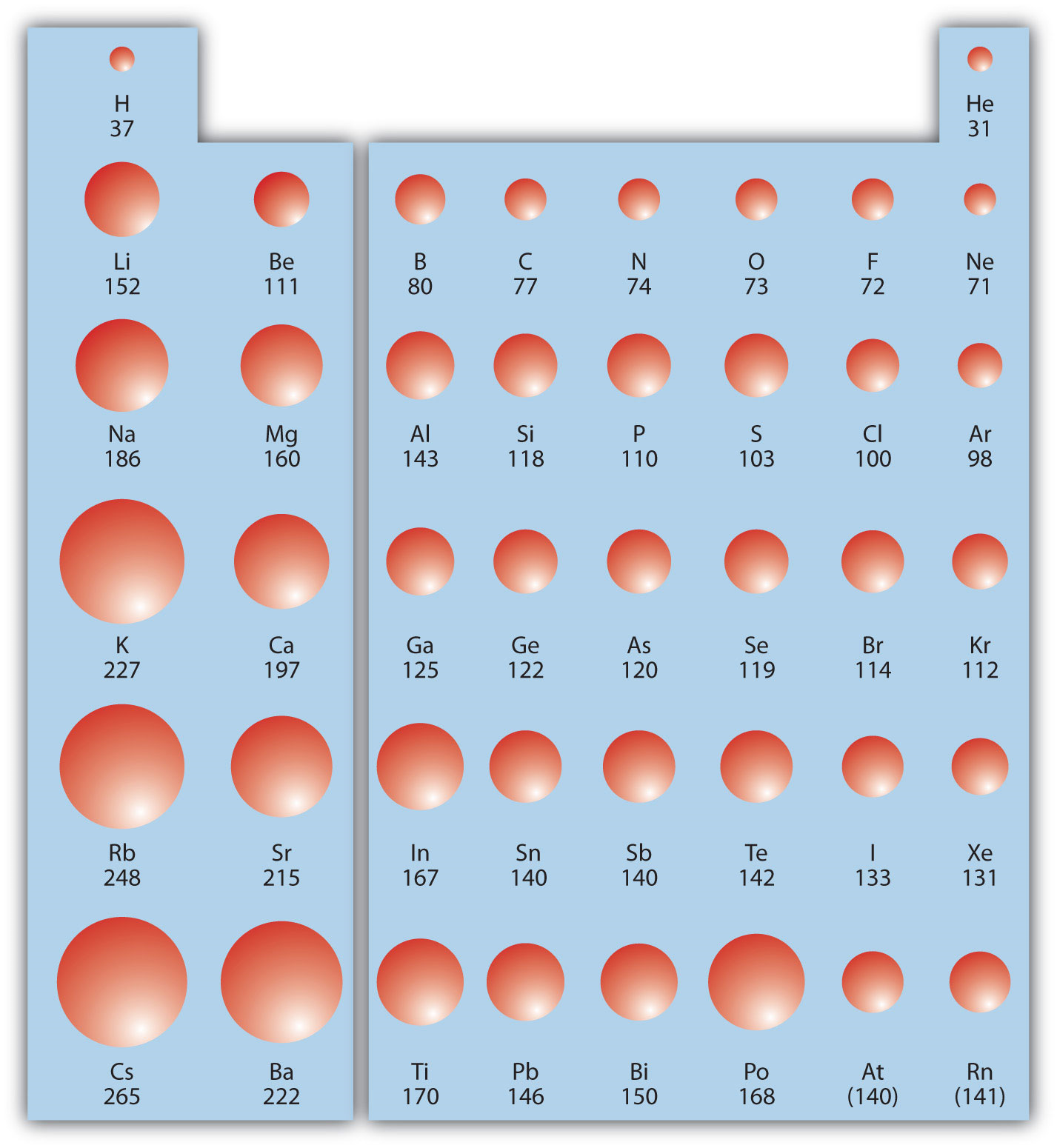
9.9 Periodic Trends Atomic Size, Ionization Energy, and Metallic
Web Atomic Radius Of All The Elements Are Mentioned In The Chart Below.
Point To The Graph To See Details, Or Click For Full Data On That Element.
Web Complete And Detailed Technical Data About The Element $$$Elementname$$$ In The Periodic Table.
Don't Let Static Charges Disrupt Your Weighing Accuracy.
Related Post: