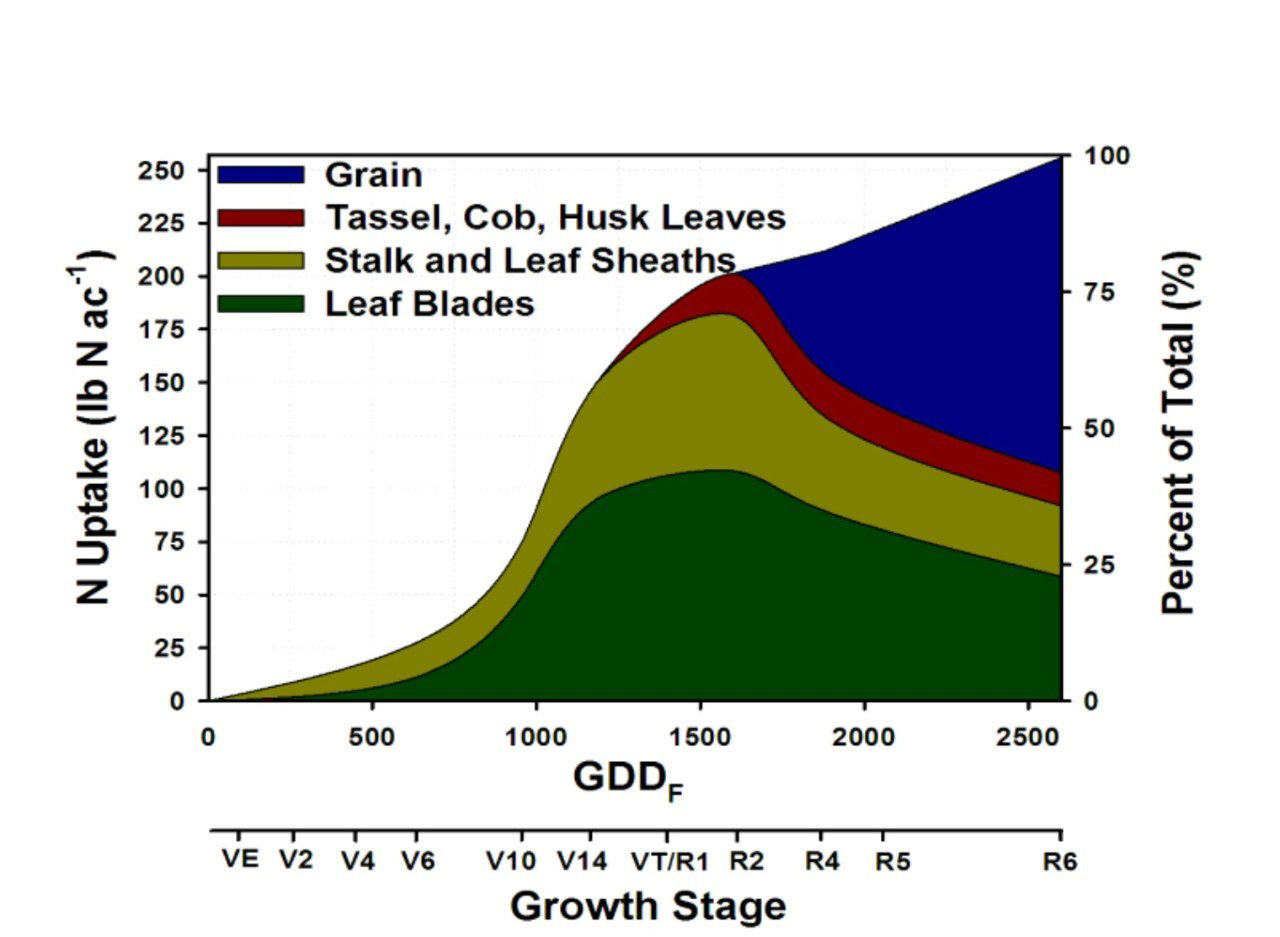
Corn Nutrient Uptake Chart
Corn Nutrient Uptake Chart - The second is just before tassel (v10 determines length of corn ear). The macronutrients, n, p, k, are often classified as primary macronutrients, because deficiencies of n, p, k are more common than the secondary macronutrients, ca, mg, and s. Approximately 38% of this demand is remobilized from vegetative tissue; Fertilizer n represents by far the largest share of total fertilization costs for field corn. Biotechnology, breeding, and agronomic advancements have propelled corn yields to new highs with little guidance as to how to fertilize modern corn hybrids to achieve their maximum yield potential. Find out more about nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium and how nutrient uptake relates to water uptake during the life cycle of the corn plant. The effects of weather and management practices on root growth and nutrient uptake. Actual nutrient removal may vary based on many factors. When it comes to nutrients timing is critical. Web this crop insights article will view nutrient uptake from a corn plant’s perspective, exploring how the corn plant regulates nutrient uptake to maintain nutritional balance during the corn plant’s life cycle. When it comes to nutrients timing is critical. Web total nutrient uptake and removal for corn averaging 230 bushels per acre.1 harvest index (%) is a percentage of total plant uptake removed with the grain. The macronutrients, n, p, k, are often classified as primary macronutrients, because deficiencies of n, p, k are more common than the secondary macronutrients, ca,. Web the following charts demonstrate that sulfur uptake usually occurs after the crop has started growing. Web crops take up around 85kg p2o5/ha. Approximately 38% of this demand is remobilized from vegetative tissue; How nutrients get to the root and the process of nutrient uptake. Total n uptake from v6 to vt, lake carl blackwell, 2006. Web this crop insights article will view nutrient uptake from a corn plant’s perspective, exploring how the corn plant regulates nutrient uptake to maintain nutritional balance during the corn plant’s life cycle. Web nutrient contents of n, p, k, s, zn, and b were determined at six incrementally spaced growth stages: Web the following charts demonstrate that sulfur uptake usually. Web total nutrient uptake and removal for corn averaging 230 bushels per acre.1 harvest index (%) is a percentage of total plant uptake removed with the grain. Third is at r2 (r2 determines test weight and kernel fill). Web corn nutrient uptake and partitioning. Web there are 6 macronutrients: How nutrients get to the root and the process of nutrient. There are three windows of opportunity that are very important for corn. Web this crop insights article will view nutrient uptake from a corn plant’s perspective, exploring how the corn plant regulates nutrient uptake to maintain nutritional balance during the corn plant’s life cycle. Strachan explains how corn plants extract nutrients from soil and illustrates how corn plants regulate the. There are three windows of opportunity that are very important for corn. Refer to extension bulletins fertilizer guidelines for montana crops (eb0161) and nutrient uptake timing (eb0191) for. Web with high yields, ~140 to 210 lbs n/acre is needed to support grain development. *n, p, k and s numbers courtesy international plant nutrition institute (ipni). Find out more about nitrogen,. Strachan explains how corn plants extract nutrients from soil and illustrates how corn plants regulate the rate of nutrient extraction, as well as what agronomic practices best support this nutrient extraction process. There are three windows of opportunity that are very important for corn. Biotechnology, breeding, and agronomic advancements have propelled corn yields to new highs with little guidance as. Web corn grain nutrient removal chart. Approximately 38% of this demand is remobilized from vegetative tissue; I’ll focus here primarily on the uptake, partitioning, and utilization of. Web nutrient contents of n, p, k, s, zn, and b were determined at six incrementally spaced growth stages: Sulfur uptake follows nitrogen uptake very closely in most crops. Web nutrient contents of n, p, k, s, zn, and b were determined at six incrementally spaced growth stages: The effects of weather and management practices on root growth and nutrient uptake. Web this crop insights by stephen d. The above graph shows results over 2 years (6 total sites in oklahoma) where corn forage n uptake can be predicted. Nitrogen (n), phosphorus (p), potassium (k), calcium (ca), magnesium (mg), and sulfur (s). Actual nutrient removal may vary based on many factors. Web five of the six macronutrients, calcium, magnesium, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and the seven micronutrients, boron, chlorine, copper, iron, manganese, molybdenum, and zinc, are extracted from soil. How the root system develops over time and the relationships. For example in corn, sulfur and nitrogen uptake doesn’t increase until after v4 stage of development. Total n uptake from v6 to vt, lake carl blackwell, 2006. Web with high yields, ~140 to 210 lbs n/acre is needed to support grain development. Find out more about nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium and how nutrient uptake relates to water uptake during the life cycle of the corn plant. Total crop uptake is around 200kg/ha. Web this crop insights by stephen d. How the root system develops over time and the relationships between root growth, shoot growth and nutrient uptake. Web corn nutrient uptake and partitioning. The effects of weather and management practices on root growth and nutrient uptake. Web estimated uptake of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium from the soil required to support a grain yield of 300 bu/acre at different corn growth stages. Water moves via saturated flow and via unsaturated flow in the soil profile. Web nutrient contents of n, p, k, s, zn, and b were determined at six incrementally spaced growth stages: Fertilizer n represents by far the largest share of total fertilization costs for field corn. Refer to extension bulletins fertilizer guidelines for montana crops (eb0161) and nutrient uptake timing (eb0191) for. How nutrients get to the root and the process of nutrient uptake. Sulfur uptake follows nitrogen uptake very closely in most crops.
How Corn Plants Regulate Nutrient Uptake Pioneer® Seeds

Nutrient Uptake MSU Extension Soil Fertility Montana State University
Corn HighYield Program
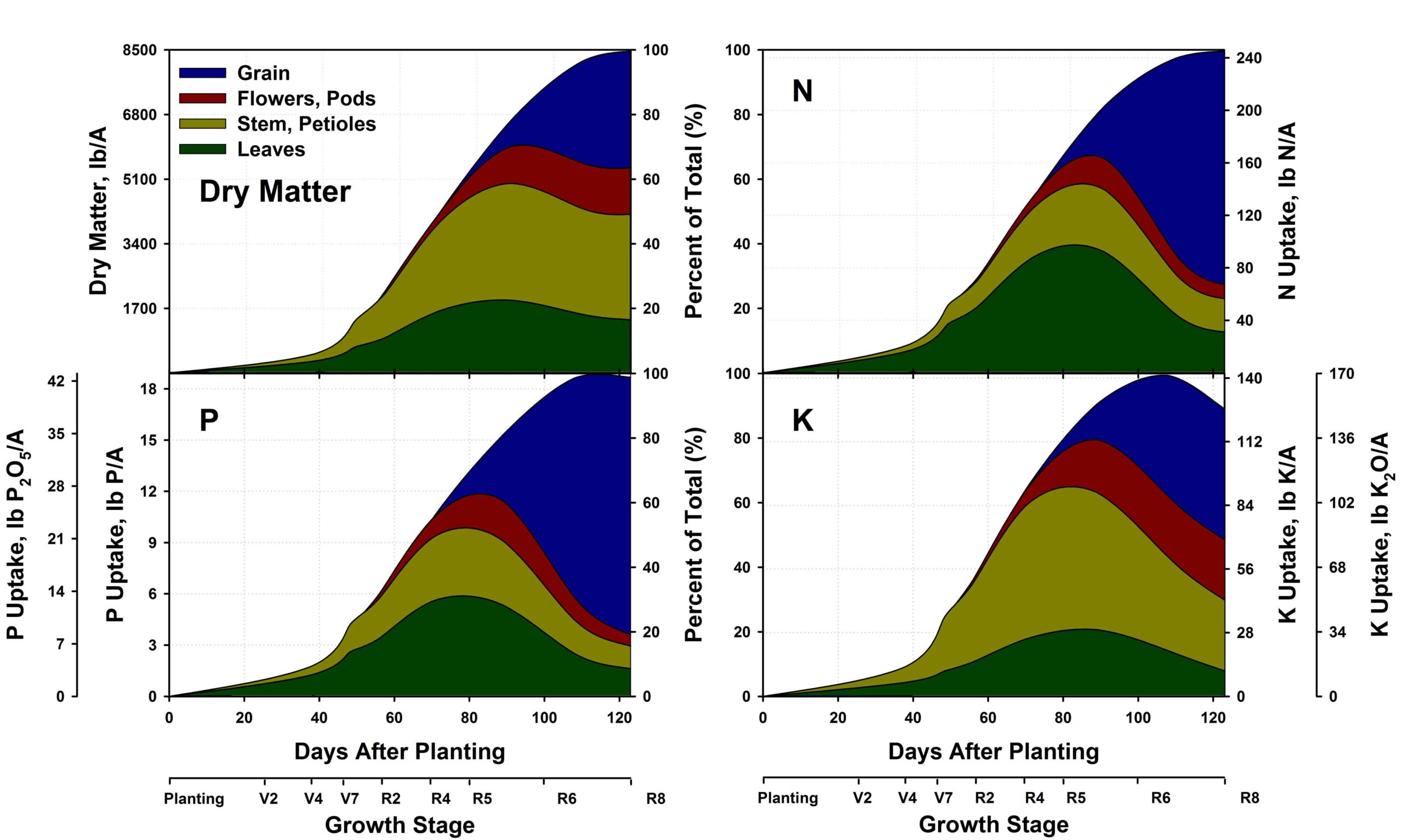
Nutrient Uptake and Partitioning Crop Physiology

Corn Nutrient Uptake and Partitioning Crop Physiology
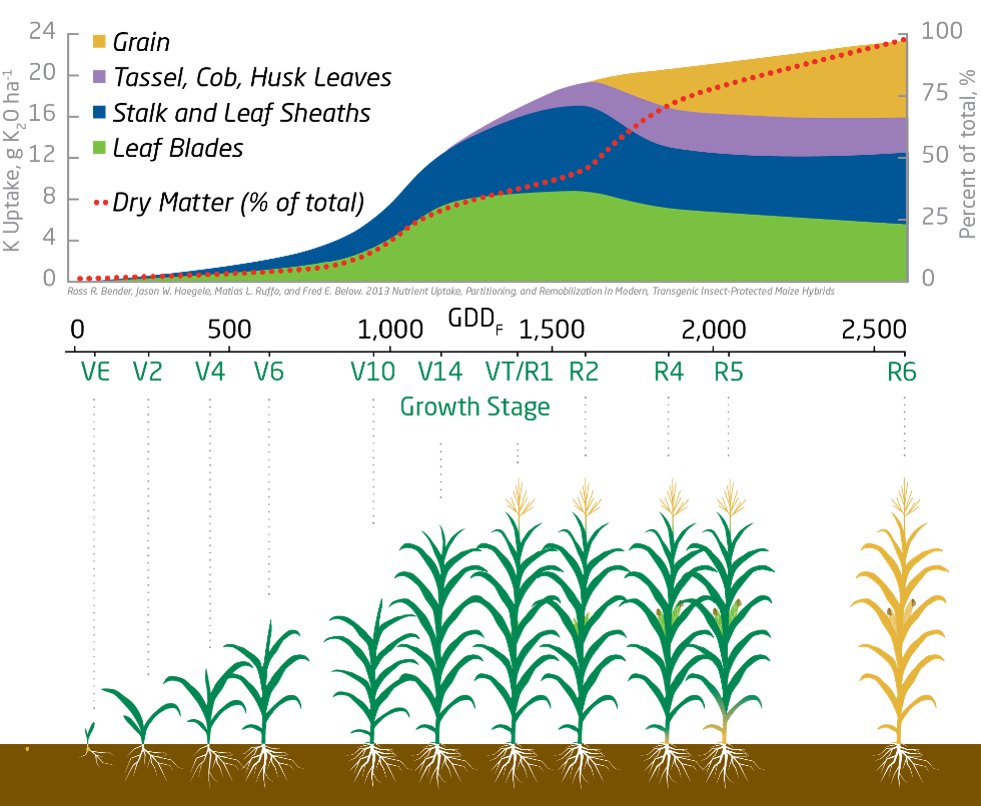
Corn Nutrition Guide
Corn Nutrient Uptake and Removal
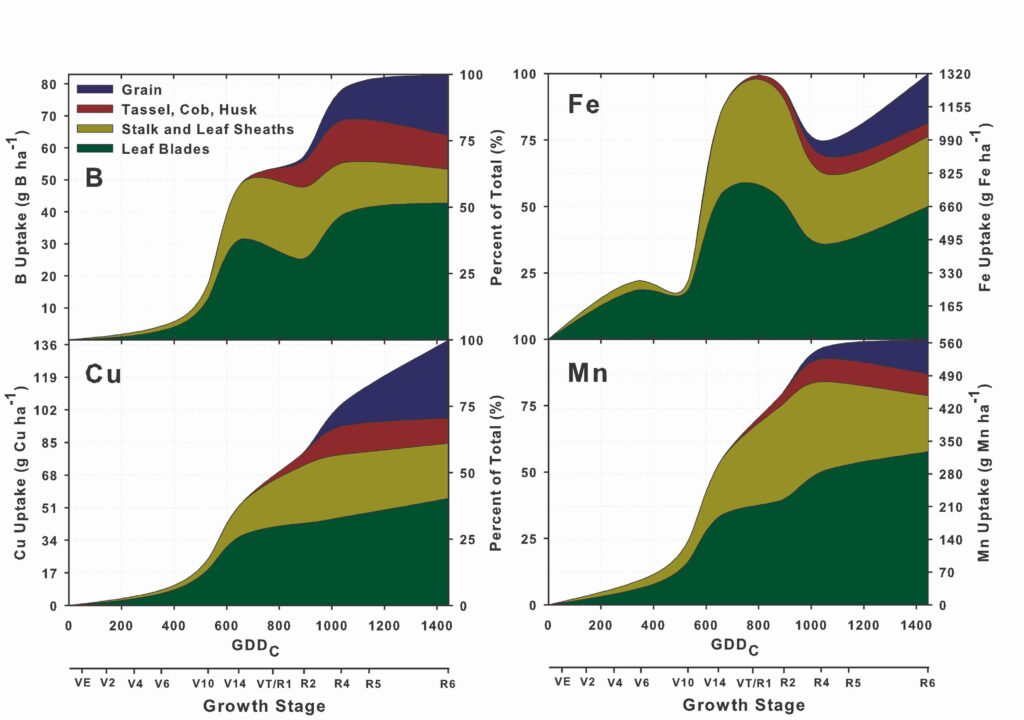
Corn Nutrient Uptake and Partitioning Crop Physiology
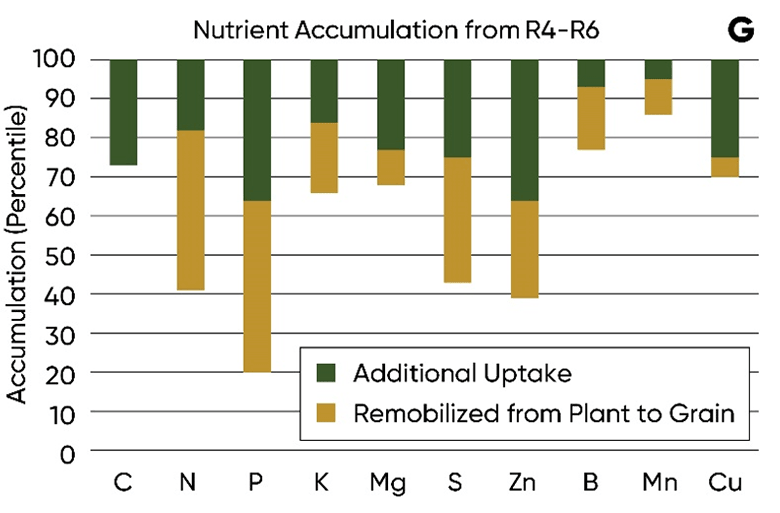
How Corn Plants Regulate Nutrient Uptake Pioneer® Seeds
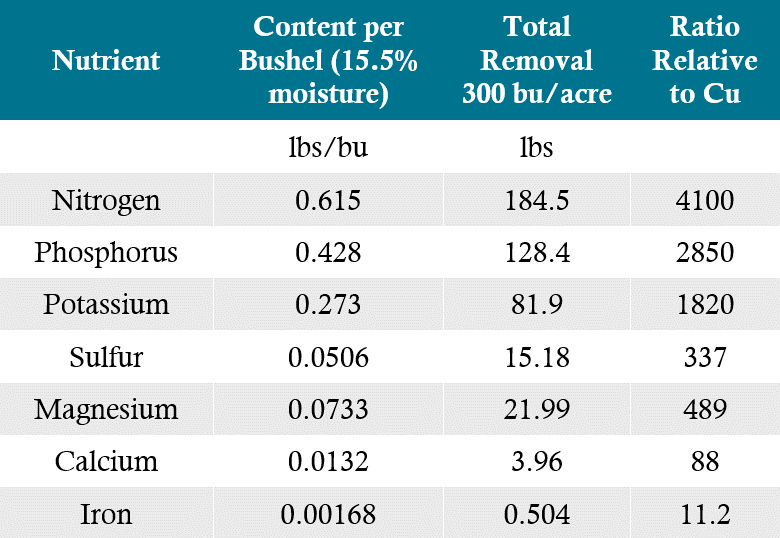
How Corn Plants Regulate Nutrient Uptake Pioneer® Seeds
Web The Graphs Below Give Nutrient Uptake Curves Throughout The Growing Season For Different Crops And Provide Information On Removal Rates.
Web There Are 6 Macronutrients:
Third Is At R2 (R2 Determines Test Weight And Kernel Fill).
Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K), Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), And Sulfur (S).
Related Post: