Chart Of Electromagnetic Radiations
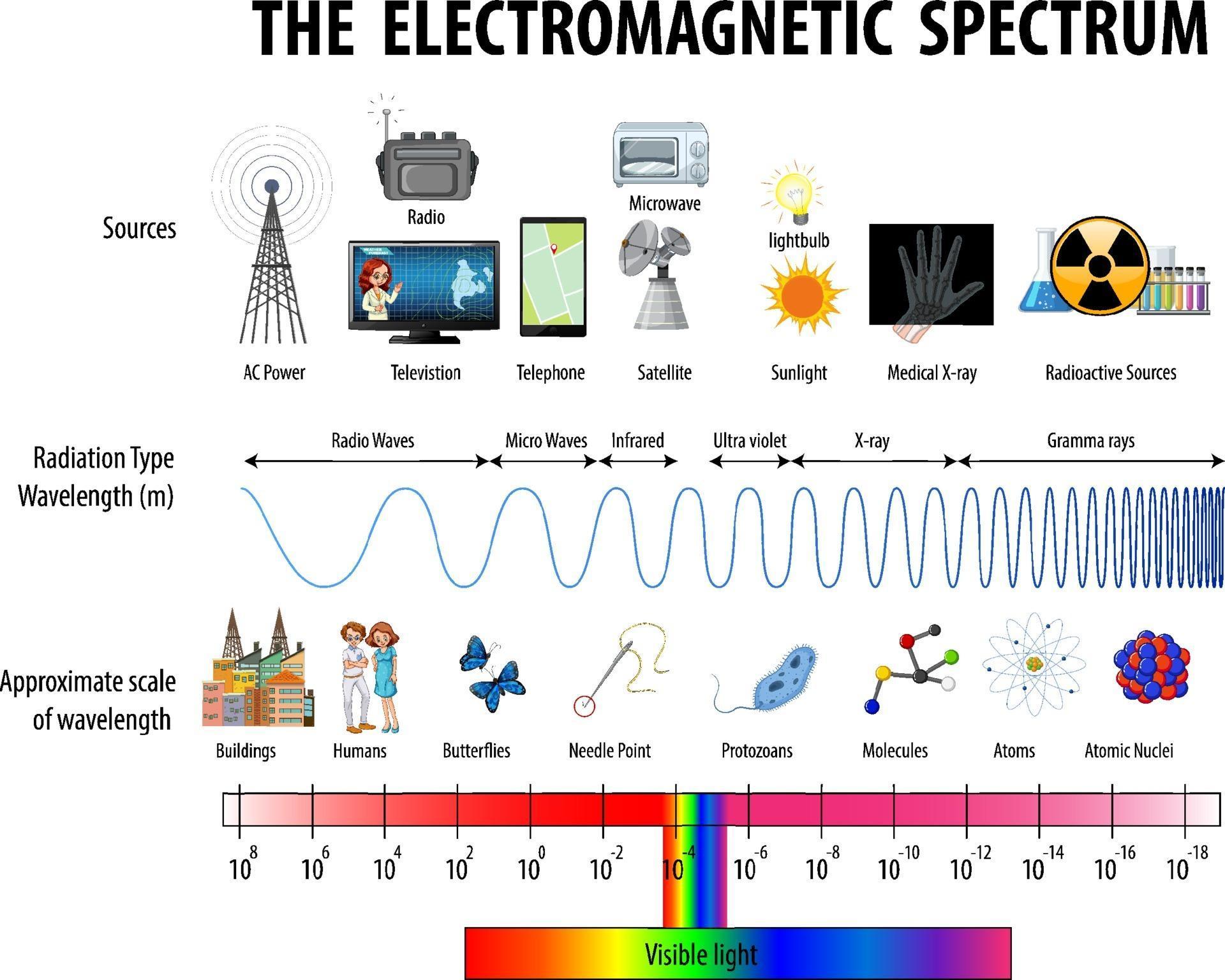
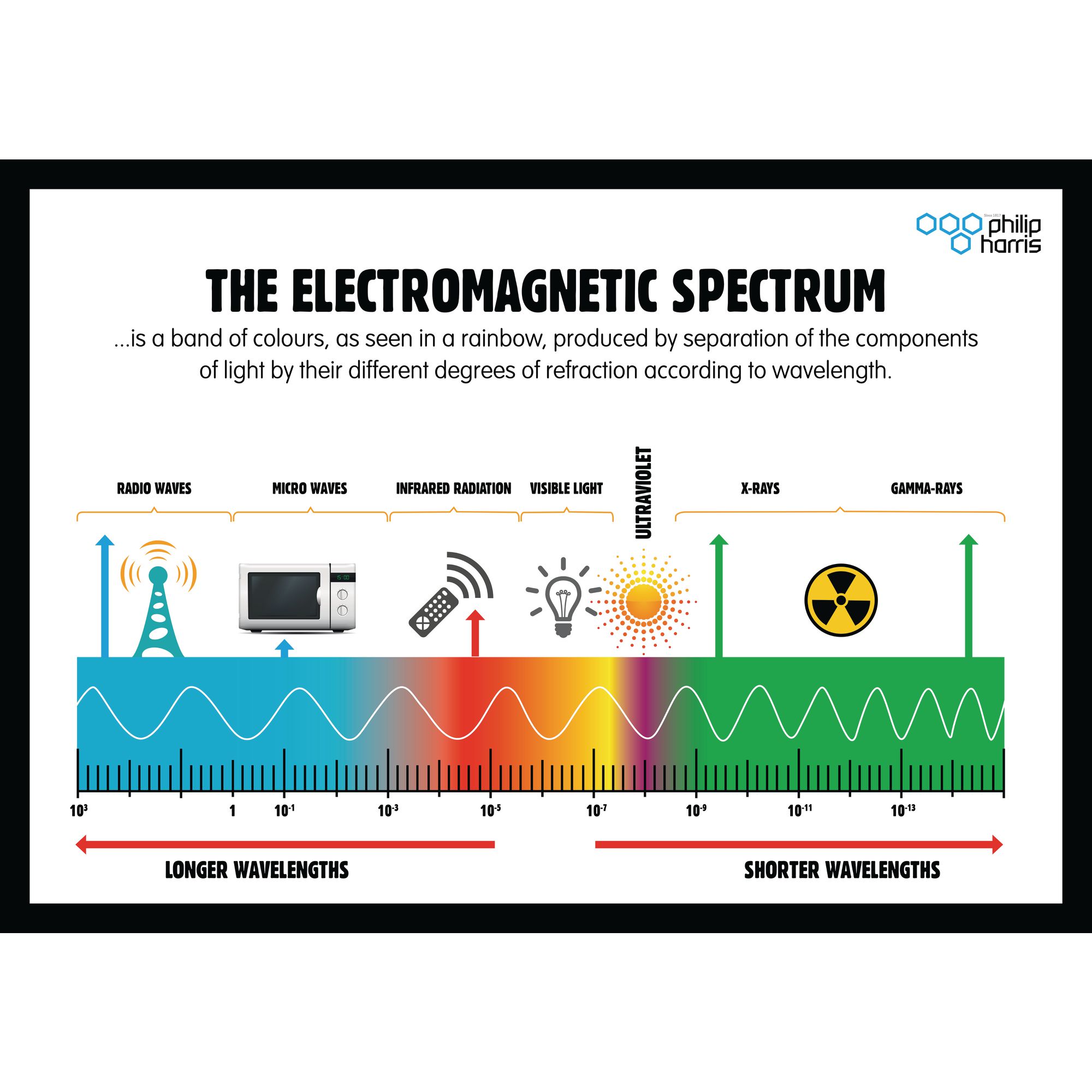
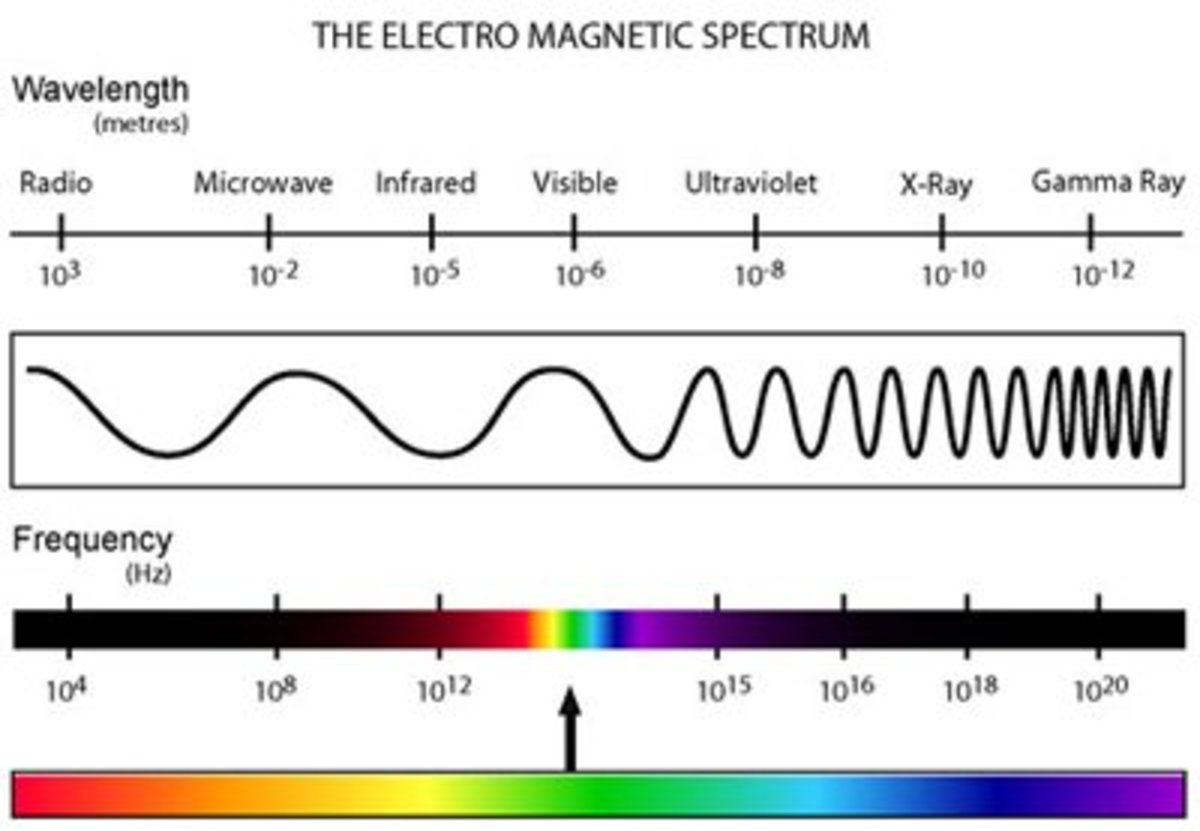
Chart Of Electromagnetic Radiations - Web electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the universal speed of light through free space or through a material medium in the form of the electric and magnetic fields that make up electromagnetic waves such as radio waves, visible light, and gamma rays. A molecule or a set of molecules can be read by the absorption of microwave radiation which provides transitions between rotational energy levels. This radiation propagates (moves) through space at 299,792 km per second (about 186,000 miles per second). Longer wavelengths with lower frequencies make up the radio spectrum. Web the electromagnetic spectrum is a range of frequencies, wavelengths and photon energies covering frequencies from below 1 hertz to above 10 25 hz, corresponding to wavelengths which are a few kilometres to a fraction of the size of an atomic nucleus in the spectrum of electromagnetic waves. Web define the electromagnetic spectrum, and describe it in terms of frequencies and wavelengths; The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. Web (more) in spite of these obvious differences of scale, all forms of electromagnetic radiation obey certain general rules that are well understood and that allow one to calculate with very high precision their properties and interactions with charged particles in atoms, molecules, and large objects. Any electromagnetic wave produced by currents in wires is classified as a radio wave, the lowest frequency electromagnetic waves. Web in physics, electromagnetic radiation (emr) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (em) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. Reflection, refraction, diffraction, oh my! The lowest frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is designated as “radio,” generally considered to have wavelengths within 1 millimeter to 100 kilometers or frequencies within 300 ghz to 3 khz. Although all electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, they do so at a wide range of frequencies, wavelengths, and. Web define the electromagnetic spectrum, and describe it in terms of frequencies and wavelengths; Web a diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths. There is a wide range of subcategories contained within radio including am and fm radio. Web listed below are the approximate wavelength, frequency, and energy limits. Each form has. Web electromagnetic radiation includes the far field part of the electromagnetic field around a transmitter. Indeed light is just one form of electromagnetic radiation. Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. Web you cannot buy this amazing chart of electromagnetic radiations anymore, but thanks to the folks at lawrence livermore national. A molecule or a set of molecules can be read by the absorption of microwave radiation which provides transitions between rotational energy levels. Any electromagnetic wave produced by currents in wires is classified as a radio wave, the lowest frequency electromagnetic waves. Web listed below are the approximate wavelength, frequency, and energy limits. Describe and explain the differences and similarities. Web by shaunacy ferro | published sep 3, 2013 9:00 pm edt. Web published 22 march 2022. Indeed light is just one form of electromagnetic radiation. Web listed below are the approximate wavelength, frequency, and energy limits. Web electromagnetic radiation transports energy from point to point. Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. Any electromagnetic wave produced by currents in wires is classified as a radio wave, the lowest frequency electromagnetic waves. Describe and explain the differences and similarities of each section of the electromagnetic spectrum and the applications of radiation from those sections There is a. Of the various regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Web published 22 march 2022. Web if you're into scientific antiques, you have to examine the details in this 1944 poster from the w.m welch scientific company: Web the electromagnetic spectrum is separated into many categories and subcategories, based on the frequency and wavelength, source, and uses of the electromagnetic waves. Web. Web electromagnetic radiation transports energy from point to point. Web electromagnetic spectrum diagram | mynasadata. Web in physics, electromagnetic radiation (emr) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (em) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. Any electromagnetic wave produced by currents in wires is classified as a radio wave, the lowest frequency electromagnetic waves. Web. Web listed below are the approximate wavelength, frequency, and energy limits. Web electromagnetic radiation includes the far field part of the electromagnetic field around a transmitter. Web electricity chart vintage style: Web a diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths. There is a wide range of subcategories contained within radio including am. Web if you're into scientific antiques, you have to examine the details in this 1944 poster from the w.m welch scientific company: Web electromagnetic radiation includes the far field part of the electromagnetic field around a transmitter. The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. That is, it travels at the speed of. Each form has different wavelengths and energy levels, resulting in unique properties and applications. Indeed light is just one form of electromagnetic radiation. Web electromagnetic radiation includes the far field part of the electromagnetic field around a transmitter. Reflection, refraction, diffraction, oh my! That is, it travels at the speed of light. Web in physics, electromagnetic radiation (emr) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (em) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. Web the electromagnetic spectrum is separated into many categories and subcategories, based on the frequency and wavelength, source, and uses of the electromagnetic waves. Web define the electromagnetic spectrum, and describe it in terms of frequencies and wavelengths; Web you cannot buy this amazing chart of electromagnetic radiations anymore, but thanks to the folks at lawrence livermore national laboratory, extremely high resolution image files of it have been placed on the flickr website. Web electromagnetic spectrum provides clearly information of molecules if they are rotational transitions, vibrational transitions, or electronic transitions. Web (more) in spite of these obvious differences of scale, all forms of electromagnetic radiation obey certain general rules that are well understood and that allow one to calculate with very high precision their properties and interactions with charged particles in atoms, molecules, and large objects. Any electromagnetic wave produced by currents in wires is classified as a radio wave, the lowest frequency electromagnetic waves. This radiation propagates (moves) through space at 299,792 km per second (about 186,000 miles per second). Web published 22 march 2022. Web if you're into scientific antiques, you have to examine the details in this 1944 poster from the w.m welch scientific company: Web electromagnetic radiation transports energy from point to point.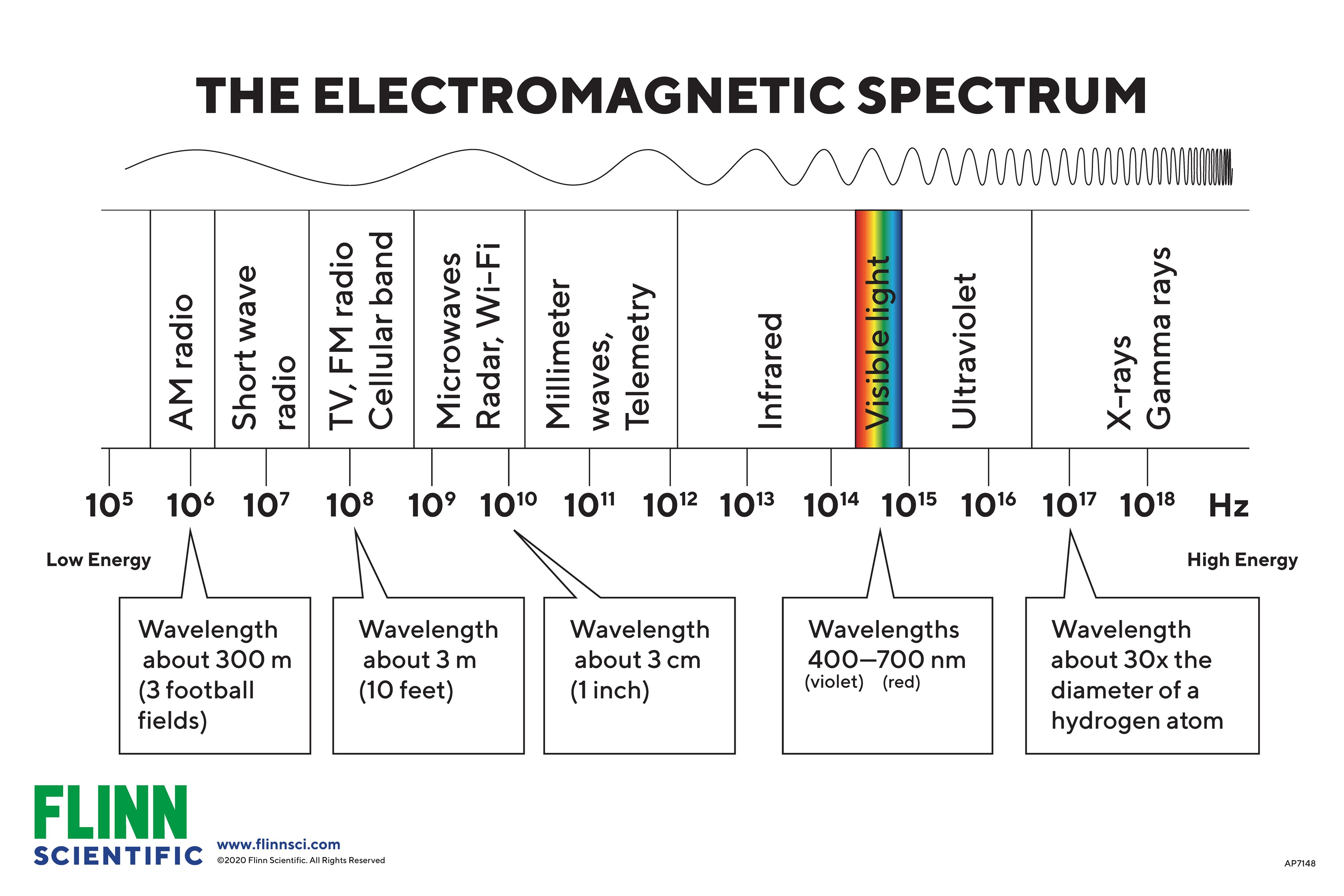
Flinn Spectrum Charts for Physics and Physical Science
Learning the Spectrum Telegraph

Understanding the Spectrum Telegraph
HE1588526 Spectrum Poster Findel Education

Full Spectrum Information collection, Physics
The Radiant Radioactive Spectrum HubPages
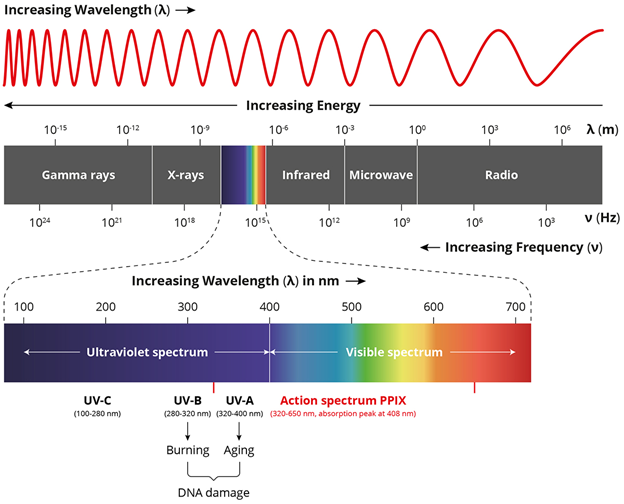
Spectrum Definition, Characteristics, Range, Diagram

Elektronik Hobi
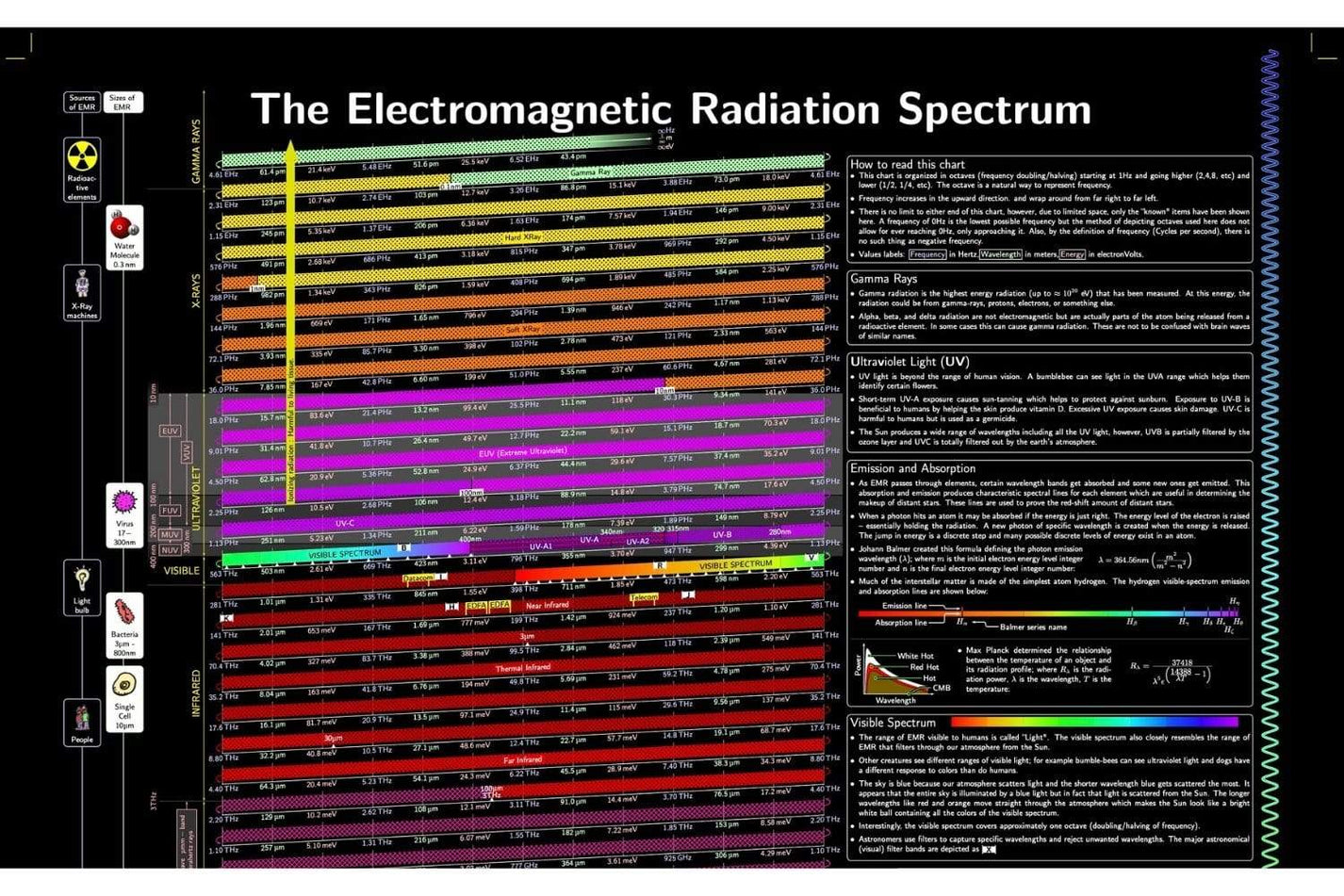
Radiation Spectrum Chart Arbor Scientific

The Spectrum Mini Physics Learn Physics
Web A Diagram Of The Electromagnetic Spectrum, Showing Various Properties Across The Range Of Frequencies And Wavelengths.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum Is The Full Range Of Electromagnetic Radiation, Organized By Frequency Or Wavelength.
Dive Into The Wonderful World Of Electromagnetic.
Classically, Electromagnetic Radiation Consists Of Electromagnetic Waves, Which Are Synchronized Oscillations Of Electric And Magnetic Fields.
Related Post: