Cell Cycle Pie Chart
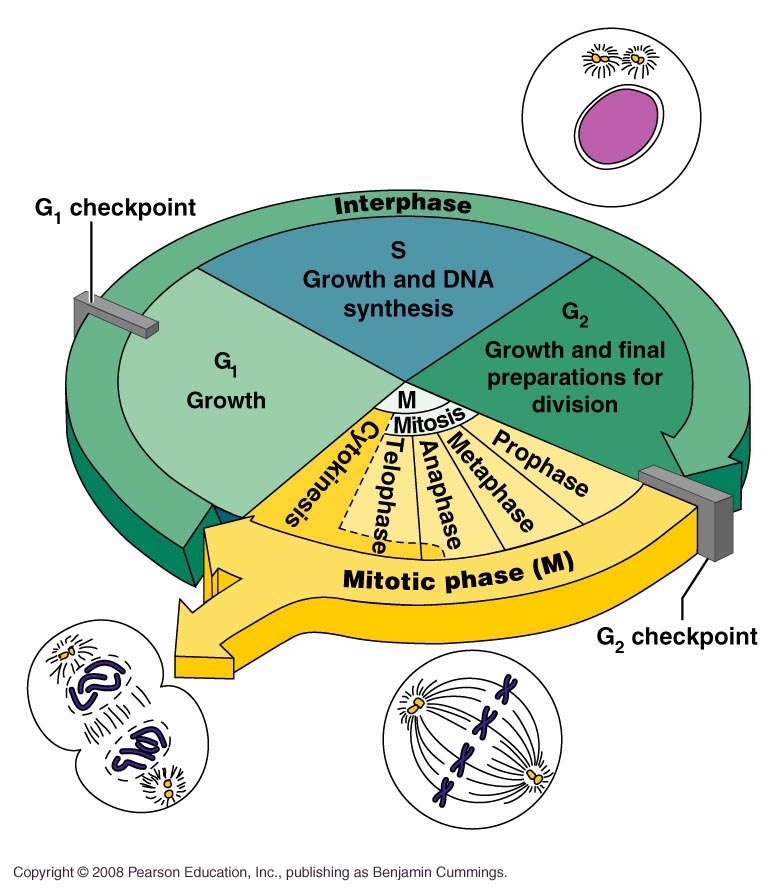
Cell Cycle Pie Chart - A common task of many research teams is the analysis of cell cycle progression through the distinct cell cycle phases. They are a great way to visualize your data without resorting to any default excel charts, allowing you to analyze massive volumes of data quickly. Interphase represents the portion of the cell cycle. Web your pie chart should start interphase at 24 hours (like how our clock starts at 12). Mitosis is a stage in the cell cycle when the nucleus divides. During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period (interphase) followed by mitosis and cytokinesis. The cell cycle is the regulated sequence of events that occurs between one cell division and the next; Web understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms both internal and external to the cell. Web stages of the cell cycle. The order of phases of the cell cycle should then go in order. Web the cell cycle describes an orderly sequence of events that are highly regulated. To divide, a cell must complete several important tasks: In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period (interphase) followed by mitosis and cytokinesis. They are a great way to visualize. Control of the cell cycle. Interphase represents the portion of the cell cycle. Web the cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells. Web the cell cycle has two major phases: Web each pie chart shows the fraction of the cell cycle devoted to each of the primary. The cycle is divided into four (4) main stages or phases: They are a great way to visualize your data without resorting to any default excel charts, allowing you to analyze massive volumes of data quickly. Web your pie chart should start interphase at 24 hours (like how our clock starts at 12). Cells increase in size, produce rna and. Which phases of the cell cycle will have cells with twice the amount of dna? This chart type is best suited to demonstrate progress toward a goal. During interphase, the cell grows and the nuclear dna is duplicated. Web the cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells.. This is the phase right after cell division. Web the cell cycle describes an orderly sequence of events that are highly regulated. Gap 1 (g 1), synthesis (s), gap 2 (g 2), and. The cell cycle has three phases: The cell cycle is a series of stages in the life cycle of a cell. Web mitosis is part of a precisely controlled process known as the cell cycle; Interphase is followed by the mitotic phase. Interphase and the mitotic phase (figure 1). Web revise mitosis, the cell cycle and how stem cells work in humans and plants for gcse biology, aqa. In which phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle do cells typically spend most. Typical timing of somatic cell division. To divide, a cell must complete several important tasks: Cell division itself consists of the overlapping processes of mitosis (nuclear division) and cytokinesis (division of the cytoplasm). In which phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle do cells typically spend most of their lives? Whether or not a cell is cycling or whether it retains. The cycle is divided into four (4) main stages or phases: Web the cell cycle consists of interphase and the mitotic phase. Which cell cycle phase a cell is in, or whether it has progressed beyond a given point of interest, such as a checkpoint or the completion of dna replication; The cell cycle has three phases: Web stages of. Web mitosis is part of a precisely controlled process known as the cell cycle; Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. During the growth phase of the cell cycle, the genetic material of the cell (chromosomes) is doubled. Interphase (g1, s and g2) nuclear division (mitosis) cell division (cytokinesis). Web revise mitosis, the cell cycle and how stem cells work in humans and plants for gcse biology, aqa. During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. The cell cycle consists of: During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. Control of the cell cycle. Web the cell cycle consists of interphase and the mitotic phase. During the mitotic phase, the replicated dna and cytoplasmic contents are separated, and the cell divides. Interphase is divided into g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Web the cell cycle has two major phases: This chart type is best suited to demonstrate progress toward a goal. Web measuring the cell cycle can include probing many aspects: Cells perform these tasks in an organized, predictable series of steps that make up the cell cycle. Cells increase in size, produce rna and synthesize proteins. Which cell cycle phase a cell is in, or whether it has progressed beyond a given point of interest, such as a checkpoint or the completion of dna replication; Interphase and the mitotic phase ( figure 6.3 ). New cells are born through the division of their “parent” cell, producing two “daughter” cells from one single “parent” cell. Web stages of the cell cycle. Web why do cells divide? Interphase and the mitotic phase (figure 1). Milks if you need a quick geometry. Web the cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells.
Cell Cycle and Cell Division Definitions, Differences and Types
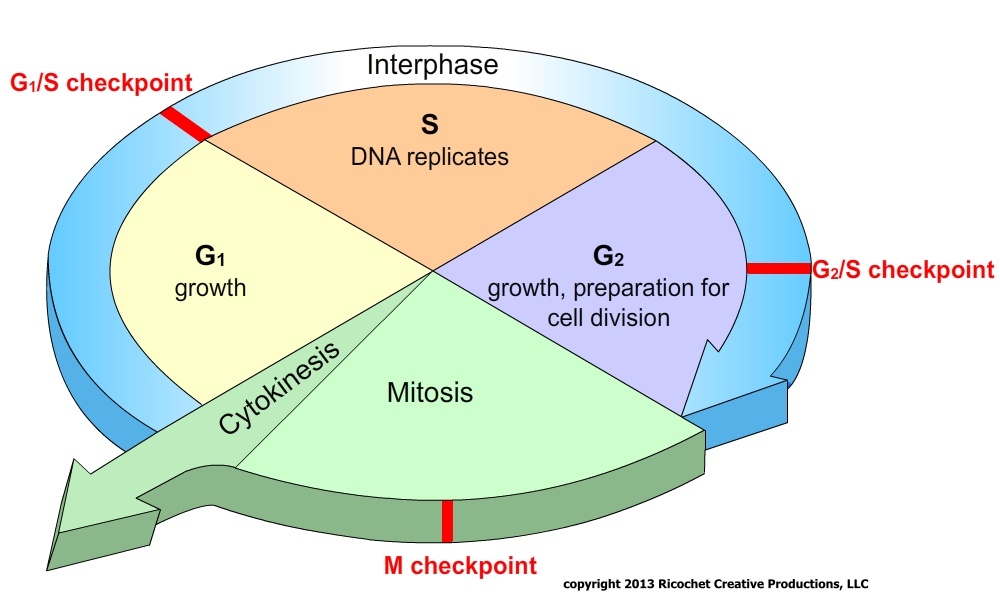
Mrs.Cruz's Biology Class Chapter 5 Cell Growth and Division

Cell cycle pie chart

Cell Cycle Graph
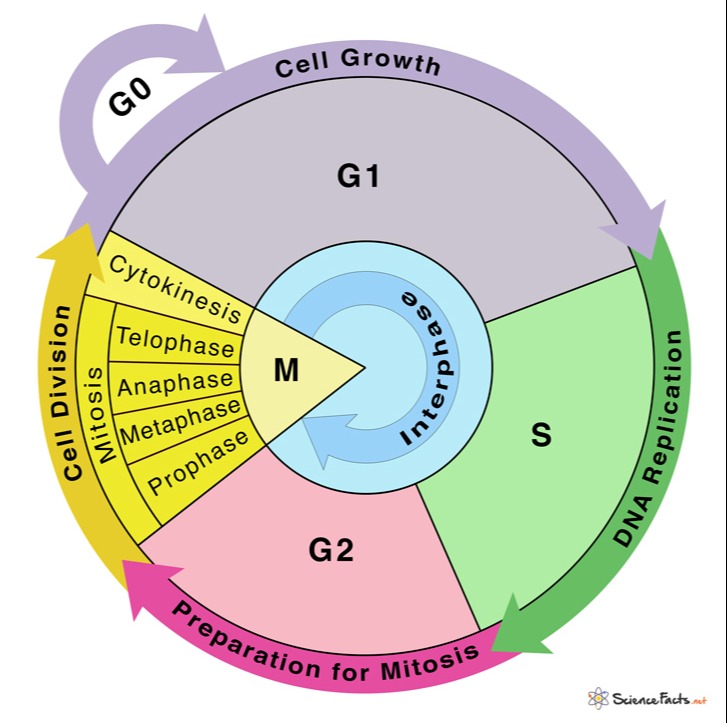
The Cell Cycle Study Guide Inspirit
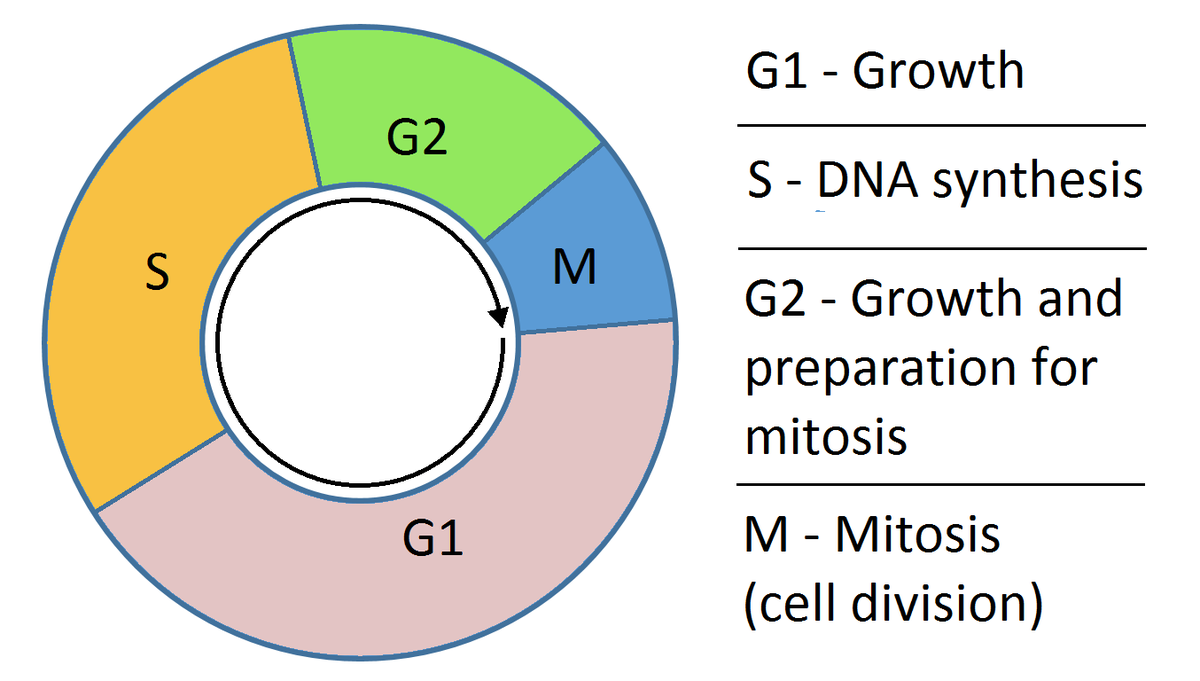
Draw a neat labelled diagram of cell cycle.
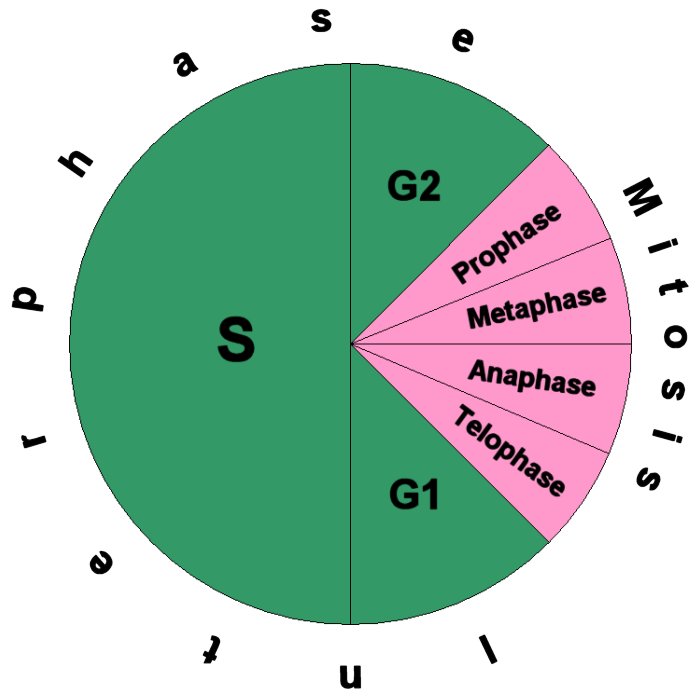
Cell Cycle Diagram ClipArt Best

چرخه سلولی link10.ir link10.ir

cell cycle pie chart Diagram Quizlet
CSIR LIFE SCIENCE PREPARATION Fundamental Processes Overview of the
Web The Cell Cycle Describes An Orderly Sequence Of Events That Are Highly Regulated.
Whether Or Not A Cell Is Cycling Or Whether It Retains The Potential To Cycle;
Cells On The Path To Cell Division Proceed Through A Series Of Precisely Timed And Carefully Regulated Stages.
The Area Of Each Chart Is Proportional To The Overall Cell Cycle Duration.
Related Post: