Canine Muscle Chart
Canine Muscle Chart - The following is an overview of some major muscles and their actions: Web external anatomy (topography) of a typical dog: Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are also illustrated. As judges, we tend to focus less on muscles than the bony landmarks and angles, yet, it is the dog’s musculature that holds everything together an facilitates its movement. Web the following diagram and paragraph attempt to explain it in brief. Excellent wall displays in vet clinics, surgeries, dog groomers, and veterinary colleges. A dog can have between 200 and over 400 muscles. Muscles help facilitate movement and provide stabilisation in dogs. Web our canine charts cover internal organ anatomy, the musculoskeletal system, common pathologies and guides to dog health and safety. Each breed has unique muscle structure and groups. Web here are presented scientific illustrations of the canine muscles and skeleton from different anatomical standard views (lateral, medial, cranial, caudal, dorsal, ventral / palmar.). Ribs easily palpated and may be visible with no palpable fat. Curiously, some dog breeds will have more than 50 muscles in their ears alone. Some evidence of other bony prominences. Skeletal muscles are responsible. Web here are presented scientific illustrations of the canine muscles and skeleton from different anatomical standard views (lateral, medial, cranial, caudal, dorsal, ventral / palmar.). Each breed has unique muscle structure and groups. Muscle condition score is graded as normal, mild loss, moderate loss, or severe loss. Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are also illustrated. Figure. When a dog barks, it contracts the diaphragm forcefully to expel air out of its lungs and through its vocal cords. The muzzle is of varying lengths, depending on the breed. • the sagittal plane divides the dog into right and left portions. Web here are presented scientific illustrations of the canine muscles and skeleton from different anatomical standard views. If this plane were in the midline of the body, this is the median plane or median sagittal plane. Web myos canine muscle formula 6.35 oz (180 g) 60 scoops per package. • the sagittal plane divides the dog into right and left portions. Muscle condition score is graded as normal, mild loss, moderate loss, or severe loss. Whiskers, present. Obvious waist and abdominal tuck. Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are also illustrated. The following is an overview of some major muscles and their actions: Some fascias, tendons, ligaments, joints were labeled. Web the canine muscle (m. Each breed has unique muscle structure and groups. Whiskers, present on the muzzle, are of some sensory use. Muscle loss is typically first noted in the epaxial muscles on each side of the spine; • the dorsal plane divides the dog into ventral and dorsal portions. Again, the amount of muscles an individual dog has depends on the breed and. Web canine muscle condition score (mcs) mcs is the physical assessment of patient’s muscle mass. Reproduced with the kind permission of the world small animal veterinary association (wsava). Web a major part of a dog's anatomy is their musculature. Web the canine muscle (m. Web biological dog anatomy illustrations. Web biological dog anatomy illustrations. A dog can have between 200 and over 400 muscles. Ribs, lumbar vertebrae and pelvic bones easily visible. Although these pictures are fairly basic, they still provide insight that can help the average dog owner gain a working idea of what's beneath all that fur. Obvious waist and abdominal tuck. Web the following diagram and paragraph attempt to explain it in brief. Obvious waist and abdominal tuck. Web the canine muscle (m. Web canine muscle condition score (mcs) mcs is the physical assessment of patient’s muscle mass. The following canine anatomy illustrations offer a look at various systems within the dog's body. Web muscle condition score is assessed by visualization and palpation of the spine, scapulae, skull, and wings of the ilia. Caninus) is called in men 'levator anguli oris'. Mcs is scored by visual examination and palpation of musculature over the spine, scapulae, skull, and pelvis: Some evidence of other bony prominences. Figure 1 recommended criteria for muscle condition scoring using. The following is an overview of some major muscles and their actions: Some evidence of other bony prominences. Curiously, some dog breeds will have more than 50 muscles in their ears alone. Ribs, lumbar vertebrae and pelvic bones easily visible. Each breed has unique muscle structure and groups. The muzzle is of varying lengths, depending on the breed. Dogs also have a ‘stop’ on their heads, which is the point where the muzzle ends and the forehead begins. A dog can have between 200 and over 400 muscles. Web this canine anatomy chart offers the following features: Lateral view of the dog showing all major muscles. If this plane were in the midline of the body, this is the median plane or median sagittal plane. The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. Some fascias, tendons, ligaments, joints were labeled. Caninus) is called in men 'levator anguli oris'. Web their tails contain between 6 and 23 caudal vertebrae. Although these pictures are fairly basic, they still provide insight that can help the average dog owner gain a working idea of what's beneath all that fur.
Canine Muscular Anatomy Chart Dog Muscles Poster Laminated
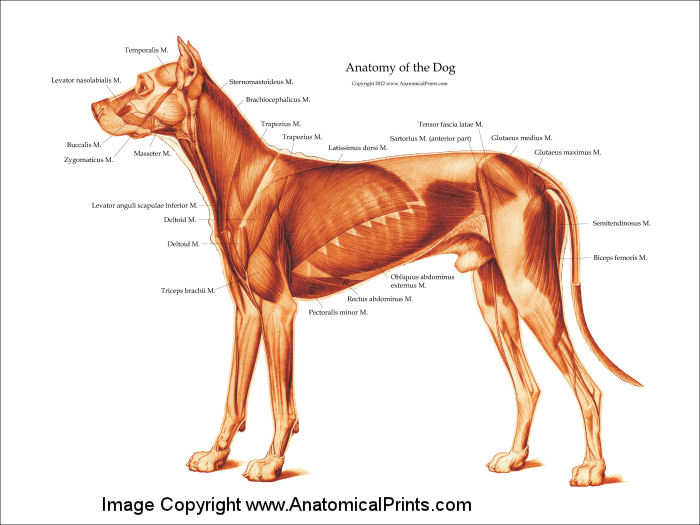
Dog Anatomical Chart Muscles


Canine Muscular Anatomy Chart Dog Muscles Poster Laminated

The Anatomy of a Canine (Muscle Anatomy)

Canine Muscular Anatomy Diagram

Dog muscles DogGroomingDIY Vet medicine, Dog anatomy, Pet vet

Canine Muscle Chart Small (11" X 17") Animal Massage Awareness
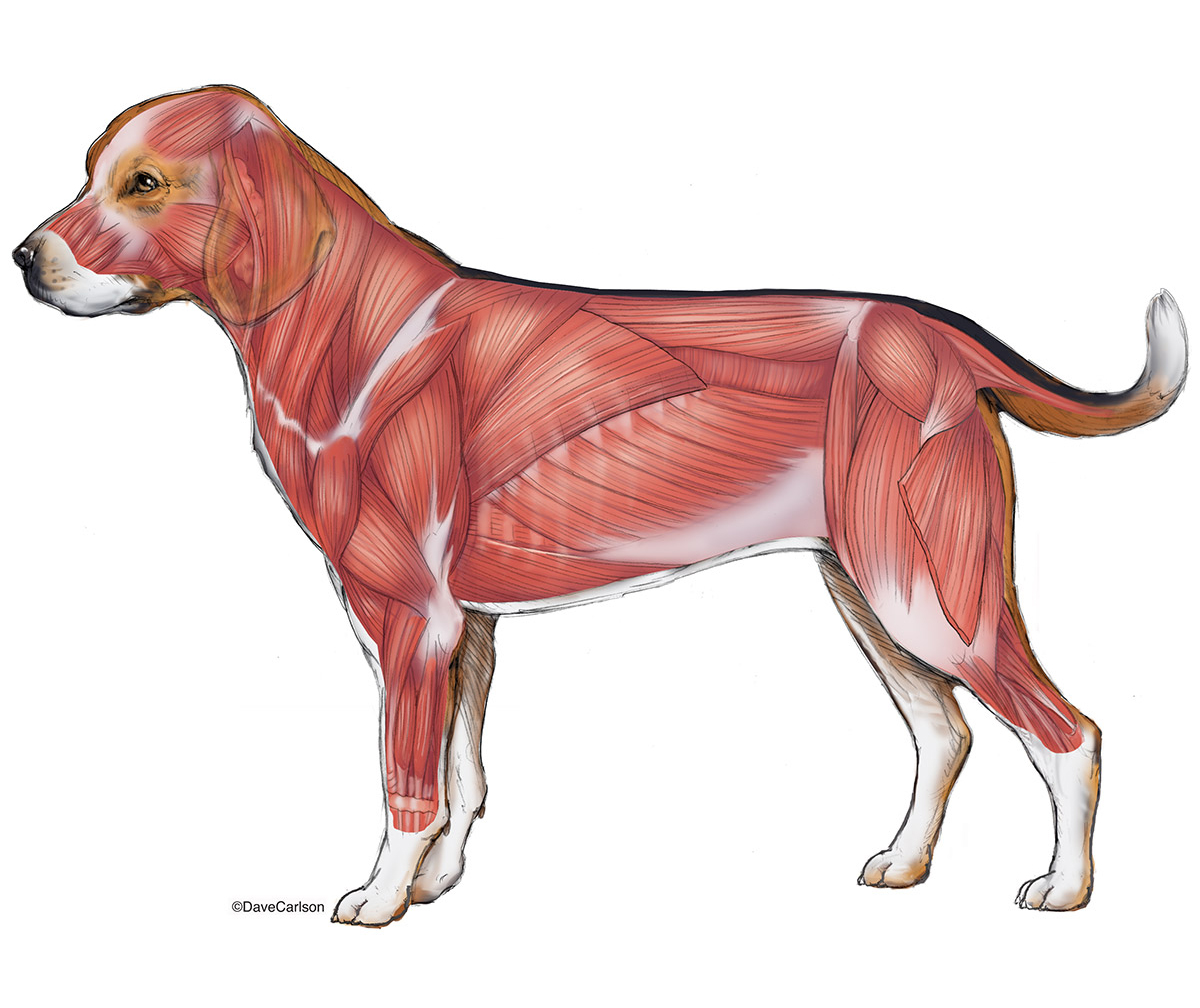
Dog Muscular Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
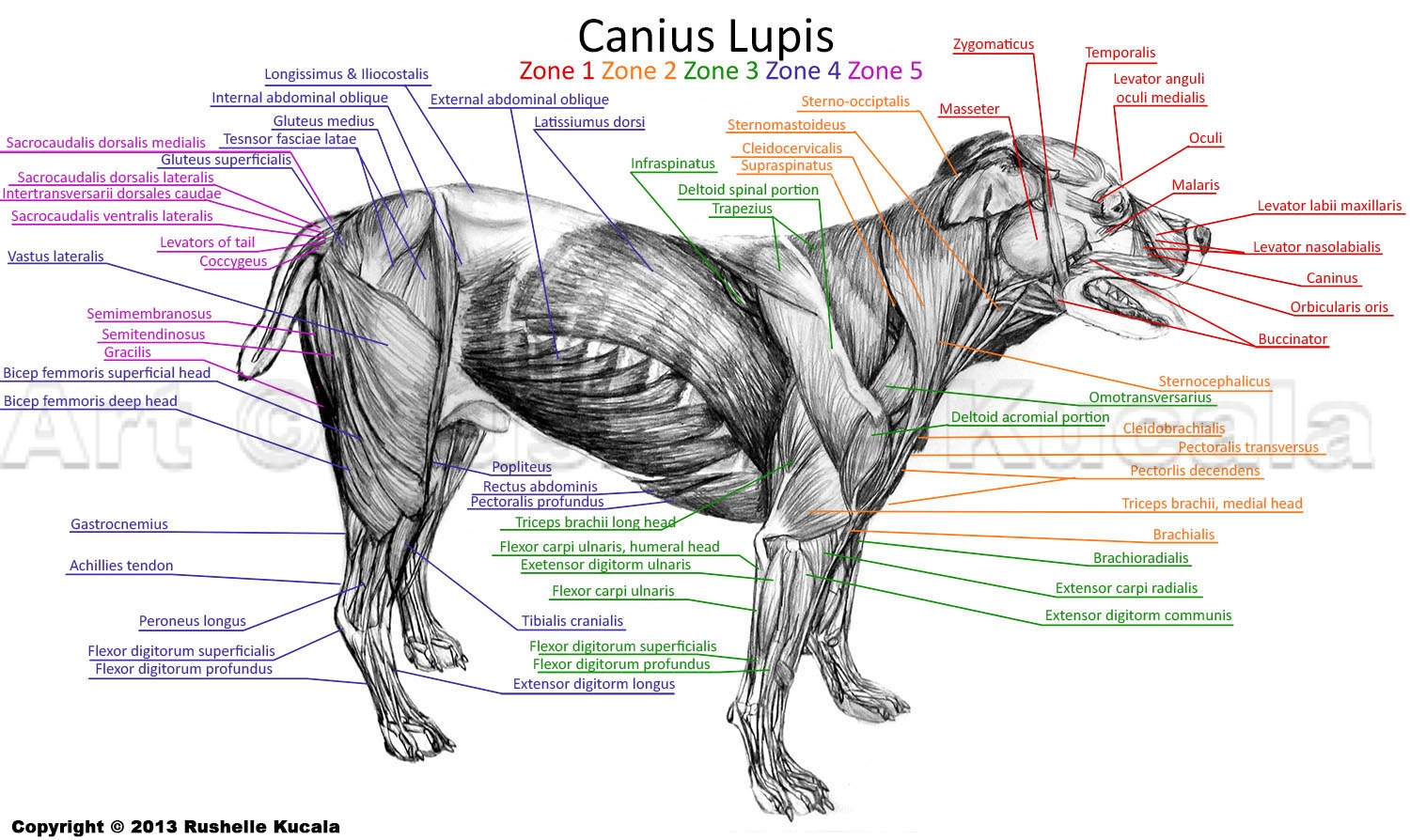
Dog Muscle Anatomy by TheDragonofDoom on DeviantArt
• The Sagittal Plane Divides The Dog Into Right And Left Portions.
• The Dorsal Plane Divides The Dog Into Ventral And Dorsal Portions.
Muscle Loss Is Typically First Noted In The Epaxial Muscles On Each Side Of The Spine;
Web Biological Dog Anatomy Illustrations.
Related Post: