Bone Anatomy Chart
Bone Anatomy Chart - There also are bands of fibrous connective tissue—the ligaments and the tendons—in intimate relationship with the parts of the skeleton. Compare and contrast compact and spongy bone. Describe how bones are nourished and innervated. Flat bones are thin, but are often curved, such as the ribs. Web for detailed discussions of specific tissues, organs, and systems, see human blood; Your bones are like the frame under the walls of your home. Bones can be classified according to their shapes. Compare and contrast compact and spongy bone. Ctrl+click on entities to quickly hide entities. Web human skeleton, the internal skeleton that serves as a framework for the body. Bones of the upper and lower limbs and the shoulder and pelvic girdles: They range in size from the tiniest found in the middle ear, to the largest that forms our thigh. Altogether, the skeleton makes up about 20 percent of a. When you look at the human skeleton the 206 bones and 32 teeth stand out. Compare and contrast. Web from human body organ diagrams to skull bones and chambers of the heart; Define and list examples of bone markings. Short bones, such as the carpals, are approximately equal in length, width, and thickness. Describe the histology of bone tissue, including the function of bone cells and matrix; Define and list examples of bone markings. Identify the structures that compose compact and spongy bone. Describe how bones are nourished and innervated. Web what is the skeletal system? Describe how bones are nourished. The surface features of bones vary considerably, depending on the function and location in the body. There also are bands of fibrous connective tissue—the ligaments and the tendons—in intimate relationship with the parts of the skeleton. Describe the histology of bone tissue. Identify the structures that compose compact and spongy bone. Web anatomy of the bone. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Identify the structures that compose compact and spongy bone. Define and list examples of bone markings. Define and list examples of bone markings. Bones of the skull, ribs, vertebral column, sternum, sacrum, coccyx, hyoid bone and auditory ossicles. Compare and contrast compact and spongy bone. The human body has an amazing array of different bones, many of. Web for detailed discussions of specific tissues, organs, and systems, see human blood; The human skeleton also includes ligaments and cartilage. Click on the background or on the x to undo selection. Identify the gross anatomical features of a bone; But look closer and you’ll see even more structures. Compare and contrast compact and spongy bone. Table 7.2 describes the bone markings, which are illustrated in ( figure 7.2.1 ). Healthcare providers usually classify bones based on their shape and size. This is the harder, outer tissue of bones. Compare and contrast compact and spongy bone. Click on the toggle below the slider to control layers individually. Describe how bones are nourished and innervated. Identify the anatomical features of a bone. Skeletal, muscular, cardiovascular, digestive, endocrine, nervous, respiratory, immune/lymphatic, urinary, female reproductive, male reproductive, integumentary. Click on the toggle below the slider to control layers individually. Web from human body organ diagrams to skull bones and chambers of the heart; Web there are a total of 206 bones in the adult human body. Use the opacity slider on the left to reveal layers. They’re made of hard, strong tissue that gives your body its shape. Identify the structures that compose compact and spongy bone. Identify the gross anatomical features of a bone; Define and list examples of bone markings. Bones can be classified according to their shapes. Describe how bones are nourished. It is part of the axial skeleton and extends from the base of the skull to the tip of the coccyx. Describe how bones are nourished and innervated. Define and list examples of bone markings. Use the searchbox at the upper right to search, or click on entities to select them. Identify the anatomical features of a bone. Healthcare providers usually classify bones based on their shape and size. Web the vertebral column (spine or backbone) is a curved structure composed of bony vertebrae that are interconnected by cartilaginous intervertebral discs. Web what is the skeletal system? Define and list examples of bone markings. They range in size from the tiniest found in the middle ear, to the largest that forms our thigh. When you look at the human skeleton the 206 bones and 32 teeth stand out. Web key facts about the main bones, joints and muscles of the body; Web there are a total of 206 bones in the adult human body. Web for detailed discussions of specific tissues, organs, and systems, see human blood; Short bones, such as the carpals, are approximately equal in length, width, and thickness. Bones can be classified according to their shapes.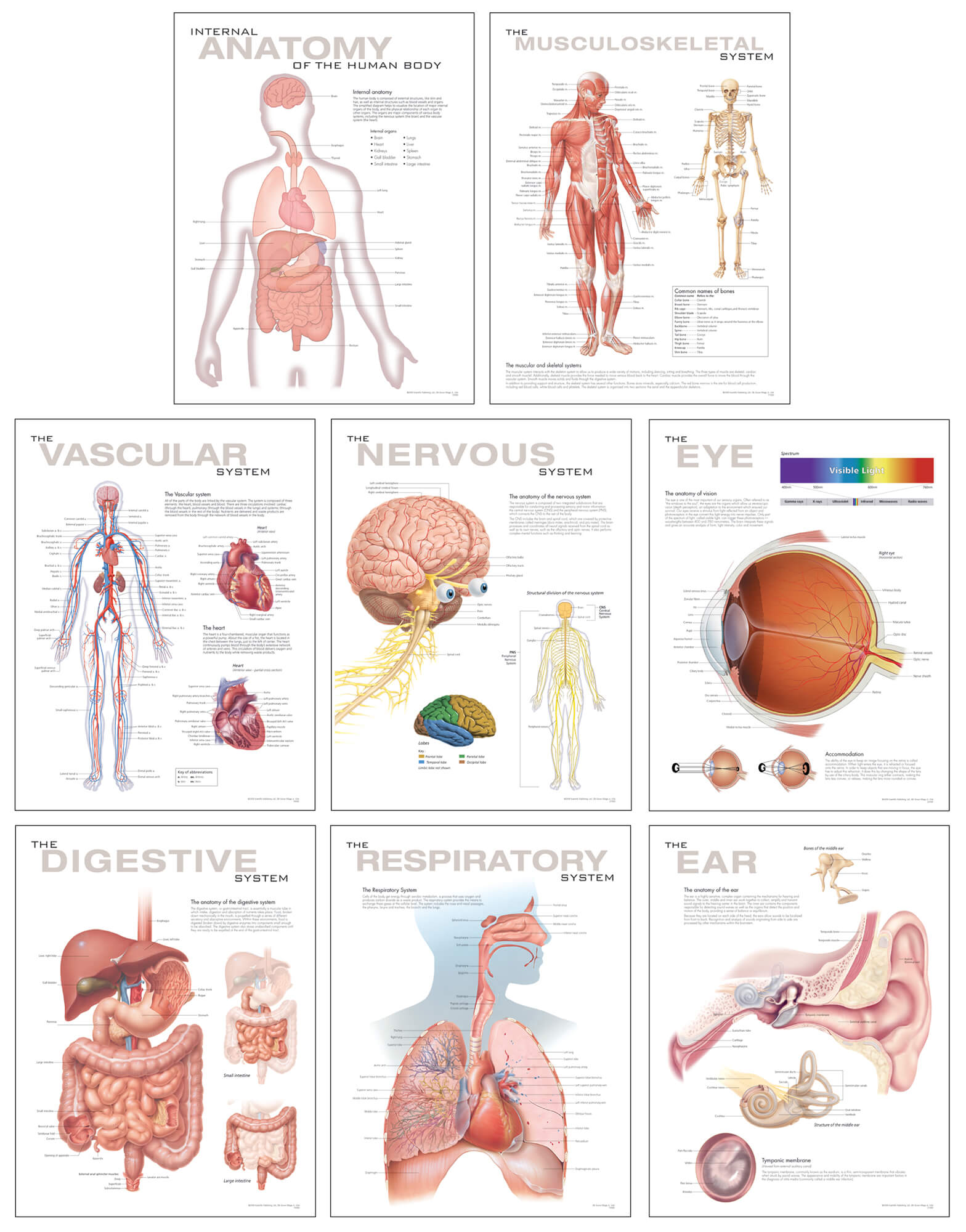
Human Bone Anatomy Chart Bones of the Human Hand. My poor right, 3rd
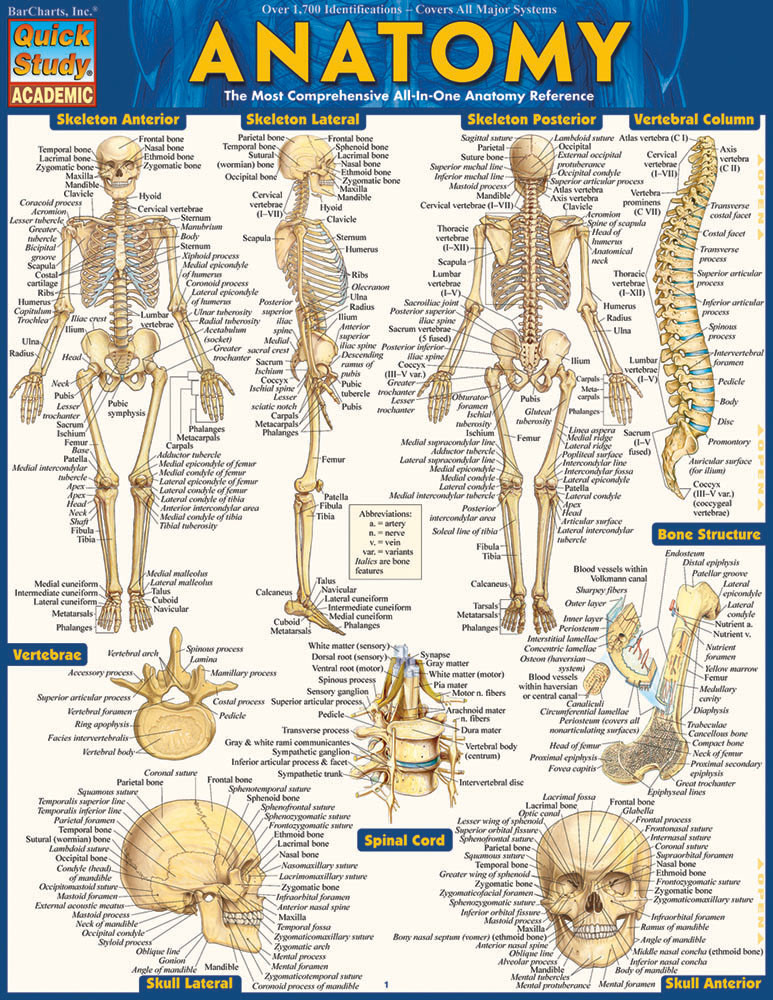
Anatomy Chart Clinical Charts and Supplies

Anatomy Of A Long Bone
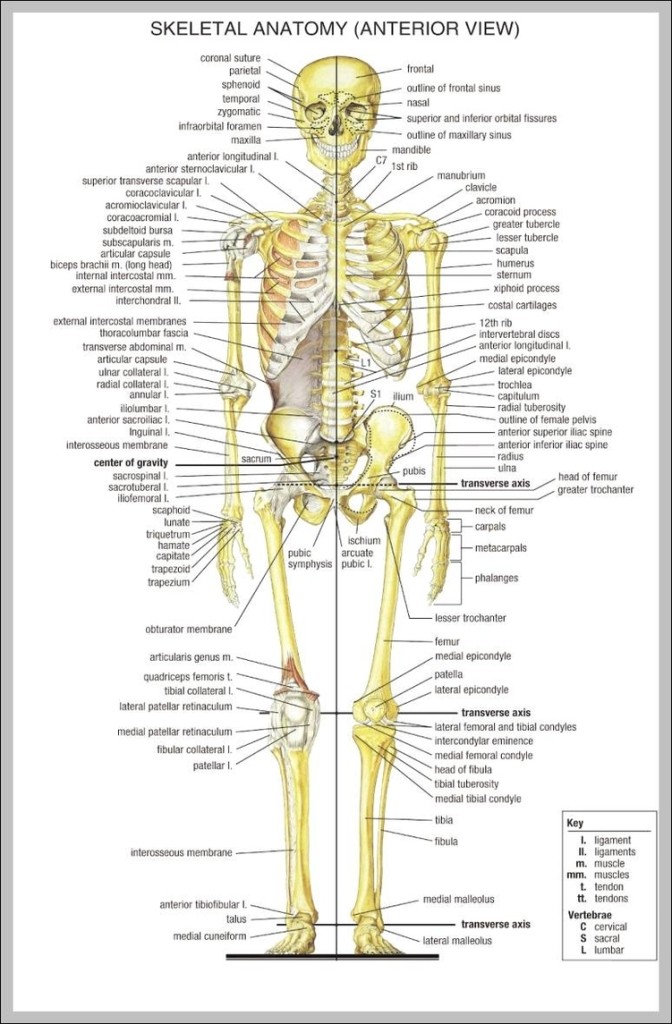
human skeleton labeled bones 744×1188 Anatomy System Human Body

Classification Of Bones Human Anatomy Chart Human Ana vrogue.co

Human Bone Anatomy Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master

Human Skeleton Anatomy and Physiology Poster Clinical Charts and

Human Body Bones Diagram For Kids, Human Skeleton Ks2 Resource Pack
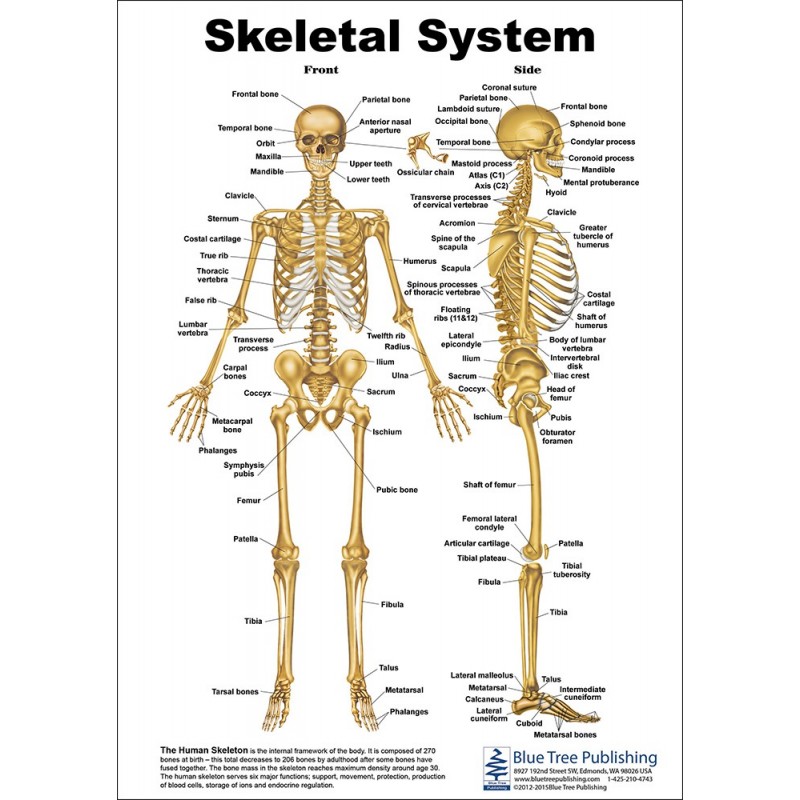
Human Bone Anatomy Chart Human Body Organs Systems Structure Diagram Images

Pin on Anatomy
Your Bones Are Like The Frame Under The Walls Of Your Home.
Altogether, The Skeleton Makes Up About 20 Percent Of A.
The Skeletal System Consists Of More Than Bones.
Bones Are Your Body’s Main Form Of Structural Support.
Related Post: