Bacteria Morphology Chart
Bacteria Morphology Chart - The prokaryotic kingdom consists of unicellular microscopic microorganisms called bacteria. Determine the characteristics of bacteria such as shape, mobility, gram staining results, and incubation temperatures. Web circular, irregular, filamentous, and. They have no nucleus, no organelles (endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, golgi apparatus, lysosomes). It is a characteristic property of a particular species. Describe the phases of growth curve. The rod (bacillus), the sphere (coccus) and the spiral type (vibrio). March 28, 2024 by sourav@bno. The morphology of bacteria cells not only tells the shape but also decides its pathogenicity. This includes morphology (shape), biochemical activities, chemical composition, nutritional requirements, and sources of energy. Web describe the structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. Also easily determine which media should be used for each bacteria listed. Describe the different types of bacteria. Bacteria are very small in size. Discuss the distinguishing characteristics of gram positive and gram negative bacteria. Bacteriology (study of bacteria) is a major part in microbiology. Bacteria are unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms that divide by binary fission, a process by which one bacterium splits into two. Rods range from 2 to 5 μm in length by 0.5 to 1.0 μm in width. Discuss bacterial structure and the function of the different bacterial components. Web circular, irregular, filamentous,. Web “a red blood cell measure 7 microns in diameter for comparison.” bacteria are prokaryote cells i.e. The shape of a bacterium cell is determined by its morphology, which also determines the pathogenicity of the bacteria. Bacterial shapes, arrangements, and forms. Bacilli (rods) bacilli (rod bacteria) may be long or short, thick or slender in form. Web characteristics of bacteria. Classify bacteria based on the shape and arrangements. Bacterial shapes, arrangements, and forms. Usually smallest in the logarithmic phase of growth. The shape of a bacterium cell is determined by its morphology, which also determines the pathogenicity of the bacteria. Web however, bacterial cells generally exist in three forms which are spheres, rods and spirals. It gives information about how much the colony rises above the agar. Web however, bacterial cells generally exist in three forms which are spheres, rods and spirals. Web bacteria can be distinguished based on their morphology and staining properties. Also easily determine which media should be used for each bacteria listed. The morphology of a bacterial cell is the most. A large component of threat reduction for biological attacks involves the use of appropriate antibiotics and/or prophylactic vaccination. Web “a red blood cell measure 7 microns in diameter for comparison.” bacteria are prokaryote cells i.e. Classify bacteria based on the shape and arrangements. To customize your own personalized figure using this template as a starting point, click use template. Cover. Bacteria are unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms that divide by binary fission, a process by which one bacterium splits into two. 0.5 to 1.0 μm in diameter. If the pdf does not display below, you may also download it here. Web streptococcus bacteria have what shape? Flat, raised, umbonate (having a knobby protuberance), crateriform, convex, and. Web thousands of species of bacteria are classified on a different basis (size, shape and arrangement of bacteria). Bacteria are unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms that divide by binary fission, a process by which one bacterium splits into two. Spirochetes are longer (up to 20 μm) and narrower (0.1 to 1.0 μm) varies with the medium and growth phase. Web bacteria can. This describes the “side view” of a colony. The prokaryotic kingdom consists of unicellular microscopic microorganisms called bacteria. Some bacteria such as mycobacteria (the cause of tuberculosis) are not reliably stained due to the The shape of a bacterium cell is determined by its morphology, which also determines the pathogenicity of the bacteria. A large component of threat reduction for. To customize your own personalized figure using this template as a starting point, click use template. If the pdf does not display below, you may also download it here. Bacilli (rods) bacilli (rod bacteria) may be long or short, thick or slender in form. It is a characteristic property of a particular species. Classify bacteria based on the shape and. Discuss bacterial structure and the function of the different bacterial components. Rods range from 2 to 5 μm in length by 0.5 to 1.0 μm in width. Cover different classification schemes for grouping bacteria, especially the use of the gram stain. Elevation of the bacterial colony: Bacterial shapes, arrangements, and forms. The shape of a bacterium cell is determined by its morphology, which also determines the pathogenicity of the bacteria. The six most common elevations of bacterial colonies are. March 28, 2024 by sourav@bno. Figure 1 shows the various shapes in which a bacterial cell can occur. The morphology of bacteria cells not only tells the shape but also decides its pathogenicity. On average, the size of bacteria ranges from 0.5 to 5 µm. Classify bacteria based on the shape and arrangements. Reason for variation in shape of bacterial cell. Usually smallest in the logarithmic phase of growth. The prokaryotic kingdom consists of unicellular microscopic microorganisms called bacteria. Spirochetes are longer (up to 20 μm) and narrower (0.1 to 1.0 μm) varies with the medium and growth phase.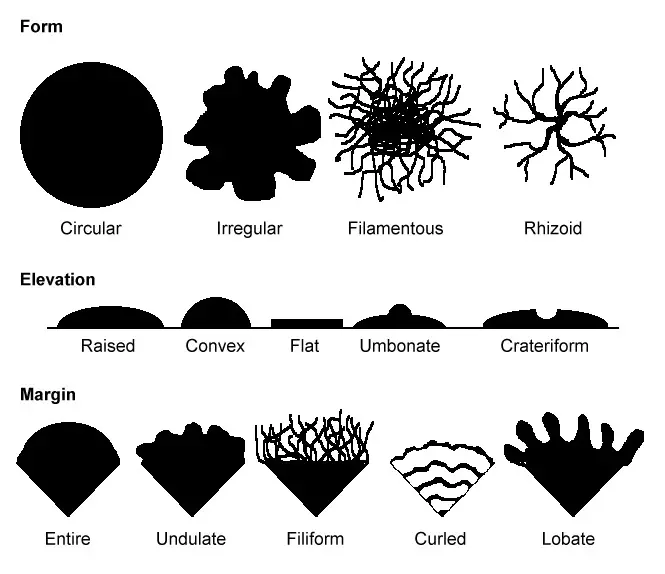
Colony Morphology of Bacteria • Microbe Online

Size, Shape, Arrangement of Bacteria • Microbe Online
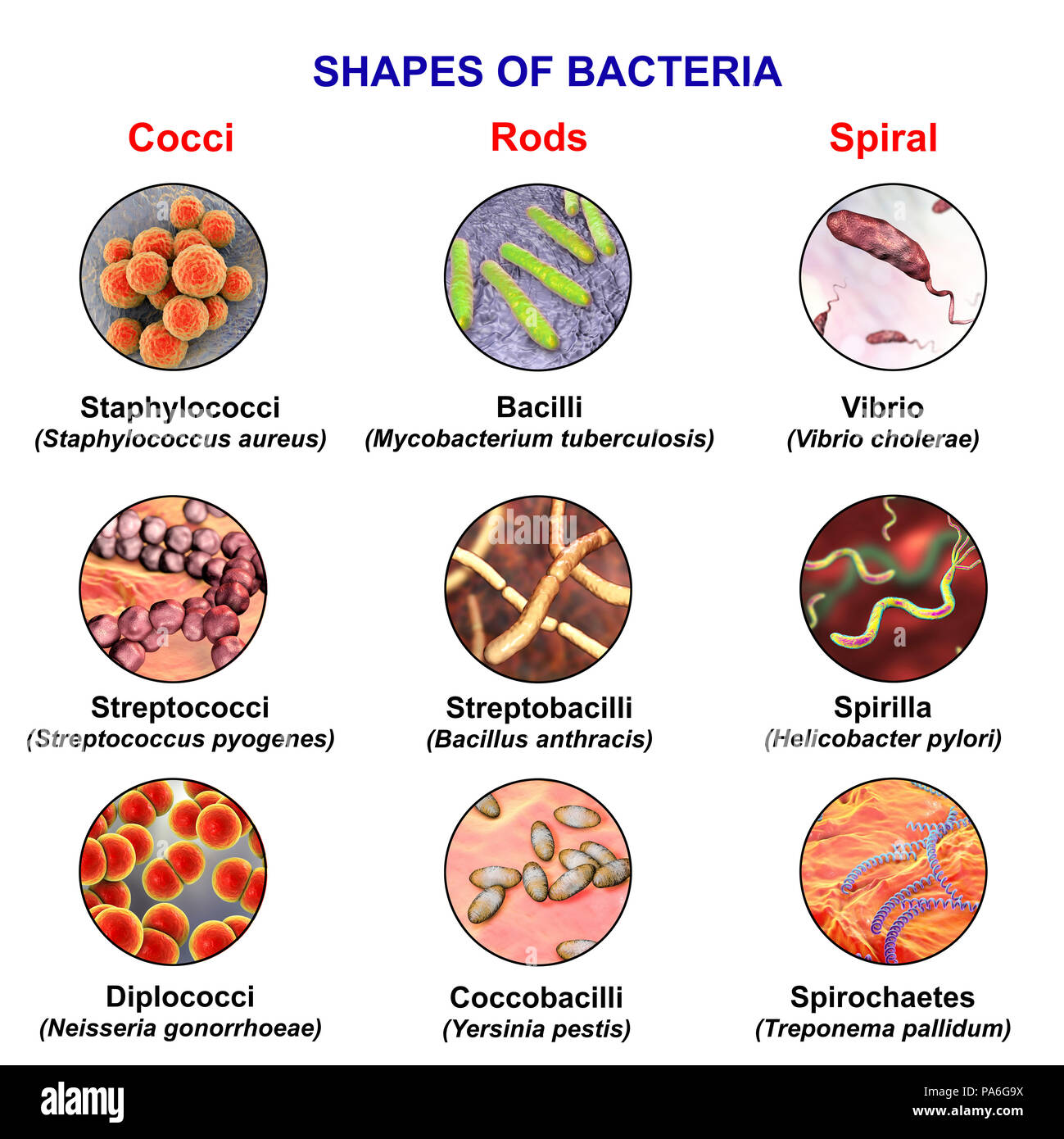
Different Morphology Of Bacteria
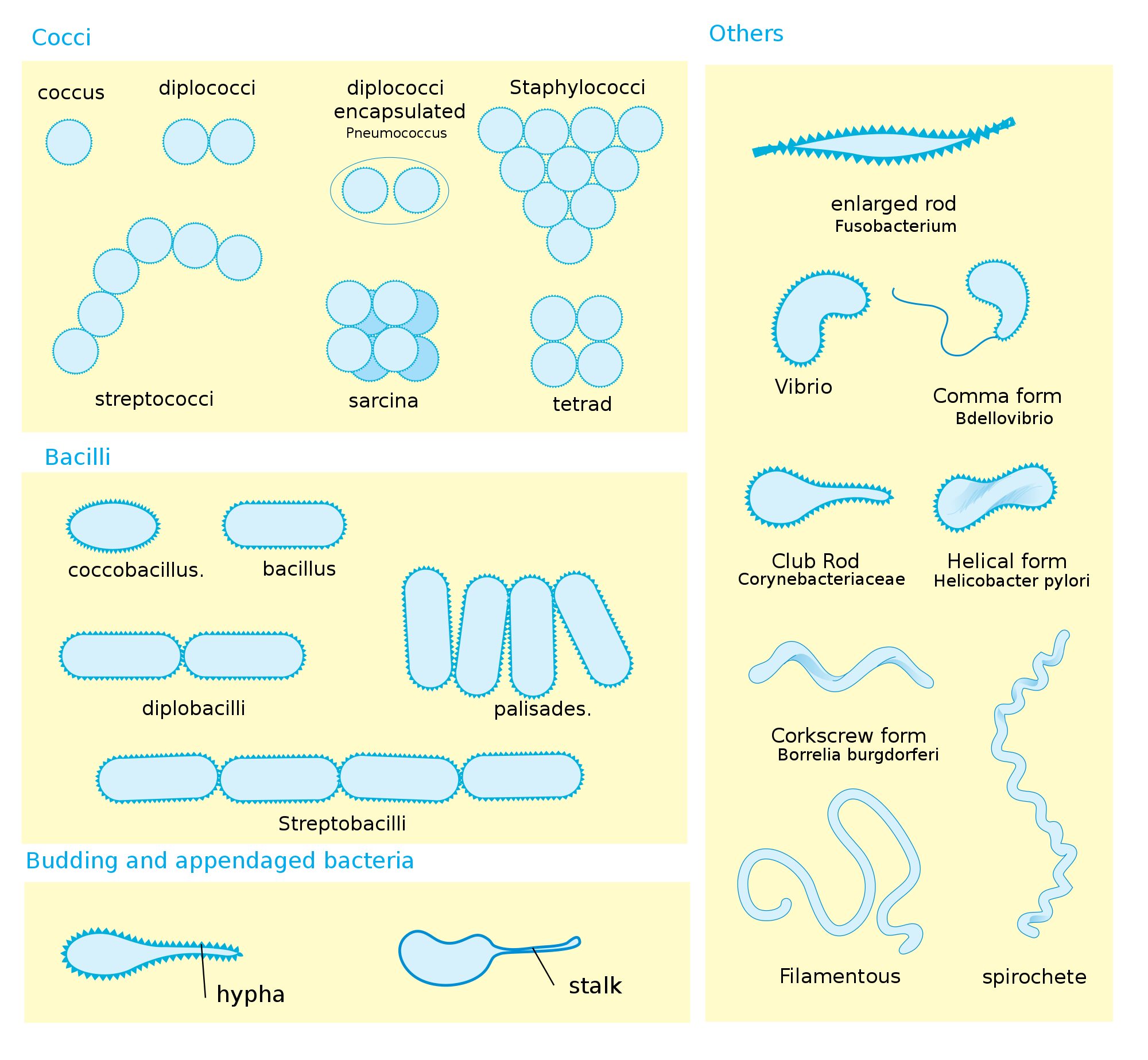
Bacteria Shape, Size, Structure and other Membrane Microbiology Notes
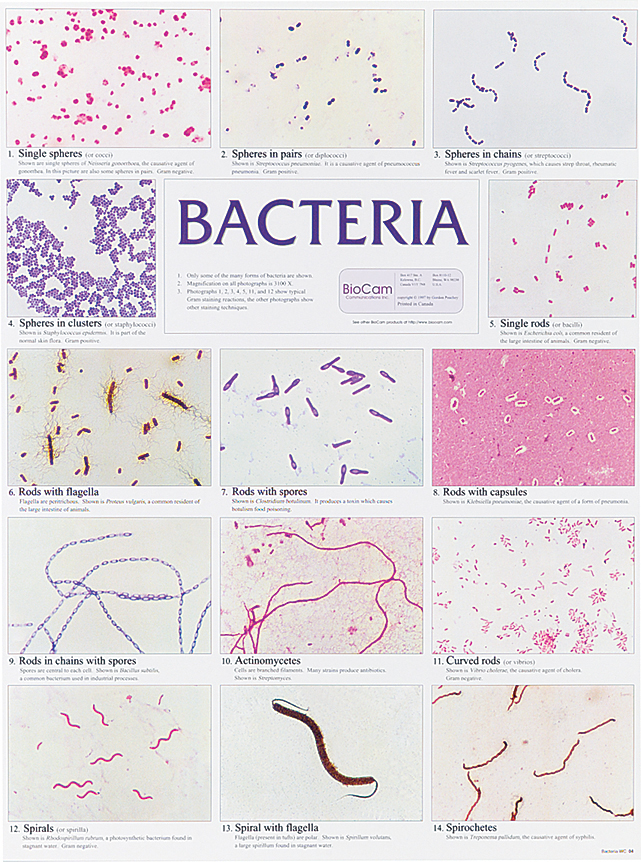
Bacterial Morphology Chart Flinn Scientific
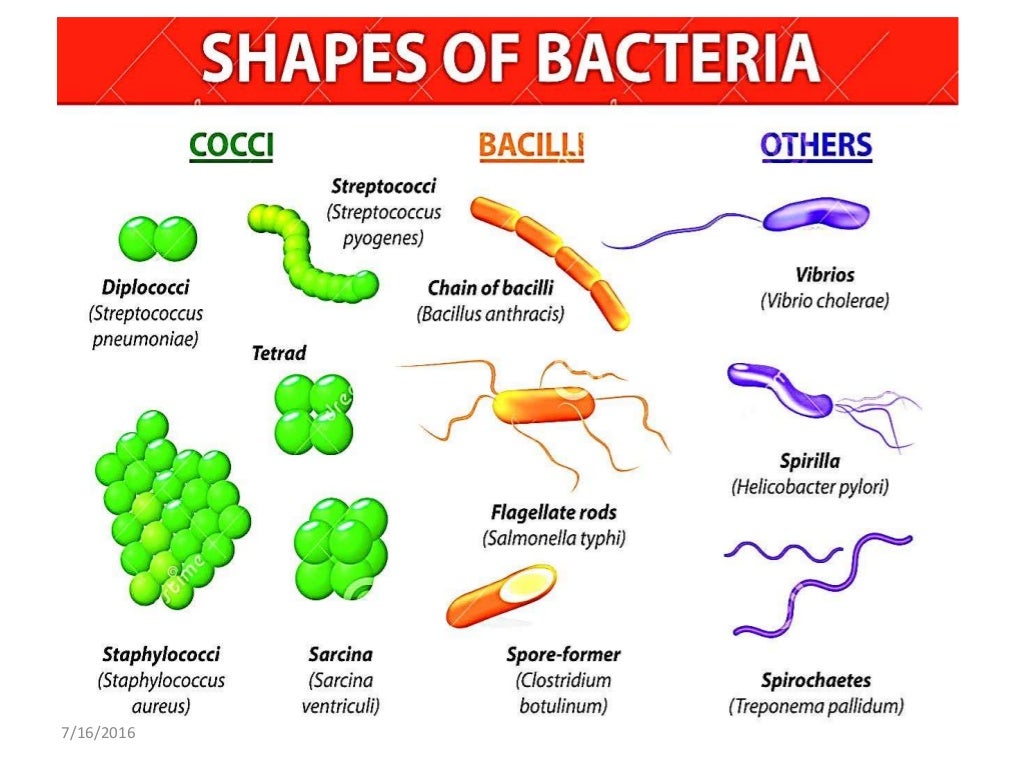
BacteriaMorphology, Reproduction and Functions
.jpeg)
Bacterial Colony Morphologies! — PathElective
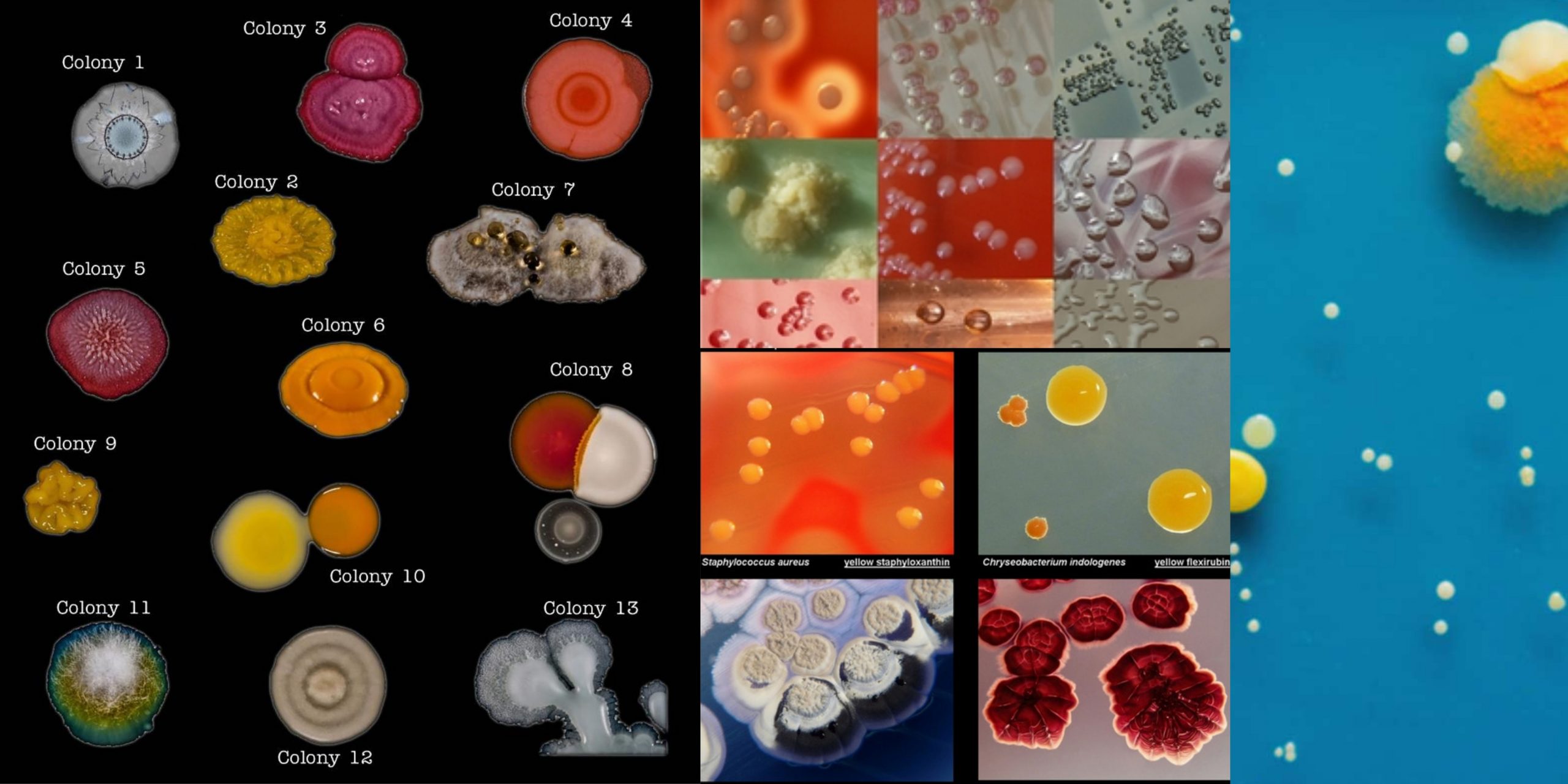
Colony Morphology of Bacteria and Examples
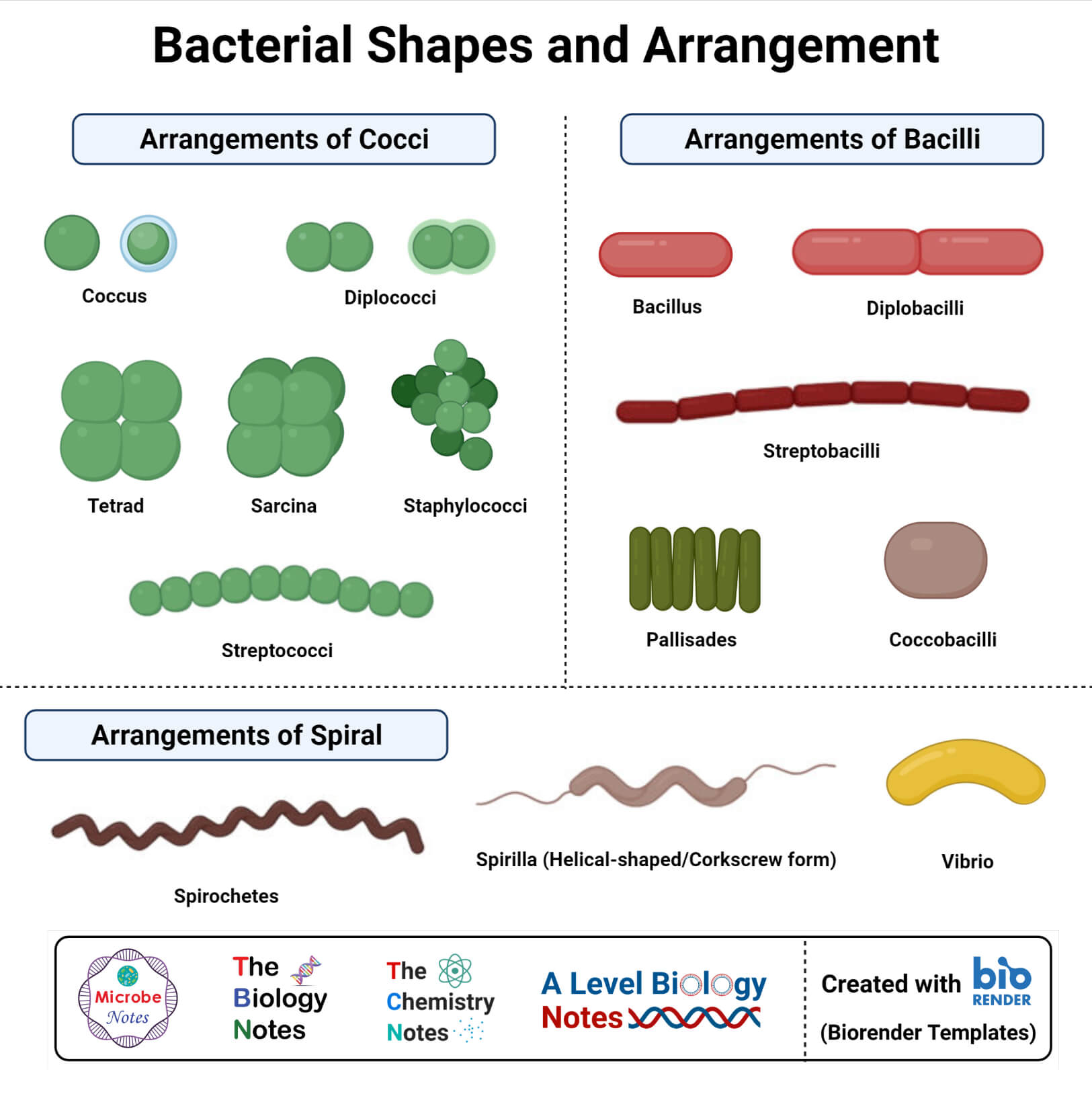
Morphology of Bacteria Sizes, Shapes, Arrangements, Examples

Bacterial morphology
Bacteria Are Unicellular Prokaryotic Microorganisms That Divide By Binary Fission, A Process By Which One Bacterium Splits Into Two.
It’s A Certain Species’ Distinguishing Feature.
A Bacteria’s Greatest Distinguishing Characteristic Is Its Morphology Or Shape.
Explain The Size Of Bacteria.
Related Post: