Atom Radius Chart
Atom Radius Chart - Web atomic radius of all the elements are mentioned in the chart below. If the two atoms are of the same kind, then the covalent radius is simply one half of the bond length. Web interactive periodic table showing names, electrons, and oxidation states. The relative size of the atoms follows a set of trends on the periodic table. Four widely used definitions of atomic. Want to join the conversation? The periodic table greatly assists in determining atomic radius and presents a number of trends. Web this table shows how the atom size, and atomic radius values change as you move horizontally and vertically across the periodic table. Web the periodic table contains nist’s latest critically evaluated data for atomic properties of the elements. Pdf without crop marks | pdf with crop marks. The atomic radius of atoms generally decreases from left to right across a period. Want to join the conversation? Four widely used definitions of atomic. Web the radius of an atom can only be found by measuring the distance between the nuclei of two touching atoms, and then halving that distance. Web (one angstrom, 1 å, equals 10 −10 metre.). Web (one angstrom, 1 å, equals 10 −10 metre.) this article was most recently revised and updated by erik gregersen. Web the radius of an atom can only be found by measuring the distance between the nuclei of two touching atoms, and then halving that distance. Web the atomic radius is the size of the atom, typically measured by the. Visualize trends, 3d orbitals, isotopes, and mix compounds. Web atomic radius of all the elements are mentioned in the chart below. (a) the covalent atomic radius, rcov, is half the distance between the nuclei of two like atoms joined by a covalent bond in the same molecule, such as cl 2. As shown in the graph below, the atomic radius. Web the atomic radius is the average distance from the center of the nucleus of a neutral atom to the outer boundary of its electron shell. Francium has the largest atomic size on the periodic table, and helium has the smallest atomic size. How atomic radius is defined, and trends across a period and down a group. If the two. Francium has the largest atomic size on the periodic table, and helium has the smallest atomic size. Web the periodic table of the elements (including atomic radius) element name. Atoms are not all the same size. The atomic radius of atoms generally increases from top. Atomic radii can be obtained from quantum mechanical calculations or. Atoms are not all the same size. Web the radius of an atom can only be found by measuring the distance between the nuclei of two touching atoms, and then halving that distance. Web the values given here for atomic radius are calculated values using methods outlined in reference 1. Practice problems on atomic radius trends. Four widely used definitions. Want to join the conversation? Atomic radii can be obtained from quantum mechanical calculations or. Web the radius of an atom can only be found by measuring the distance between the nuclei of two touching atoms, and then halving that distance. Definitions of the atomic radius. The atomic radius of atoms generally decreases from left to right across a period. Atomic radii can be obtained from quantum mechanical calculations or. Web (one angstrom, 1 å, equals 10 −10 metre.) this article was most recently revised and updated by erik gregersen. The left hand diagram shows bonded atoms. As there are no physical existence of orbital in atoms, it is difficult to measure the atomic radius. Atoms consist of a nucleus. Web the periodic table of the elements (including atomic radius) element name. Web explore how atomic radius changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. The atomic radius of atoms generally decreases from left to right across a period. Web the values given here for atomic radius are calculated values using methods outlined in reference. 1 å = 1 × 10−10 m = 100 pm. Web atomic radius of all the elements are mentioned in the chart below. Below mentioned radii are the van der waals radius in picometer (pm)). The editors of encyclopaedia britannica. Atomic radii can be obtained from quantum mechanical calculations or. Four widely used definitions of atomic. Web atomic radius of all the elements are mentioned in the chart below. In general, atomic radius or atom size decreases as you move from left to right. As you can see from the diagrams, the same atom could be found to have a different radius depending on what was around it. Pdf without crop marks | pdf with crop marks. Visualize trends, 3d orbitals, isotopes, and mix compounds. The left hand diagram shows bonded atoms. This is due to the way electrons form shells around the nucleus. Web the atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the size of its atom, usually the mean or typical distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost isolated electron. The atomic radius of atoms generally decreases from left to right across a period. How atomic radius is defined, and trends across a period and down a group. 1 å = 1 × 10−10 m = 100 pm. Atoms consist of a nucleus with positively charged protons and neutral neutrons surrounded by shells of electrons. Web (one angstrom, 1 å, equals 10 −10 metre.) this article was most recently revised and updated by erik gregersen. If the two atoms are of the same kind, then the covalent radius is simply one half of the bond length. Below mentioned radii are the van der waals radius in picometer (pm))..png)
CK12Foundation

Atomic Radius of Elements The Periodic Table
Periodic Behavior Presentation Chemistry
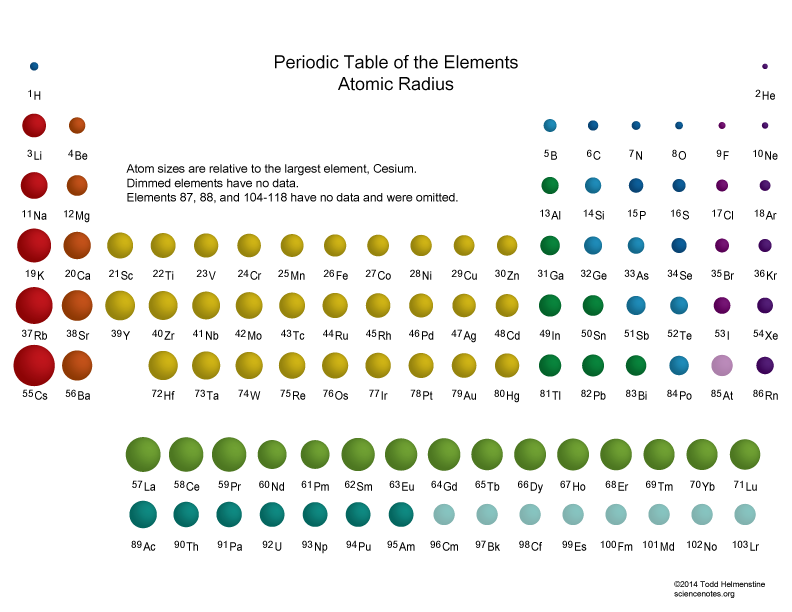
Atomic Radius Trends of the Periodic Table

Atomic Radius and Ionic Radius
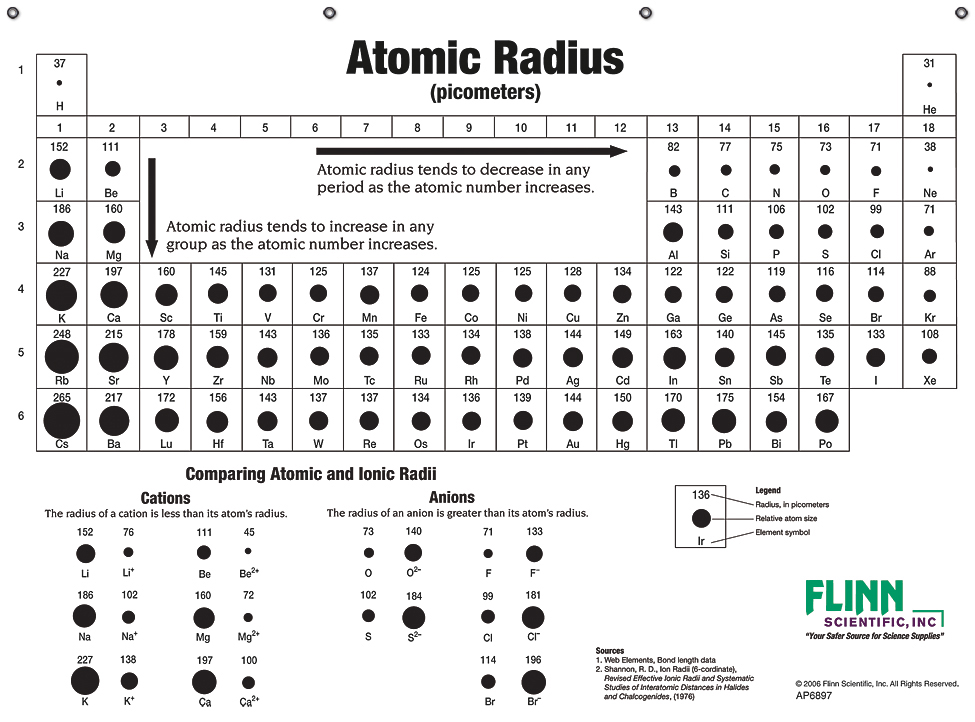
Atomic Radius Periodic Table Chart

Atomic Radius of Elements
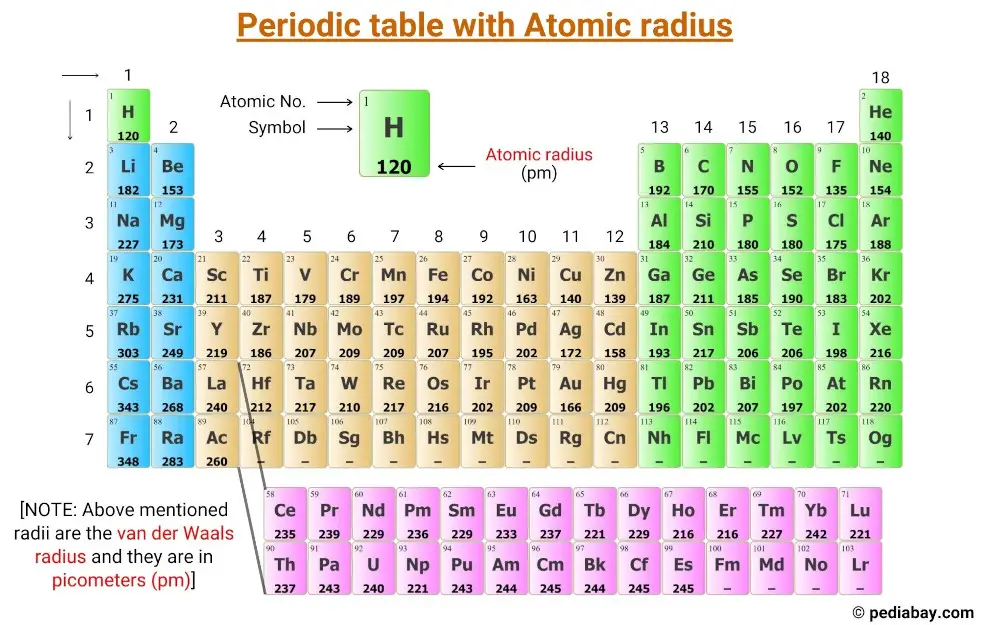
Atomic Radius of Elements (With Periodic table Chart) Pediabay

Periodic Trends SSC Chemistry
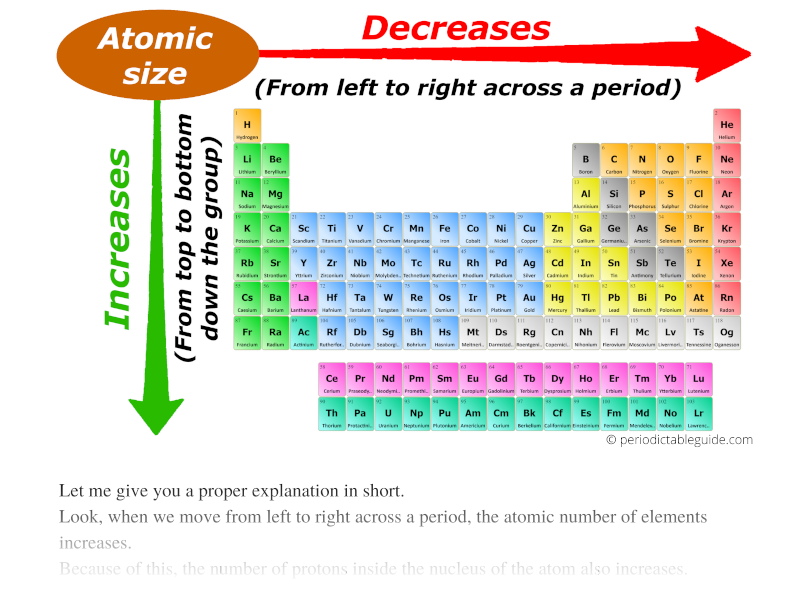
Atomic radius chart mindsstorm
Web The Periodic Table Contains Nist’s Latest Critically Evaluated Data For Atomic Properties Of The Elements.
Web Complete And Detailed Technical Data About The Element $$$Elementname$$$ In The Periodic Table.
For Isolated Neutral Atoms, The Atomic Nucleus Ranges From 30 Picometers (Trillionths Of A Meter) And 300 Pm.
Web The Atomic Radius Is The Average Distance From The Center Of The Nucleus Of A Neutral Atom To The Outer Boundary Of Its Electron Shell.
Related Post:
.PNG)