Antiderivative Chart
Antiderivative Chart - How many antiderivatives does a given function have? 4.10.3 state the power rule for integrals. Web those would be derivatives, definite integrals, and antiderivatives (now also called indefinite integrals). We are integrating, we need to be able to recognise standard forms. When you learn about the fundamental theorem of calculus, you will learn that the antiderivative has a very, very important property. Check out this free printable derivatives formula chart i created for my ap calculus. Find the general antiderivative of a given function. In the present example, suppose that condition is \(f(2) = 3\); Parts, partial fractions, trig substitution, etc. Web the fundamental theorem of calculus connects differential and integral calculus by showing that the definite integral of a function can be found using its antiderivative. Web if \(f\) is an antiderivative of \(f\), we say that \(f(x)+c\) is the most general antiderivative of \(f\) and write \[\int f(x)dx=f(x)+c.\] the symbol \(\int \) is called an integral sign, and \(\int f(x)dx\) is called the indefinite integral of \(f\). Web 4.10.1 find the general antiderivative of a given function. Sometimes, it may be possible to use one. 4.10.2 explain the terms and notation used for an indefinite integral. The antiderivative rules help us to make the process of finding the antiderivatives easier and simpler. Let's learn how to draw these functions. A*e^ (x + b) is the only function that has a differentiating period of 1, so to say. 1 a+1 xa+1 a6= 1 logjxj a= 1. State the power rule for integrals. List of general antiderivatives function antiderivative f(x) = xn (n 6= −1) f(x) = 1 n+1 xn+1 +c f(x) = x−1 = 1 x f(x) = ln|x|+ c f(x) = ex f(x) = ex + c f(x. 4.10.3 state the power rule for integrals. For a longer list of antiderivative formulas, see your textbook.. Web 4.10.1 find the general antiderivative of a given function. Web if \(f\) is an antiderivative of \(f\), we say that \(f(x)+c\) is the most general antiderivative of \(f\) and write \[\int f(x)\,dx=f(x)+c.\nonumber \] the symbol \(\displaystyle \int \) is called an integral sign, and \(\displaystyle \int f(x)\,dx\) is called the indefinite integral of \(f\). Check out this free printable. Web table of antiderivatives of basic functions (table 7.2.1 in the textbook) function antiderivative function antiderivative f(x) = k (k is constant) f(x) = kx +c f(x) = cosx f(x) = sinx +c Given the graph of a function’s derivative, how can we construct a completely accurate graph of the original function? 4.10.3 state the power rule for integrals. State. Web solve definite and indefinite integrals (antiderivatives) using this free online calculator. Web the fundamental theorem of calculus connects differential and integral calculus by showing that the definite integral of a function can be found using its antiderivative. On other occasions, some manipulation will be needed first. Find the general antiderivative of a given function. Check out this free printable. State the power rule for integrals. Web table of antiderivatives of basic functions (table 7.2.1 in the textbook) function antiderivative function antiderivative f(x) = k (k is constant) f(x) = kx +c f(x) = cosx f(x) = sinx +c 1 a+1 xa+1 a6= 1 logjxj a= 1 x logx ( +1+1) 1x+1 logx ( +1) 2x exponents e xe ax. Find the general antiderivative of a given function. There is a table in the back watermark. What do those antiderivatives all have in common? Web these antiderivative rules help us to find the antiderivative of sum or difference of functions, product and quotient of functions, scalar multiple of a function and constant function, and composition of functions. Web solve definite. Web those would be derivatives, definite integrals, and antiderivatives (now also called indefinite integrals). We are integrating, we need to be able to recognise standard forms. Check out this free printable derivatives formula chart i created for my ap calculus. List of general antiderivatives function antiderivative f(x) = xn (n 6= −1) f(x) = 1 n+1 xn+1 +c f(x) =. Web if \(f\) is an antiderivative of \(f\), we say that \(f(x)+c\) is the most general antiderivative of \(f\) and write \[\int f(x)dx=f(x)+c.\] the symbol \(\int \) is called an integral sign, and \(\int f(x)dx\) is called the indefinite integral of \(f\). The antiderivative rules help us to make the process of finding the antiderivatives easier and simpler. State the. Substituting the value of 2 for \(x\) in \(f(x) = \dfrac{1}{3} x^3 + c\), we find that 4.10.2 explain the terms and notation used for an indefinite integral. 4.10.3 state the power rule for integrals. There is a table in the back watermark. In the present example, suppose that condition is \(f(2) = 3\); Parts, partial fractions, trig substitution, etc. How many antiderivatives does a given function have? Web the fundamental theorem of calculus connects differential and integral calculus by showing that the definite integral of a function can be found using its antiderivative. On other occasions, some manipulation will be needed first. Check out this free printable derivatives formula chart i created for my ap calculus. Having trouble remembering all of the different derivative rules? What do those antiderivatives all have in common? Find the general antiderivative of a given function. Let's learn how to draw these functions. Web the antiderivative graph is the graph of the antiderivative or integral of a given function. Web if \(f\) is an antiderivative of \(f\), we say that \(f(x)+c\) is the most general antiderivative of \(f\) and write \[\int f(x)\,dx=f(x)+c.\nonumber \] the symbol \(\displaystyle \int \) is called an integral sign, and \(\displaystyle \int f(x)\,dx\) is called the indefinite integral of \(f\).
Proportional Integral Derivative Deals Cheapest, Save 49 jlcatj.gob.mx
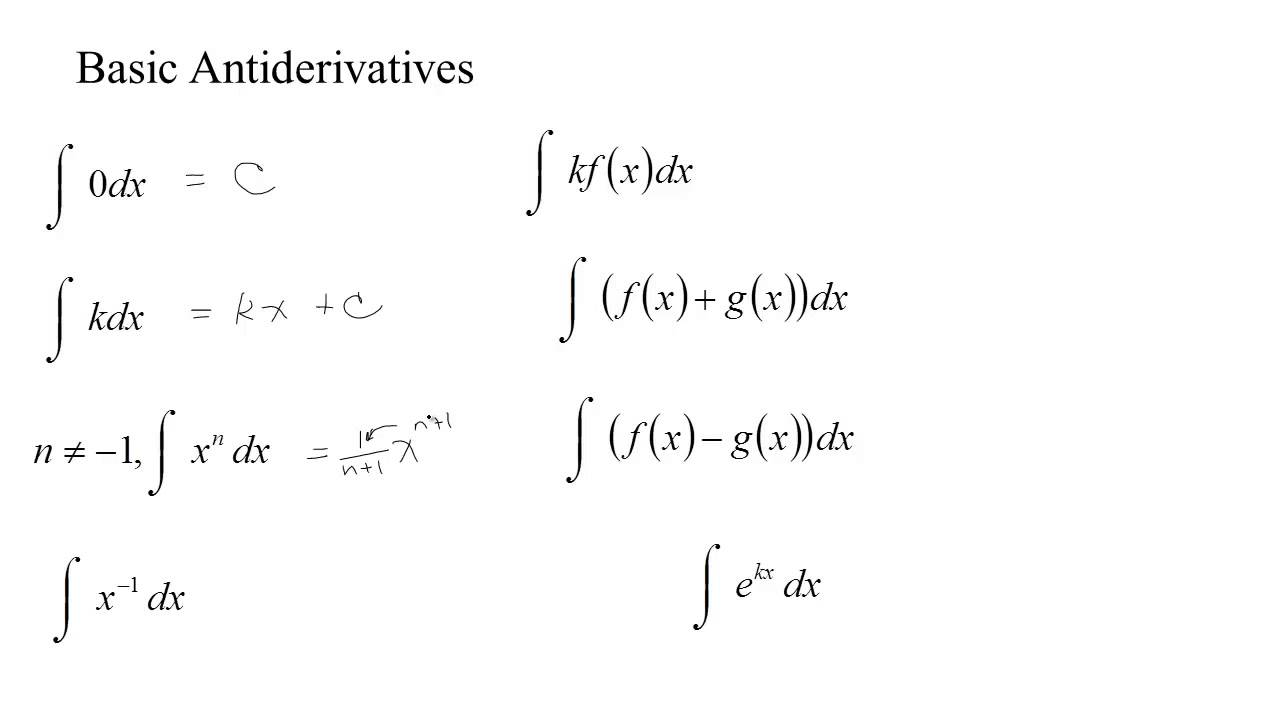
4.81 Notation for Antiderivatives and some basic antiderivatives YouTube
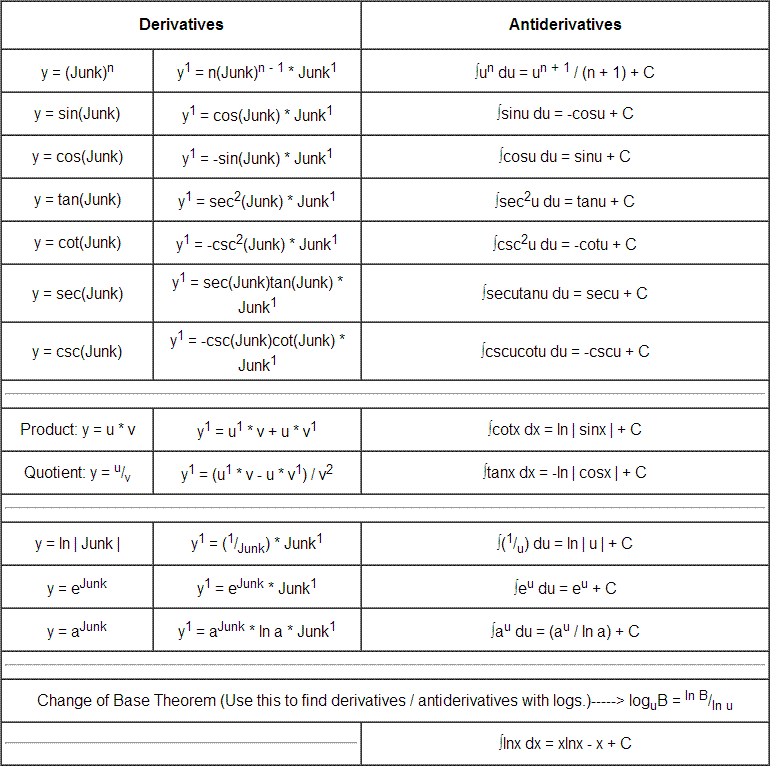
Table of Derivatives/ Antiderivatives

Antiderivative Rules Cheat Sheet
Antiderivative Rules

Common Antiderivatives Diagram Quizlet

Introduction to antiderivatives StudyPug
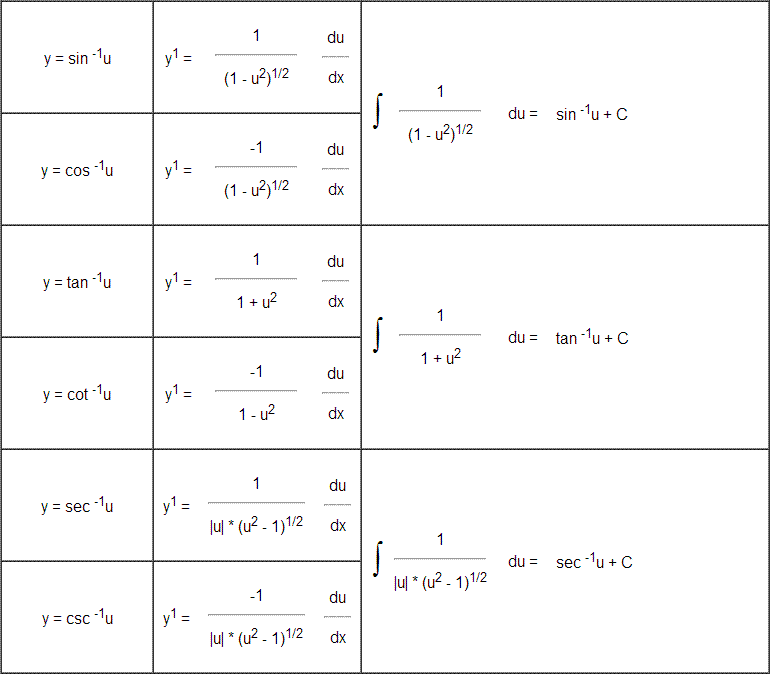
Table of Derivatives/ Antiderivatives

Introduction to antiderivatives StudyPug
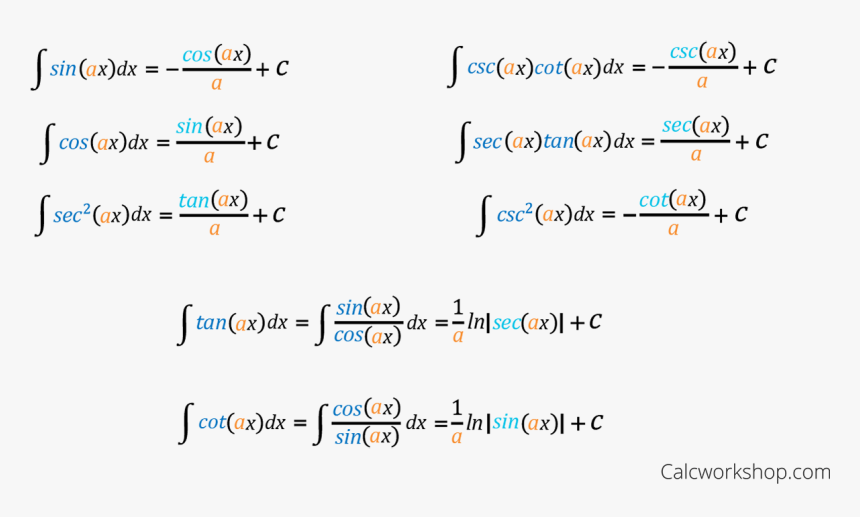
Rules For Integrating Trig Functions Antiderivative Trig Chart, HD
Web 5.1 Constructing Accurate Graphs Of Antiderivatives.
List Of General Antiderivatives Function Antiderivative F(X) = Xn (N 6= −1) F(X) = 1 N+1 Xn+1 +C F(X) = X−1 = 1 X F(X) = Ln|X|+ C F(X) = Ex F(X) = Ex + C F(X.
Web If \(F\) Is An Antiderivative Of \(F\), We Say That \(F(X)+C\) Is The Most General Antiderivative Of \(F\) And Write \[\Int F(X)Dx=F(X)+C.\] The Symbol \(\Int \) Is Called An Integral Sign, And \(\Int F(X)Dx\) Is Called The Indefinite Integral Of \(F\).
For A Longer List Of Antiderivative Formulas, See Your Textbook.
Related Post: